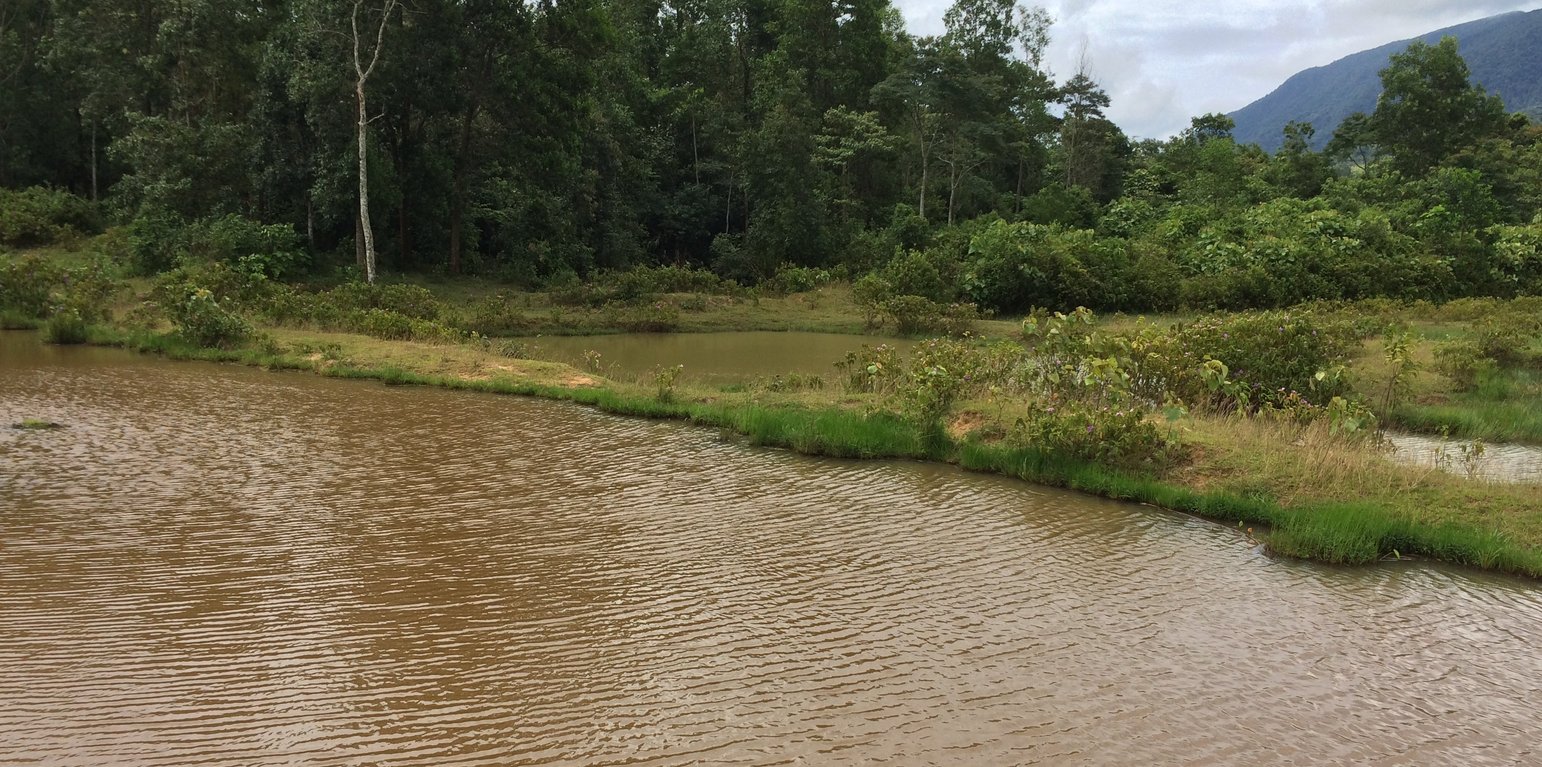




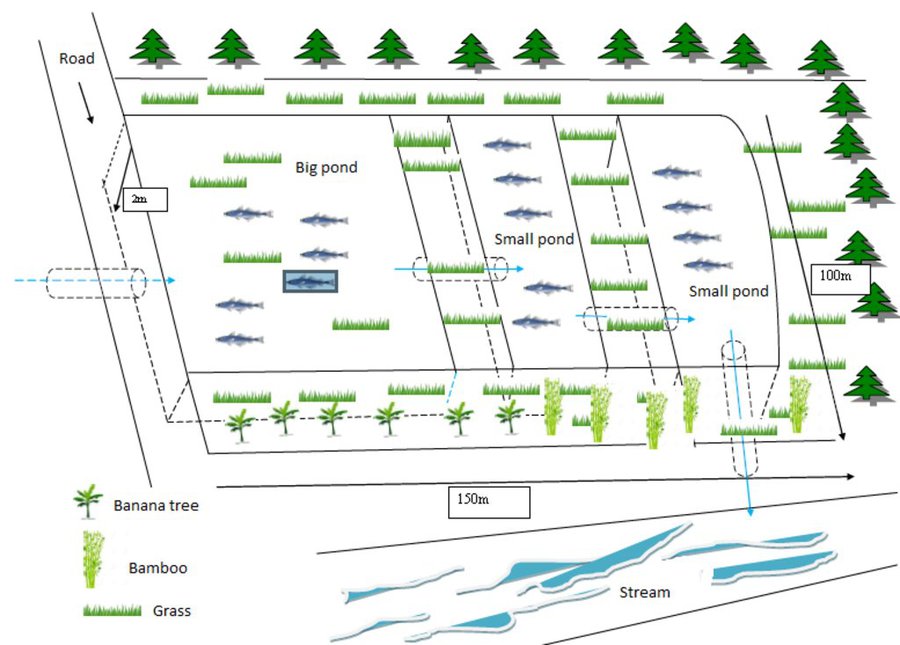
At Asoy village and its neighboring villages in the Salavan Province of Lao PDR some rice fields were regularly flood prone during rainy season (August ̶ October) because of a newly constructed road containing culverts leading first through the rice fields and then into natural water ways. Therefore, in 2005 one of the village's land users spread the idea to convert this regularly damaged and increasingly unproductive rice land into fish ponds. The soil texture in this area is mostly clayey and therefore also generally not very suitable for agriculture, but certainly appropriate for water holding throughout the year. Thus, the main objective of these pond constructions was the raising of fishes for income generation and for getting water for household purposes during dry season; e.g. for gardening, fodder production, and for banana and bamboo cultivation along the edges of the pond dikes. The fishpond should also provide water for livestock such as cattle, buffalo, and poultry farming. The construction of the ponds in the case documented here started by shutting off the culvert at the inlets by using sawn wood and clay to close the concrete pipe (Ø80 cm) crossing the road. After, vegetation clearance was required by using a bulldozer. A backhoe then was applied to excavate an area of 1.5 ha to create a first big pond (150 m long and 100 m wide). The excavated soil was used directly for the dike construction. The dikes were around 2.5 m high and 2 m wide. For the first big pond only two dikes had to be shaped because the other two sides were road and fallow. At completion of the big pond, two smaller ponds have been constructed also by backhoe directly next to it. The first of them encompasses an area of 2,000 square meters (20 m x 100 m) and the second 3,000 square meters (30 m x 100 m). After this, four new Ø40 cm drainage pipes were installed; a first one throughout the road leading into the first pond, two of them connecting the ponds and the last pipe is needed to lead the water finally into the natural water way. The pipes have to be installed at a height of 50 cm from the edges. To stabilize the ponds Napier grass, banana, and bamboo can be cultivated on the top of the dikes. Maintenance of the pond requires regular cutting of the Napier grass, which is done by hand. Also regular weeding of the dike’s edges is required, as well as the stabilization of the embankments by using timber and soil. Where repair is required, the timber can be placed vertically, and then filled out with soil. The ponds are hold and maintained individually by the land owner and the benefit of them is considerable. The annual fish production is approximately 1 ton , equivalent to 15 million Kip . The ponds also store water for utilization during dry season especially for the animals (cattle, buffalos, and poultries). The grass growing on the edges can serve as fodder for animals. Banana and bamboo shoots can be consumed and sold for income generation. Material from branches of bamboo trees is used for handicrafts such as baskets and bamboo sheets for house walls, etc. The fishpond improves the aquatic ecosystem habitats in the area. The pond provides spawning areas for a large variety of fish, shrimp, crab, and frog species. However, with changing climate and rainfall patterns it happened that the ponds dried up and the soil became hard with rapidly growing weed around the ponds. Plants such as Napier and banana that are cultivated on the edge of the dikes can die. On the other hand in particular years, there flash floods occur that can affect the dikes due to rapid water runoff; in consequence also fish and other aquatic species can be lost and crops can be damaged. Nonetheless, the land owners at Asoy village prefer this technology and want to expand and improve it, when they have capability or when support from external institutions can be expected (e.g. training in fish breeding and required equipment such as hapa fish net for fish nursery, air pump, dip nets and harvesting net). Finally, the fishponds have been expanded to neighboring villages as well.
Localização: Asoy village, Samoaui district, Salavan province, República Democrática Popular do Laos
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados: Local único
Difusão da tecnologia: Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?:
Data da implementação: 2005; 10-50 anos atrás
Tipo de introdução





| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (kip) | Custos totais por entrada (kip) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| labour | person-day | 50,0 | 50000,0 | 2500000,0 | 100,0 |
| excavator | machine | 1,0 | 3000000,0 | 3000000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | |||||
| hoe | piece | 20,0 | 50000,0 | 1000000,0 | 100,0 |
| shovel | piece | 20,0 | 30000,0 | 600000,0 | 100,0 |
| knife | piece | 5,0 | 20000,0 | 100000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | |||||
| fodder | bunch | 3,0 | 20000,0 | 60000,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | |||||
| Fry | Fry | 2400,0 | 1000,0 | 2400000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 9'660'000.0 | ||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 1'136.47 | ||||
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (kip) | Custos totais por entrada (kip) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| labour | person | 6,0 | 50000,0 | 300000,0 | |
| Equipamento | |||||
| hoe | piece | 1,0 | 50000,0 | 50000,0 | |
| shovel | piece | 2,0 | 30000,0 | 60000,0 | |
| knife | piece | 1,0 | 20000,0 | 20000,0 | |
| trolley | piece | 2,0 | 250000,0 | 500000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 930'000.0 | ||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 109.41 | ||||
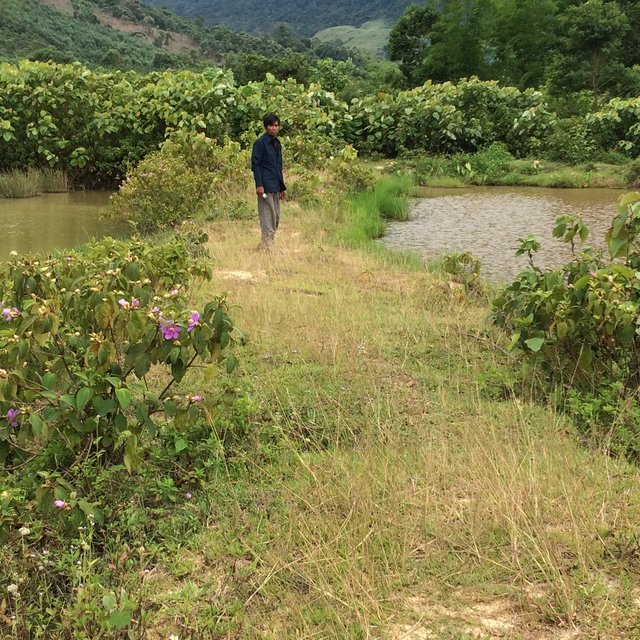
After ponds construction various crops can be planted on the dike of the ponds.
Quantidade anterior à GST: Very rare
Quantidade posterior à GST: 1 ton of fish
Before, only small amount of fish was captured because the fish came only from natural water bodies. The farmer also increased the poultry due to the fish ponds.
Before, only small amount of fish was captured because the fish came only from natural water bodies. The farmer also increased the poultry due to the fish ponds.
Before they was only a not very suitable natural bog area that accumulated peat from dead plant material and contained only shallow water. After the pond construction the water was deep enough for fish production, drinking water for livestock and also for crop irrigation.
After completion of the pond the farmer has to buy costly fish breed every year from Vietnam (1000 kip/fry)
Before the pond construction the farmer produced only for reaching self sufficiency without any income from the agricultural production. After implementation of the technology the farmer got income from fish, crop and fruit at around 15 million kip/year.
Previously there is not any income from agriculture produce, after pond have been complete, they have many kind of produce for sell such as banana, vegetation, fish
Previously the farmer relied on natural wetland without substantial maintenance work. Then after completing the ponds the farmer has to spend quite a lot of work time to maintain them properly.
After pond construction the family was able to increase food sedcurity and self-sufficiency as they got supplmentary fish, fruits and other crops for self-consumption. Futher, they were able to sale the products and by this getting money when required.
The pond serves now as recreational site for fishing and swimming.
Before, the water streamed though the land without beeing harvested. Since the creation of the ponds - which were surrounded by dykes - the water were collected and stored easily for different already mentioned purposes.
There are many kind of animals in the area including prey ( rats, fish, frogs...) and predators ( snakes, snake fish, bird...), all acting as a small food chain elements.
The increase in animal types and animal species in the area indicates the increase of the habitat diversity.