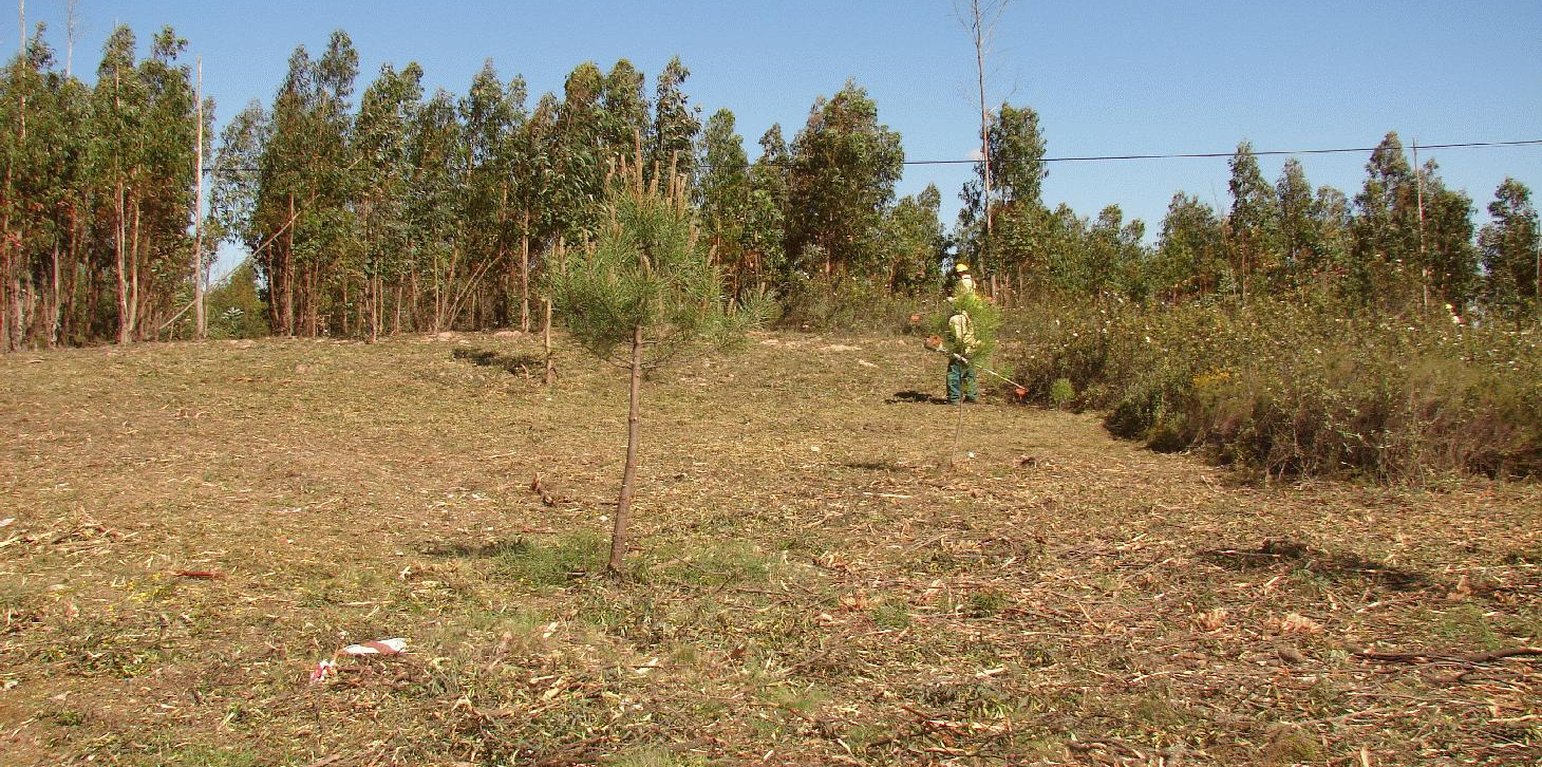




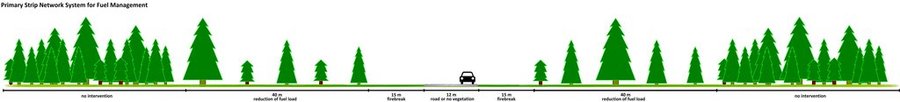
There are three types of strip for fuel management in forest areas: primary, secondary and tertiary, defined by the Law 17/2009. The most important differences between them are in terms of size (primary being the widest and the tertiary the narrowest) and scale (primary referring to the district level, secondary to the municipal level and tertiary to the parish level). The primary strip network system for fuel management (RPFGC) is integrated in the National System to Prevent and Protect Forest against Fires and it is defined by the National Forest Authority (AFN).
Purpose of the Technology: The RPFGC aims to re-arrange landscape elements, through the establishment of discontinuities in the vegetation cover, in forest areas and in the rural landscape (for example using water bodies, agricultural land, pasture, rocky outcrops, shrubland and valuable forest stands). Land tenure is private in most of the areas covered by the RPFGC. The main objectives of this technology are: to decrease the area affected by large fires; to enable direct access by fire fighters; to reduce fire effects and protect roads, infrastructures and social equipment, urban areas and forest areas of special value; and to isolate potential fire ignition sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: These primary strips are ≥ 125 metres wide and preferably between 500 and 10,000 ha in area. The tree cover should be less than 50% of the area and the base of the tree canopy should not be lower than 3 metres. The RPFGC concept should include the adoption of a maintenance programme. The implementation and maintenance operations can be performed through different agro-forest technologies, such as clearance of bushes and trees, pruning, prescribed fire, harrowing and cultivation of the ground beneath the trees. Timber products can be sold and the removed litter can be used in a biomass power plant or applied to the fields to improve soil fertility, using mulching technology.
Natural / human environment: This SWC Technology needs considerable financial resources in terms of labour and equipment at the implementation phase. Costs, however, undergo considerable reduction thereafter. The implementation of this infrastructure to prevent and protect the land from forest fire is entirely funded by the government and implemented by the forest municipal services.
Localização: Santarém / Mação, Portugal, Portugal
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados:
Difusão da tecnologia: Uniformemente difundida numa área (400.0 km²)
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?:
Data da implementação: menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
Tipo de introdução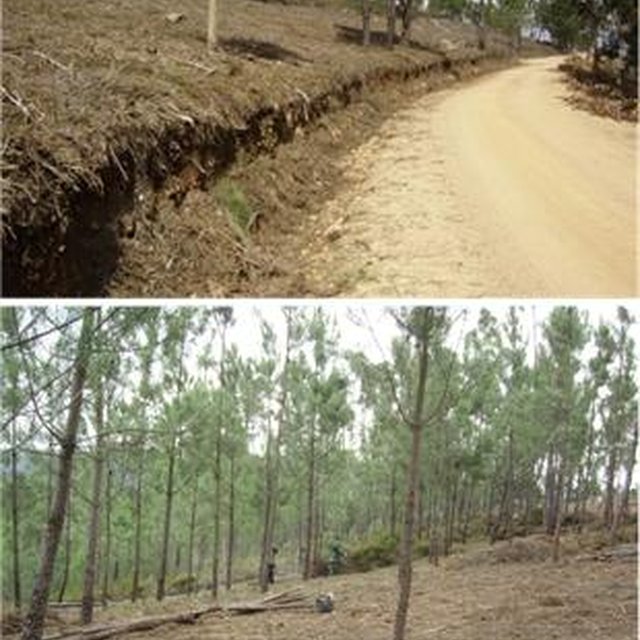





| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (Euro) | Custos totais por entrada (Euro) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Labour | ha | 1,0 | 1076,0 | 1076,0 | |
| Equipamento | |||||
| Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 568,0 | 568,0 | |
| Transport | ha | 1,0 | 100,0 | 100,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 1'744.0 | ||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 2'294.74 | ||||
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, produces fresh growth for grazing.
The new growth provides more diverse and nutritious fodder.
The low fuel load can be maintained through grazing.
Most of the primary system will be implemented in zones of low productivity. However, in some areas tree thinning can cause a decrease in wood production.
The use of wood as a fuel for a power station and the use of vegetation to feed the cattle can promote the development of new crops and land uses.
In some areas, the implementation of the primary system can occupy productive land. The main aim of this technology is always to provide protection from forest fires instead of creating productive land.
After cutting the shrubs, biomass is taken to a plant to energy production.
The cleared ground, on mountain summits, of the primary system is used for wind farms. Cleared vegetation could be used as fuel for a power station.
The implementation of the primary system is very costly.
Improved air quality by reducing forest fires risk.
Some forest owners can have some difficulties in accepting the loss of their land to this technology. This can be even more difficult if they have some wood production on such land, so that it represents an income reduction.
reduced risk of wildfire
Associated with the vegetation removal.
Associated with the vegetation removal.
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, enhances the diversity of the new vegetation cover. In some cases thinning the trees will have a positive effect by reducing the competition for water, sunlight and nutrients and (...)
Sometimes a loss which is associated with the immediate effects of vegetation removal.
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, enhances the appearance of new plants.
The fuel load management in the primary system, involving the implementation of good forest practices, including the removal and control of invasive species.
Vegetation removal, either by machinery or prescribed fire, enhances the appearance of new plants and consequently of new associated animals. The installation of fodder on the strips will promote grazing activities, increasing the number of goats, (...)
But also increased habitat fragmention
In some cases, where there is a total removal or a huge reduction in vegetation cover.
This technology is an impediment to forest fire propagation and therefore reduces fire risk.
Usually, the soil in the areas designated for the implementation of the primary system is thin and poor. The use of machinery and vegetation removal can accelerate the soil erosion processes.
Forest area.
The technology aims to reduce forest fire frequency and intensity, and the associated damage.