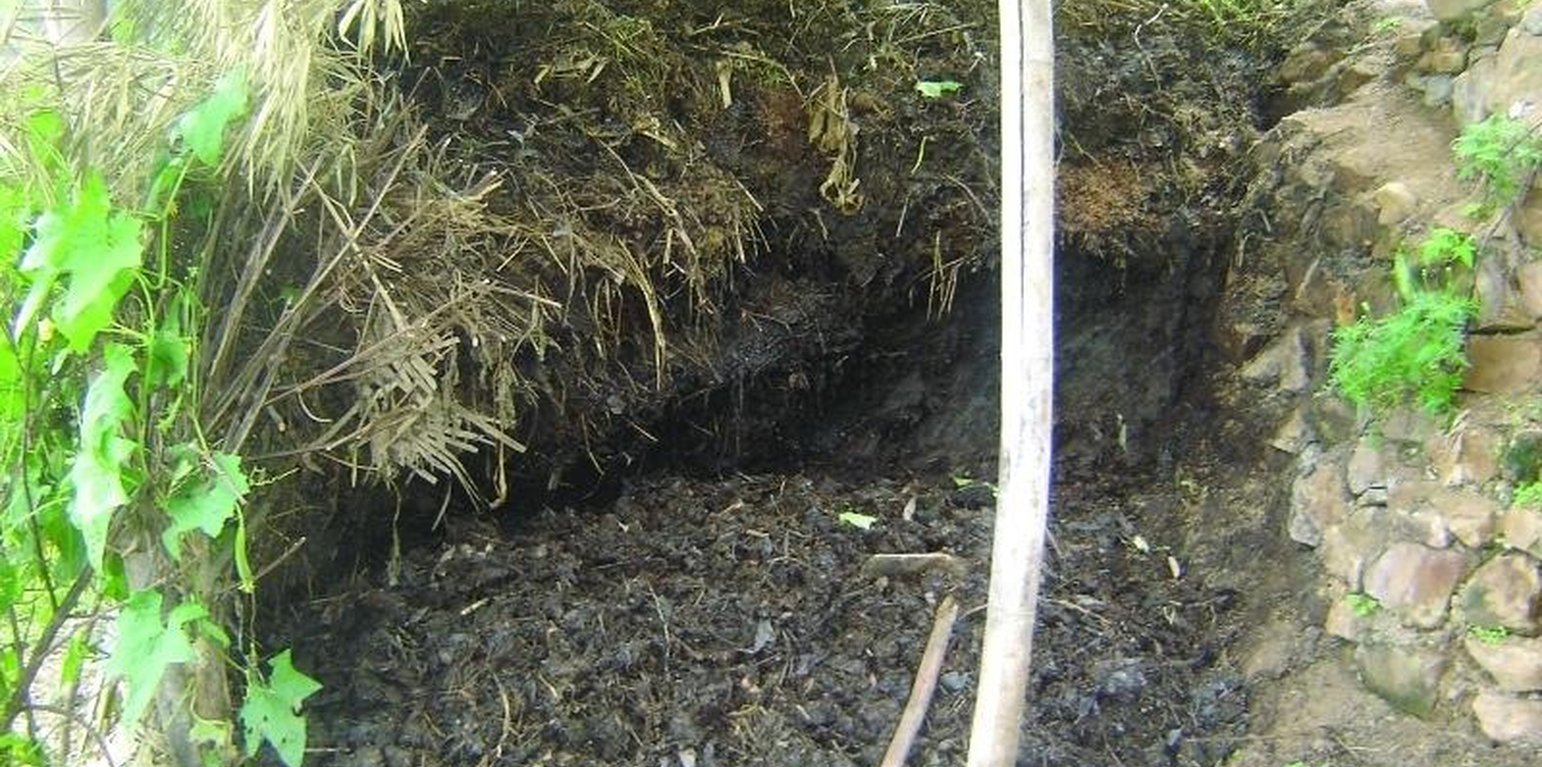




Farmyard manure - a varying mixture of animal manure, urine, bedding material, fodder residues, and other components - is the most common form of organic manure applied in the midhills of Nepal. Farmyard manure has a high proportion of organic material which nurtures soil organisms and is essential in maintaining an active soil life. Only about half of the nutrient content of farmyard manure becomes available for crop growth during the first year after it has been applied to the soil - the rest is channeled through soil biotic processes and the nutrients are released in the following years. The high organic matter content and the active soil life improve or maintain friable soil structures, increase the cation exchange capacity, water holding capacity, and infiltration rate, and reducing the risk of soil pests building up.
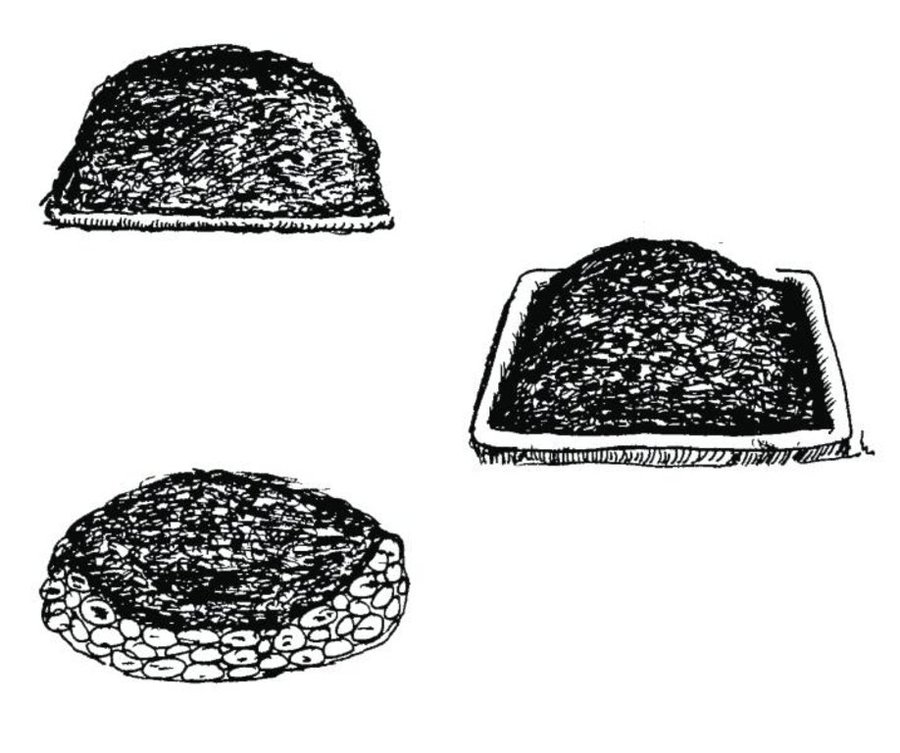
Indigenous methods of preparing and using farmyard manure vary widely depending on the ecological zone, access to bedding material from crop or forest land, access to crop residues and fodder, labour availability, and other factors. A prerequisite for the manure having a positive impact on soil fertility is that it is properly decomposed. The application of partially decomposed manure can increase the number of white grubs, red ants and other soil pests.
Decomposition is enhanced and the time it takes to happen is reduced if the manure is kept warm and moist (but not wet) at all times. Heaping the manure up or storing it in a pit helps. Whether it is best to heap up the manure or put it in a pit depends on the local climate. Heaping has the advantage of being less costly, while the pit method reduces runoff and the loss of nutrient rich fluids. Adding nitrogen in the form of urine (N) improves the carbon to nitrogen ratio.
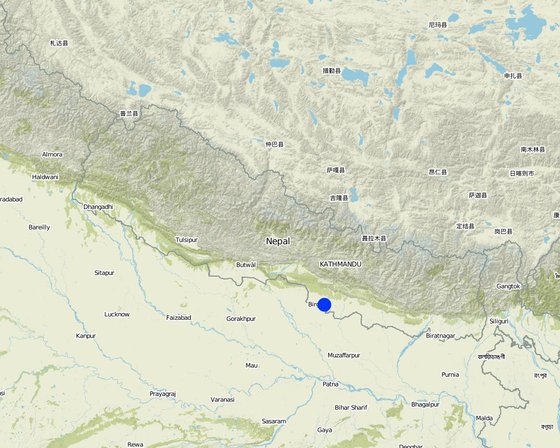
Localização: Midhills districts of Nepal, Nepal
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados:
Difusão da tecnologia: Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?:
Data da implementação:
Tipo de introdução



| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (USD) | Custos totais por entrada (USD) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Preapring manure pit | Persons/day | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 2.0 | ||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 2.0 | ||||
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (USD) | Custos totais por entrada (USD) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Decompose manure | Persons/day | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 2.0 | ||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 2.0 | ||||
Reduced cash expenses on agrochemicals (fertilisers, pesticides; substituted by labour)
Reduced influx of nutrients into water bodies