Keyhole Garden [Бангладеш ]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: John Brogan
- Редактор: Shahid Kamal
- Хянагчид: Alexandra Gavilano, Deborah Niggli, Alvin Chandra
PUSTI BAGAN ("Garden for nutrition")
technologies_779 - Бангладеш
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Varadi Daniel
daniel.varadi@greendots.ch
Greendots
www.greendots.ch
Швейцар
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Taylor Sheila
sheila.taylor@greendots.ch
Send a Cow UK & Greendots
WASH Advisor:
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Terre des Hommes (Terre des Hommes) - Швейцар1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
02/08/2012
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологи азрын доройтлыг бууруулахад нөлөө үзүүлэхгүй тул газрын тогтвортой менежментийн технологи болж чадахгүй юу?
Үгүй
1.5 ГТМ-ийн Арга барилын талаархи санал асуулгын(д) суурь мэдээлэл

Peer to Peer Pass-on Approach with Women [Бангладеш ]
Terre des hommes and Greendots introduced the Peer to Peer pass-on system to enable women's groups in Bangladesh to spread the Keyhole Garden technique within their communities with the aim of enabling year-round homestead vegetable production despite the risk of flooding and tidal surge.
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: John Brogan
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
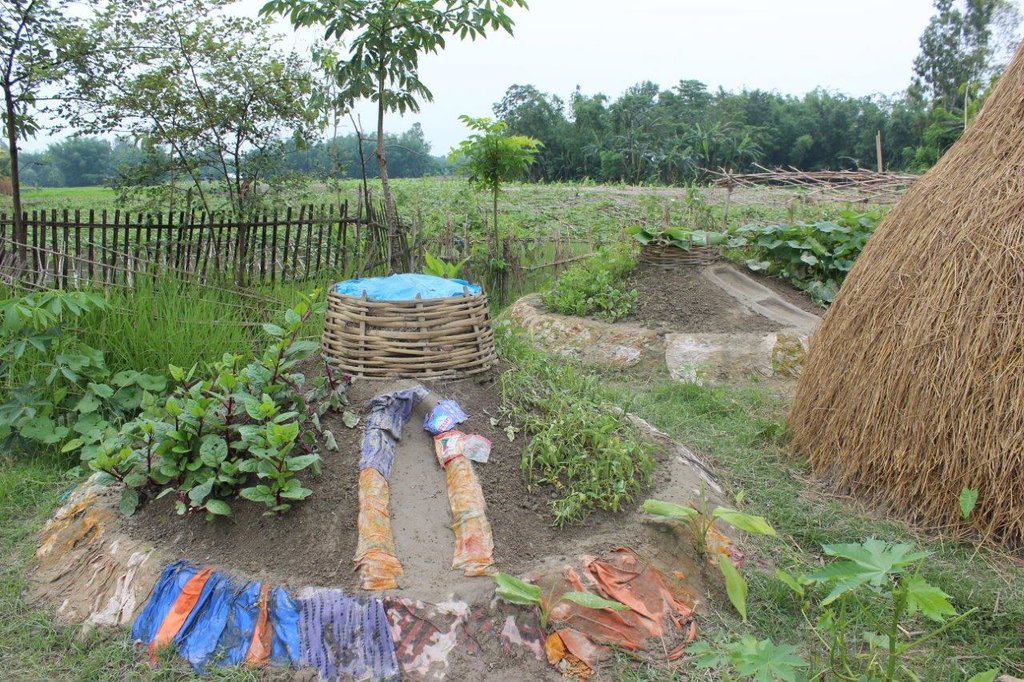
The Keyhole Garden model of homestead vegetable cultivation enhances the resilience of families living in areas with climate-related hazards, such as flooding and drought. Keyhole gardens have been shown to increase vegetable production in all seasons, thereby improving household food autonomy and dietary diversity.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
First initiated in Ugandan communities by Send a Cow UK, the keyhole garden technique is widespread in Africa. In 2011, Terre des hommes (Tdh) and Greendots piloted Keyhole Gardens for the first time in Asia, effectively adapting the design and methodology in Africa to the conditions of flood prone areas of Bangladesh, and eventually India. The garden is a good way to enhance dietary diversity, especially for poor/landless families.
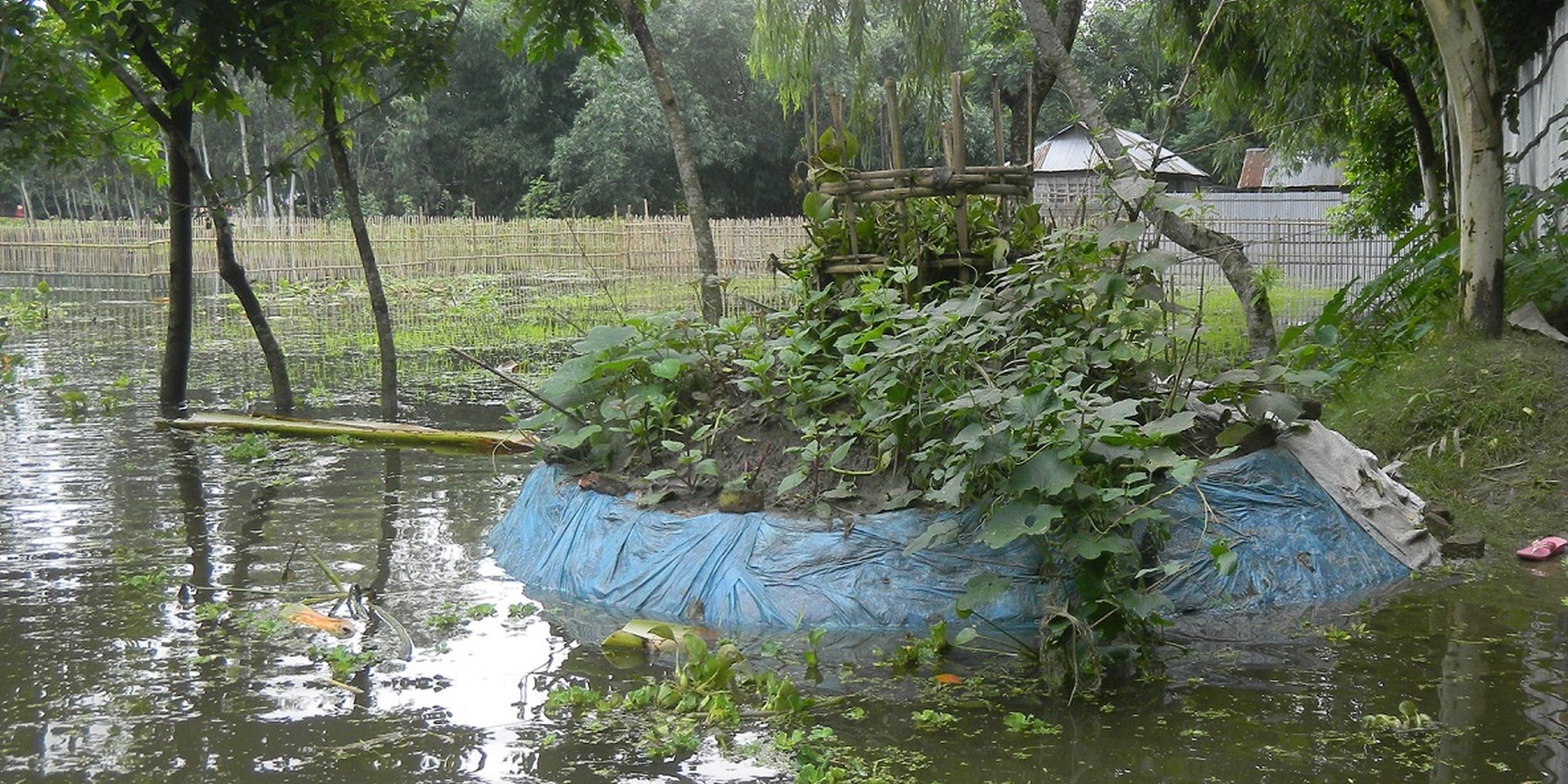
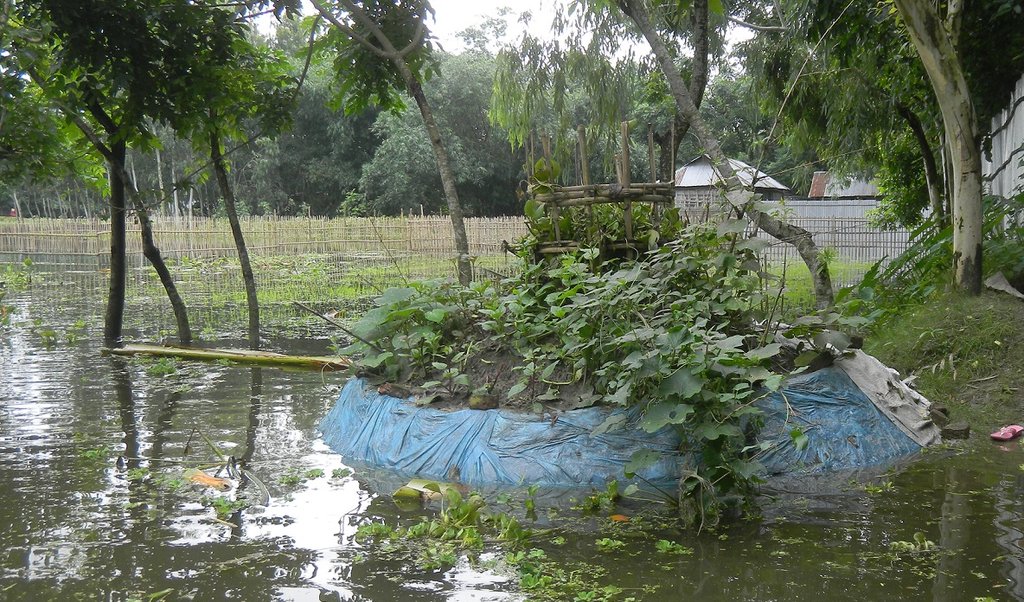
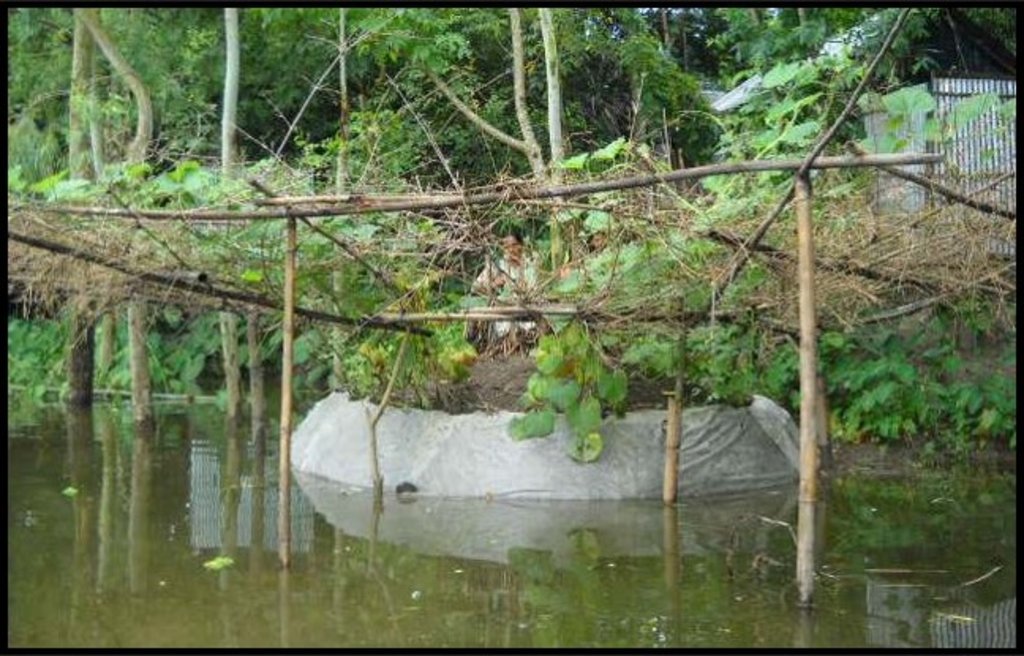
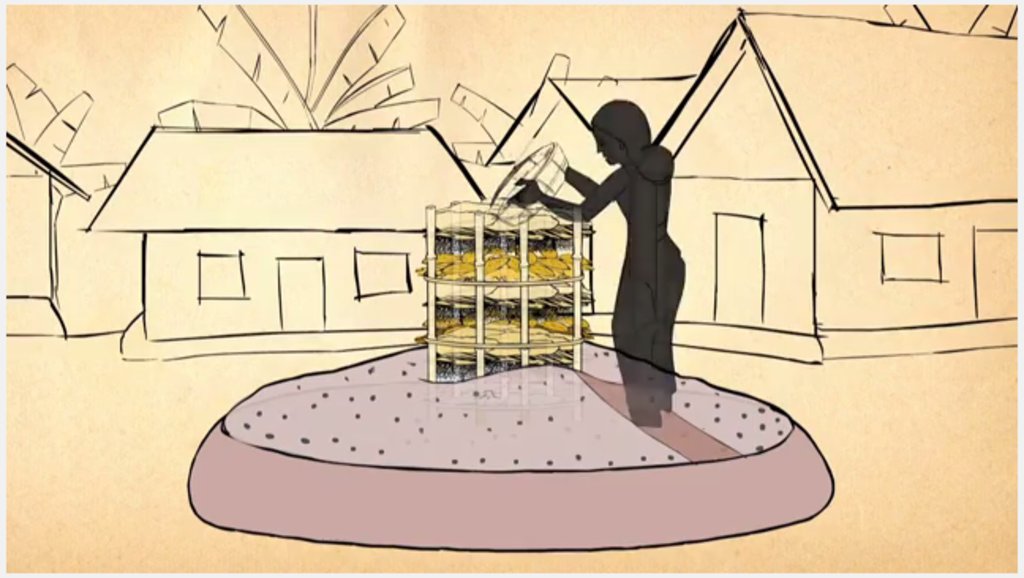
Keyhole gardens consist of a raised circular garden made of clay, shaped like a horseshoe or keyhole, with a maximum diameter of approximately three meters. For flood prone areas in Bangladesh and India, the plinth height depends on the location and is typically the same as the house plinth to resist flooding. A compost basket is built at the center of the garden. Organic matter (kitchen cuttings) and residual water are added on a regular basis through the compost pit. In some countries, bricks or stones are used to make the plinth.
The keyhole garden is a typical Low External Input Sustainable Agriculture (LEISA) approach that includes integrated composting, water retention, use of local materials, natural pest and disease control techniques, natural soil fertility measures, and proximity to the kitchen for both harvesting and care of the garden. In regions with mild conditions of flooding, tidal surge and drought, the garden increases the duration of gardening period during the year thus reducing the risk of disaster. In the aftermath of cyclone Mahasen, keyhole gardens demonstrated DRR utility: although many were partially damaged, none had to be rebuilt entirely. Where plants did not survive the storm, users were able to sow seeds immediately. On the other hand, the traditional ground-level plots used for pit and heap gardening were completely flooded / waterlogged and unusable.
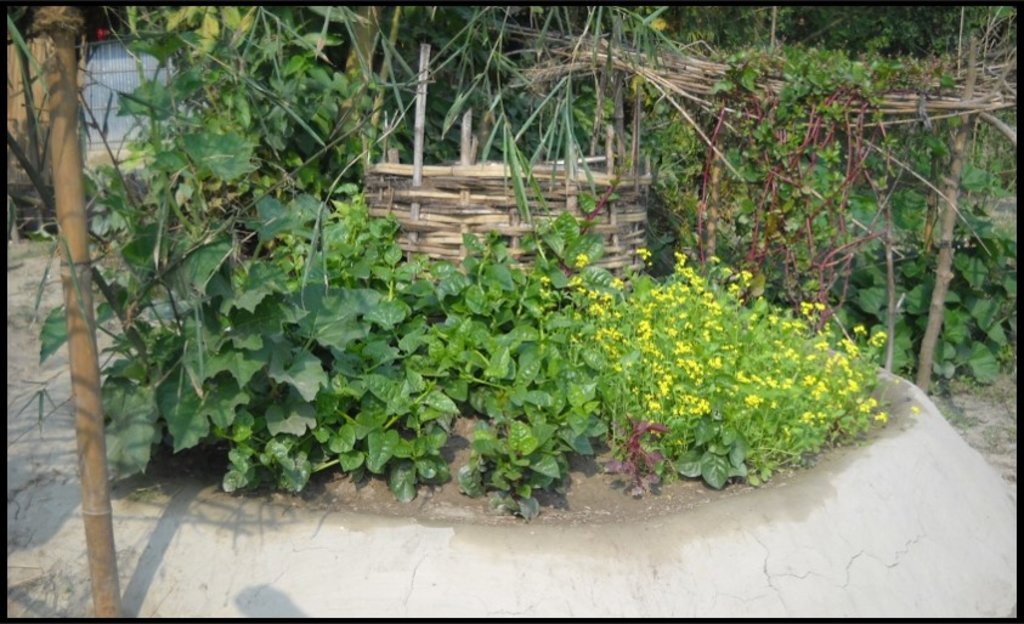
Benefits of the technology include: compact size, proximity to the household for convenient maintenance and harvesting, composting of kitchen cuttings in the basket; and an ergonomic structure (raised, accessible). The small size is also ideal to facilitate training on vegetable growing, soil fertility and pest & disease management to first-time gardeners and students in schools. Keyhole gardens are highly productive—in Lesotho a typical garden can satisfy vegetable needs for a family of eight persons (FAO, 2008). Combined, these factors are scalable as an appropriate technology for landless and marginal farmers. In Bangladesh, the gardens enabled families to produce vegetables even during the monsoon period. As the keyhole garden normally does not need to be rebuilt every year it is a more efficient technique in the long-term than traditional methods such as pit and heap.
Users say that their garden produce tends to be larger and tastier than conventional gardens or market produce; and many indicated that they were able to meet their own vegetable consumption needs and to sell surplus or gift vegetables. For some women it was difficult to access sufficient amounts of soil, which meant that they needed to walk long distances to build the plinth. (Fortunately many received support from other villagers.) Secondly, during the monsoon, while most of the land is flooded, the keyhole garden remains dry. Consequently, it may provide shelter to certain animals (e.g. rats) and attract higher number of pests. Regardless of these two limitations users agree that the benefits greatly
outweigh any observed limitations.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.4 Технологийн дүрс бичлэг
Тайлбар, товч тодорхойлолт :
https://vimeo.com/44042261
The Keyhole garden was originally developed by African farmers to preserve their crops from the wind and the sand. Locally adapted in Bangladesh in Afzal’s vegetables garden with the help of Terre des hommes staff, the Keyhole garden can also protect the crops from the heavy monsoon rain and the salt water brought by flooding and storms. These literally destroy the crops. Widely adopted, it could help in preventing malnutrition by preserving the farmer's crops.
“Two days ago, my vegetable garden was wrecked by salt water and the monsoon rains”, says Afzal, who was the first person to test the new design proposed by Tdh and its technical partner Greendots. “The storm destroyed everything – except the keyhole garden, which is intact.”
Он, сар, өдөр:
14/06/2012
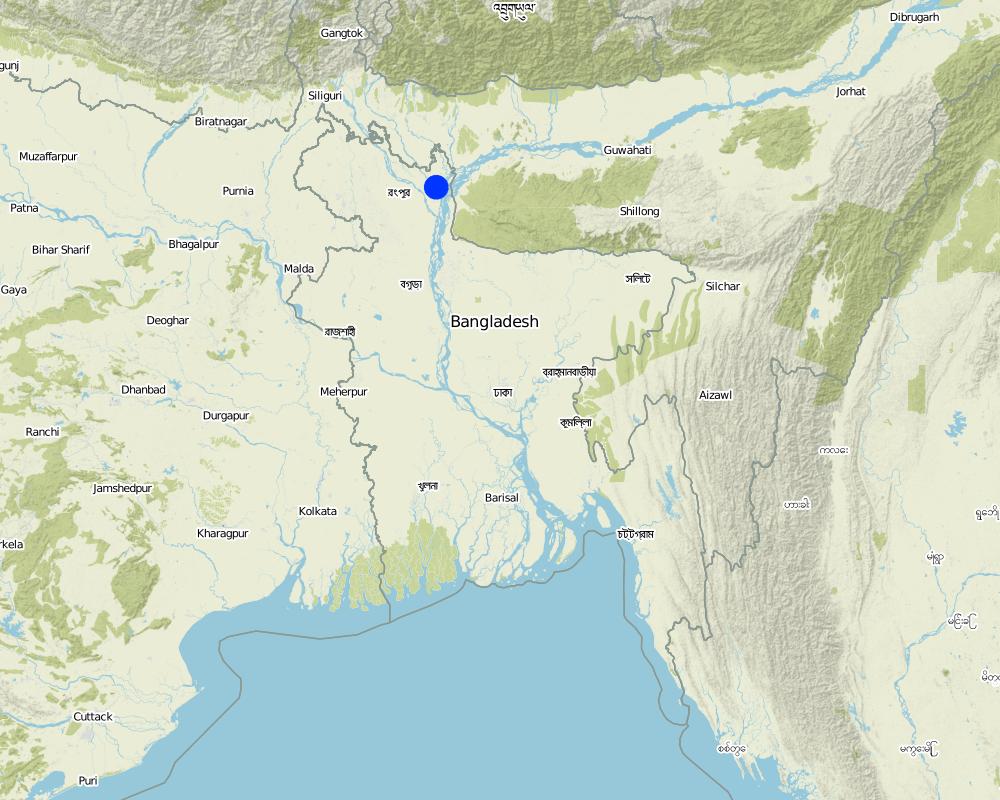
Байршил :
Patharghata, Barguna District, Barisal Division, Bangladesh
Зураглаачийн нэр :
Julien Lambert, Image of Dignity
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Бангладеш
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Kurigram District / Rajshahi and Barguna District / Barisal
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Kurigram municipality (Kurigram), Patharghata Union (Barguna)
Тайлбар:
Kurigram and Pataharghata, Bangladesh
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжих огноо
Хэрэгжүүлсэн он:
2012
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Газар ашиглагчдын санаачилгаар
- Туршилт/судалгааны үр дүн
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Үйлдвэрлэлийг сайжруулах
- гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
- Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ эрс тэс байдал болон түүний нөлөөлөлд дасан зохицох
- Уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт, түүний үр нөлөөг багасгах
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)

Тариалангийн газар
- Homestead Gardening
Гол нэрийн үр тариа (арилжааны болон хүнсний таримал):
Winter Season: red amaranth, spinach, green chilli, tomato, eggplant, carrot, radish, onion, garlic, country bean, pumpkin, cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli.
Summer & Rainy Seasons: red amaranth, green amaranth, Indian spinach, Chinese watercress, green chili, okra, eggplant, yard long bean, bitter gourd, ash gourd, cucumber, pumpkin
3.3 Газар ашиглалтын нэмэлт мэдээлэл
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн/усалгаа хосолсон
Нэг жил дэх ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 3
Тодорхойлно уу:
In Bangladesh the gardens produced in all seasons, with most challenges coming in the dry season due to soil salinity in some areas.
3.4 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- Хөрсний үржил шимт цогц менежмент
- Хортон шавьж, өвчлөлийн нэгдсэн менежмент (органик хөдөө аж ахуй)
- Гэрийн цэцэрлэг
3.5 Технологийн тархалт
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- тодорхой газар хэрэгжсэн/ жижиг талбайд төвлөрсөн
Тайлбар:
Applied in homesteads.
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Агрономийн арга хэмжээ
- А1: Ургамал/ хөрсөн бүрхэвч
- А2: Органик нэгдэл/ хөрсний үржил шим

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S11: Бусад
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Газрын доройтлыг багасгах сааруулах
Тайлбар:
See details in section 2.2
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
4.2 Техникийн үзүүлэлтүүд/ техникийн зургийн тайлбар
Gardens should be built in close vicinity to the beneficiary’s house, because gardens that are easily accessible and clearly visible are visited more regularly and maintained better.
The design is highly adaptable to local conditions and availability of free construction materials. The radius of the garden is 150CM and the delineated radius of the circular compost basket (in the center of the garden) is 45cm. The diagrams show (1) the location is near to house as an entry point for maintaining the garden; (2) the plinth is built to the same level of the house and a step is included where the plinth is high; (3) mulching to conserve the moisture; (4) interplanting a diversity of vegetables for both good vegetable health and good family nutrition; (5) using interplanted natural repellent plants as pest control for vegetables; (6) covering the basket during times of high sun intensity or heavy rain; (7) using liquid manures and plant teas as top dressing fertilisers.
Establishing what is the best height for your plinth very much depends on the local climatological conditions. In Bangladesh, the plinth is built from subsurface clayey soil, typically 2-3 feet in height - dependent on the location and level of seasonal flooding. The house plinth is a good gauge for how high to build the garden plinth. If the plinth is built too high, the roots of the plant will not be able to access sufficient water; and if built too low the next flood during the monsoon season may destroy the garden. Depending on dryness or soil/groundwater salinity, daily maintenance usually includes irrigating the soil. The outer rim of the plinth is protected with mud (and plastic or cloth) or stones. On top of the plinth is a mixture of soil and compost/manure (ratio 2:1) sloped up to the basket at a 30 - 40 degree angle. The central compost basket is filled with layers of fresh and dried vegetable matter, manure and ash to ensure that the soil fertility of the garden.
Women devised a number of different solutions to protecting the wall of the plinth and garden: Plastic bags, a combination of rice sacks (around the plinth edge) and plastic entrance way because of wear and tear (rice sacks erode faster), palm matting and old cloth. Some women put extra manure in the plinth walls to protect against flooding.
Sam Rich (www.fourthway.co.uk) has produced other technical drawings in addition to "How to Make Liquid Manure" such as: "How to make a Natural Pesticide" and "How to Make Plant Tea". There is also a version of the "How to Make a Keyhole Garden" in English from the experience in Africa.
4.3 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Нэгжийг тодорхойл:
Keyhole Garden
Үнэ өртөгийг тооцоход ашигласан мөнгөн нэгж:
- Америк Доллар
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өрдийн ажлын хөлсийг тодорхойл:
U.S.$2.50
4.4 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clear land; mark out basket and external boundary using rope and stick pivoted from the centre) | Бүтцийн | Anytime |
| 2. | Build plinth (highest monsoon flood level+30cm); | Бүтцийн | Anytime |
| 3. | Construct basket at the centre from local materials. Fill basket with composting materials; | Бүтцийн | Anytime |
| 4. | Bring soil and heap it around the central basket. Any available animal dung can also be added into the soil mix for greater initial productivity. | Бүтцийн | Anytime |
| 5. | Plant vegetable seeds around the garden - a mix for good family nutrition and to stop the spread of pests and diseases; | Агрономийн | According to the seasonal varieties |
| 6. | Mulch between plants to protect the soil. | Агрономийн | Anytime |
| 7. | Protect the walls with rice sacks or other waterproof protection if neccessary. | Бүтцийн | Anytime |
4.5 Байгуулалтад шаардагдах зардал ба материал
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Building the garden | person-days | 3.0 | 2.5 | 7.5 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | clay | 20.0 | ||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 7.5 | |||||
Тайлбар:
Firstly, building the garden requires an initial investment in terms of labour and (locally available) inputs, such as soil and wood and clayey soil for the plinth (stones and bricks are frequently used for the plinth in Africa). These inputs are available on the homestead or in the community and generally free of cost. In rare cases families paid to have soil carted to their homestead, thus increasing the initial structural costs.
4.6 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Арга хэмжээний төрөл | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding, harvesting, watering | Менежментийн | Daily |
| 2. | Structural maintenance on the garden | Бүтцийн | Annual |
4.7 Засвар үйлчилгээ / урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах зардал ба материал (жилээр)
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Maintenance | person-days | 11.0 | 2.5 | 27.5 | 100.0 |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Structural maintenance on the garden | person-days | 1.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
| Барилгын материал | Earth Clay -depends on height: ex .4m plinth) | cubic meter | 11.0 | |||
| Барилгын материал | Manure (quantity depends on design) | cubic meter | 2.0 | |||
| Барилгын материал | Basket (sticks/bamboo with thin sticks to weave the basket | Sticks | 15.0 | |||
| Барилгын материал | Protective material, rice bags/stones/plastic | Square meter | 18.0 | |||
| Технологийг арчилах тордоход шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 30.0 | |||||
Тайлбар:
In Bangladesh, women referred to the time spent working on the keyhole garden as “leisure time” and that they do this work after they have completed their domestic chores. Women estimated 45 minutes daily of such activity to maintain the garden. Calling it "leisure time" is misleading, but it suggests that most women generally enjoy working in the garden and do not regard it as heavy labour. The daily wage of an agricultural labourer differs per region. In Tdh's project area, wages are relatively low, especially for women. While male labourers may earn 200 BDT ($2.50) per day, women usually earn only 90 to 150 BDT. For the calculation, we applied the principle of equal pay for equal work, taking 200BDT per day.
4.8 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг зардлыг тодорхойлох гол хүчин зүйлсийг дурьдана уу:
Over the last few years, people in disaster-affecteed areas of Bangladesh have become familiar to receiving during humanitarian distributions; and expect “hand-outs” if they were to participate in a development project. The Keyhole garden project, however, follows the LEISA approach and does not rely on giving free inputs to the participants. (In a few cases where the local population was lacking seeds and experience in seed production, women's groups were given seeds and training.) A lack of reliance on external inputs or subsidies contributes to the sustainability of the project. The inputs (clay, manure, sticks, rocks, etc.) are locally available and usually do not require additional expenses. This may not be the case in all contexts.
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
2666.00
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
Applied in areas with monsoon and drought like conditions in the project areas in Bangladesh.
Суурь болгон авсан цаг уурын станцын нэр:
http://data.worldbank.org/indicator/AG.LND.PRCP.MM
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Чийглэг
- Хагас чийглэг
- Хагас хуурай
The technology is adapted to semi-arid areas/countries in Africa like Uganda and Tanzania.
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- шаардлагагүй
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Хүнд (шаварлаг)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- Хүнд (шаварлаг)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Дунд (1-3 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээм ба чанар
Хөрсний усны гүн:
< 5 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
Хангалттай
Усны чанар (цэвэрлээгүй):
Муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны давсжилт асуудал болдог уу?
Тийм
Тодорхойлно уу:
In project sites along the Bay of Bengal
Энэ газар үер усанд автдаг уу?
Тийм
Тогтмол байдал:
Олон удаагийн
5.5 Биологийн төрөл зүйл
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- Дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- Амь зуух арга хэлбэрийн (өөрийгөө хангах)
- Холимог (амь зуух/ худалдаа наймаа
Фермээс гадуурх орлого:
- Нийт орлогын %10 доош хувь
- Нийт орлогын % 10-50 хувь
Чинээлэг байдлыг харьцангуй түвшин:
- Нэн ядуу
- Ядуу
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Хувь хүн / өрх
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- Хүнд хүчир ажил
- Амьтны зүтгүүр
Хүйс:
- Эмэгтэй
- Эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- Дунд нас
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шаардлагатай шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Using a methodology called the problem tree analysis it is understood that the people living in the two working areas regularly experience health-related problems, economic challenges, and agricultural difficulties.
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчдын эзэмшдэг эсвэл түрээслэдэг газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ нь жижиг, дунд, том оворт тооцогдох уу (орон нутгийн чиг баримжаагаар)?
- Бага-хэмжээний
Тайлбар:
The majority of the project beneficiaries are "landless" having access to small homestead areas and without cropland. Most households have access to small (< 16 decimal) or very small (< 6 decimal) homestead areas.
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Хувь хүн, тодорхой цол эргэмгүй
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- Хувь хүн
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- Нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
боловсрол:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
техник дэмжлэг:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зах зээл:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
эрчим хүч:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зам ба тээвэр:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
ундны ус ба ариутгал:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
Газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
ГТМ хэрэгжхээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
<5% of pilot families growing vegetables in all 3 seasons
ГТМ хэрэгжсэнээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
50% of the pilot families able to grow vegetables in 3 seasons
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Before the project started, the majority of the participants were not able to produce vegetables year round. Especially during the monsoon months, people were dependent on produce available at the local market. The baseline survey indicated that in both regions more than 50% of the households would cultivate vegetables for a maximum of 3 months per year and in Kurigram 30% of the participants were not able to grow vegetables at all.
This situation has changed significantly after the introduction of the keyhole gardens. At least 50% of the households were able to produce vegetables during each season. Where in the past almost no one was able to cultivate during the monsoon period, now on average 63% of the households in Kurigram and 73% of the households in Patharghata were growing vegetables in the wet season.
The summer figures are actually lower than the monsoon figures. Seeds did not germinate well, because participants were not fully prepared to deal with the dry and saline conditions during this season. Learning from this experience, and with adequate support from Tdh, participants should be able to achieve higher cultivation rates in the future.
олон янз бүтээгдэхүүн
ГТМ хэрэгжхээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
Average of 2-4 types of vegetables grown.
ГТМ хэрэгжсэнээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
Average of six types of vegetables grown
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
During the field visits and individual interviews in June 2013, the majority of the participants indicated that in the keyhole garden they usually grow 6 or more different types of vegetables at any given time. This is a marked difference from previous years, when the majority of people in Patharghata would only grow 2 types of vegetables. In Kurigram the baseline was somewhat higher (31% cultivated 4 types of vegetables per year on average), but still significantly lower than in 2013. By increasing the different types of vegetables grown, the families have access to a more diversified diet.
Үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
ГТМ хэрэгжхээс өмнөх тоо хэмжээ:
0
ГТМ хэрэгжсэнээс хойшхи тоо хэмжээ:
333
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
In addition to the 175 pilot keyhole gardens, an additional 158 gardens were started on homesteads either via peer to peer pass-along system or spontaneous copy/replication of the technology.
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
эрүүл мэндийн байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The Keyhole Garden supports a diversified diet by enabling year-round vegetable production; thus boosting the resilience of homesteads exposed to extreme weather patterns (drought or monsoon/flood seasons).
Нийгэм, эдийн засгийн хувьд эмзэг бүлгийнхний нөхцөл байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Gardens will quickly increase household vegetable production, easing economic burden and providing for the household consumption or surplus to sell or gift. The latter can increase social bonding and benefit peer to peer linkages.
Teaching
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Keyhole garden building and maintenance teaches lessons of good soil, water and vegetable management that can be transferred to field crops or plain large scale vegetable growing.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Хөрс
хөрс алдагдах
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Precious topsoil is not lost during flooding events.
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
үер усны нөлөө
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Gardens that are not submerged by floods continue to produce in the monsoon season.
Бусад экологийн үр нөлөө
Surpluses can be used for selling or gifting; increased vegetables especially at times when they are not usually available enables families to save money on expensive purchases out of the normal vegetable season
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Teaching
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Keyhole garden building and maintenance teaches lessons of good soil, water and vegetable management that can be transferred to field crops or plain large scale vegetable growing.
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт ба Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул/гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагч нарын дүгнэлтээр)
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюулууд (гамшигууд)
Цаг уурын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Тропикийн шуурга | Дунд зэрэг |
| Орон нутгийн аянга цахилгаантай бороо | Сайн |
Гидрологийн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | Маш сайн |
| Далайн үер / задгай усны үер | Сайн |
Бусад уур амьсгалд хамаарах үр дагаварууд
Бусад уур амьсгалд хамаарах үр дагаварууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Ургалтын хугацаа багасах | Маш сайн |
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
Тайлбар:
No long term study available.
In most cases no (or very low) investment cost in materials and a low investment cost in labor was necessary. Thus the establishment and maintenance costs are relatively low compared to the benefit of increased homestead vegetable production and access to produce for increasing dietary diversity. The benefit increases when the technology supports resilience to flooding as was the case from flooding (Kurigram), and partially from a cyclone (Patharghata).
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
- 50 -иас их %
Боломжтой бол, тоогоор илэрхийл (өрхийн тоо эсвэл бүрхэх талбай):
333 from the pilot study. Subsequent projects by Tdh from 2013-2015 have seen over 3'500 keyhole gardens created in Bangladesh and India.
Технологийн нэвтрүүлсэн иргэдээс хэд нь өөрийн санаачлагаар буюу өөр эх үүсвэрээс материалын болон мөнгөн дэмжлэг авалгүй нэвтрүүлсэн бэ?
- 90-100 %
Тайлбар:
All of the adopters did so with training but without inputs. Spontaneous adoption of the Keyhole Garden without training is not easy to measure, but Tdh's experience shows a conservative average of 11% (38 of 333 gardens).
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Хувьсан өөрчлөгдөж буй нөхцөл байдалд Технологид сүүлд ямар нэг шинэчлэл хийгдсэн үү?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол ямар өөрчлөлтийг даван туулахад шинэчлэл хийгдсэн бэ?
- уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт/ эрс тэс байдал
Технологийн дасан зохицох байдлыг тодорхойл (хийц, материал, төрөл зүйл г.м.):
The technology was adapted from semi-arid zones in Africa (where soil amelioration and water conservation were priorities and materials such as stones and brick are available) to areas of South Asia prone to flood and tidal surge.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
Seasonal local agriculturalists reported that gardens yielded high productivity with good vegetable quality and diversity; withstood heavy monsoon rains lasting for several days; and withstood a salt water tidal intrusion that destroyed adjacent traditional gardens. During the FGDs women clearly expressed a lot of enthusiasm for the project and all the participants indicated that they would continue with their garden, even if Tdh would no longer provide any support. One volunteer reported successfully harvesting five common vegetables usually impossible to grow in monsoon conditions: - In plain land we can cultivate once in a year but in keyhole garden we can harvest vegetables in three seasons and they don't go underwater in the rainy season - Save money for the family: don't need to buy fertilizers or vegetables and some people earn money by selling the garden product - We can collect vegetables for the children’s requirements directly from the garden when they need them - In a small space you can have lots of different vegetables and the taste is much better because the garden depends on compost – no chemicals - The cost to make is it very low, but you need labour; by our own labour we can build it - Because of composting the garden can always get nutrients |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
|
The keyhole garden project has been very successful and has largely achieved its core objective to improve year-round access to nutritious food from the homestead area. These benefits are summarized again as: - Appropriate size for landless homesteads, also ideal to facilitate training on LEISA techniques to first-time gardeners and students in schools. - Proximity to the household for convenient maintenance and harvesting, composting of kitchen cuttings in the basket; - Ergonomic structure (raised, accessible). - Highly adaptable to local conditions that supports resilience to flood and drought conditions. - Highly productive—families produced vegetables even during the monsoon period. - As the keyhole garden normally does not need to be rebuilt every year it is a more efficient technique in the long-term than traditional methods such as pit and heap. Therefore, the reviewer did not suggest any major changes to the technique or project; rather to focus on specific issues that could help making the project more efficient and that could help broaden its impact. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
|
No major weaknesses in the technology or design were expressed. However for some women it was difficult to access sufficient amounts of soil, which meant that they needed to walk long distances to bring soil to build the plinth. In coastal areas where saline intrusion in groundwater and soils is on the rise, growing and irrigating crops is difficult in the dry season. |
Some women received support from other family members or neighbours; identify a support network for families having challenges to access soil to build the plinths. Continue to look for for alternative irrigation sources and/or groundwater recharge innovations as well as soil conservation techniques to protect against salinity. Likewise, saline resistant vegetable varieties may be available. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
|
More careful planning of the location for the keyhole garden is needed. In Patharghata 11 women decided to relocate their garden within the first year. This suggests that the women appreciate the benefits of the garden, but having to break down and move the garden is a rather laborious activity. Not surprisingly, women who have less time to work in the homestead area, e.g. due to work or other out-of-home responsibilities, are not able to maintain their keyhole garden so well. |
Spend more time to assist the participants with identifying the most suitable locations to construct the garden for a keyhole garden in the homestead area at the start of the project. While maintaining a focus on women, involve the husband or other family members/ neighbours and ensure that they are also trained and ensure that the garden is clearly visible and can be accessed. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн аргууд / эх сурвалжууд
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
50: The project evaluation took place from 4 June to 12 June 2013 with field visits in the two project areas, Kurigram and Patharghata. In total 5 Focus Group Discussions (FGD), with approximately 10 participants per FGD, were organized during this period. The core objective of the FGDs was to assess whether keyhole gardens have contributed to increases in vegetable production throughout the year and if this has lead to improved consumption practices. The additional aim of the FGDs was to learn directly from the participants about their nutritional needs and their ideas to further improve the keyhole garden project.
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
8: In addition to the FGDs the consultant carried out eight individual interviews with project
participants from the two regions. The individual interviews provided more detailed
information about production techniques and about the impact of the project at the
household level.
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
Al-Amin S, 2012 and 2013, Tdh Bangladesh, Monthly Situation Reports for Garden Projects (unpublished)
Taylor S, 2013, Discussion paper for the Agrobiodiversity Conference, Dhaka, 28 January
2013, “Keyhole Gardens – great potential for improving homestead crop diversity and
mother & child nutrition”
Taylor S, 2012, Tdh Bangladesh, Project Report Homestead Garden for Greendots (unpublished)
Van Hout, 2013, Keyhole Gardens: Improved Access to Homestead Vegetables and Dietary Diversification, External Evaluation and Capitalization of the Keyhole Garden Project in Bangladesh (unpublished)
Varadi D, 2011, Tdh Bangladesh Field Visit Report for Greendots (unpublished)
7.2 Хүртээмжтэй ном, бүтээлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
"Keyhole Gardens: Improved Access to Homestead Vegetables and Dietary Diversification- External Evaluation and Capitalization of the Keyhole Garden Project in Bangladesh", Van Hout, R., 2013
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Freely available: Terre des hommes Lausanne Asia Desk: info@tdh.ch
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
“Keyhole Gardens – great potential for improving homestead crop diversity and mother & child nutrition”, Taylor S, 2013, Discussion paper for the Agrobiodiversity Conference, Dhaka, 28 January 2013
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
Freely available: Terre des hommes Lausanne Asia Desk: info@tdh.ch
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
"Keyhole Gardens in Lesotho", FAO Nutrition and Consumer Protection Divis"ion (AGN), 2008 (with Send a Cow UK)
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
http://www.fao.org/ag/agn/nutrition/docs/FSNL%20Fact%20sheet_Keyhole%20gardens.pdf
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет дэх нээлттэй холбоосууд
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Greendots - Terre des hommes technical partner for Keyhole Gardens in South Asia
URL:
www.greendots.ch
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Send a Cow UK: How to make an African style raised bed (YouTube, ex. Uganda)
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ykCXfjzfaco
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Send a Cow UK - Keyhole Garden resources (Learning from Africa: How to make a Keyhole Garden)
URL:
http://www.sendacow.org.uk/lessonsfromafrica/resources/keyhole-gardens
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Fourthway's posters online: Smallholder organic agriculture (Uganda, including Keyhole gardens)
URL:
http://www.fourthway.co.uk/posters/
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Fourthway's posters online: Smallholder organic agriculture (Bangladesh, including Keyhole gardens)
URL:
http://www.fourthway.co.uk/bangladesh/index.html
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Terre des hommes: First Keyhole Garden in Asia (to resist storm surge/floods in Bangladesh)
URL:
https://vimeo.com/44043929
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд

Peer to Peer Pass-on Approach with Women [Бангладеш ]
Terre des hommes and Greendots introduced the Peer to Peer pass-on system to enable women's groups in Bangladesh to spread the Keyhole Garden technique within their communities with the aim of enabling year-round homestead vegetable production despite the risk of flooding and tidal surge.
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: John Brogan
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна