Through targeted measures, forest management (FM) to enhance land-based climate change mitigation can be applied to all forested land within Germany. The aim is to increase carbon (C) uptake and storage in forests. FM options generally include forest protection (e.g. by taking forest area out of wood use), increasing forest carbon stocks (e.g. by extending the harvest cycle, and reducing the number of harvested trees), forest adaptation (e.g. increasing resilience of forest stands through the introduction of adapted species and varieties), and increasing the carbon stock in harvested wood products (e.g. by increasing the share of long-lived products).
This case study covers the whole 11.4 million hectares under forest in Germany. Coniferous trees make up 54% and deciduous trees cover 46% of the forest area. Half of the forests are privately owned, with an average property size of 3 ha. About 50% of private forest properties are under 20 ha and only 13% of private forest owners manage forests of more than 1,000 ha.
Incentive systems for rewarding ecosystem and environmental protection services in land use in general, and climate protection services in forest management in particular, should be established, so that forest owners have a source of income besides cutting and selling timber. Such a system should reward the efforts and ambitions to develop forests’ contribution towards a more climate resilient ecosystem that further provides society with clean air, water retention capacities, healthy soils, biodiversity and contributes crucially to the goal of C removal.
The measures to promote carbon sinks in the forest can be implemented on the existing forest area, which means that, in contrast to other land-based climate protection measures, there is no direct competition for land.
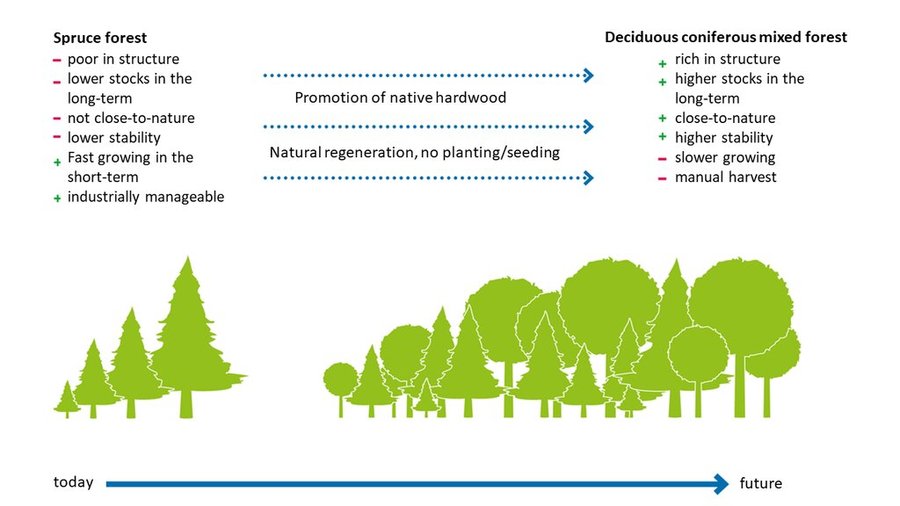
Synergies with the protection of biodiversity can result if native deciduous tree species are promoted and, above all, a higher proportion of older deciduous trees is left in the forest. In addition, a higher proportion of deadwood and a greater diversity of deadwood structures (lying, standing; different dimensions) also contribute. Promoting more deciduous trees in the forest can lead to higher groundwater percolation rates compared to coniferous stands.
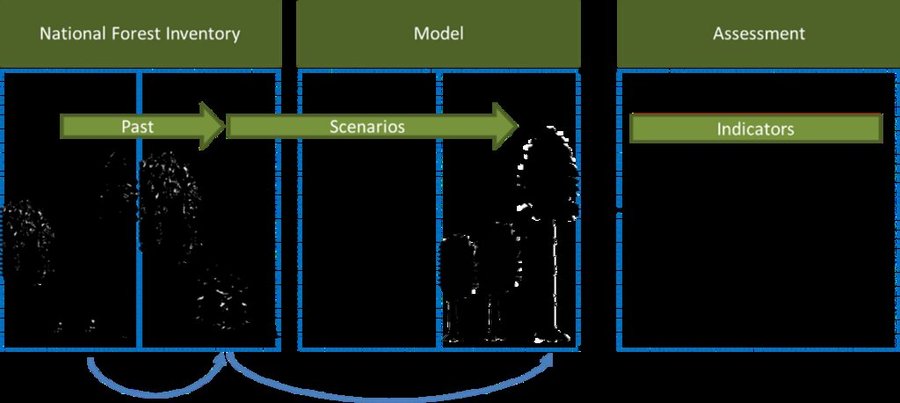
Oeko-Institut has been developing the Forestry and Agriculture Biomass Model (FABio) since 2015. FABio-Forest describes the growth of individual trees as a distance-independent individual tree growth model. Parameters for tree growth and mortality are derived from National Forest Inventory (NFI) data. Assumptions on forest management as well as for climate change drive the future development of tree stands.
In addition, FABio includes modules for estimating carbon stored of wood products, forest litter and soil. The model is based on the following components:
•a model for the characterisation of tree growth based on diameter, height, site productivity and forest stand density;
•an ingrowth model for the characterisation of new trees based on stand density and tree species;
•a mortality model for the characterisation of dieback processes depending on tree species, site productivity, age and stand density;
•a deadwood model factoring in decomposition of dead trees;
•a soil carbon model simulating the decomposition of biomass in litter and soil over time depending on climate factors; and
•a model for the sorting and classification of wood products, i.e., to sort harvested trees into use categories and quantify carbon retention times of wood products.
FABio supports scenario analyses for various silvicultural practices and management scenarios and their effects on wood supply, carbon sequestration and aspects of nature conservation.
Байршил: Nationwide, Germany, Герман
Дүн шинжилгээнд хамрагдсан технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын тоо: >1000 байршилд
Технологийн тархалт: газар дээр жигд тархсан (approx. > 10,000 км2)
Тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт?: Үгүй
Хэрэгжилтийн огноо: <10 жилийн өмнө (саяхны)
Нутагшууллын төрөл