Permeable rock dams [Буркина Фасо]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Dieter Nill
- Редактор: –
- Хянагчид: Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger, Joana Eichenberger
Digues filtrantes (French)
technologies_1617 - Буркина Фасо
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Dorlöchter-Sulser Sabine
Misereor
Герман
ГТМ мэргэжилтэн :
Mamadou Abdou Sani
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP)/GIZ
Нигер
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Manual of Good Practices in Small Scale Irrigation in the Sahel (GIZ )Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) - ГерманТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Misereor - Герман1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологи азрын доройтлыг бууруулахад нөлөө үзүүлэхгүй тул газрын тогтвортой менежментийн технологи болж чадахгүй юу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Permeable rock dams serve to restore seriously degraded farmland and forest/rangeland and are used to fill in gullies and control water flow.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
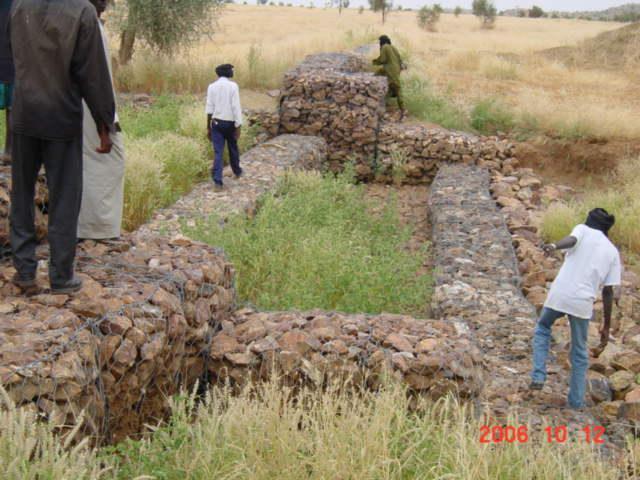
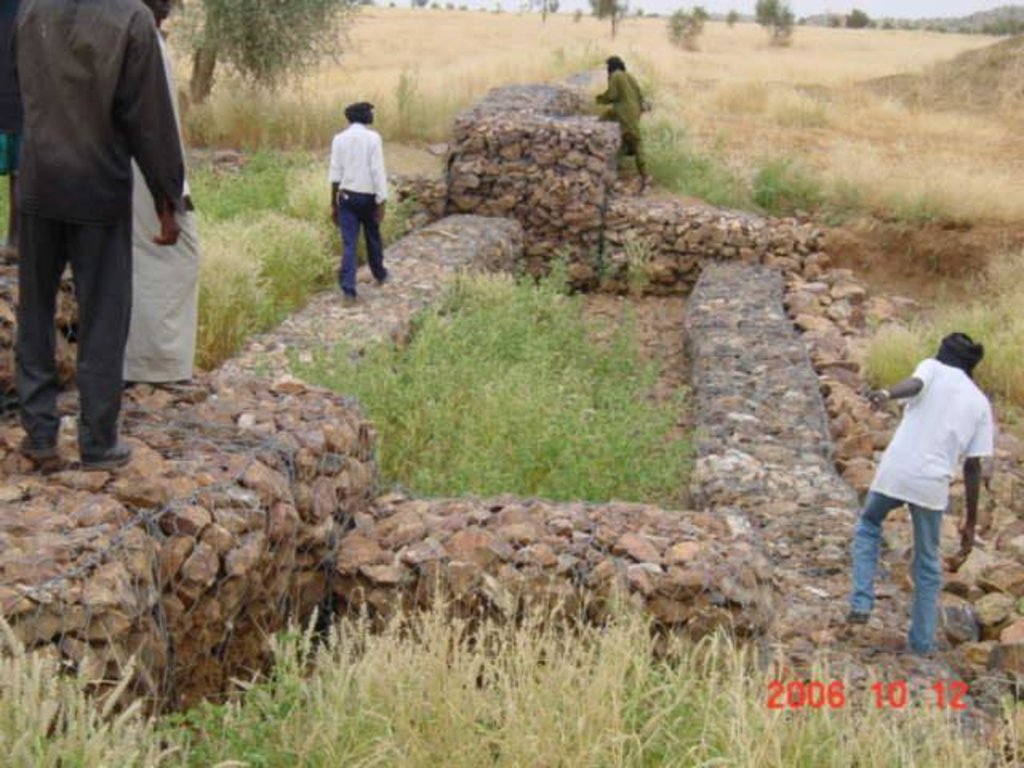
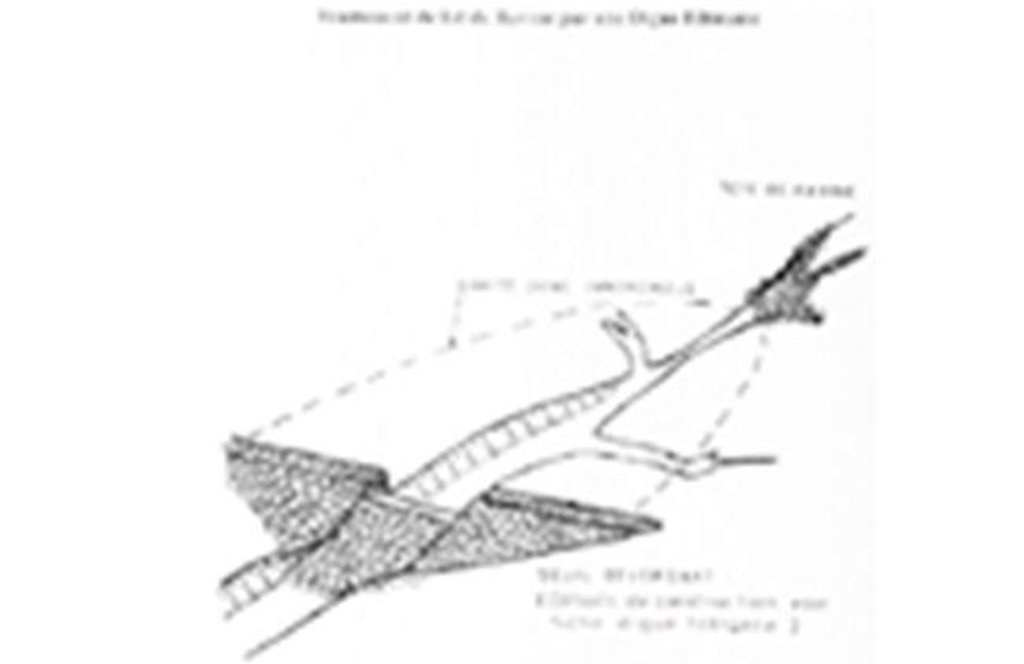
The permeable rock dam is a structure built in gullies using loose rocks and stones and sometimes reinforced with gabions. A filtering layer (blanket of gravel or small stones) is laid in a foundation trench. Further layers of medium-sized and large stones and rocks are laid on top. They are between 0.50 and 3 metres high, and the width of the foundation and the crest depends on the estimated volume of water flow. The structure built across the gully is extended to the sides with the construction of wingwalls that spread the water over a larger area to the sides of the dam. The total width of the structure is generally at least three times its height. The dams can be constructed with or without a spillway. A spillway is required when flood water flow is stronger.
Purpose of the Technology: Permeable rock dams are used to fill in gullies and control water flow. They slow the flow of floodwaters and spread the water over adjacent land. This improves infiltration, and sediment builds up behind the dams. In time, the sediment fills in the gully. This stops lateral drainage from the land on either side, increasing its productivity. High infiltration upstream of the dam contributes to recharging the groundwater system. These structures are therefore also effective in raising the water table in wells and in protecting the bottom-lands from sand filling and gully erosion. They are used in combination with other measures, such as reforestation and stone bunds, to protect and improve the surrounding area, and to increase the area of land that can be used for growing crops.
By dissipating the flow of floodwaters, they ensure better use of rainwater and are therefore important in dry periods. The conservation of water for longer periods and the fine particles of earth trapped by the structure favour the establishment of natural vegetation along it, which helps to stabilise the dam. Seeds are also trapped, favouring the spontaneous growth of grass and trees upstream and downstream, which contributes to restoring and conserving biodiversity.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The sustainability of permeable rock dams depends on the quality of construction and whether they are maintained regularly. A certain amount of expertise and good community organisation is required to repair any cracks in
the dam. Biological measures (sowing grass and planting trees) increase the stability of the structure.
The size of a permeable rock dam can vary considerably from one site to another. The cost is also affected by the distance of the site from the quarry, the topography of the terrain and the actual amount of rock carried in each lorryload. It costs less to construct this type of structure with loose stones and rocks than with gabions.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Буркина Фасо
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Burkina Faso, Chad
Тайлбар:
Burkina Faso & Chad
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжих огноо
Байгуулсан тодорхой оныг мэдэхгүй бол баримжаа хугацааг тодорхойл:
- 10-50 жилийн өмнө
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by GIZ (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation), and PATECORE (project for land development and resource conservation in Plateau Central Burkina Faso)
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Тийм
Газар ашиглалтын холимог тогтолцоог (тарилан/бэлчээр/ой мод) тодорхойл:
- Агро-бэлчээр (тарилан-мал аж ахуйн хослуулсан тогтолцоог хамруулан ойлгоно)

Тариалангийн газар
- Нэг наст үр тариа
Нэг жил дэх ургамал ургах улирлын тоо:
- 1
Тодорхойлно уу:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: August to October

Бэлчээрийн газар
Тайлбар:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil erosion, surface runoff, unfertile land
Constraints of common grazing land
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- Налуугийн хөндөлн огтлолын дагуух арга хэмжээ
- урсац өөрчлөх ба урсац бүрдүүлэх
- Гадаргын усны менежмент (булаг шанд, гол, нуур, далай)
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Барилга байгууламжийн арга хэмжээ
- S5: Далан, хотгор, цөөрөм
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл
- Wc: Нуур, далайн эргийн эвдрэл

Хөрсний химийн доройтол
- Cn: Үржил шим болон органик агууламж буурах (элэгдлийн шалтгаангүй)

Биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах

Усны доройтол
- Ha: Хуурайшилт
- Hg: Гүний ус / усан судалт давхаргын түвшин өөрчлөгдөх
Тайлбар:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted land use methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), floods, droughts, population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land)
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх
- Хүчтэй доройтсон газрыг нөхөн сэргээх/ сайжруулах
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зурагтай уялдана):
Permeable rock dam with spillway
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5-3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 9
Зохиогч:
PATECORE
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг зардлыг тодорхойлох гол хүчин зүйлсийг дурьдана уу:
The size of a permeable rock dam can vary considerably from one site to another. The cost is also affected by the distance of the site from the quarry, the topography of the terrain and the actual amount of rock carried in each lorryload. The use of gabions also increases the cost considerably.
cost items:
- Topographical surveying
- supply of quarry rock/stones: 113 m3 per 100 linear metres.
- Labour: depends on the size of the dam.
- Transportation by lorry: 23 lorryloads (skip loader – 4.5 m3 per load).
Other costs: Equipment (pickaxes, shovels, wheelbarrows, water-tube level, etc.).
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Хагас хуурай
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
Гадаргын талаархи тайлбар ба бусад тодорхойлолт:
Slopes on average: Also moderate (6-10%), rolling (11-15%)
Landforms: Also valley floors
Altitudinal zone: Also 1000-1500 m a.s.l.
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Дунд зэрэг (шавранцар)
- Хүнд (шаварлаг)
Боломжтой бол хөрсний бүрэн тодорхойлолт, боломжит мэдээллийг өгнө үү, жишээ нь хөрсний төрөл, хөрсний урвалын орчин/хүчиллэг байдал, катион солилцох чадавхи, азотын хэмжээ, давсжилт г.м.
Soil fertility: Medium and low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium and poor
Soil water storage capacity: Medium and low
5.4 Усны хүртээм ба чанар
Хөрсний усны гүн:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
Дунд зэрэг
5.5 Биологийн төрөл зүйл
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Бага
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Чинээлэг байдлыг харьцангуй түвшин:
- Нэн ядуу
- Ядуу
Хүйс:
- Эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчдын бусад шаардлагатай шинж чанарыг тодорхойл:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4% (mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчийн ашигласан газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ нь жижиг, дунд, том оворт тооцогдох уу (орон нутгийн чиг баримжаагаар)?
- Бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Төр засаг
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- Нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- Нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Тайлбар:
traditional land use rights on fields, common lands on pasture and forest land
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
боловсрол:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
техник дэмжлэг:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зах зээл:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
эрчим хүч:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зам ба тээвэр:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
ундны ус ба ариутгал:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
Газар тариалангийн үйлдвэрлэл
тэжээл үйлдвэрлэл
модлогийн бүтээмж
Үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Орлого, зарлага
тариалангийн газрын орлого
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
хүнсний аюулгүй байдал/ өөрийгөө хангах
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын талаархи мэдлэг
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
As these dams are used in valley bottoms and the beds of seasonal streams to increase infiltration, they can also contribute to raising the water table. Such sites are particularly suitable for horticulture and market gardening, which is important in the off-season. The produce supplements the food available and is an extra source of income.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
ус хураах / цуглуулах
гадаргын урсац
гүний усны түвшин / уст давхарга
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
шимт бодисын эргэлт/ сэргэлт
Биологийн: ургамал, амьтан
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
Доод урсгалын үер
урсацын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдана
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт ба Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул/гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагч нарын дүгнэлтээр)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | Сайн |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюулууд (гамшигууд)
Цаг уурын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Орон нутгийн аадар бороо | Сайн биш |
| Орон нутгийн салхин шуурга | Сайн |
Уур амьсгалын гамшигууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Ган гачиг | Сайн |
Гидрологийн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| усны үер (гол) | Сайн биш |
Бусад уур амьсгалд хамаарах үр дагаварууд
Бусад уур амьсгалд хамаарах үр дагаварууд
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Ургалтын хугацаа багасах | Сайн |
Тайлбар:
Physical structures can be biologically stabilized through planting of grass, bushes or trees. Damages are generally small but need to be repaired quickly.
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Эерэг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
Тайлбар:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The potential for replication depends on the type of terrain and whether there is a supply of rocks nearby.
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Permeable rock dams are used to fill in gullies and control water flow. They slow the flow of floodwaters and spread the water over adjacent land. This improves infiltration, and sediment builds up behind the dams. In time, the sediment fills in the gully which favours the establishment of natural vegetation along it, which helps to stabilise the dam. Seeds are also trapped, favouring the spontaneous growth of grass and trees upstream and downstream, which contributes to restoring and conserving biodiversity. |
| By dissipating floodwater flow, they also contribute to reducing sand filling in valleys further downstream. |
| As these dams are used in valley bottoms and the beds of seasonal streams to increase infiltration, they can also contribute to raising the water table. Such sites are particularly suitable for horticulture and market gardening, which is important in the off-season. The produce supplements the food available and is an extra source of income. |
| increase the area of land that can be used for growing crops |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| Depending on the size of the dam, the construction of this type of structure may require a high level of engineering expertise (topographical surveying, calculation of floodwater flow).It also requires a large amount of quarry rocks, which means that the cost of the structure and the labour and transport required is significantly higher than for structures made with stones. As the data required for calculating floodwater flow is often unavailable, the dams must be observed during the first few years, so that they can be reinforced and repaired if necessary. | It is important for farmers to have access to partners providing the necessary know-how, means of transport and support for community organisation. The community must be trained to carry out repair work. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн аргууд / эх сурвалжууд
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
01/07/2012
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
URL:
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна