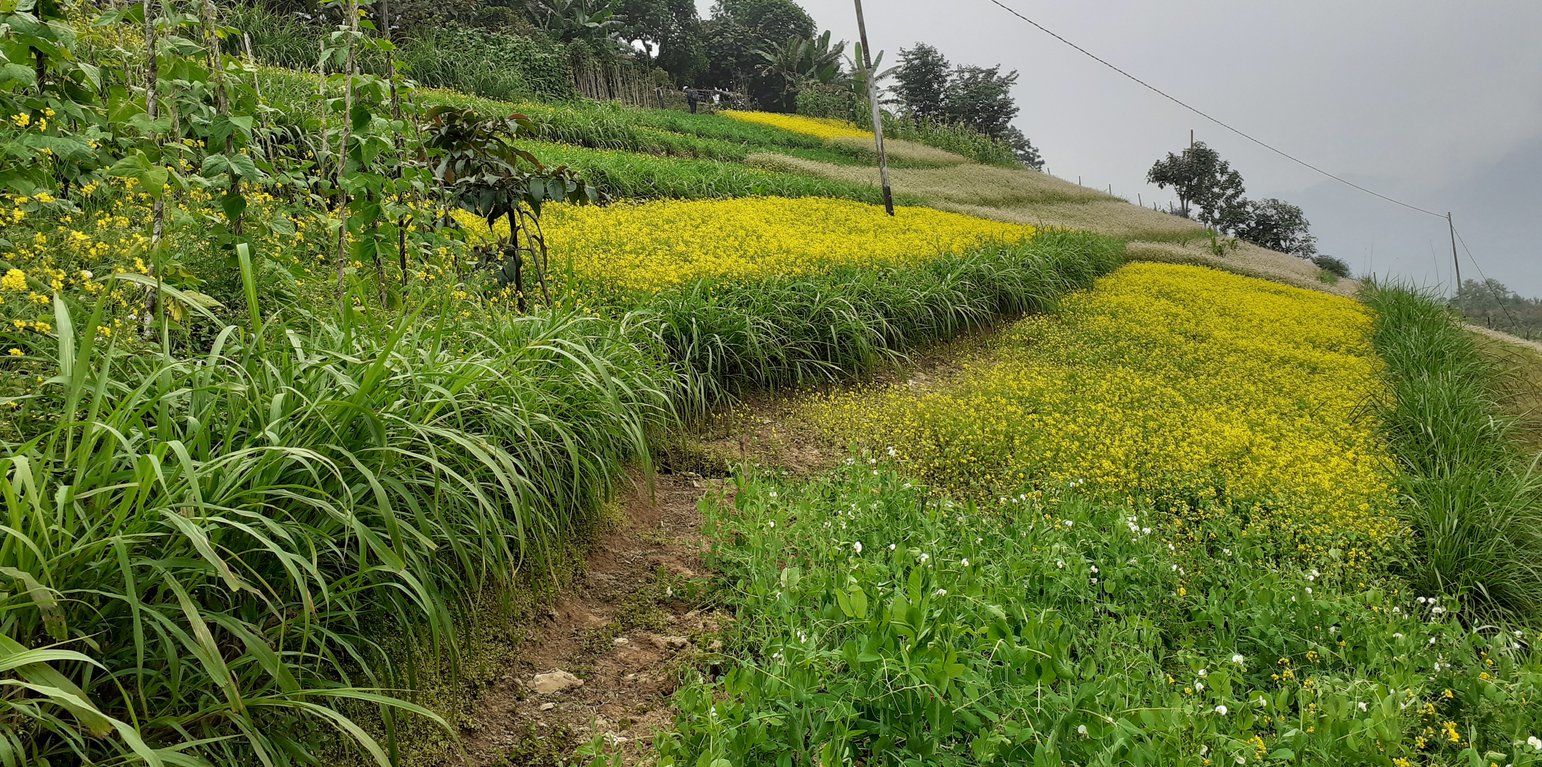




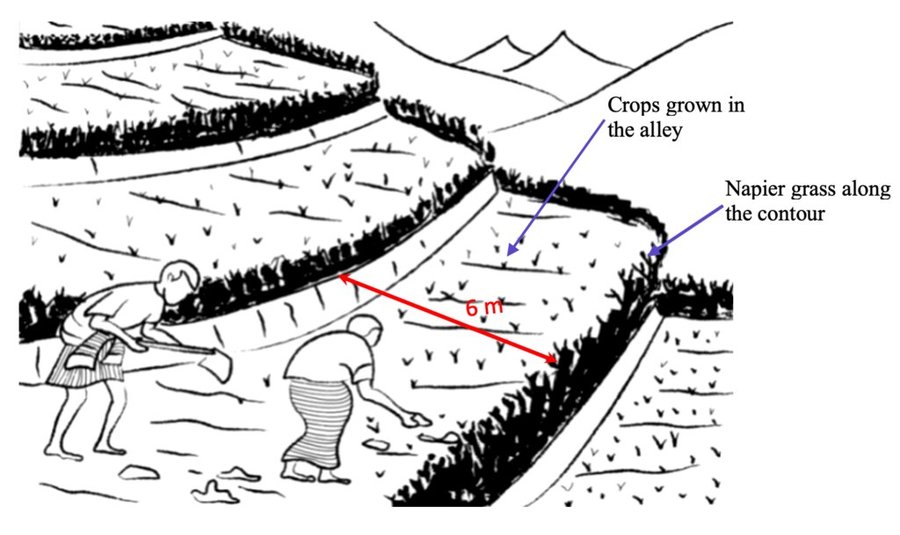
Contour hedgerows are a soil and water conservation technology that involves planting Napier stem cuttings along contour lines on slopes. They are planted at a horizontal distance of 6 meters between rows and 15-20 centimeters between cuttings within lines. On average it requires 3500-4000 Napier slips to cover one acre (0.4 ha). Hedgerows form living barriers that trap sediment and reduce surface runoff. With time, as the sediment builds up behind the hedges, the area between the hedgerows develops into flat alleys or “terrace beds”. This technology is effective in reducing soil erosion and conserving water. The hedgerows also boost crop productivity. The contour hedgerow system is widely used in hilly terrain in Bhutan and elsewhere.
The main purposes of the technology are to 1) serve as a barrier to check the movement of soil and water down the slope, 2) effectively utilize sloping areas for agricultural purposes, and 3) increase crop and fodder production.
The major activities/ inputs needed to establish/ maintain contour hedgerows are: 1) surveying of the area by an SLM specialist (planning and site assessment), 2) selecting suitable hedgerow planting materials, 3) registration of interested farmers, 4) training of farmers, 5) layout of contour lines using A-frames, 6) distribution of planting materials and establishment of hedgerows in farmland, 7) monitoring and evaluation of hedgerows, and 8) maintenance of hedgerows. Maintenance includes replacement of cuttings in gaps - either damaged by cattle or natural mortality and trimming of grass back to 15 centimeters after reaching 1 meter. Inputs required include: 1) planting materials (Napier grass), 2) A-Frame for contour lines, 3) spades, pickaxes, shovels, crowbars, etc., and 4) human resource input by SLM specialists.
Contour hedgerows have many benefits/ impacts on the livelihood of the land users including 1) soil and water conservation, 2) use of the sloping areas for crop or fodder production, 3) effective conservation through using local materials with a 90% survival rate, 4) habitat for natural predators, pollinators, insect-eating birds, and rodent predators, 5) groundwater recharge, and 6) they beautify the overall agricultural landscape. Another important benefit of the hedgerows is the availability of fodder grass for livestock, which otherwise would have to be collected from the forest. The disadvantages include the need for regular maintenance and gapping up. At times, conflicts arise within the community due to grazing of hedges by neighbors’ cattle.
Localização: Boucholing village, Thangrong gewog (block), Mongar Dzongkhag (district), Mongar, Butão
Nº de sites de tecnologia analisados: 10-100 locais
Difusão da tecnologia: Uniformemente difundida numa área (approx. 10-100 km2)
Em uma área permanentemente protegida?: Não
Data da implementação: 2014
Tipo de introdução




| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (Ngultrum) | Custos totais por entrada (Ngultrum) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| Labours | person-days | 4,0 | 250,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | |||||
| Napier | bundle | 35,0 | 200,0 | 7000,0 | |
| Outros | |||||
| Payment for resource persons | No of days | 5,0 | 1500,0 | 7500,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 15'500.0 | ||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 188.84 | ||||
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade (Ngultrum) | Custos totais por entrada (Ngultrum) | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra |
| Mão-de-obra | |||||
| labour | person-days | 2,0 | 250,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | |||||
| Napier slips | Bundle | 10,0 | 200,0 | 2000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 2'500.0 | ||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 30.46 | ||||
Crop production is higher than in the past since the contour hedgerows have helped control soil erosion and allowed for proper land utilization. The land user reported about a 25% increase compared to the past.
The crop quality is also relatively better now compared to the past when the technology was not applied. The land users reported that crops near the hedgerows were found more greener.
Quantidade anterior à GST: No fodder was produced
Quantidade posterior à GST: After napier plantation, napier are harvested as fodder for cattle.
Napier grass was not planted in the past. It was introduced by the National Soil Services Center as part of this technology. The Napier grass planted along the contour has helped not only with soil erosion control but also provided fodder grass for the cattle. The land user reported that there was a 100% increase in fodder because unlike in the past now they don't have to send their cow for grazing in the forest.
Compared to normal grass that the cattle would graze on, napier is nutrient-rich and of better quality than the normal grass.
The napier plantation has helped prevent soil erosion that would normally occur in the farm lands thereby preventing crop failure due to soil fertility and moisture conservation.
With the help of the project, the land users were able to utilise the sloping land. This enabled land users to grow crops other than maize.
The contour hedgerows have allowed for the sloping and degraded lands to be revitalised into usable cultivable lands.
Quantidade anterior à GST: Hard manual land management
Quantidade posterior à GST: mechanization of the agriculture in the community
With the help of the project, farm lands in the community were made into terraces and made land management easier compared to the past.
The expenses on agricultural inputs have stayed relatively the same, however, has made working on the farm land easier.
With fodder availability, land users can now focus more on agriculture instead of herding cattle for grazing. The project has also allowed for land users to diversify their products.
Workload has decreased due to farm mechanization through use of power tillers, which was not possible prior to the SLM intervention.
Prior to hedgerow establishemt, there was serious surface erosion, which is not the case now.
Quantidade anterior à GST: primarily maize was cultivated
Quantidade posterior à GST: maize, cole crops, tubers and chilies are cultivated
In the past, the community members would normally cultivate maize and small amounts of vegetables for self consumption, but now a diverse variety of crops are cultivated.
Downstream flooding is relatively less, since the hedgerows has prevented or reduced surface eorsion which would otherwise impact the downstream settlements and water bodies.