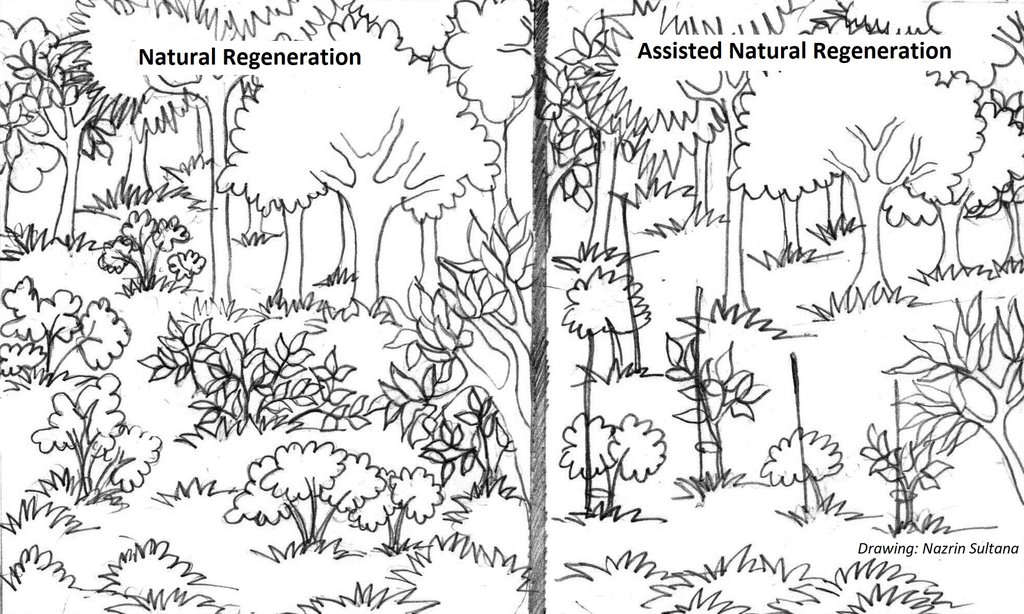
Assisted Natural Regeneration [Бангладеш ]
- Шинийг нээх:
- Шинэчлэх:
- Мэдээлэл цуглуулсан: Fazlay Arafat
- Редактор: –
- Хянагчид: Nicole Harari, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Ursula Gaemperli
ANR
technologies_4372 - Бангладеш
Бүлгүүдийг үзэх
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаах1. Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
1.2 Технологийг үнэлэх, баримтжуулах ажилд хамаарах мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүс, байгууллагуудын холбоо барих мэдээлэл
Мэдээлэл өгсөн хүн (с)
Газар ашиглагч :
Morshed Hoq Mahabub
Bangladesh Forest Department
Бангладеш
Газар ашиглагч :
Islam Md. Saiful
Bangladesh Forest Department
Бангладеш
Газар ашиглагч :
Rahman Md.
Community Patrolling Group (CPG), Medhakocchopia
Бангладеш
Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн төслийн нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Технологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
Bangladesh Forest Department (Bangladesh Forest Department) - БангладешТехнологи баримтжуулах/үнэлэх ажилд дэмжлэг үзүүлсэн байгууллага(ууд)-ын нэр (шаардлагатай бол)
FAO Bangladesh (FAO Bangladesh) - Бангладеш1.3 WOCAT-аар баримтжуулсан өгөгдлийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцөл
Эмхэтгэгч болон гол мэдээлэгч хүн(хүмүүс) WOCAT аргачлалаар баримтжуулсан мэдээллийг ашиглахтай холбоотой нөхцлийг хүлээн зөвшөөрсөн.
Тийм
1.4 Технологи тогтвортой гэдгийг баталгаажуулах
Энэ технологи азрын доройтлыг бууруулахад нөлөө үзүүлэхгүй тул газрын тогтвортой менежментийн технологи болж чадахгүй юу?
Үгүй
2. ГТМ Технологийн тодорхойлолт
2.1 Технологийн товч тодорхойлолт
Технологийн тодорхойлолт:
Assisted natural regeneration (ANR) is a simple, low-cost forest restoration method that can effectively convert deforested lands to more productive forests.
2.2 Технологийн дэлгэрэнгүй тайлбар
Тодорхойлолт:
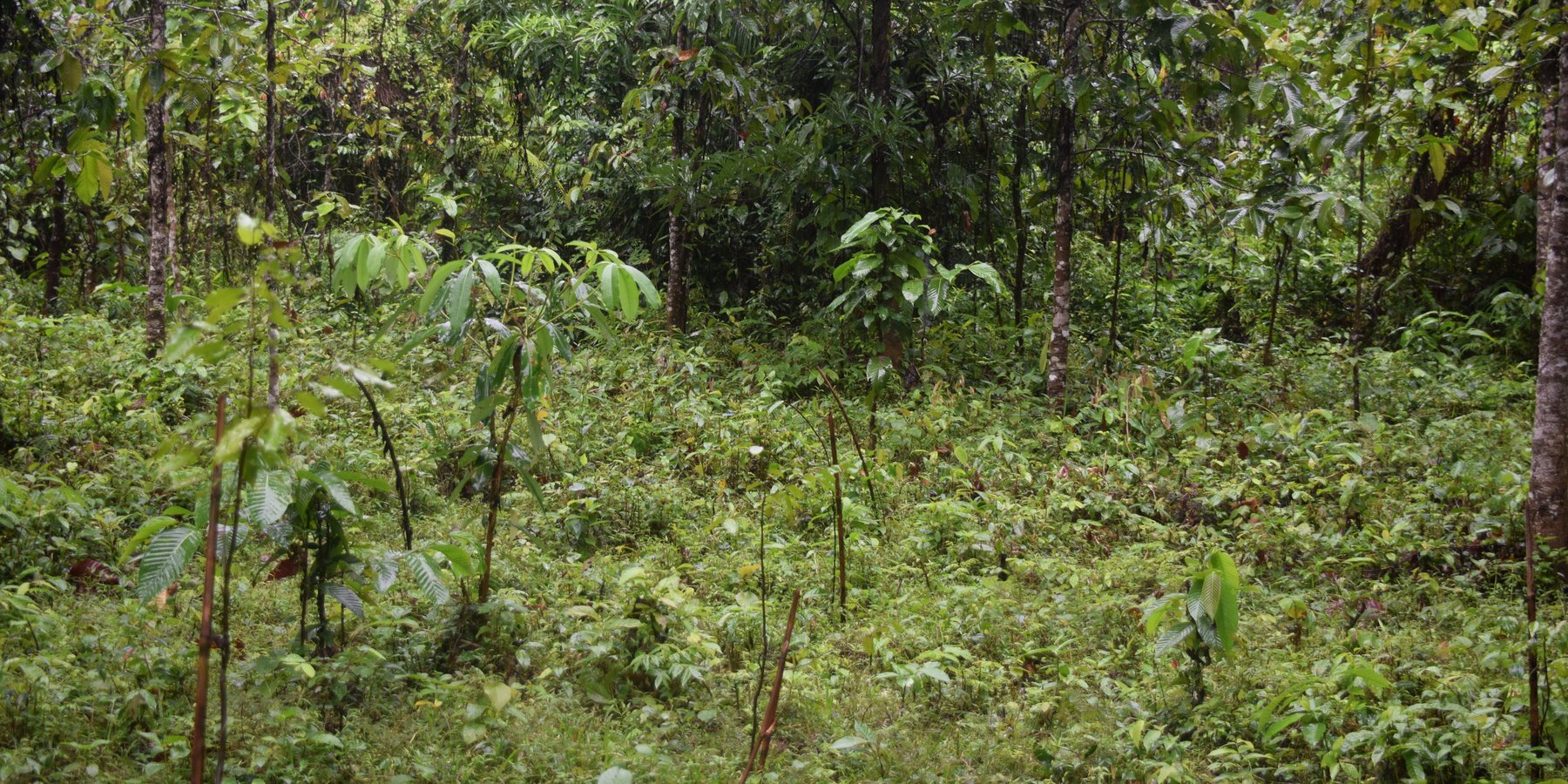
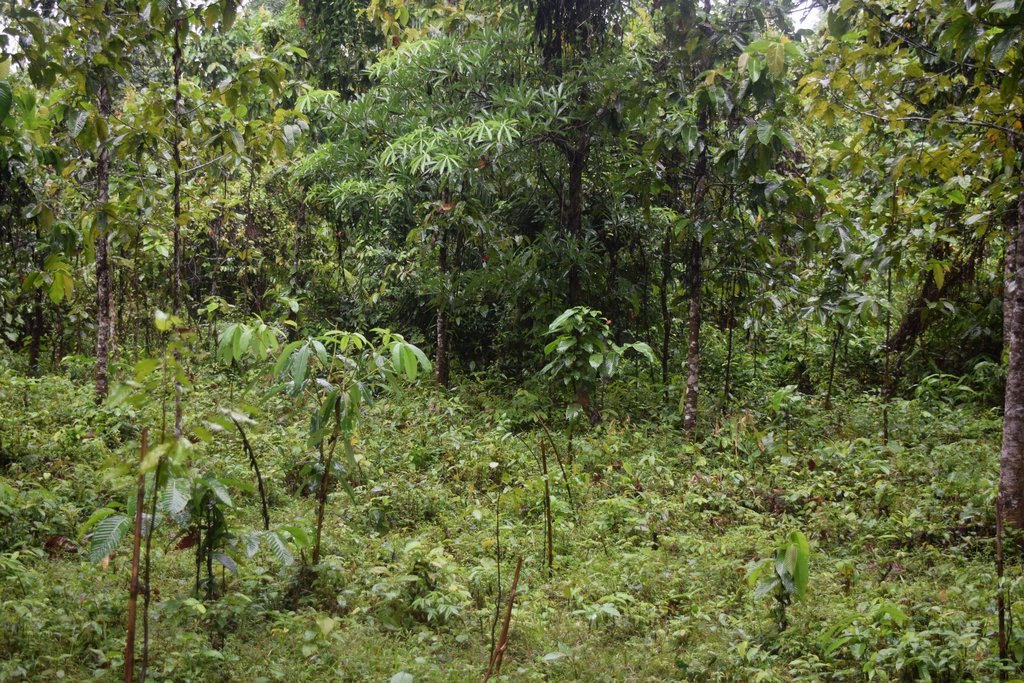
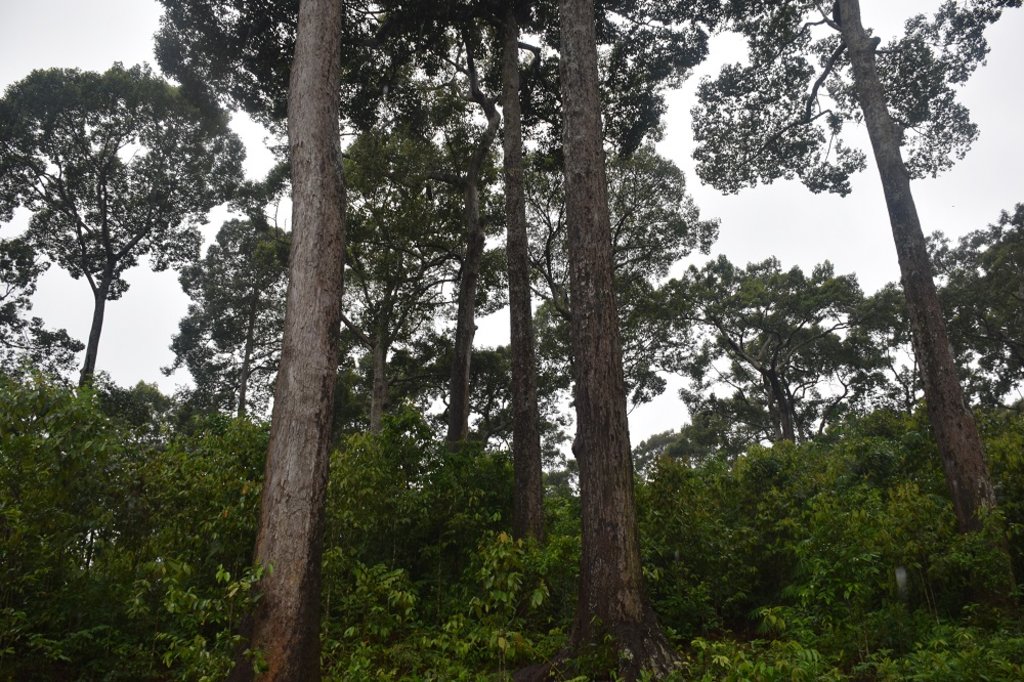
Medhakachapia National Park (MKNP) is nationally known for protecting the most extensive stands of mature critically endangered Garjan (Dipterocarpus turbinatus) trees in Bangladesh. Other native trees present in MKNP include Telsur Hopea odorata, Boilam Anisoptera scaphula, Gamar Gmelina arborea and Chapalish Artocarpus chaplasha. MKNP is tropical semi-evergreen forest in the low hills of the Fulchari Forest Range and covers 396 hectares. The park is located in Chakaria Upazila, not far from Cox’s Bazar in the southeast part of the country. Originally, the entire park area was densely covered with Garjan forest, but now there are about 9000 mature Garjan trees as many parts have been encroached upon with agriculture. MKNP is bordered by 13 villages where most of the people depend directly or indirectly upon the forest. Encroachment by settlements and agriculture has been associated with illegal tree cutting, hunting, and collection of fuel wood, bamboo and cane and other forest products. These activities are encouraged by sawmills in the vicinity and unemployment. Due to reduced canopy coverage, the forest soils have been exposed degraded. In order to restore forest health, the Bangladesh Forest Department introduced Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR) practice. The access for public recreation and education and research is allowed inside national park. However, the collection of fuel woods and non-timber forest product from national park area by the local communities is a common scenario here.
ANR aims to accelerate, rather than replace, natural succession processes by removing or reducing barriers to natural forest regeneration such as competition with weedy species and recurring disturbances (e.g., fuel wood collection, grazing, fire and wood harvesting). Compared to conventional reforestation methods, which involve planting tree seedlings, ANR offers the significant advantage avoiding costs associated with propagating, raising, and planting seedlings. ANR is most effectively utilized at the landscape level in restoring the forest protective functions, such as soil protection, and is most suitable for restoring areas where some level of natural succession is already in progress. ANR offers distinct advantages over other forest restoration methods but also has some limitations. ANR is much cheaper to implement and can be applied over larger areas than other restoration planting approaches, but may be less effective in enhancing floristic diversity at the initial stages. Some of ANR’s disadvantages can be overcome by enrichment planting with desirable species. ANR aims to accelerate, rather than replace natural succession process by removing or reducing barriers to natural forest regeneration.
Soil degradation of MKNP has been greatly reduced through practicing ANR and co-management. In MKNP co-management was established on 2009 engaging local communities. As a part of co-management activities, the Forest Department (FD) formed a Community Patrolling Group (CPG) with 35 members from the local community to protect the Garjan trees and look after the whole forest along with forester officers. Under the support from Climate-Resilient Ecosystems and Livelihoods (CREL) project of USAID, the CPG along with FD intensively patrol the forest in rotating groups to ensure that no harm is done to the mature trees and natural seedlings. As a result, sufficient tree regeneration is now taking place and their growth is accelerating. Even where weeds dominate, seedlings of pioneer tree species are often found. The minimum required number of preexisting seedlings to implement ANR depends on the acceptable length of time for the forest to be restored and site-specific conditions that influence the rate of forest recovery. As a general reference, a density range of 200–800 seedlings/ha (>15 cm in height; counting clumps in 1 m2 as one seedling) has been suggested for ANR reforestation, and it has been estimated that at least 700 seedlings/ha are needed during the early treatment period in order to achieve canopy closure within three years. Although the forest restored through ANR in MKNP will have lower commercial value in terms of timber, it will support greater biodiversity and more effectively provide for the subsistence needs of the local people compared to commercial plantations.
2.3 Технологийн гэрэл зураг
2.5 Энэ үнэлгээнд хамрагдсан технологийг хэрэгжүүлсэн улс орон / бүс нутаг / байршил
Улс :
Бангладеш
Улс/аймаг/сум:
Chittagong division
Байршлын дэлгэрэнгүй тодорхойлолт:
Medakacchapia National Park under Cox's Bazar North Forest division
Технологи өргөн дэлгэрсэн эсхийг тодорхойл:
- газар дээр жигд тархсан
Хэрэв талбайн хэмжээ тодорхойгүй бол талбайн хэмжээг ойролцоогоор тодорхойлно уу.
- 1-10 км2
Технологи(иуд) нэвтрүүлсэн талбай байнгын хамгаалалттай газар нутагт байрладаг уу?
Тийм
Хэрэв тийм бол, тодруулна уу:
Medakacchapia is a National Park with an area of 395.92 ha. In Bangladesh, the access for public recreation and education/research is allowed inside national park. However, the collection of fuel woods and non-timber forest product from national park area by the local communities is a common scenario here.
Map
×2.6 Хэрэгжих огноо
Хэрэгжүүлсэн он:
2014
2.7 Технологийн танилцуулга
Технологийг хэрхэн нэвтрүүлснийг тодорхойл:
- Гадны төсөл/хөтөлбөрийн дэмжлэгтэйгээр
Тайлбар (төслийн төрөл г.м.):
Climate-Resilient Ecosystems and Livelihoods (CREL) project of USAID
3. ГТМ технологийн ангилал
3.1 Технологийн үндсэн зорилго (д)
- Газрын доройтлыг бууруулах, сэргийлэх, нөхөн сэргээх
- Экосистемийг хамгаалах
- Биологийн төрөл зүйлийг хамгаалах / сайжруулах
- Нийгэмд үзүүлэх үр нөлөөг бий болгох
3.2 Технологи хэвтрүүлсэн газрын одоогийн газар ашиглалтын хэлбэр(д)
Нэг газр нутгийн хэмжээнд хэрэгжих холимог газар ашиглалт:
Үгүй

Байгалийн ой / модтой газар
- (Сайжруулсан) байгалийн ой/мод бүхий газар
(Хагас)байгалийн ой/тармаг ойд: Менежментийн төрлийг тодорхойлно уу:
- Хатсан мод/мөчрийг авах
- Tropical semi-evergreen forest
- Dipterocarpus turbinatus, Syzygium grande, Chukrasia tabularis, Hopea odorata
Дээр дурьдсан модны төрөл навч, шилмүүсээ гөвдөг үү эсвэл мөнх ногоон уу?
- холимог нөвч, шилмүүсээ гөвдөг/мөнх ногоон
Бүтээгдэхүүн ба үйлчилгээ:
- Мод бэлтгэл
- Түлшний мод
- Жимс, самар
- Байгалийн нөөцийг хамгаалах
- Амралт, аялал жуулчлал
- Oil from Dipterocarpus turbinatus
3.3 Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээс газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
Технологи хэрэгжүүлснээс газар ашиглалтад өөрчлөлт гарсан уу?
- Үгүй (3.4 хариулт руу шилжинэ үү)
3.4 Усан хангамж
Технологи хэрэгжүүлсэн газрын усан хангамж:
- Байгалийн усалгаатай
3.5 Технологи ГТМ-ийн аль бүлэгт хамаарах
- Байгалийн ба хагас-байгалийн ойн менежмент
- гадаргын/ ургамал бүрхэвч сайжрах
3.6 Технологийг бүрдүүлэх ГТМ арга хэмжээ

Ургамалжилтын арга хэмжээ
- V1: Мод ба бут, сөөг

Менежментийн арга хэмжээ
- М2: Ашиглалтын менежмент/эрчимийг өөрчлөх
Тайлбар:
Earlier the ground vegetation was suppressed by weeds and non-valuable plant species. Various alien invasive plant species also disturbed the natural succession process of these area. The management practice also changed from plantation in vacant area to assisted natural regeneration with the involvement of local community.
3.7 Технологийн шийдвэрлэсэн газрын доройтлын үндсэн төрлүүд

Хөрс усаар эвдрэх
- Wt: Хөрсний гадаргын угаагдал
- Wg: Гуу жалгын элэгдэл

Биологийн доройтол
- Bc: Ургамлан нөмрөг багасах
- Bq: Хэмжээ/ Биомасс буурах
- Bs: Ургамлын чанар, төрөл зүйл, олон янз байдал буурах
3.8 Газрын доройтлоос урьдчилан сэргийлэх, сааруулах ба нөхөн сэргээх
Газрын доройтолтой холбоотойгоор Технологи ямар зорилго тавьсан болохыг тодорхойл:
- Газрын доройтлыг багасгах сааруулах
Тайлбар:
Canopy coverage of the area were poor and top soil erosion occurred due to exposed forest cover. Through ANR the canopy coverage will be regained and reduce land degradation.
4. Техникийн нөхцөл, хэрэгжилтийн үйл ажиллагаа, материал ба зардал
4.1 Технологийн техникийн зураг
Техник тодорхойлолт (техник зурагтай уялдана):
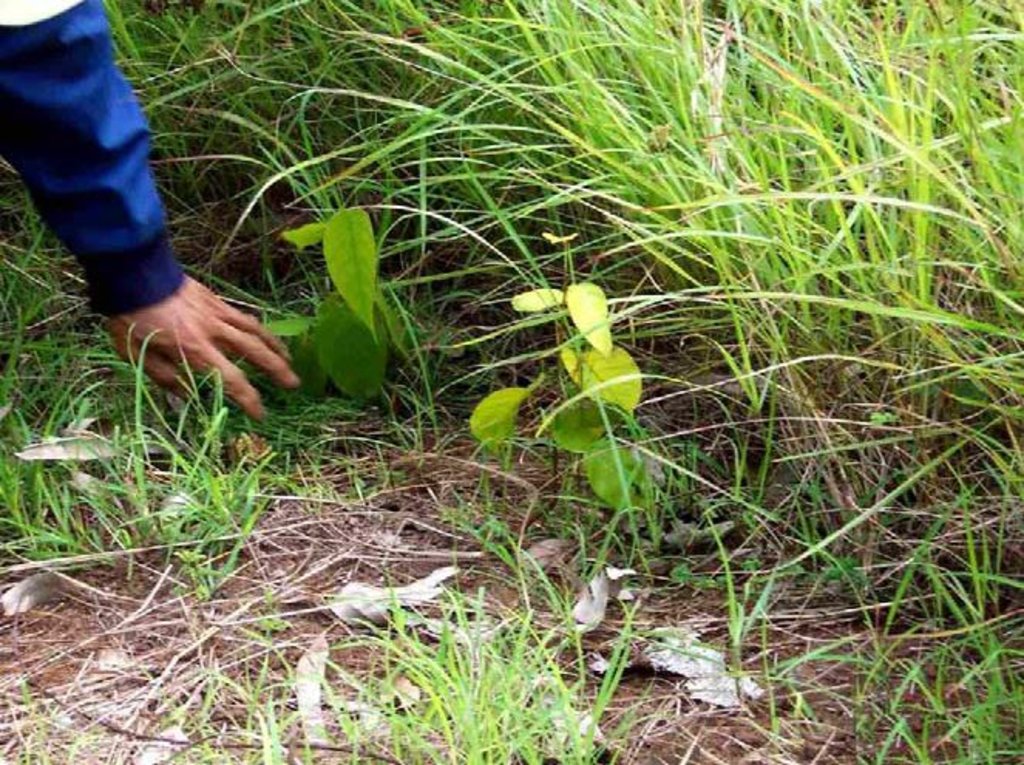
Step 1: Marking of Woody Regeneration
Once the target area is identified and its boundaries are demarcated, the site is surveyed to assess its succession status and to locate any natural woody regeneration growing in the weedy vegetation. The located seedlings should be clearly marked with stakes. Decision on the minimum size of seedlings to be protected and released depends on the density and distribution of seedlings in the area, as well as budget and time constraints. However, the seedlings should be large enough to have a reasonable chance of survival.
Step 2: Liberation and Tending of Woody Regeneration
The next step is to accelerate the growth of the marked seedlings by reducing competition from the weedy species for water, nutrients, and light. The initial weeding and climber cutting should be implemented at the onset of the rainy season so that the liberated seedlings will have the full growing season of accelerated growth. All competing vegetation such as weeds and climbers within at least 0.5 m radius around the stem of the marked seedlings are removed. In some cases, clumps of woody seedlings may need to be thinned in order to liberate the largest individuals or the more desirable species.
Step 3: Protection from Disturbance.
Protecting against fire and other forms of disturbance is the most important ANR activity. Establishing firebreaks around blocks of ANR-treated sites is important, if the area is prone to fire. If animal grazing is prevalent in the area, fencing should be established, or patrols/guards should be assigned to protect the site from such activity. Long-term community involvement and support is critical in preventing the re-occurrence of disturbance events that will set back succession to the before-treatment state.
Step 4: Maintenance and Enrichment Planting.
It is suggested that the maintenance of weeding, and liberation of any additional seedlings that establish or that are newly found, should be conducted three times in first two years and two times in next two years. In the fifth year one climber cutting should be conducted in rainy season. The frequency of maintenance operations can be adjusted according to field observation and monitoring data on the growth of the liberated seedlings and the density of natural woody regeneration. Enrichment planting can also be carried out to accelerate canopy closure, add useful tree species, and increase floral diversity. Even after the restoration of canopy cover, large-seeded primary forest trees and rare species are unlikely to colonize naturally. If restoring some of the floral diversity of the original forest is one of the restoration objectives, species or functional groups of trees lacking in natural regeneration will need to be planted either at the initial treatment stage or after canopy closure depending on the ecological requirements of the species.
Зохиогч:
Nazrin Sultana
Он, сар, өдөр:
16/04/2019
4.2 Материал болон зардалд хамаарах ерөнхий мэдээлэл
Үнэ өртөг, оруулсан хувь нэмрийг хэрхэн тооцсоныг тодорхойл:
- Технологийн нэгж тус бүр
Хэмжээ ба нэгж талбайг тодорхойл:
1 hectare
Хэрэв өөрийн уламлалт талбай хэмжээг ашиглаж байгаа бол нэг гектарт шилжүүлэх коэффициент (жишээ нь 1 га = 2.47 акр): 1 га =:
1 ha = 2.47 acres
бусад/үндэсний мөнгөн нэгж (тодорхойл):
BDT
Хэрэв боломжтой бол үндэсний валютын Америк доллартай харьцах харьцааг бичнэ үү (тухайлбал, 1 ам.дол. = 79,9 Бразил реал): 1 ам.дол. =:
84.0
Хөлсний ажилчны нэг өрдийн ажлын хөлсийг тодорхойл:
500 BDT
4.3 Байгуулах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа (улирал) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site preparation (Boundary demarcation, site map preparation with GPS, marking of woody regeneration) | May-June |
| 2. | Care and maintenance of natural regeneration (liberation and tending of woody regeneration, protection from disturbance) | June-July |
4.4 Байгуулалтад шаардагдах зардал ба материал
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Survey for map preparation and marking of woody regeneration | person-days | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Tying up seedlings and young trees | person-days | 4.0 | 500.0 | 2000.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Tending of woody regeneration | person-days | 10.0 | 500.0 | 5000.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | Application of fertilizers | person-days | 4.0 | 500.0 | 2000.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Weeding equipment (manual weeding tool) | lump sum | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Bamboo sticks for tying up seedlings | pieces | 800.0 | 2.0 | 1600.0 | |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Rope | lump sum | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | |
| Бордоо ба биоцид | Compost fertilizer | Kg | 625.0 | 4.0 | 2500.0 | |
| Барилгын материал | Rod, Cement, Sand, Khoa, etc for RCC signboard | Lump sum | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | |
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг | 16600.0 | |||||
| Технологи бий болгох нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 197.62 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагчаас нийт өртөгийн 100%хүрэхгүй зардал гарсан бол хэн үлдсэн хөрөнгө оруулалтыг хийснийг тодорхойл.
Bangladesh forest department is the land user and the total cost of the establishment borne by CREL project
4.5 Засвар үйлчилгээ / давтагдах үйл ажиллагаа
| Үйл ажиллагаа | Хугацаа/ давтамж | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1st year weeding | 3 times |
| 2. | 2nd year weeding | 3 times |
| 3. | 3rd year weeding | 2 times |
| 4. | 4th year weeding | 2 times |
| 5. | 5th year climber cutting | 1 time |
4.6 Засвар үйлчилгээ / урсгал үйл ажиллагаанд шаардагдах зардал ба материал (жилээр)
| Хөрөнгө оруулалтыг дурьдана уу | Хэмжих нэгж | Тоо хэмжээ | Нэгжийн өртөг | Материал бүрийн нийт өртөг | % газар ашиглачаас гарсан зардал | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | 1st year weeding | person-days | 15.0 | 500.0 | 7500.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | 2nd year weeding | person-days | 15.0 | 500.0 | 7500.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | 3rd year weeding | person-days | 10.0 | 500.0 | 5000.0 | |
| Хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт | 4th year weeding and 5th year climber cutting | person-days | 15.0 | 500.0 | 7500.0 | 100.0 |
| Тоног төхөөрөмж | Weeding equipment (manual weeding tools) | lump sum | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | |
| Технологийг арчилах тордоход шаардагдах нийт үнэ өртөг | 28500.0 | |||||
| Технологи сайжруулах нийт үнэ өртөг, ам.доллар | 339.29 | |||||
Хэрэв газар ашиглагчаас нийт өртөгийн 100%хүрэхгүй зардал гарсан бол хэн үлдсэн хөрөнгө оруулалтыг хийснийг тодорхойл.
The 4th year weeding and 5th year climber cutting borne by forest department
4.7 Зардалд нөлөөлж байгаа хамгийн чухал хүчин зүйл
Өртөг зардлыг тодорхойлох гол хүчин зүйлсийг дурьдана уу:
The most important factor affecting the costs is labor
5. Хүн, байгалийн хүрээлэн буй орчин
5.1 Уур амьсгал
Жилийн нийлбэр хур тундас
- <250 мм
- 251-500 мм
- 501-750 мм
- 751-1,000 мм
- 1,001-1,500 мм
- 1,501-2,000 мм
- 2,001-3,000 мм
- 3,001-4,000 мм
- > 4,000 мм
Жилийн дундаж хур тунадас (хэрэв мэдэгдэж байвал), мм:
3770.00
Хур тунадасны талаархи тодорхойлолт/ тайлбар:
The driest month is December. The greatest amount of precipitation occurs in June.
Агро-уур амьсгалын бүс
- Чийглэг
Mean annual temperature is 25.6 °C
5.2 Байрзүйн зураг
Дундаж налуу:
- Тэгш (0-2 %)
- Бага зэрэг хэвгий (3-5 %)
- Дунд зэрэг хэвгий (6-10 % )
- Долгиорхог (11-15 %)
- Толгодорхог (16-30 %)
- Эгц налуу (31-60 % )
- Огцом эгц налуу (>60 %)
Гадаргын хэлбэр:
- Тэгш өндөрлөг/тэгш тал
- Зоо, хяр
- Уулын энгэр, хажуу
- Ухаа, гүвээ, дов толгод
- Уулын бэл
- Хөндий, хоолой, нам хотос
Өндөршлийн бүс:
- 0-100 м д.т.д
- 101-500 м д.т.д
- 501-1,000 м д.т.д
- 1,001-1,500 м д.т.д
- 1,501-2,000 м д.т.д
- 2,001-2,500 м д.т.д
- 2,501-3,000 м д.т.д
- 3,001-4,000 м д.т.д
- > 4,000 м д.т.д
Технологи дараах асуудалд хандсан эсэхийг тодорхойл:
- шаардлагагүй
5.3 Хөрс
Хөрсний дундаж зузаан:
- Маш нимгэн (0-20 см)
- Нимгэн (21-50 см)
- Дунд зэрэг зузаан (51-80 см)
- Зузаан (81-120 cм)
- Маш зузаан (>120 cм)
Хөрсний бүтэц (өнгөн хөрс):
- Дунд зэрэг (шавранцар)
Хөрсний бүтэц (>20 см-ээс доош):
- Дунд зэрэг (шавранцар)
Өнгөн хөрсний органик нэгдэл:
- Дунд (1-3 % )
5.4 Усны хүртээм ба чанар
Хөрсний усны гүн:
5-50 м
Гадаргын усны хүртээмж:
Сайн
Усны чанар (цэвэрлээгүй):
Муу чанарын ундны ус (цэвэршүүлэх шаардлагатай)
Усны чанар гэж:
гадаргын ус
Усны давсжилт асуудал болдог уу?
Үгүй
Энэ газар үер усанд автдаг уу?
Үгүй
5.5 Биологийн төрөл зүйл
Зүйлийн олон янз байдал:
- Дунд зэрэг
Амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал:
- Дунд зэрэг
5.6 Технологи нэвтрүүлсэн газар ашиглагчидын онцлог шинж
Суурьшмал эсвэл нүүдлийн:
- Суурьшмал
Үйлдвэрлэлийн системийн зах зээлийн чиг баримжаа:
- холимог (амьжиргаа ба худалдаанд)
Фермээс гадуурх орлого:
- Нийт орлогын %10 доош хувь
Чинээлэг байдлыг харьцангуй түвшин:
- Ядуу
Хувь хүн эсвэл бүлэг:
- Ажилтан (компани, засгийн газар)
Механикжилтын түвшин:
- Хүнд хүчир ажил
Хүйс:
- Эмэгтэй
- Эрэгтэй
Газар ашиглагчийн нас:
- Залуус
- Дунд нас
- Ахимаг нас
5.7 Технологи нэвтрүүлэхэд газар ашиглагчийн ашигласан газрын дундаж талбай
- < 0.5 га
- 0.5-1 га
- 1-2 га
- 2-5 га
- 5-15 га
- 15-50 га
- 50-100 га
- 100-500 га
- 500-1,000 га
- 1,000-10,000 га
- > 10,000 га
Энэ нь жижиг, дунд, том оворт тооцогдох уу (орон нутгийн чиг баримжаагаар)?
- Бага-хэмжээний
5.8 Газар эзэмшил, газар ашиглах эрх, ус ашиглах эрх
Газар өмчлөл:
- Төр засаг
Газар ашиглах эрх:
- Нэгдлийн хэлбэрээр (зохион байгуулалттай)
Ус ашиглах эрх:
- Нээлттэй хүртэх (зохион байгуулалтгүй)
Газар ашиглалтын эрх уламжлалт эрхзүйн тогтолцоонд суурилдаг уу?
Үгүй
Тодорхойлно уу:
Under co-management system
Тайлбар:
Co-management of forest ensures active participation of all concerned parties in the management or maintenance of natural resources on the basis of consensus among the stakeholders involved in the management of the natural resources of an area
5.9 Дэд бүтэц, үйлчилгээний хүртээмж
эрүүл мэнд:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
боловсрол:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
техник дэмжлэг:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
хөдөлмөр эрхлэлт (жишээ нь, ХАА-аас өөр):
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зах зээл:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
эрчим хүч:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
зам ба тээвэр:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
ундны ус ба ариутгал:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
санхүүгийн үйлчилгээ:
- Ядуу
- Дунд зэргийн
- Сайн
6. Үр нөлөө ба дүгнэлт
6.1 Технологийн талбай дахь үр нөлөө
Нийгэм-эдийн засгийн үр нөлөө
Үйлдвэрлэл
модлогийн бүтээмж
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
ANR support the growth of woody vegetation and regular monitoring of ANR also provide security to the mature trees of the stand
ой/модтой газрын чанар
ойн дагалт баялаг буюу бүтээгдэхүүн
үйлдвэрлэл зогсох эрсдэл
Үйлдвэрлэлийн газар
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Through ANR the fellow and degraded forest land now bring under productive forest
газрын менежмент
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
ANR is a comparatively easy method than clear felling with artificial regeneration, mixed plantation or enrichment plantation to manage forest area
Орлого, зарлага
орлогын олон янз эх үүсвэр
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
The local communities can collect NTFP from the ANR site. Due to the increase of vegetation and presence of wildlife in MKNP, the area also attract tourists. The CPG people also worked as tourist guide
Нийгэм-соёлын үр нөлөө
Соёлын боломжууд
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
aesthetic beauty of forest improved
амралт, нөхөн сэргээлтийн боломжууд
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
eco-tourism increased
ГТМ/ газрын доройтлын талаархи мэдлэг
Нийгэм, эдийн засгийн хувьд эмзэг бүлгийнхний нөхцөл байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Poor people working in Community Patrolling Group (CPG) taking care of ANR with forest department. Social status of these poor people improved.
Экологийн үр нөлөө
Усны эргэлт/ илүүдэл
гадаргын урсац
гүний усны түвшин / уст давхарга
ууршилт
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to increased canopy coverage evaporation decreased
Хөрс
хөрсний чийг
хөрсөн бүрхэвч
хөрс алдагдах
шимт бодисын эргэлт/ сэргэлт
хөрсний органик нэгдэл/ хөрсөнд агуулагдах С
Биологийн: ургамал, амьтан
Ургамал бүрхэвч
газрын дээрхи / доорхи С
ургамлын төрөл, зүйл
түрэмгий, харь зүйл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Through ANR only native plant species promoted to grow here
амьтны төрөл, зүйл
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Animal diversity increased as the habitat improved
Ашигт төрөл зүйл
амьдрах орчны олон янз байдал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
habitat diversity increased with the canopy coverage and tree density improvement
Уур амьсгал болон гамшгийн эрсдлийг бууруулах
хөрсний гулсалт/ чулуун нуранги
нүүрстөрөгч ба хүлэмжийн хийн ялгаруулалт
6.2 Технологийн талбайн гадна үзүүлсэн үр нөлөө
хуурай улиралд ашиглах найдвартай, тогтвортой урсгал
Тайлбар/ тодорхой дурьдах:
Due to the presence of vegetation on slope the stream flow become stable
урсацын адагт лаг шавар хуримтлагдана
хүлэмжийн хийн нөлөө
6.3 Технологийн уур амьсгалын өөрчлөлт ба Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюул/гамшигт үзэгдэлд өртөх байдал ба эмзэг байдал (газар ашиглагч нарын дүгнэлтээр)
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
Уур амьсгалын аажим өөрчлөлт
| Улирал | Өсөх эсвэл буурах | Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Жилийн дундаж температур | Өсөлт | Сайн | |
| Улирлын температур | Зун | Өсөлт | Сайн |
| Жилийн дундаж хур тундас | Бууралт | Дунд зэрэг | |
| Улирлын хур тундас | Чийглэг/борооны улирал | Өсөлт | Дунд зэрэг |
Уур амьсгалаас хамаарах аюулууд (гамшигууд)
Гидрологийн гамшиг
| Технологи түүний нөлөөг хэрхэн бууруулж байна? | |
|---|---|
| Хөрсний гулсалт | Сайн биш |
Тайлбар:
Note to coping with landslides; Due to the events of landslides in the upper slope sometimes the seedlings and young trees suffered at the foot slope. The degraded upland area can be recovered through ANR with enrichment planting to reduces the events of landslides and slope stabilization.
6.4 Зардал ба үр ашгийн шинжилгээ
Үр ашгийг барилга байгууламжийн зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Бага зэрэг сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
Үр ашгийг засвар үйлчилгээ/ урсгал зардалтай (газар ашиглагчдын үзэл бодлоор) хэрхэн харьцуулах вэ?
Богино хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Бага зэрэг сөрөг
Урт хугацаанд эргэн төлөгдөх байдал:
Маш эерэг
6.5 Технологи нутагшуулах
- 1-10 %
Технологийг өөрийн талбайд нэвтрүүлсэн бусад иргэдээс хэд нь үүнийг өөрийн хүчээр, өөрөөр хэлбэл ямар нэг материал, техникийн дэмжлэг, төлбөр авалгүй хийсэн бэ?
- 91-100%
6.6 Дасан зохицох
Хувьсан өөрчлөгдөж буй нөхцөл байдалд Технологид сүүлд ямар нэг шинэчлэл хийгдсэн үү?
Үгүй
6.7 Технологийн давуу тал/боломжууд
| Газар ашиглагчдын тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| It is a low cost intervention to regain the protective roles of the forest. |
| Community Patrolling Group (CPG) are involved in maintenance of ANR forest through co-management of natural resources. Regular patrolling activity reduces the disturbance in forest and help to prevent land degradation. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон давуу тал/боломжууд |
|---|
| Biodiversity conservation and wildlife habitat restoration are accelerated through ANR. |
6.8 Технологийн дутагдалтай/сул тал/аюул болон тэдгээрийн хэрхэн даван туулах арга замууд
| Газар ашиглагч нарын тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| ANR is less effective in enhancing floral diversity than techniques e.g. mixed plantation, enrichment plantation, selection cum improvement etc. It promotes the existing regeneration and significant portion of regeneration comes from the dominant trees of the stand. | Enrichment plantations with ANR can increase the floral diversity. |
| The forest restored through ANR may have less commercial value in terms of timber compared to commercial plantation. This weakness of ANR is only valid for the forest which is managed for production purpose. | Desirable timber species can be planted as enrichment with ANR. |
| Эмхэтгэгч, бусад мэдээлэл өгсөн хүмүүсийн өнцгөөс тодорхойлсон сул тал/ дутагдал/ эрсдэл | Тэдгээрийг хэрхэн даван туулах вэ? |
|---|---|
| ANR is suitable for areas where some level of natural succession is in progress. This, because sufficient tree regeneration must be present on the targeted site so their growth can be accelerate through ANR. | Plantation activity with other restoration method should be practiced where natural succession is low or absent. |
7. Ном зүй ба холбоосууд
7.1 Мэдээллийн аргууд / эх сурвалжууд
- Хээрийн уулзалт, судалгаа
number of informants: 04
- Газар ашиглагчтай хийсэн ярилцлага
number of informants: 03
- ГТМ-ийн мэргэжилтэн/шинжээчтэй хийсэн ярилцлага
number of informants: 02
- тайлан болон бусад эх сурвалжийн бүрдэл
number of informants: 02
Мэдээллийг хэзээ (газар дээр нь) цуглуулсан бэ?
15/01/2019
7.2 Хүртээмжтэй ном, бүтээлийн ишлэл
Гарчиг, зохиогч, он, ISBN:
Shono, K., E. A. Cadaweng & P. B. Durst (2007) Application of assisted natural regeneration to restore degraded tropical forestlands. Restoration Ecology, 15, 620-626.
Хаанаас авч болох вэ? Зардал?
http://www.fao.org/forestry/19102-0bf30dd3d800687636a5ddc85e409044a.pdf
7.3 Холбогдох мэдээллийн интернет холбоос
Гарчиг/ тодорхойлолт :
Medhakachapia National Park
URL:
http://nishorgo.org/project/medhakachapia-national-park/
7.4 Ерөнхий мэдээлэл
The WOCAT questionnaire covers all the technical aspects of this SLM practice
Холбоос ба модулууд
Бүгдийг харуулах Бүгдийг хаахХолбоосууд
Холбоос байхгүй байна
Модулууд
Модуль байхгүй байна