



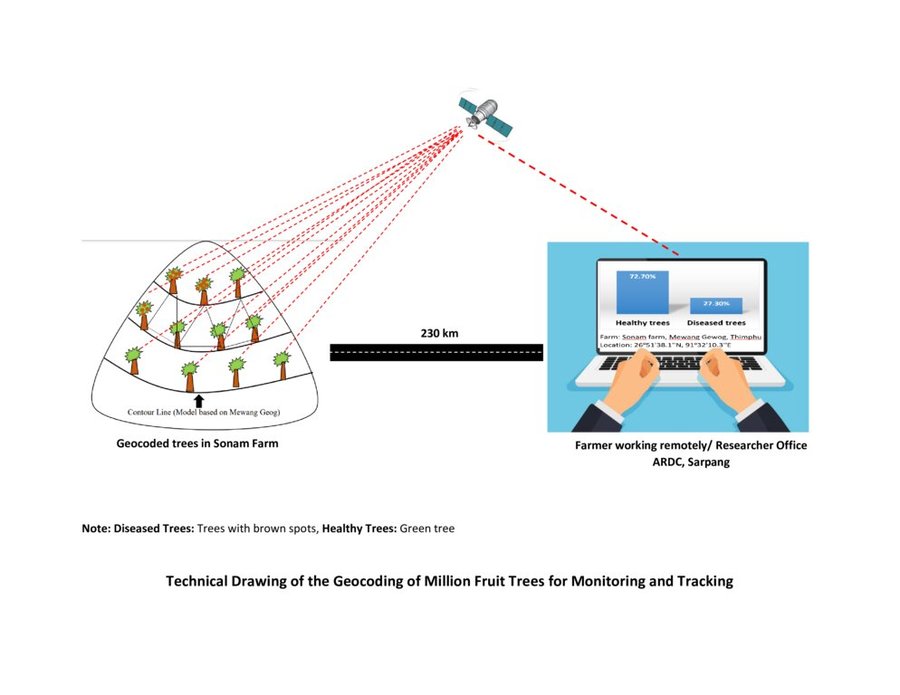
Geocoding of the “million fruit trees” initiative has been carried out across Bhutan. Different fruit trees suitable for particular agroecological zones were planted in farmers' fields in twenty districts and each sapling was geocoded.
The main elements of geocoding fruit trees involve assigning unique geographical codes or coordinates to individual trees within an orchard, utilizing technical specifications and equipment such as handheld GPS to accurately determine the location. The potential benefits of this form of geocoding include:
1. Location Mapping: Geocoding allows fruit trees to be accurately located on a map, providing a visual representation of their spatial distribution. This mapping can help identify patterns, clusters, and gaps in tree distribution.
2. Data Integration: Geocoded data can be integrated with geographic information systems (GIS) and other data sources, such as climate data, soil information, and topography. This integration provides a holistic view of the factors influencing fruit tree growth and productivity.
3. Precision: Geocoding provides precise coordinates for each fruit tree, enhancing the accuracy of data collection and analysis. This precision is crucial for making informed decisions regarding tree management and resource allocation.
4. Monitoring and Management: Geocoded fruit tree data enables efficient monitoring of tree health, growth, and potential issues. It facilitates targeted interventions, such as irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, based on the specific needs of individual trees or clusters.
5. Yield Estimation: By combining geocoded data with relevant environmental and growth information, it's possible to estimate the potential fruit yield in specific areas. This information aids in resource planning and harvest predictions.
6. Disease and Pest Management: Geocoded data can help identify patterns of disease or pest infestations. Early detection through geocoded monitoring can enable prompt intervention and prevent the spread of pests or diseases.
7. Biodiversity Analysis: Geocoding allows researchers to study the diversity of fruit tree species in different regions. This analysis can be useful for conservation efforts and understanding the ecological impact of specific tree species.
8. Research and Analysis: Geocoded fruit tree data serves as a valuable resource for scientific research. Researchers can study the effects of climate change, urbanization, and land use changes on fruit tree populations and ecosystems.
9. Decision-Making: Geocoded data assists farmers, agricultural agencies, and policymakers in making informed decisions about land use, tree planting initiatives, and resource allocation for sustainable agriculture.
10. Community Engagement: Geocoded maps of fruit trees can be shared with communities, promoting awareness of local resources, fostering community engagement, and encouraging initiatives like urban orchards or community gardens.
11. Data Visualization: Geocoded data can be visualized using maps and spatial tools, making it easier to interpret and communicate information to various stakeholders.
12. Long-Term Tracking: Geocoded data allows for long-term tracking of changes in fruit tree populations, aiding in the assessment of the success of planting initiatives and the overall health of the environment.
The major activity of the technology is marking the fruit trees with the help of GPS so that these geocoordinates can be useful in tracking down the exact location of the plant. Geocoding is labour-intensive as the field workers need to be physically present in the field while carrying out the activity. Then the data recorded in GPS is transferred to the computer and analyzed using ArcGIS. This information is available to the policymakers and Agriculture officers and is shared with the Extension Agents through which it is disseminated to the land users.
Байршил: Sigay Chiwog, Mewang Gewog, Thimphu Dzongkhag, Бутан
Дүн шинжилгээнд хамрагдсан технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газрын тоо: нэг байршилд
Технологийн тархалт: тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Тусгай хамгаалалттай газар нутагт?: Үгүй
Хэрэгжилтийн огноо: 2022
Нутагшууллын төрөл





| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ (Ngultrum (Bhutanese Currency)) | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг (Ngultrum (Bhutanese Currency)) | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | |||||
| Desuup (Guardians of peace) - Volunteers | Person-days | 6.0 | |||
| Farmers | Person-days | 10.0 | 800.0 | 8000.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | |||||
| Shovel | No. | 10.0 | 100.0 | ||
| crow-bar | No. | 5.0 | 100.0 | ||
| Spade | No. | 20.0 | 100.0 | ||
| GPS remote | No | 6.0 | 12000.0 | 72000.0 | |
| Tabs/ mobile phones | No. | 6.0 | 15000.0 | 90000.0 | |
| таримал материал | |||||
| Apple | No. | 3500.0 | 70.0 | 245000.0 | |
| Walnut | No. | 1000.0 | 120.0 | 120000.0 | |
| Almond | No. | 500.0 | 120.0 | 60000.0 | |
| Peach | No. | 1000.0 | 70.0 | 70000.0 | |
| Pear | No. | 2000.0 | 70.0 | 140000.0 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | |||||
| Manure and fertillizers | Metric Tonnes | 16.0 | 1600.0 | 25600.0 | 100.0 |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 830'600.0 | ||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 10'053.26 | ||||
| Зардлын нэр, төрөл | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн үнэ (Ngultrum (Bhutanese Currency)) | Зардал бүрийн нийт өртөг (Ngultrum (Bhutanese Currency)) | Нийт дүнгээс газар ашиглагчийн төлсөн % |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | |||||
| Weeding and fertilizer application | Per year | 4.0 | 1600.0 | 6400.0 | 100.0 |
| Irrigation | Litres | ||||
| Geocoding | per plant | 8000.0 | |||
| таримал материал | |||||
| Replacement of plants | per plant | 10.0 | 70.0 | 700.0 | |
| Технологийн арчилгаа/урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 7'100.0 | ||||
| Технологи арчилах ба урсгал ажлын нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 85.94 | ||||
The drinking water is insufficient as some households face scarcity of drinking water.
The technology aids in the monitoring and improves health and ease management of the already established orchard. Therefore, it indirectly increases crop production.
Remote or constant monitoring ensures timely management to prevent biotic and abiotic factors deteriorate the crop quality.
Geocoding enables land user to determine potential risk so that the land user can use appropriate methods to prevent crop failure.
The technology is not directly related to the product diversity. However, it provides data on existing fruit tree diversity so that the land user can plan and plant different fruit trees based on the market need which indirectly increases diversity.
Geocoding enables the land user to remotely view the cropped area and the area where the crop failed (could be due to dying of the seedlings/diseased). It enables the land user to narrow their focus on the specific area, learn about the issues causing the crop loss, provide appropriate management, and conduct plantation in that area which indirectly increases production area.
Due to increased production area with no increase in the quantity of irrigation water, water availability is likely to reduce.
There is increased demand for irrigation water for new plantations. However, with the use of technology land users can monitor the water requirement and use efficiently based on the need of the tree whereby the land users can avoid watering the trees that require less water and provide to those that require more water.
Minimal increase in expenses on agriculture inputs as planting materials (except manure) were provided to the land users for free of cost.
Once the fruit trees starts bearing fruits, income is expected to increase.
The technology is expected to reduce economic disparity by providing equal opportunity for the land users to generate income.
Workload for the project implementors or land users are significantly reduced as they need not go to the actual site to determine the progress of the Million Fruit Trees Plantation Project.
The technology indirectly aids in the increased production making an individual land user and the nation self-sufficient in fruits.
With reduced workload, land users can engage in recreational activities.
The technology will enable the project implementors to determine specific knowledge gaps and provide training in that particular field to the land users. Improving knowledge of both project implementors and land users.
Land users willing to be involved in fruit tree plantation are supported without discrimination of their social status or economic background and geocoding services are provided. This leads to the improved situation of socially and economically disadvantaged groups.
The total water quantity remains same. However, the available water per tree or sapling is reduced.
Due to the absorption of water by the roots of the fruit trees, surface run-off is decreased.
Evaporation will be decreased due to an increase in the vegetation cover from the plantation of the fruit trees.
Slight increase in the soil moisture in long run due to addition of soil organic matter and monitored irrigation.
The technology enhances easy monitoring of the trees and encourages increased soil cover.
The technology enhances soil cover reducing the soil loss from erosion.
Geocoding enables the land user to have overview of the nutrient content of the production area aiding land users to add nutrient based on the need.
Generally, there will be an increase in the soil organic matter due to an increase in production area and management practice such as the addition of manures by the land user.
Increase due to the scheduled irrigation applied to the fruit trees.
Slight increase due to proper management and care provided to the orchard.
Animal diversity in the case of pollinators such as bees increases as the fruit trees mature and start flowering.
Beneficial species such as bees are attracted to the orchards.
Pest and diseases control improves with the use of remote monitoring facilitated by this technology.
Once the fruit trees establish themselves, landslides can be reduced significantly due to vegetation cover.
This technology could potentially reduce greenhouse gas as trees utilize carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
In the long run, a well-established orchard can act as a windbreak and reduce wind velocity and damage it poses to the property.
An orchard can act as a micro-climate harbouring many plants and insect species.
Fruit trees require irrigation which reduces the availability of water for other purposes.
Having a land cover with vegetation compared to barren land reduces greenhouse gases.