Participatory Learning and Action Research approach to Integrated Rice Management [Madagascar]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2571 - Madagascar
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da abordagem
Agric. R&D consultant:
Defoer Toon
tdefoer@aliceadsl.fr
Najac, France
França
Especialista em GST:
Wopereis Marco
wopereis@cgiar.org.
Africa Rice Center
Cotonou
Benin
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - SuíçaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
Africa Rice Center (AfricaRice) - Costa do Marfim1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da abordagem de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da abordagem
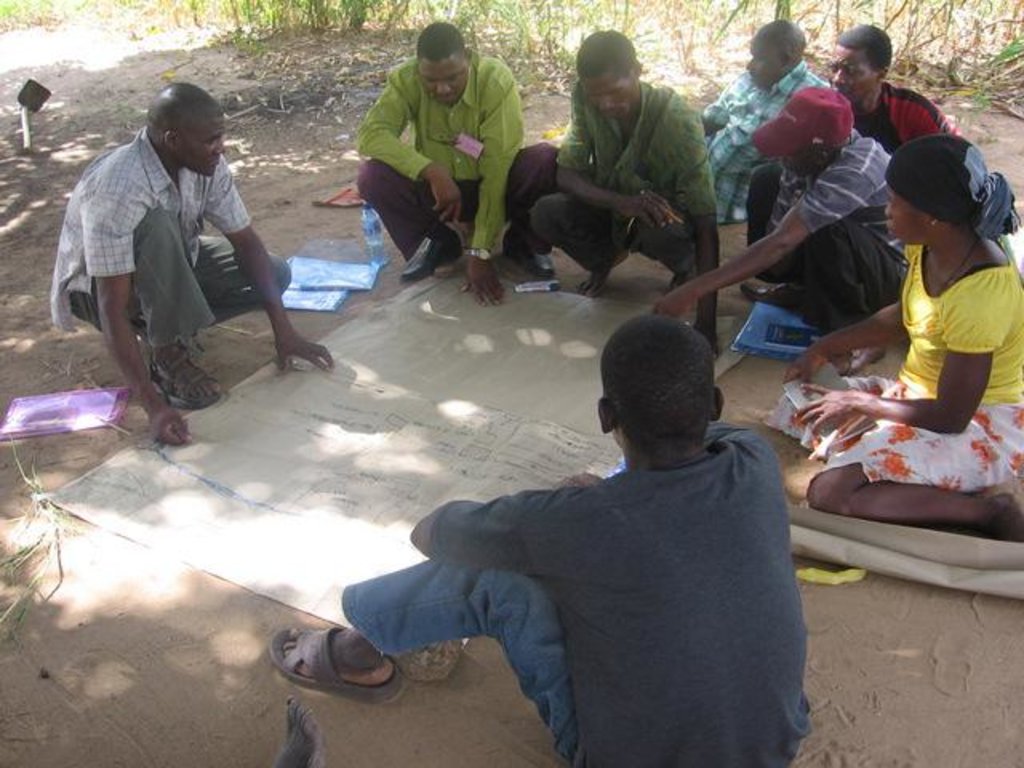
The Participatory Learning and Action Research approach to Integrated Rice Management (PLAR-IRM) is a bottom-up, social and experiential learning approach, leading to sustainable agricultural improvements, based on mutual support and communication among farmers.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da abordagem
Descrição detalhada da abordagem:
Aims / objectives: Innovation and agricultural change is aimed for, through capacity strengthening of all major stakeholders involved in the rice sub-sector. IRM refers to the production system and value chain as a whole. Innovation is not limited to technological change; it also includes time management and the building of social networks and institutions for mutual collaboration between farmers and other stakeholders within the rice value chain. A step-wise, self-discovery learning mode encourages the stakeholders to find solutions for their own site-specific problems. During the first years, groups of 25-30 producers are supported by a programme facilitator who animates the learning and innovation sessions. The main instruments are the learning modules dealing with specific crop management practices, harvest and post-harvest practices (involving processors and entrepreneurs also), as well as the agro-ecological and socio-economic conditions of rice production. The sessions aim to strengthen farmers’ and other rice stakeholders' capacity to observe, analyze, interpret, make decisions, innovate and share knowledge and experiences. PLAR is based on locally relevant knowledge, practices and skills. Exchanges about current practices, and their logic or justification, are the starting point in all modules.
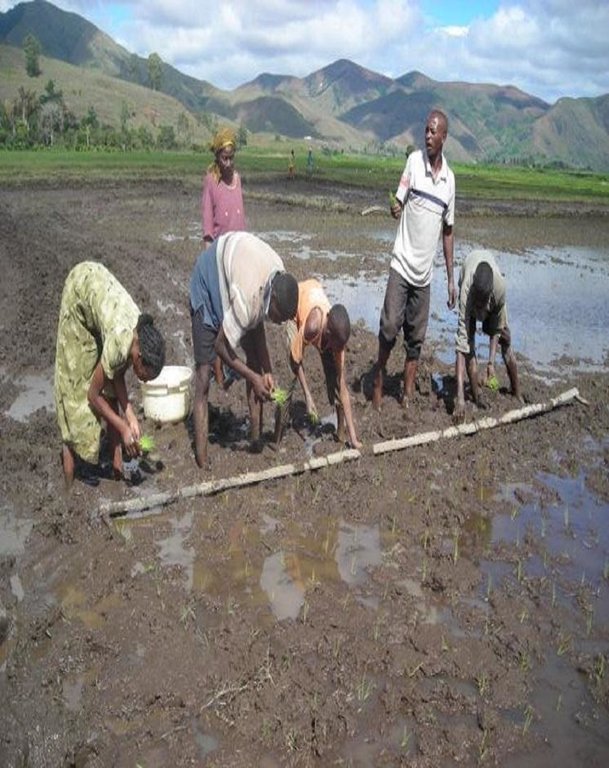
Methods: In a learning-by-doing approach farmers are encouraged to try out any new ideas identified during PLAR sessions on some parts of their fields reserved for new practices (“innovation space”). This allows them to assess the impact of such innovations on their rice yield, or on the profitability of rice growing and the rice business as a whole, and consequently to adapt and fine-tune the measures taken according to their needs. These innovation spaces are regularly visited as part of learning sessions for knowledge sharing between farmers. Since 2005, innovations in land preparation, early transplanting of seedlings, weeds and water management - basically without external inputs - have resulted in three times higher yields, benefitting thousands of farmers. Rice value chain activities started in 2008 with a view to empowering farmers' position within the chains and improving the competitiveness. Groups are unifying into PLAR centres with common marketing of rice, and contract input providers and rice processors.
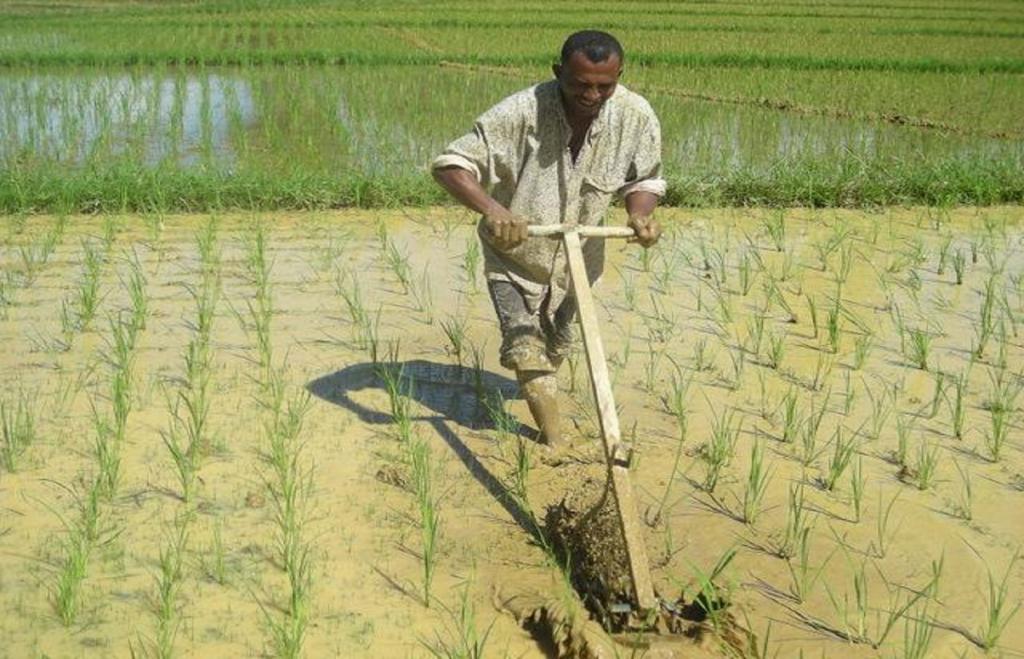
2.3 Fotos da abordagem
2.5 País/região/locais onde a abordagem foi aplicada
País:
Madagascar
Especificação adicional de localização:
Sofia Region
Map
×2.7 Tipo de abordagem
- Baseado em projeto/programa
2.8 Principais metas/objetivos da abordagem
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (value chain develop¬ment: collective storage and marketing of rice; contractual arrangements with input providers and rice processors)
Sustainably improving food security, livelihoods and incomes of poor rice farmers by boosting the profitability of rice production and increasing the efficiency and competitiveness of the rice sub-sector; Capacity strengthening of all stake-holders involved in the rice-subsector
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Low yields in rice production; Most farmers live below subsistence level; Absence of government and NGO support; Limited access to markets, lack of infrastructure
3. Participação e papel das partes interessadas envolvidas
3.1 Partes interessadas envolvidas na abordagem e seus papéis
- Usuários de terra/comunidades locais
rice farmers
marginalised poor rice farmers are targeted
- Setor privado
private service providers (e.g. input suppliers), rice processors and buyers
- Governo local
- Organização internacional
Aga Khan Foundation
3.2 Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais nas diferentes fases da abordagem
| Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais | Especifique quem estava envolvido e descreva as atividades | |
|---|---|---|
| Iniciação/motivação | Participativo | |
| Planejamento | Participativo | |
| Implementação | Participativo | |
| Monitoramento/avaliação | Nenhum | |
| Research | Nenhum |
3.4 Decisão sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias de GST
Especifique quem decidiu sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias a serem implementadas:
- Somente usuários da terra (iniciativa própria)
Explique:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. Suporte técnico, reforço das capacidades e gestão do conhecimento
4.1 Reforço das capacidades/ formação
Foi oferecida formação aos usuários da terra/outras partes interessadas?
Sim
Especifique quem foi capacitado:
- Usuários de terra
- Equipe de campo/consultores
Tipo de formação:
- Em exercício
- Agricultor para agricultor
Assuntos abordados:
crop management practices, harvest and post-harvest practices (incl. storage, marketing), socio-economic and ecological conditions of rice farming; curriculum based on needs assessment
4.2 Serviço de consultoria
Os usuários de terra têm acesso a um serviço de consultoria?
Sim
Especifique se foi oferecido serviço de consultoria:
- nas áreas dos usuários da terra
Descreva/comentários:
Name of method used for advisory service: modular learning sessions guided by a facilitator, farmer-to-farmer extension; Approach is based on indigenous knowledge
4.5 Pesquisa
A pesquisa foi parte da abordagem?
Sim
Dê mais detalhes e indique quem realizou a pesquisa:
crop management practices
Research was carried out on-farm
5. Financiamento e apoio material externo
5.1 Orçamento anual para o componente de GST da abordagem
Caso o orçamento exato seja desconhecido, indique a faixa:
- 100.000-1.000.000
Comentários (p. ex. principais fontes de recursos/principais doadores):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international: 10.0%; national non-government: 30.0%; private sector: 10.0%; local community / land user(s): 50.0%
5.2 Apoio financeiro/material concedido aos usuários da terra
Os usuários da terra receberam apoio financeiro/material para a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias?
Sim
5.3 Subsídios para entradas específicas (incluindo mão-de-obra)
- Equipamento
| Especifique quais entradas foram subsidiadas | Em que medida | Especifique os subsídios |
|---|---|---|
| Ferramentas | Totalmente financiado | Two sarcleuses (weeding equipment) per starting group are provided for free and remain property of the group |
Comentários:
Two sarcleuses (weeding equipment) per starting group are provided for free and remain property of the group
5.4 Crédito
Foi concedido crédito segundo a abordagem para atividades de GST?
Sim
Especifique as condições (taxa de juros, reembolso, etc):
Interest rate charged: 2.5%; repayment conditions: Was supported by the approach in collaboration with an existing microfinance institution; loan period: 6-8 months, 2.5% monthly (!) interest rate.
6. Análise de impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos da abordagem
A abordagem auxiliou os usuários da terra a implementar e manter as tecnologias de GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
yields have increased by > 200% (on innovation spaces)
A abordagem concedeu autonomia aos grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
marginalised poor rice farmers are targeted
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
from 2005-2009 PLAR groups have increased from 6 up to 102, involving 3782 families and extended to 4200 non grouped farmers
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
SLM practices result into a net benefit of > 700 US$/ha
6.2 Principal motivação dos usuários da terra para implementar a GST
- Produção aumentada
- Lucro (lucrabilidade) aumentado, melhora da relação custo-benefício
- Afiliação a movimento/projeto/grupo/rede
6.3 Atividades de sustentabilidade de abordagem
Os usuários da terra podem manter o que foi implementado através da abordagem (sem apoio externo)?
- Sim
Caso afirmativo, descreva como:
In a 2nd phase farmers who are organised in PLAR groups gradually build up the capacity to manage the innovation and mutual learning approach on their own without programme support: Farmers facilitators are trained to take over the lead of PLAR groups with backstopping from programme facilitators.
6.4 Pontos fortes/vantagens da abordagem
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Farmers learn basic principles of rice management and develop their own locally adapted options for improvements; the innovation comes from inside the groups. |
| Farmers build up individual and organisational capacity to find solutions to their problems and build confidence as efficient partners with other value chain actors. |
6.5 Pontos fracos, desvantagens da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Labour intensive improvements | provision of group credit to PLAR group members in collaboration with a local microfinance institution |
| Learning intensive approach, with regular group learning sessions | PLAR groups elaborate their own learning programmes and curricula according to their availability and needs |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Defoer T., M. Wopereis, S. Diack, and P. Idinoba. 2008. Apprentissage participatif et recherche action pour la gestion intégrée du riz à Madagascar: Manuel du facilitateur AKF, Genève, Suisse. Defoer T., M. Wopereis, P. Idinoba T. and Kadisha. 2006. Participatory Learning and Action Reseaerch (PLAR) for Integrated Rice Management in inland valleys in sub-saharan Africa: Facilitators’ manual. WARDA- the Africa Rcie Center, Bouaké, Côte d’Ivoire.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Defoer T., M. Wopereis, P. Idinoba T. and Kadisha. 2006. Participatory Learning and Action Reseaerch (PLAR) for Integrated Rice Management in inland valleys in sub-saharan Africa: Facilitators’ manual. WARDA- the Africa Rcie Center, Bouaké, Côte d’Ivoire.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos