The soil doctor network for integrated farming [Tailândia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Areerat Wangkaew
- Editor: –
- Revisores: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
approaches_7279 - Tailândia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da abordagem
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Saihoe Kasem
Tailândia
usuário de terra:
Saengdao Prakob
Tailândia
usuário de terra:
Ushi Chai
Tailândia
co-compilador/a:
Srithanboon Supranee
Land Development Department
Tailândia
Partners:
Jakkraraj Usa
Land Development Department
Tailândia
Partners:
Phonruang Vichit
Land Development Department
Tailândia
Partners:
Nonseelat Yutthana
Land Development Department
Tailândia
Partners:
Phonruang Tossaporn
Land Development Department
Tailândia
Editor:
Jintaridth Bunjertluk
Land Development Department
Tailândia
Editor:
Yamklee Pramote
Land Development Department
Tailândia
Editor:
Tarnnate Prapa
Land Development Department
Tailândia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/avaliação da Abordagem (se relevante)
Land Development Department (Land Development Department) - Tailândia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da abordagem de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da abordagem
A “soil doctor” network in Khon Kaen province has transformed saline areas previously dedicated to rice cultivation into sustainable, integrated farming systems.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da abordagem
Descrição detalhada da abordagem:
Most agricultural areas in Northeast Thailand rely on rainfall, and some face the added challenge of saline soils. Rice is the dominant crop, cultivated primarily under rain-fed conditions. However, climate variability has intensified, leading to changes in rainfall distribution and creating further uncertainty for farmers. Additionally, labour shortages have emerged due to an ageing population and rising labour costs. In response to these challenges, adjusting the agricultural system from monoculture rice cultivation to integrated farming offers a viable alternative for enhancing sustainability. Integrated farming promotes product diversity and food security, helping farmers reduce risks associated with climate variability and market fluctuations.
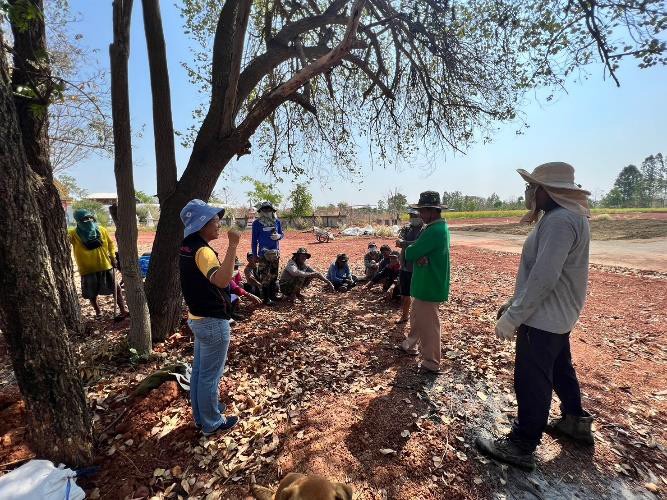
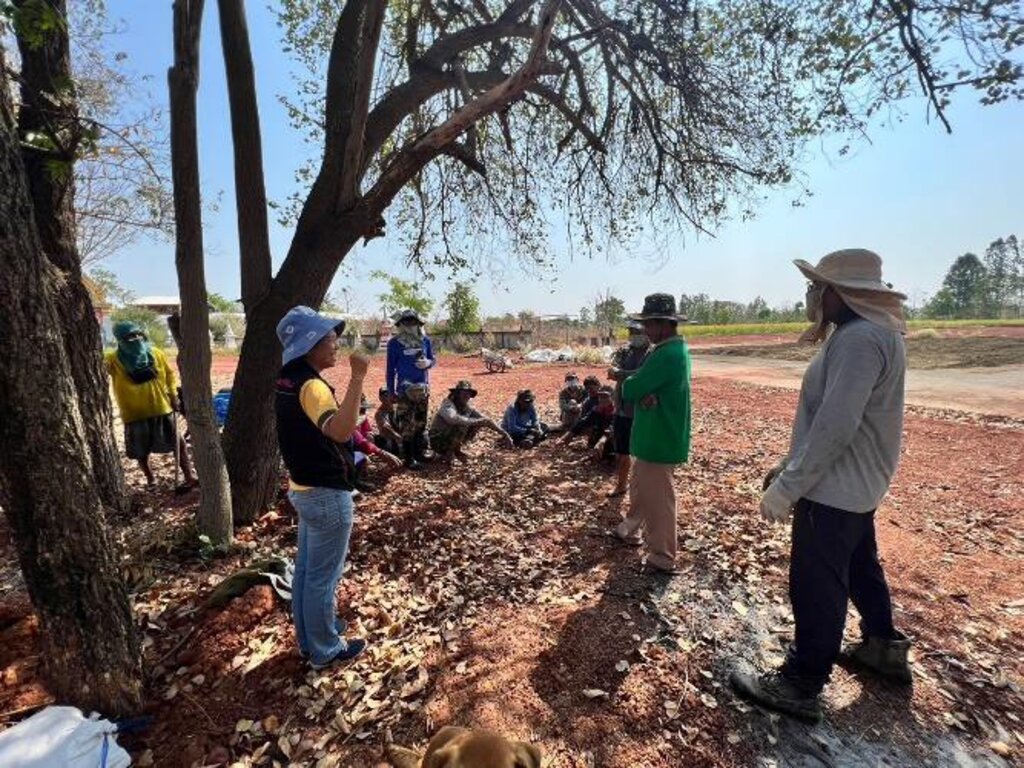
The Soil Doctor Network, a community-based initiative supported by the Land Development Department, plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainable land management. The program trains and empowers local farmers to become volunteer “soil doctors” who serve as local experts and advisors. These soil doctors undergo extensive training in soil management, integrated farming techniques, and sustainable agricultural practices. They assist fellow farmers in improving soil health and adopting more resilient farming methods. Soil doctors are organized into local networks at the village or sub-district level. Experienced soil doctors lead these networks, acting as coordinators to ensure effective communication and collaboration among members. They also liaise with government agencies to secure technical support, financial assistance, and up-to-date information on sustainable farming practices.
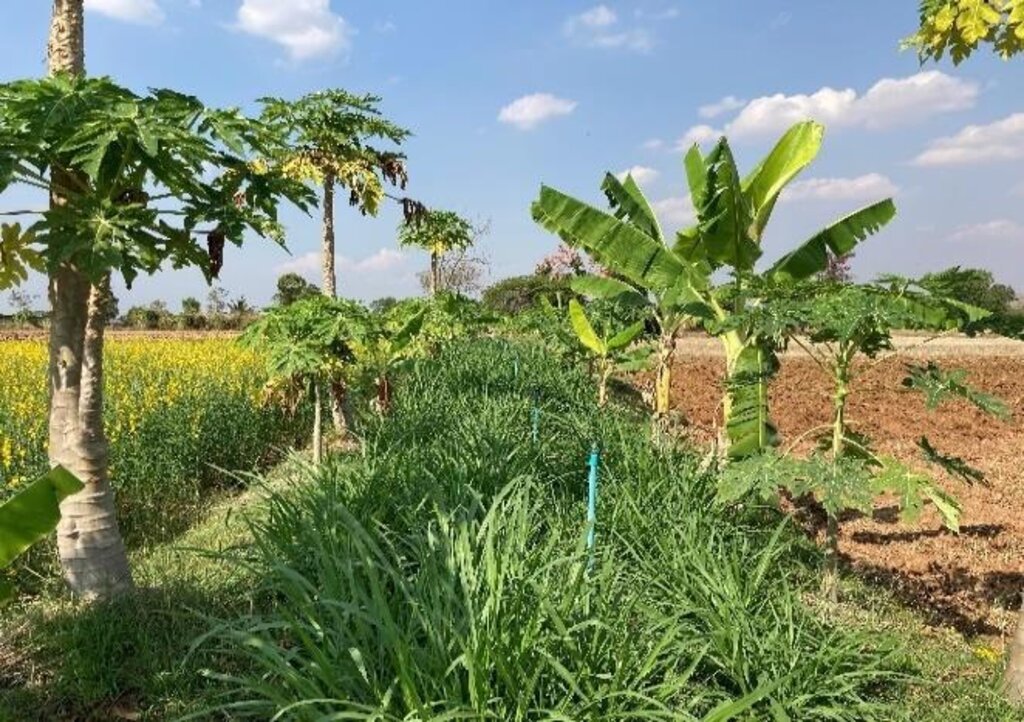
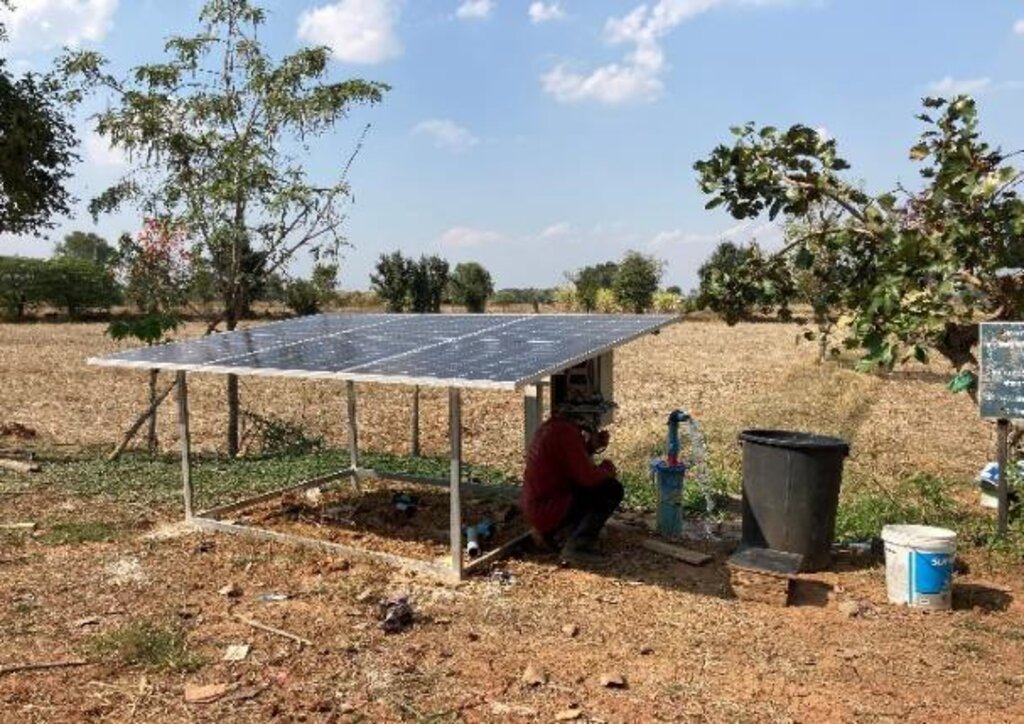
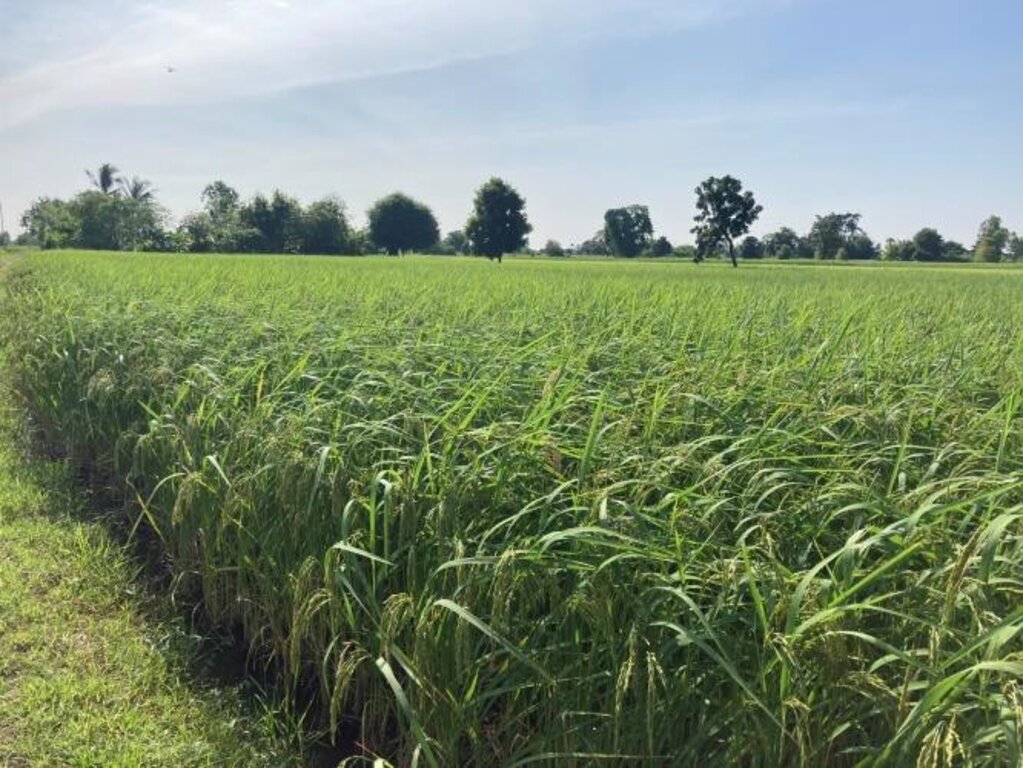
A Soil Doctor Network’s impact can be witnessed in Ban Doo Noy, Non Daeng sub-district, Non Sila district, Khon Kaen province. This area, previously dedicated to monoculture rice cultivation conducted once a year, has undergone significant transformation through the adoption of integrated farming. Farmers have leveled fields, widened levees, dug ponds, drilled artesian wells, and diversified their crop production. Today, the farms in Ban Doo Noy feature a variety of crops, including rice, papaya trees, bananas, and grass for livestock grown on the levees, alongside vegetable cultivation. Post-harvest crops such as sunn hemp, sweet corn, sugar cane, and cattle raising have been incorporated, further enhancing productivity and resilience. The integrated farming system has also effectively addressed the issue of saline soils by improving soil structure, preserving moisture, and reducing salinity accumulation. The use of cover crops, crop rotation, and organic matter enrichment has played a crucial role in mitigating soil salinity and preserving the natural ecosystem. These sustainable practices have improved soil fertility and water retention, enabling farmers to maintain long-term agricultural productivity.
Through the sustained efforts of the Soil Doctor Network, local land users in Northeast Thailand are now better equipped to manage their land sustainably. By fostering knowledge-sharing and community-driven initiatives, the network has empowered farmers to reduce their reliance on external support while ensuring long-term productivity and resilience in the face of climate and economic challenges.
2.3 Fotos da abordagem
2.5 País/região/locais onde a abordagem foi aplicada
País:
Tailândia
Região/Estado/Província:
Non Daeng sub-district, Non Sila district, Khon Kaen province
Map
×2.6 Datas de início e término da abordagem
Indique o ano de início:
2017
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada de início da abordagem:
menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Tipo de abordagem
- Baseado em projeto/programa
2.8 Principais metas/objetivos da abordagem
1.To establish a network of soil doctors who apply integrated farming techniques for the sustainable use of saline soil areas.
2.To disseminate knowledge on creating food diversity for households located in saline soil regions.
3.To facilitate access to support from both government and private sectors.
2.9 Condição que propiciam ou inibem a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias aplicada(s) segundo a abordagem
Disponibilidade/acesso a recursos e serviços financeiros
- Propício
Volunteer soil doctors and government agencies provided assistance and resources, including funding and knowledge.
Colaboração/coordenção de atores
- Propício
A group of volunteer soil doctors with knowledge and expertise in the area and surrounding areas lent their assistance and collaboration.
Conhecimento sobre GST, acesso a suporte técnico
- Propício
The Soil Doctor Network emphasizes educating local farmers and community leaders on SLM principles, including soil health management, erosion control, and sustainable farming practices. By equipping soil doctors with this knowledge, they can provide guidance and support to other farmers, ensuring the effective application of soil management technologies.
3. Participação e papel das partes interessadas envolvidas
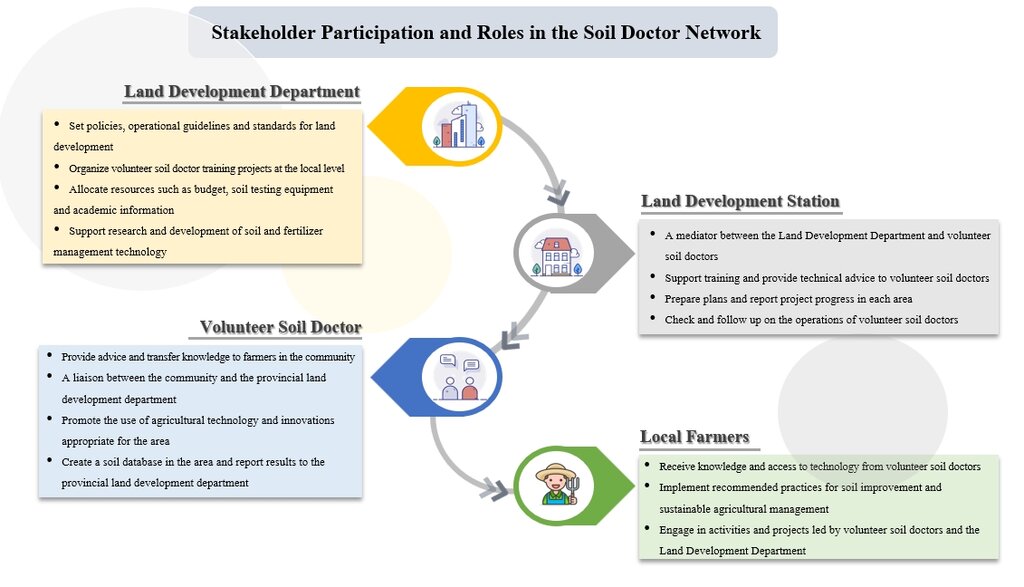
3.1 Partes interessadas envolvidas na abordagem e seus papéis
- Usuários de terra/comunidades locais
The group of farmers of the soil doctor network
It is the one implementing the approach of using the integrated farming technology in its own agricultural areas. There are 10 members participating in the network.
- Especialistas em GST/ consultor agrícola
Land Development Department officers
They are the ones who transfer knowledge, support production factors such as Sunn hemp seeds etc., including giving advice regarding putting in use correctly, suitably and mutually studying changes occurring in areas with saline soil.
- Governo local
Government agencies and local agencies
Government agencies and local agencies are the ones supporting in terms of knowledge of other related areas.
- local land users
Farmers and the interested general public
Applying knowledge to develop their own agricultural areas due to the fact that production factors can be made locally with prices not so high
3.2 Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais nas diferentes fases da abordagem
| Envolvimento do usuários de terra/comunidades locais | Especifique quem estava envolvido e descreva as atividades | |
|---|---|---|
| Iniciação/motivação | Participativo | Focusing on creating awareness and building interest among local land users, SLM specialists, together with representatives from the Soil Doctor Network, engage local leaders, farmers, and landowners through meetings, workshops, and demonstrations to introduce the concept of integrated farming and its benefits. They emphasize raising awareness of the benefits of sustainable land management, such as improved soil health and increased productivity. Land users are motivated by the potential for higher yields, cost reduction, and long-term sustainability. |
| Planejamento | Participativo | Local land users are actively involved in the development of customized plans tailored to their specific needs and environmental conditions. |
| Implementação | Participativo | The implementation phase involves hands-on application of the planned activities, with local communities taking the lead. |
| Monitoramento/avaliação | Participativo | Local land users are actively involved in the development of customized plans tailored to their specific needs and environmental conditions. Participatory monitoring, data collection, and community feedback are conducted periodically to review progress, share experiences, and discuss challenges. Adjustments and Scaling Up based on the evaluation, necessary adjustments are made to improve practices. Successful methods are scaled up, and new farmers are encouraged to join the network. |
3.3 Fluxograma (se disponível)
3.4 Decisão sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias de GST
Especifique quem decidiu sobre a seleção de tecnologia/tecnologias a serem implementadas:
- Principalmente especialistas em GST, após consulta com usuários da terra
Explique:
SLM specialists begin by conducting field assessments and consultations with local land users to understand the specific challenges, then identify appropriate technologies, considering factors such as local soil type, climate, land use, and farming practices.
Especifique em que base foram tomadas as decisões:
- Avaliação de conhecimento bem documentado de GST (tomada de decisão baseada em evidências)
4. Suporte técnico, reforço das capacidades e gestão do conhecimento
4.1 Reforço das capacidades/ formação
Foi oferecida formação aos usuários da terra/outras partes interessadas?
Sim
Especifique quem foi capacitado:
- Usuários de terra
- Equipe de campo/consultores
Caso seja relevante, especifique gênero, idade, status, etnia, etc.
Individuals of all genders, aged 20 to 60, are trained.
Tipo de formação:
- Agricultor para agricultor
- Áreas de demonstração
- Reuniões públicas
4.2 Serviço de consultoria
Os usuários de terra têm acesso a um serviço de consultoria?
Sim
Especifique se foi oferecido serviço de consultoria:
- nas áreas dos usuários da terra
- Em centros permanentes
4.3 Fortalecimento da instituição (desenvolvimento organizacional)
As instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas através da abordagem?
- Sim, significativamente
Especifique a que nível (níveis) as instituições foram fortalecidas ou estabelecidas:
- Regional
- Nacional
Descreva instituição, papéis e responsabilidades, membros, etc.
Institution roles and responsibilities: 1.Policy Formulation: Develops national policies, guidelines, and standards for sustainable land management.
2.Technical Support: Provides training, tools, and materials to local soil doctors and communities. 3.Capacity Building: Organizes training programs to enhance the skills of local soil doctors. 4.Monitoring and Evaluation: Oversees the implementation of the Soil Doctor Network and ensures that land users follow SLM practices effectively. 5.Research and Innovation: Conducts research on innovative farming technologies and sustainable practices and disseminates findings to local communities.
Especifique o tipo de apoio:
- Reforço das capacidades/ formação
- Equipamento
Dê mais detalhes:
The approach fosters collaboration between institutions at different levels—government, local communities, research bodies, and the private sector, to ensure sustainability and scalability. Strengthening these institutions enhances local capacity, promotes shared responsibility, and ensures the continued success of the Soil Doctor Network for Integrated Farming.
4.4 Monitoramento e avaliação
Monitoramento e avaliação são partes da abordagem?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, esta documentação é destinada a ser utilizada para monitoramento e avaliação?
Não
4.5 Pesquisa
A pesquisa foi parte da abordagem?
Não
5. Financiamento e apoio material externo
5.1 Orçamento anual para o componente de GST da abordagem
Caso o orçamento exato seja desconhecido, indique a faixa:
- < 2.000
Comentários (p. ex. principais fontes de recursos/principais doadores):
Farmers and landowners spent their own money.
5.2 Apoio financeiro/material concedido aos usuários da terra
Os usuários da terra receberam apoio financeiro/material para a implementação de tecnologia/tecnologias?
Não
5.3 Subsídios para entradas específicas (incluindo mão-de-obra)
- Nenhum
5.4 Crédito
Foi concedido crédito segundo a abordagem para atividades de GST?
Não
5.5 Outros incentivos ou instrumentos
Foram utilizados outros incentivos ou instrumentos para promover a implementação das tecnologias de GST?
Não
6. Análise de impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos da abordagem
A abordagem concedeu autonomia aos usuários locais de terra, melhorou a participação das partes interessadas?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
A abordagem melhorou a coordenação e a implementação economicamente eficiente da GST?
- Não
- Sim, pouco
- Sim, moderadamente
- Sim, significativamente
6.2 Principal motivação dos usuários da terra para implementar a GST
- Produção aumentada
- Lucro (lucrabilidade) aumentado, melhora da relação custo-benefício
Integrated farming can be effectively conducted in the area, encompassing a variety of agricultural activities, thereby contributing to food security and enhancing family income.
6.3 Atividades de sustentabilidade de abordagem
Os usuários da terra podem manter o que foi implementado através da abordagem (sem apoio externo)?
- Sim
Caso afirmativo, descreva como:
Land users can form local groups or cooperatives to share resources, exchange knowledge, and collectively address challenges. This reduces the need for external intervention by fostering peer-to-peer support. They can use locally available resources such as produce organic fertilizers (e.g., compost, manure) and soil amendments, reducing reliance on external inputs. Using simple soil-testing tools and techniques learned through the network, land users can periodically monitor soil health and adjust practices accordingly.
6.4 Pontos fortes/vantagens da abordagem
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Having an opportunity to see managing the integrated farming area which has been achieved and being able to adjust it in their own areas. |
| Having points of exchanging learning in the community, being able to access them easily. |
| Having an opportunity to receive advice and exchange knowledge both from officers and the soil doctor network. |
| Having an opportunity to receive support from government agencies and local agencies. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Transferring the technology of the soil doctor network about self-reliance, family labor and factors in the farm. This helps reduce production costs. |
| Prototype soil doctors always provide knowledge data regarding production and give advice regarding suitable practices. This helps bring about security in occupation of the network group using integrated farming technology. |
6.5 Pontos fracos, desvantagens da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Requiring a period of time for at least 3 years until changes can be seen in areas of saline soil. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Agricultural areas are still affected from water qualities for agriculture from artesian wells in terms of receiving brackish water during the dry season. | Some farmers solve the problem by digging a pond in the field to pull water from the artesian well to be stored before using it in the agricultural plot. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
12
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
3
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
3
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos