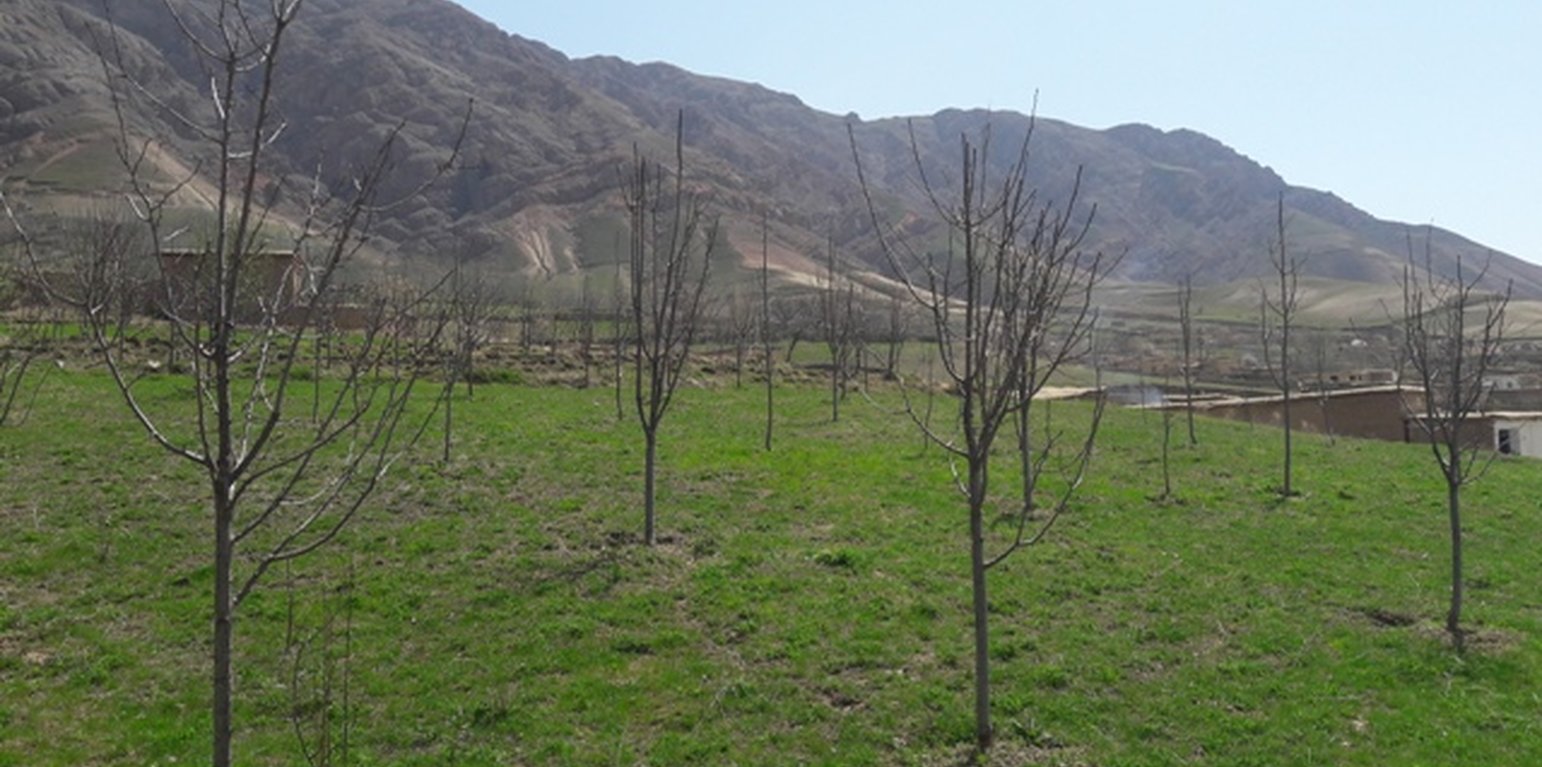




Project supported implementation of improved orchards and vineyards has taken place in the villages Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai, located in Chokar watershed of Rustaq District in Northern Afghanistan. The Chokar watershed is a mountainous area situated between 600 - 2,500 m above sea level. The climate is semi-arid with harsh and cold weather in winter and hot and dry summers. The annual precipitation in average years is 580mm. Land degradation affects all forms of land use and includes low vegetation cover, heavy top soil erosion from water, and poor soil fertility. Unsustainable agricultural practices, over-exploitation and high pressure on the natural resources are adversely impacting on the socio-economic well-being of local communities as well as contributing to the risk for being adversely affected by drought as well as landslides and flash foods triggered by heavy rainfall. The data used for the documentation of the technology is based on field research conducted in Chokar watershed, namely in the villages: Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai. These villages represent the upper, the middle and the lower zone of Chokar watershed, respectively. They differ considerably in access to services and infrastructure, but in general are poorly served. The communities depend on land resources for sustaining their livelihoods. In a good year with high yields, wheat-self-sufficiency lasts about 5 months. The three villages are home to ethnic Qarluq communities. Since 2012 the Livelihood Improvement Project Takhar (LIPT) implemented by Terre des hommes (Tdh) Switzerland has initiated a range of NRM interventions.
The rural population in Rustaq district of Afghanistan traditionally grows local varieties of apples, pears and grapes. Mostly it is subsistence farming with a small-scale local marketing. Shortage of irrigation water and lack of specific knowledge about horticultural and viticulture practices, negatively affects fruit yields. Apart of providing diverse fruits for consumption, orchards are also important for providing fodder for the livestock, retaining soil moisture and protecting the soil from erosion.
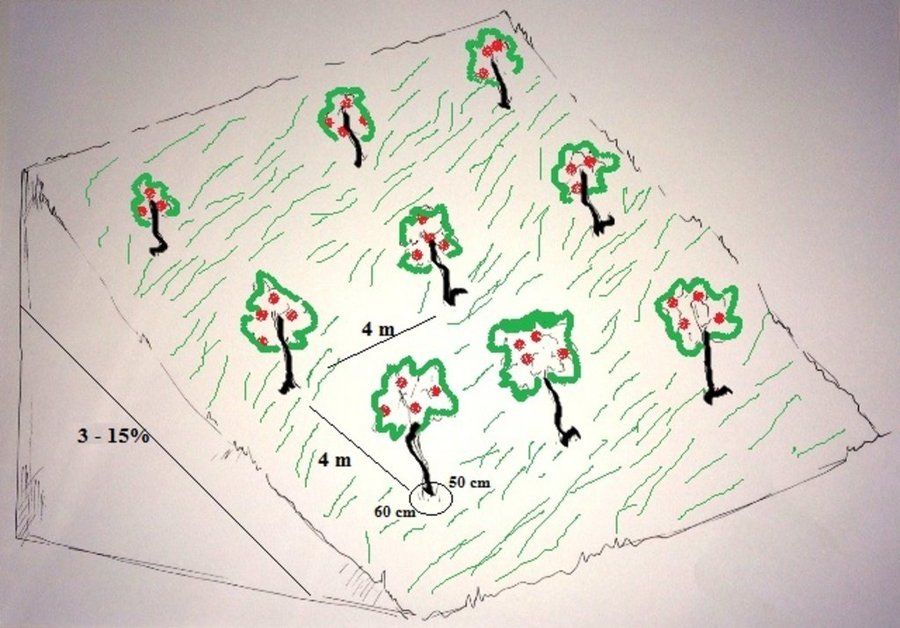
The local land users interested in the establishment of improved orchards and vineyards were mobilized through the Natural Resources Management Committees (NRMC) in Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai villages. In addition to the local varieties of pears, apples and grapes, new improved varieties were used for orchards and vineyards on 6.5 ha of degraded land. Such orchards were established inside or close to the villages on mountain slopes with gentle (3-5%) and moderate (6 -15%) steepness. Fruit trees are planted on locally identified dark and light soils, which correspond to moderately deep and loamy soil of medium soil fertility. Considering the medium quality of the soil, the first step of tree plantation is application of organic fertilizer. Afterwards, the plot is designed according to 4m x 4 m spacing between the trees. Under such parameters, on 1 jirib (0.2 ha) of land 125 fruit tree (apple or pear) seedlings are planted. The depth of the planting pits is 60 x 50 cm. The planted tree is watered and the lower trunk is covered with lime and water solution. Alfalfa is sown under the trees to serve as a fodder for the livestock. The orchards are irrigated mostly during summer once a week. In areas where there is shortage of irrigation water the trees are rainfed. Other maintenance activities include pest and disease control provided by a trained local specialist.
The new orchards only recently started giving fruits. The actual fruit yields are expected in 2017-2018. Expected higher yields of improved verities of pears, apples and grapes serves as a strong incentive for the local land users and their families to establish and maintain the orchards. Orchards are very demanding, but their reward is very promising in terms of improved harvest and more opportunities to sell the produce. Some land users have successful experience on their plots and already have fruits in their gardens and plan to enlarge their garden and plant more varieties of fruit trees, such as persimmons. Alfalfa which grows under the trees has important production value, particularly during the early years after the establishment phase, when the trees are too young to give fruits.
Female members of the households, which implemented orchards are also involved in establishing and maintaining orchards and vineyards. They take part in planting trees, watering, hay making and protecting the trees from livestock and people. Their contribution, plays an important part for the successful implementation of improved orchards and vineyards in Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai.
Localização: Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, Dashti Mirzai, Takhar Province, Rustaq District, Afeganistão
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados: 10-100 locais
Difusão da tecnologia: Uniformemente difundida numa área (approx. < 0,1 km2 (10 ha))
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?:
Data da implementação: menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
Tipo de introdução










| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (USD) | Custos totais por entrada (USD) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Application of manure | person-day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 83,0 |
| Design of tree spacing | person-day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | |
| Digging pits for planting | person-day | 15,0 | 5,3 | 79,5 | 83,0 |
| Planting trees, sowing alfalfa and watering | person-day | 10,0 | 5,3 | 53,0 | 83,0 |
| Equipamento | |||||
| Meter | piece | 1,0 | 2,25 | 2,25 | |
| Rope | Meter | 500,0 | 0,07 | 35,0 | |
| Shovel | piece | 2,0 | 3,8 | 7,6 | |
| Pick axe | piece | 1,0 | 2,25 | 2,25 | |
| Material vegetal | |||||
| Seedlings (apple/pear) | piece | 625,0 | 0,75 | 468,75 | |
| Alfalfa seeds | kg | 17,5 | 0,42 | 7,35 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | |||||
| DAP | Kg | 250,0 | 0,9 | 225,0 | |
| Urea | Kg | 250,0 | 0,45 | 112,5 | |
| Animal manure | ton | 10,0 | 60,0 | 600,0 | |
| Pesticide | cc | 500,0 | 0,9 | 450,0 | |
| Lime | Kg | 25,0 | 1,5 | 37,5 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 2'133.7 | ||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 31.85 | ||||
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (USD) | Custos totais por entrada (USD) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Irrigation | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Weeding | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Pruning | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Lime application | person day | 5,0 | 5,3 | 26,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | |||||
| Scissors for pruning | piece | 2,0 | 9,0 | 18,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | |||||
| Lime | Kg | 25,0 | 1,5 | 37,5 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 161.5 | ||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 2.41 | ||||
The local and new improved varieties of fruit trees planted and managed sustainably give better fruit yields. Enhanced fruit production is also due to proper and timely control of pests and disease.
The grass (alfalfa and sainfoin), which is planted under the fruit trees is used as fodder for livestock.
Indirect contribution to animal production is achieved through availability of more fodder for the livestock from the grass in the orchards. Animals also feed on the tree leaves in autumn.
Production of wood is limited. Fuel wood is made from seasonal pruning of the trees.
Multiple varieties of fruit trees are grown, also through grafting techniques.
The new practice of establishing orchards and vineyards ensures better yields. New variety of fruits such as apples, pears, almonds and grapes improve the diversity of household's production and consumption. The households have better opportunity to earn more from selling their fresh and dried fruits on the local market.
Land users learned new methods of planting trees according to the soil conditions and water availability. They were trained with such skills as grafting, pruning, pest and disease control and were introduced to improved verities of fruit trees.
Female headed households are not included. Technology is implemented on private land, therefore people without land are excluded. However, they have they opportunity to earn income as a hired worker for the SLM implementers.
Improved vegetation cover resulting from the tree plantations and the grass.