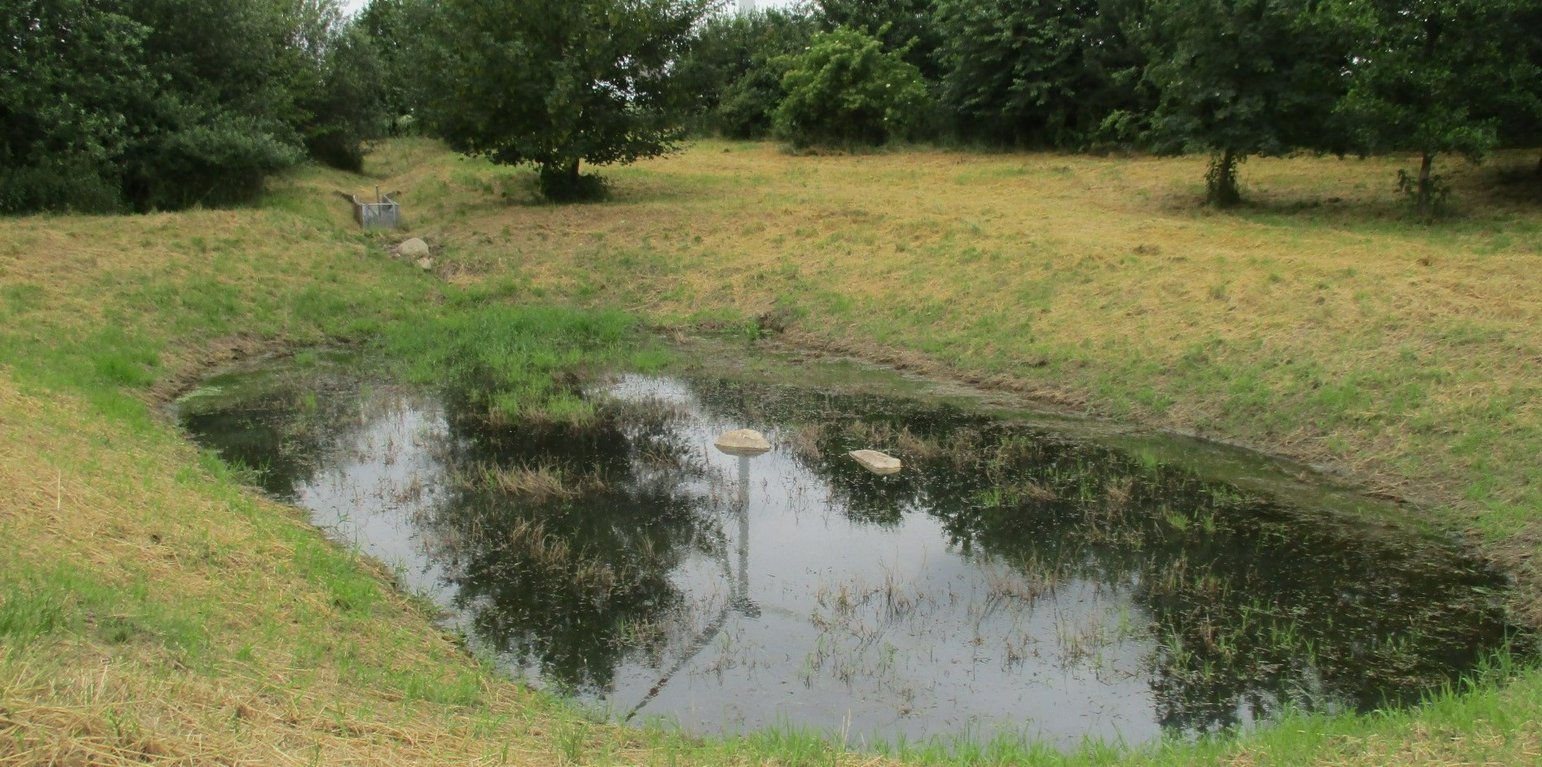




This documentation focuses on a detention basin constructed to hold surface runoff at the lowest point of an agricultural catchment. A well-designed detention pond is an effective flood control and landscape management measure. It stores surface runoff and releases it through controlled flow, infiltration, or evaporation (or a combination), and reduces nutrient inputs to the adjacent water body by filtering out sediment and nutrients through particle deposition, or nutrient uptake by plants. On average, water treatment in a detention pond can remove about 50-60% of suspended solids, 30-35% of total phosphorus and total nitrogen, and 25-65% of metals. Ponds also provide habitat for terrestrial, riparian and aquatic species. In addition to their ecological impact, they have an aesthetic and cultural value to society, for example, as a demonstration of effective sustainable water management.
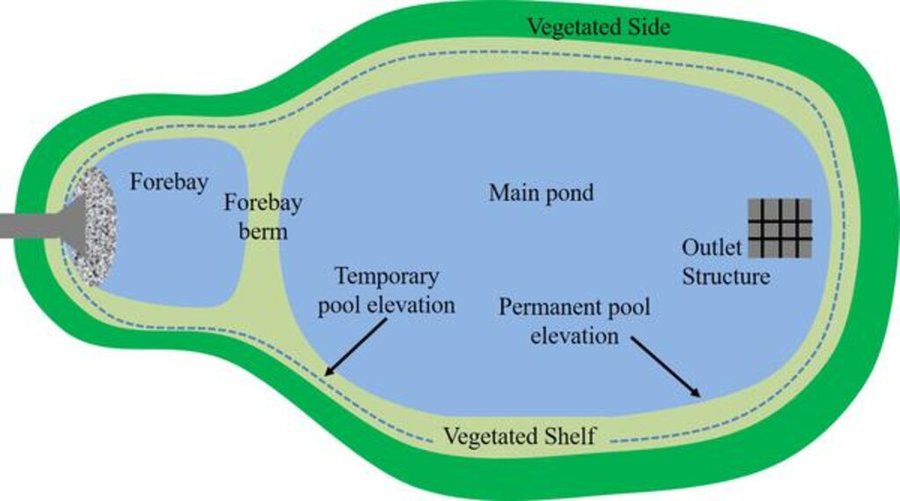
The detention basin described here was constructed by excavating a new depression and ditch system. It consists of a 450 m long inlet channel, a 250 m² pond, and an overflow channel that diverts excess water downstream to the nearest river (Schwarzer Schöps). However, there are no outlet structures for draining water that is captured in the pond (apart from the overflow). All the collected water seeps into the ground and soil particles settle. As a general rule, the size of such a pond should be 3-7% of the upstream catchment and should be able to hold at least the precipitation of a 1 in 30 year rainfall event. However, as the infiltration of the collected water is rather slow, the efficiency is reduced for successive events and overflowing is common. The depth should be between 1.2 m and 2.0 m. A deeper pond can lead to stratification and anoxic conditions, while a shallower pond may cause algal blooms and high biological activity in the summer. Water stored in the pond should remain for at least 20 days to ensure biological treatment.
The construction of the detention pond in this documentation was initiated as a compensation and replacement measure for the construction of a new road in 2016. Accordingly, the road construction authority, the landscape conservation association and a farmer were involved in the implementation.
As usual with such measures there are drawbacks as well as positive impact for landowners. The measure consumes a lot of land, which automatically results in yield losses. It is expensive to build and not easy to construct - and requires the help of an engineering firm while also being time-consuming to maintain. Maintenance is required to sustain the benefits of the technology. For a pond such as that documented here, the following maintenance activities are necessary: during the first three years, maintenance includes mowing the surrounding green area and the dried out pond and channel three times per year. After the fourth year, maintenance includes (a) an annual function check, (b) a check for pest infestation every two years, and (c) suppression of excess woody growth every eight to ten years. Twice a year (mid-June and late August), the grass around the pond and in the intake channel is mowed and the clippings are removed. Shrubs and woody plants are maintained, especially by pruning woody plants (every 8 to 10 years) and coppicing sections of shrubs (every 10 to 15 years). In the long term, it may be necessary to remove the deposited sediments in order to maintain the retention capacity.
Localização: Reichenbach, Saxony, Alemanha
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados: Local único
Difusão da tecnologia: Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?: Não
Data da implementação: 10-50 anos atrás
Tipo de introdução






not on agricultural inputs, but establishment and maintenance consume a lot of money.
Improved water quality of subsequent river Schwarzer-Schöps.
Soil moisture next to the retention pond increased due to infiltration.
More plant diversity compared to normal farmed grassland.