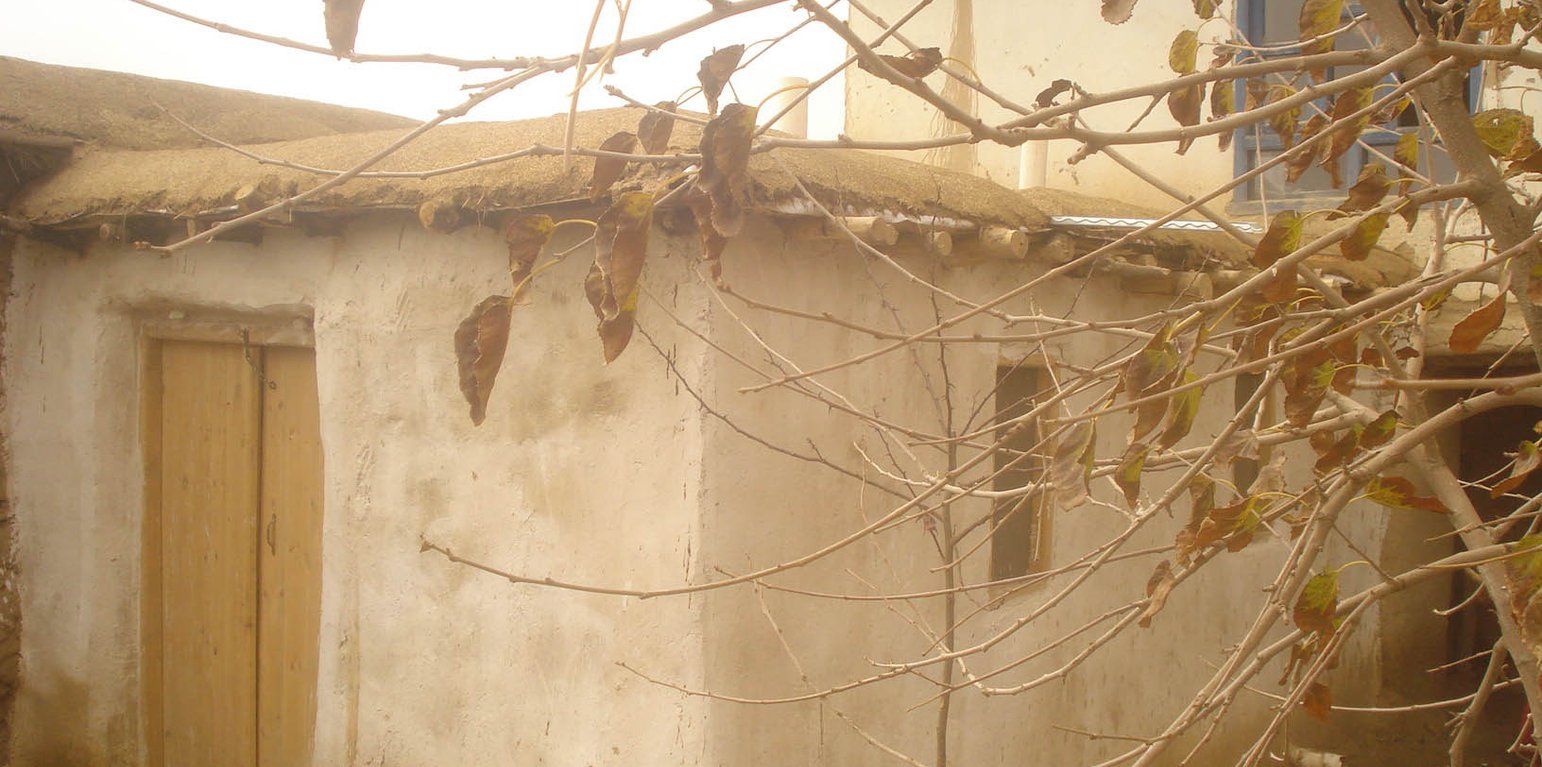




Livestock keeping is one of the key livelihood strategies in rural Rustaq - in addition to cultivation of agricultural crops. Families rely on their livestock not only for consumption of meat and dairy products, but also as means of transportation (donkeys), labour force in agriculture (oxen, donkeys) and as a source of cash income. When crops fail to produce enough, families sell their livestock to survive until the next season. The pressure to sell livestock is more acute during winter months, when cases of livestock loss increases - from diseases, lack of fodder and the harsh cold winter. These factors, along with poor conditions for livestock keeping, expose the animals to various negative impacts, affecting health, productivity and low quality/ quantity of meat and milk.
This situation is observed mainly in Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana and Dashti Mirzai villages, although Dasthi Mirzai has limited grazing land and livestock keeping is not as prevalent as in the two other villages. All three villages were selected to demonstrate improved livestock sheds, which are among the key factors for productive livestock keeping, along with stable supplies of quality fodder. Improved livestock sheds are part of the chain of activities introduced in the three villages to support livestock production, and at the same time improve the availability and quality of fodder, and restore the degraded and overgrazed pastures.
The Natural Resources Management Committee in the respective villages select a farmer, who is active in livestock keeping and already has a livestock shed. The farmer agrees to provide his livestock shed to serve as a demonstration. The farmer is supported technically and financially to renovate his shed in accordance with the defined requirements. The internal and external walls of the shed are covered with plaster made from a clay mixture to block all holes and protect the building from wind and rain. The roof is renovated to prevent leaking from snow and rain. Windows, a door and a ventilator are installed to ensure air circulation, decrease humidity levels, and protect the animals from cold and heat. A water trough and feeding racks are installed inside the shed. All the costs for the material are covered by the project. The farmer contributes with his labour.
The improved shed is vital for keeping livestock healthy. It also contributes to lowering livestock loss through decreasing the risks of diseases and cold stress during winter. The overall benefit towards livelihoods is significant, since animals are an important household asset and a coping strategy for the majority of households in the villages. The wives of the farmers benefit particularly from the renovated livestock sheds, because they are the ones who feed and water the animals, and they clean the shed of manure.
However, the costs for carrying out renovation of livestock sheds are perceived too high by the farmers. Many are unwilling to make such investments, despite the benefits.
Localização: Sari Joy, Jawaz Khana, Dashti Mirzai villages, Takhar Province, Rustaq District, Afeganistão
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados: 2-10 locais
Difusão da tecnologia: Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Data da implementação: 2014; menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
Tipo de introdução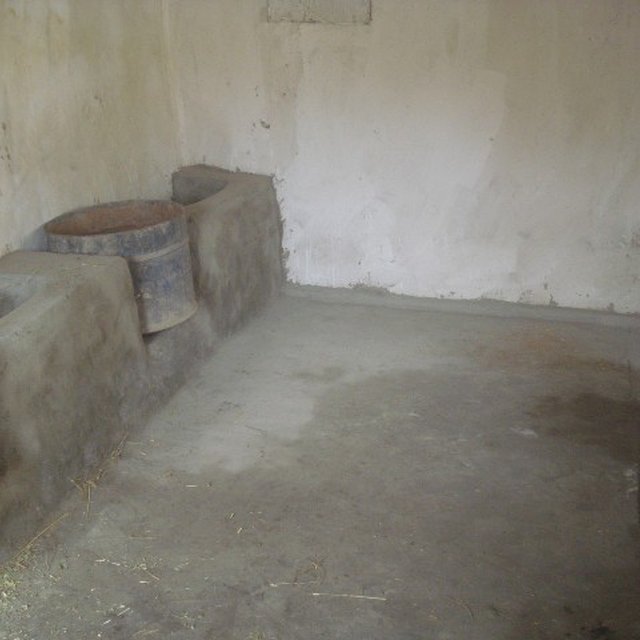
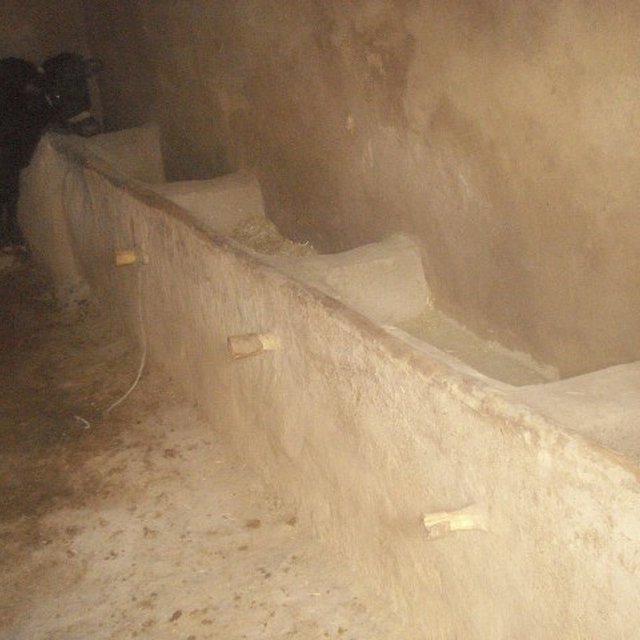



Especificações técnicasThe size of an improved livestock shed is 5 m x 3 m. The internal and external walls of the shed are covered with plaster made from a clay mixture to block all the holes and protect the building from the external elements of rain and wind. The roof is renovated to prevent leaking from snow and rain. Two windows, sized 60 cm x 30 cm and an entrance door 1.5 m x 2 m are installed. 3 ventilation pipes are installed on the roof. The installation of windows, entrance door and ventilators ensure air circulation, decrease humidity levels and protect the animals from cold winters and hot summers. A water trough and feeding racks are installed inside the shed. All the costs for the material are covered by the project. The farmer contributes through labour.
|
|||||||||||
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (Dólares norte-americanos) | Custos totais por entrada (Dólares norte-americanos) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Transportation of construction materials | person-day | 1,0 | 52,0 | 52,0 | |
| Preparation works | person-day | 2,0 | 5,3 | 10,6 | |
| Rennovation works (doors, windows, water tanker and feed slot) | person-day | 14,0 | 5,3 | 74,2 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | |||||
| Pipe for air ventilation | piece | 3,0 | 7,4 | 22,2 | |
| Lime | Bag | 1,0 | 14,0 | 14,0 | |
| Cement | Bag | 10,0 | 5,2 | 52,0 | |
| Door | piece | 1,0 | 59,0 | 59,0 | |
| Window | piece | 2,0 | 22,0 | 44,0 | |
| Cloth | Meter | 12,0 | 1,8 | 21,6 | |
| Outros | |||||
| Water tank for animals | piece | 2,0 | 8,9 | 17,8 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 367.4 | ||||
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (Dólares norte-americanos) | Custos totais por entrada (Dólares norte-americanos) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Repair of the roof | person day | 2,0 | 5,3 | 10,6 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 10.6 | ||||
Land users learned how to implement SLM practices.
Female headed households are not included. Technology is implemented on private land, therefore people without land are excluded. However, they have the opportunity to earn income as a hired worker for the SLM implementers.