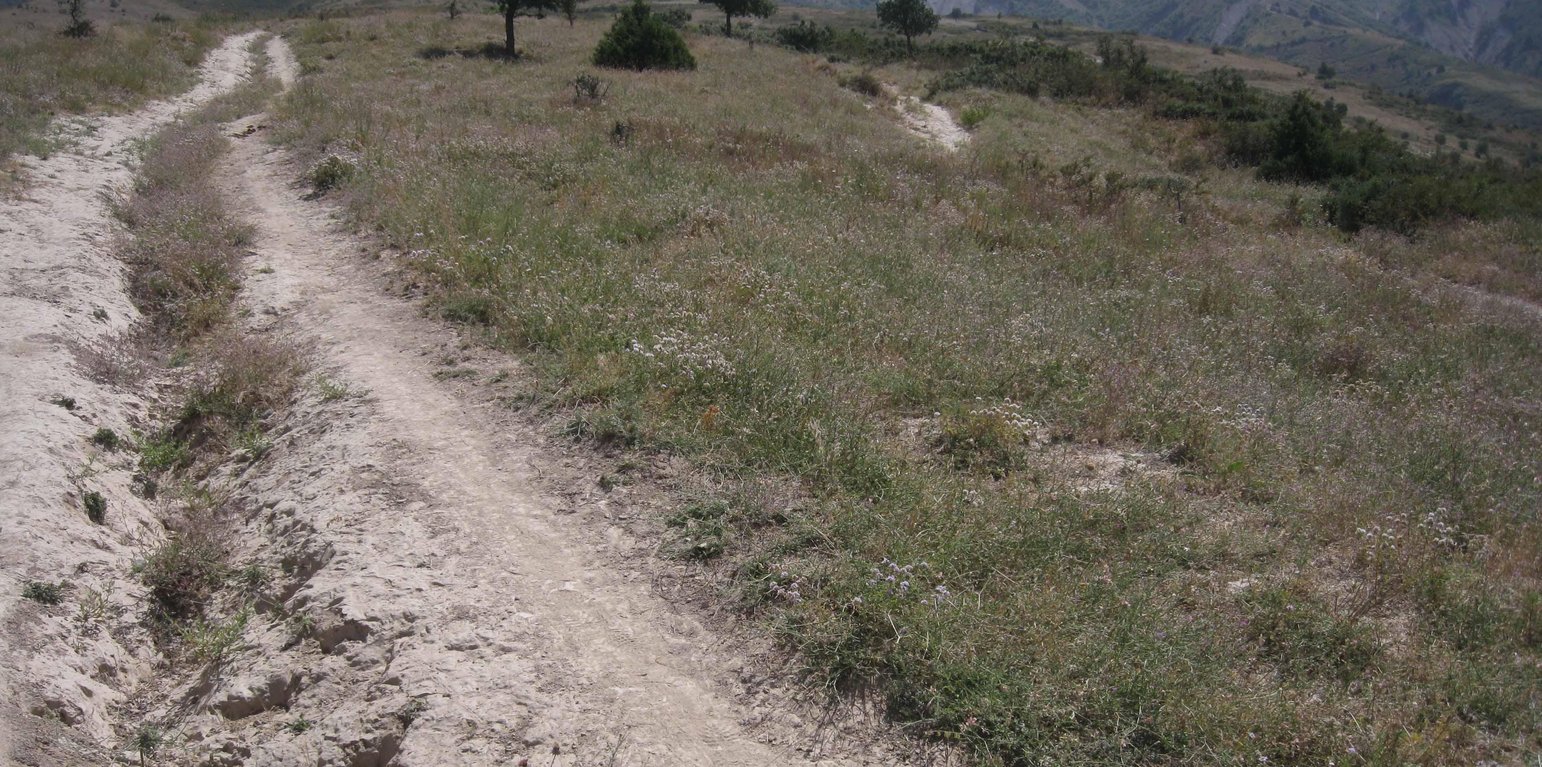




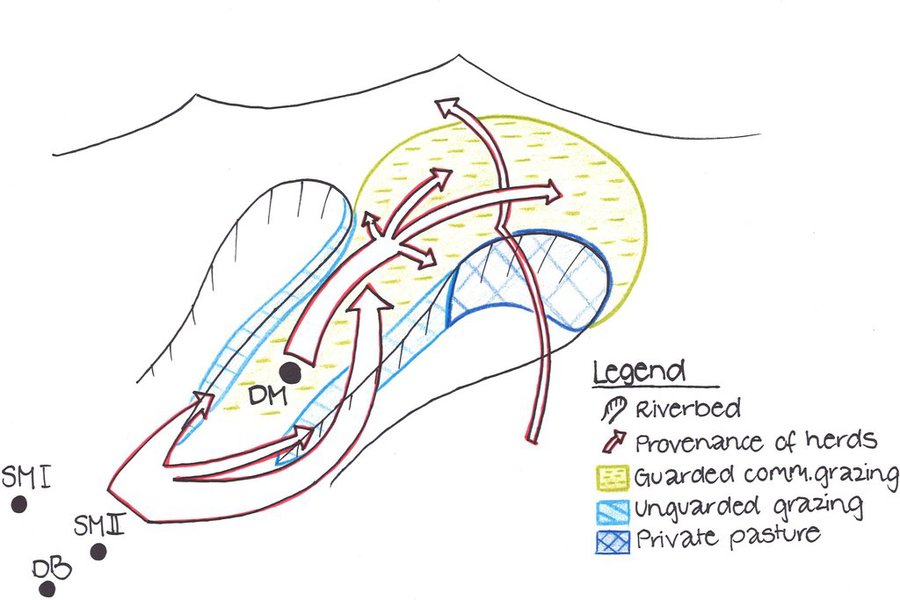
The total area of the pasture accounts for 300 – 500 ha. The pasture is property of the Doshmand village but it includes also some private properties, mainly potato and wheat crops. After the harvest, livestock is also grazing on these crops. Eighteen households are currently using the pasture with a total of 150 cows and 500 small animals. Additionally, three groups of herds from other villages graze irregularly on this pasture mainly on the lateral parts as it is less guarded by the villagers. The interviewee estimates that over 1000 cows, goats and sheep are coming from other villages. Other herds cross this pasture when migrating to or coming back from the summer pasture in spring and autumn, respectively. Nevertheless Doshmand residents claim that this intrusive grazing is accepted as “every animal has to be fed”. This shows the need of a pasture management not only on village but also on watershed level.
During Soviet time the inhabitants of Doshmand were forced to migrate to the valley. In 2003, the resettlement of the ancient location started with two families. Simultaneously, the pasture management was established and joined by each family who resettled. The controlled area is divided in 4 subparts. The herd switches daily within them. Every household looks after the herd for a day, which results in a rotational cycle of 18 days. There are no fixed and regular meetings for pasture management within the village pasture. However, two subsequent herders communicate to know where the herd has been grazing and where to graze the next time.
Purpose of the Technology: Purpose of the rotational grazing is to graze on one subpart, while the three other areas are resting. This reduces the impact of grazed and trampled areas per subpart and allows the growth and recovery of the vegetation in the other parts.
The task of herding is shared among the families. The rotational grazing is organized orally and freely, why it’s not sure if that approach is strictly binding. Discussions about pasture management rise only in case of need.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Doshmand village got the pasture in a good condition at the time of establishment. Vegetation cover was high. The only investment consisted in building a water point for the livestock. A further investment was to buy a water pipe and dig out a channel for the pipe to conduct the water from the water point to the village. Money was collected by the families and many villagers were involved in digging the channel.
No further input was and is required except coordination between the herders.
Natural / human environment: The pasture of Doshmand village is located in the middle and upper zone of the watershed. Thanks to the distance to other settlements, the pasture is less affected by overgrazing than other communal pastures in the watershed. Nevertheless, the pasture is heterogeneously grazed, with some areas which are difficult to access even for livestock and hence abundant vegetation. Other areas, especially those situated next to the village show a more bare vegetation cover.
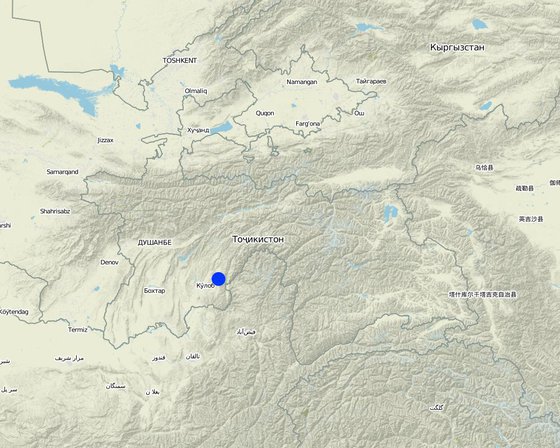
Localização: Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan, Tajiquistão
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados:
Difusão da tecnologia: Uniformemente difundida numa área (approx. 1-10 km2)
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?:
Data da implementação: 10-50 anos atrás
Tipo de introdução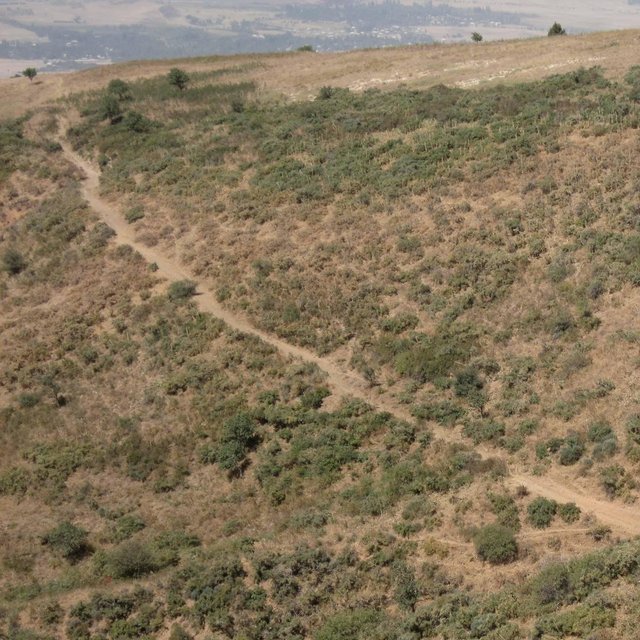







| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (USD) | Custos totais por entrada (USD) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Coordination with villagers and herders | - | 1,0 | |||
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (USD) | Custos totais por entrada (USD) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Consultation with village herders | - | 1,0 | |||
Not the whole pastureland can be grazed at once
Strenghtening of the community sense and awareness through increased coordination for rotational grazing between villagers. Higher fodder availability leads to healthier livestock.