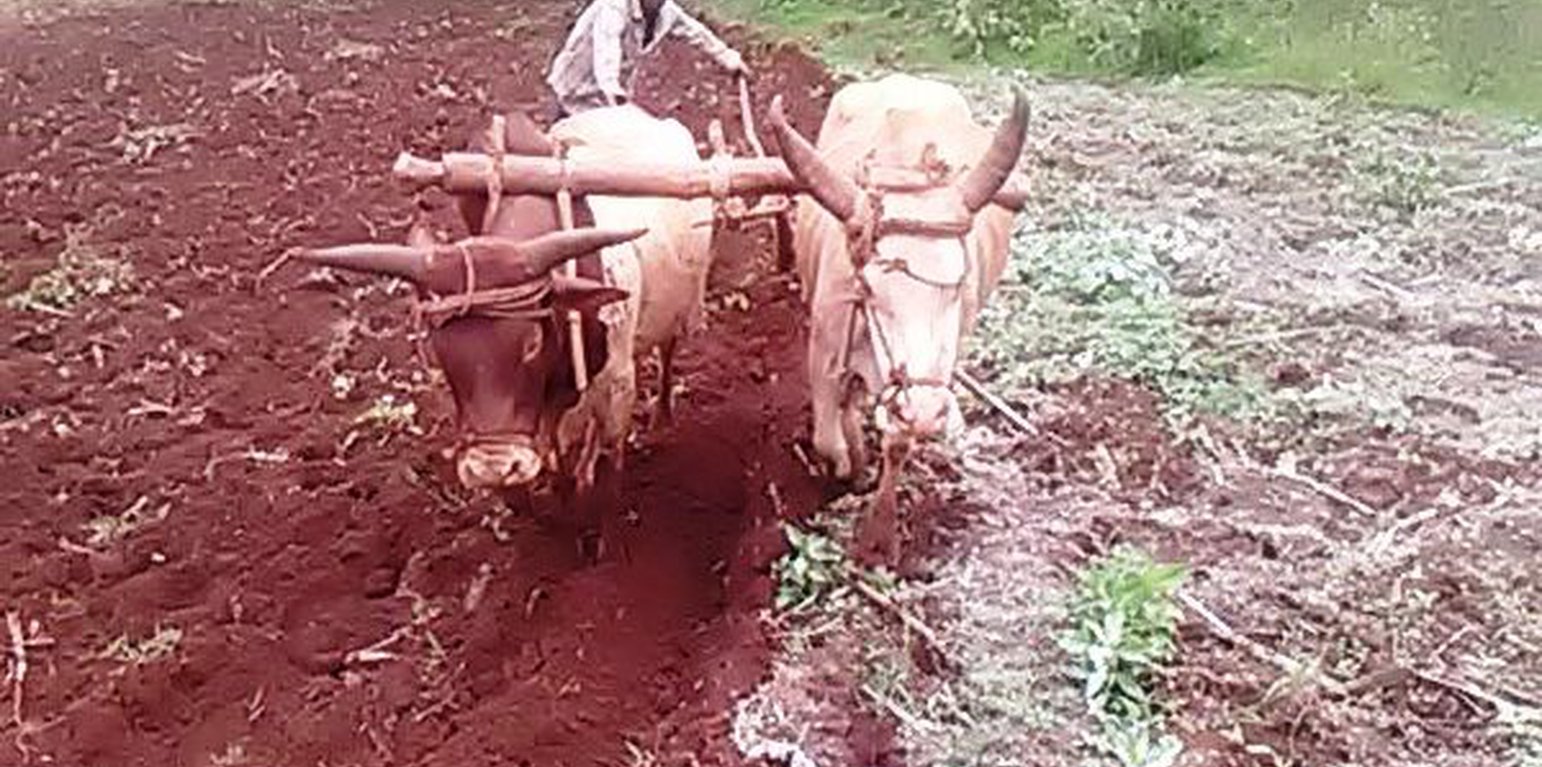




Acidic soils deprive crops of their full nutrient absorption capacity. The farm under the assessment has soil with a pH below 5.0. Lime application to these soil (liming) makes them less acidic. It breaks the barrier that fixes nutrients and ensures crops access to vital soil nutrients that unleash their productivity potential. Soil amendment with lime needs to be at least a month in advance of planting the intended crop. It requires thoroughly mixing the lime powder into the soil. The crop response from the treated soil is gradually visible, particularly during the second cropping season. Lime application takes place after the soil is pulverized very well. Most small cereals (for example “tef”, Eragrostis tef, wheat and barley) need tillage at least four times to create a good environment for the small seeds to emerge and quickly compete effectively with the weeds.
Treating exhausted acidic soils enhances the availability of nutrients that otherwise remain fixed by non-leaching mineral elements in the soil. Application of lime along with organic fertilizers improves soil structure, soil pore space, and soil infiltration capacity. Treating acid soil increases crop production and productivity of the soil. It reduces labour costs relative to output, since it leads to a relatively high yield from a small area. The practice helps to stop land being converted from cropping to grazing. Even when this conversion occurs, the grazing land itself is poor because of the acidity and may be abandoned and simply become unproductive degraded land.
However, availability and accessibility of lime, transportation, and manual application to the farmland are challenging. Based on the degree of soil acidity, the amount of lime required can be high. Apart from the large quantity required (4 or more tonnes per ha), the price per unit is discouraging to smallholder farmers. The high price, poor supply, and delays in delivery are the main challenges to effectively address the prevailing issues of soil acidity.
Localização: Gechi district, Gito kebele, Oromia, Etiópia
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados: Local único
Difusão da tecnologia: Uniformemente difundida numa área (approx. < 0,1 km2 (10 ha))
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?: Não
Data da implementação: 2017
Tipo de introdução







| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (ETB) | Custos totais por entrada (ETB) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Land preparation | PDs | 8,0 | 400,0 | 3200,0 | 100,0 |
| Lime transportation | PDs | 10,0 | 100,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Lime application | PDs | 4,0 | 400,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | |||||
| Lime | ton | 2,0 | 5000,0 | 10000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 15'800.0 | ||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 297.44 | ||||
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (ETB) | Custos totais por entrada (ETB) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Land preparation | PDs | 8,0 | 400,0 | 3200,0 | 100,0 |
| Lime application | PDs | 4,0 | 400,0 | 1600,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | |||||
| Lime | ton | 2,0 | 5000,0 | 10000,0 | 50,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 14'800.0 | ||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 278.61 | ||||
Quantidade anterior à GST: 0.4 ton
Quantidade posterior à GST: 4 tons
Highly increased. With proper application of lime to acid soil crop production increased from about 0.4 to 4 tons on a hectare of land.
Significantly increases as compared to crop production without liming the farm.
As liming increases biomass production, it contributes to fodder production through the supply of surplus crop residue.
The attributes converge with the availability of quality fodder.
Land management is simplified as liming promotes high biomass production in combination with the use of organic and inorganic fertilizers.
As it improves crops absorption of the available nutrients by releasing the nutrients that are otherwise fixed in the soil, it reduces the investment in more inputs/fertilizers.
Lime transporting and application demands a large number of labor.
It converges with good harvest and access to nutritious food.
Improved through evidence based practical learning.
No facts supporting this particular claim.
Liming unfix the available nutrients in the soil system and newly applied ones.
Soil acidity highly reduced by the application of appropriate amount of lime.
As the intervention is a recent one, this estimation is more conceptual than the actual one.
As the intervention is a recent one, this estimation is more conceptual than the actual one.
The growth of dense biomass reduces soil movement which causes pollution.