Technology of fastening Aral sea's drained bottom' s soil [Cazaquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Vladimir Kaverin
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
no
technologies_1089 - Cazaquistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Salimov Abdul
RGP, SPC of forest facility
Kirov str.,58 city Schuchinsk, Akmola region
Cazaquistão
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
SPC of Forest Facility (SPC of Forest Facility) - Cazaquistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
09/12/2003
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Technology of fastening Aral Sea's drained bottom's soil
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
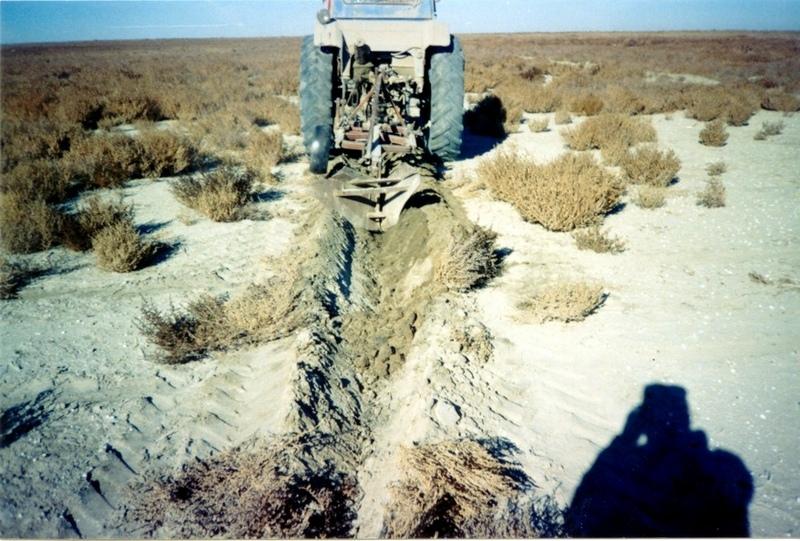
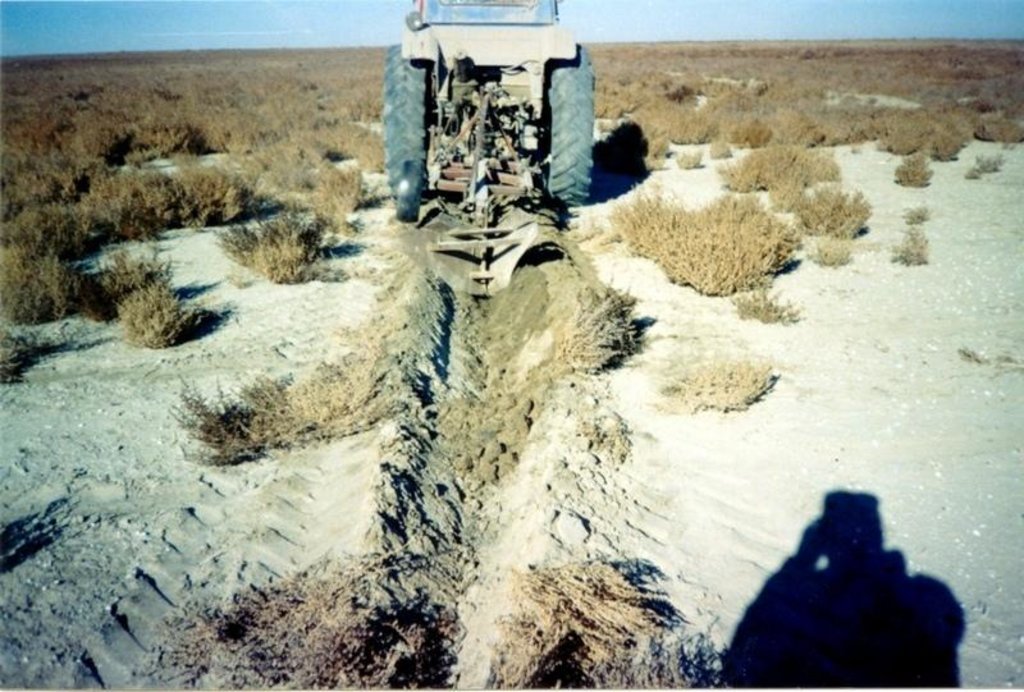
Planting of the saplings on the lots of the dried seabed of the Aral Sea was done in holes and uninterrupted furrows, which were formed by hands or cultivated KON – 2.8 PM . Depth of holes and furrows is 20-25 cm. Distance between holes was 1.5-2 m. Furrows were perpendicular to the prevailing winds (west-east) and placing mould in several options: 1 – moulds on both sides; 2 – the same from the southern side of a furrow; 3 – the same from the northern side. Furrows alternated with holes rows. Length of rows variants in repetition was 100 m. Saplings were filled up by hands or in rows in 1-2 meters, distance between rows was 2-2.5 meters. For the last 30 years Aral Sea level is falling and in 2001 it fell by 20 meters. More over 35 thousands sq. km of sea bottom came to the surface. Pace of falling during the last ten years is 0.9-0.8 meters per year according to the instrumental observations, that’s why area of dry land increases by 3-4 thousand sq. km annually.
Formation of moving sand dunes with the height of 2-5 meters, which move at the speed 20-30 meters per year in the southern and south-eastern direction, occurs on the area of more over 10 thousand sq. km. Width of dune ridges and ranges achieves 10-15 km and length up to 40-60 km. Ecosystems of brackish waste grounds lacking flora, difficult to traverse and dangerous were formed non the area 20 thousand sq. km of the former sea bottom. They are the source of dust-salt material to the major oasis agriculture in the delta of Syrdaria River.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Cazaquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Kyzylorda
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kazalinsk state
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Was developed by kazakh - investigation institute of forest facility (1996-2001)
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
major cash crop: Wood for fuel and agroforestmeliorative

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Nomadismo
Principais espécies animais e produtos:
half nomadism
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): exudative salinization, forming of the salty ring on the surface, lov percent of natural overgroving.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): rarely distribution of the bush-trees and presence of bared heathlands, which makes territory useful for land-use.
Grazingland comments: private sector of peasanting and farming predominate
Clear felling of (semi-)natural forests: stocking up for fuel, every year
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Degradation of saxaul and tugay forests in result of desertification processes: subsoil waters level reduction, deflation, poverty of population. Constant reorganization of forest facilities.
Forest products and services: fuelwood, grazing / browsing, nature conservation / protection
Type of grazing system comments: private sector of peasanting and farming predominate
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 208; Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Redução de riscos de desastre baseada no ecossitema
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 1-10 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 4 m2.
only 2% from 35000 sq.km of Aral sea's drained bottom
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A4: Tratamento do subsolo

Medidas estruturais
Comentários:
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: cover cropping, breaking compacted topsoil
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -against wind
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - Excessive water-fence on an irrigation from the rivers Syrdarya and Amurdarya.)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (High wind activity in region (prevalence of winds with a speed up to 5 min/sec).)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
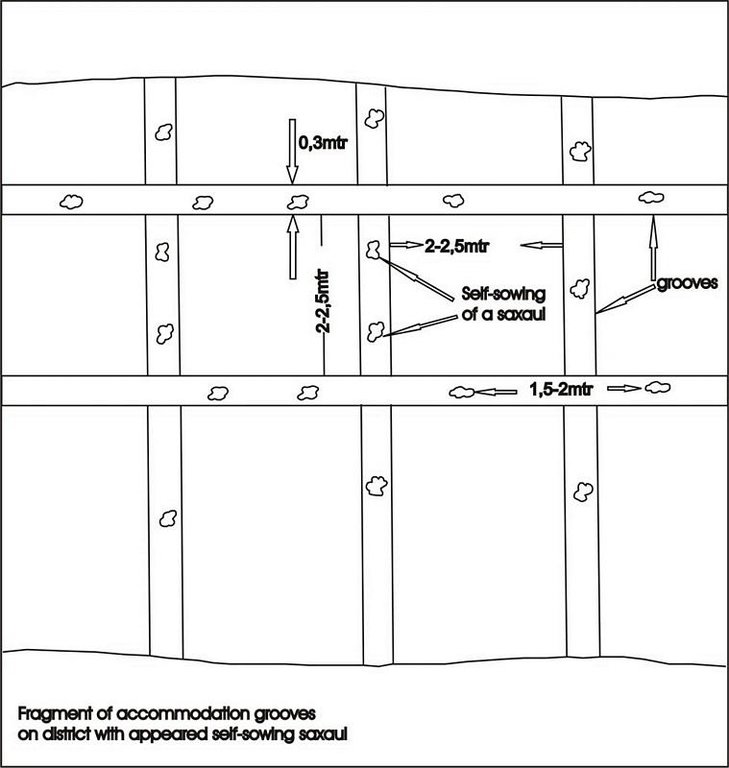
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Fragment of accommodation grooves on district with appeared self-sowing saxaul
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, improvement of soil structure
Cover cropping
Material/ species: saxsaul
Quantity/ density: 150
Remarks: protective planting
Breaking compacted topsoil
Remarks: breaking salturing up before planting by layout
Aligned: -against wind
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 150
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1,5-2,0
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 30-35
Trees/ shrubs species: saxsaul, combseller
Structural measure: sediment sand / trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3
Spacing between structures (m): 2
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,7
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,7
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0,5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0,7
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 100
Construction material (earth): fine-grained sand
Construction material (wood): saxsaul
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
15.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | groove cutting | Vegetativo | summer |
| 2. | slips planting | Vegetativo | spring, autumn |
| 3. | groove cutting | Estrutural | summer |
| 4. | creating traps for sand | Estrutural | after planting |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Traps for sand, cutting and planting | persons/day | 3,0 | 15,0 | 45,0 | 66,0 |
| Equipamento | Others | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 29,0 |
| Material vegetal | Others | ha | 1,0 | 125,0 | 125,0 | 83,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 190,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | groove cutting | Agronômico | spring, autumn / every year |
| 2. | slips planting | Agronômico | spring, autumn / every year |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
saxsaul planting in the 100m * 100m. Sized beared heathlands due to enclosed SWC circuit
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
transportation of technique to the work place and gooves cutting
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Average long-termed rainfall quantity makes 124 mm per year
Zona agroclimática
- Árido
Arid deserted
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Landforms: Weak inclined primary -sea plain
Landforms: It is complicated with accumulative forms of colian relief
Altitudinal zone: 36 - 51 m a.s.l.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Soils were not formed yet, horizons are absent
Topsoil organic matter: 0,19%-0,24%
Soil fertility is low with 0,24% of humus
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor in suclay, medium for clay and good loam-sandy and sandy soils
Soil water storage capacity is low - very low
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
- Pobre
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: catche fish grow vegetable - melon cultures and realizate them
Market orientation of production system: Firewood stocking and raise of forage capasity.
Level of mechanization: Using shovel for manual labour and tractor MTZ-30 for mechanised labour.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
Comentários:
Also 2-5 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
In adverse years
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
In adverse years
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Exspenses for fuel decrease
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
employment at farm
Comentários/especificar:
Production increase
groove cuting tools
Comentários/especificar:
High rent payment for technique
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
Population's employment
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Ecological education
educational and cultural level of former members
Comentários/especificar:
Native population's not understanding benefits of using SWC
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
Humus accumulation
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Salt removal of top horizons
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
30
Quantidade posterior à GST:
10
Comentários/especificar:
Increase of kinds structure
Outros impactos ecológicos
biodiversity
Comentários/especificar:
Activity of wind stream decrease
soil fertility
Comentários/especificar:
Avoidance of blowing
fuel supply
Comentários/especificar:
4-5 hectare per year
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Comentários/especificar:
Soil surface's erosion stop's
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
13 households covering 1 percent of stated area
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 10-50%
Comentários:
10 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
3 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: small farmer's economical vell-being improves
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
forest territory are restoring How can they be sustained / enhanced? during saxaul communities life |
|
soil deflation's speed and temps decrease How can they be sustained / enhanced? during saxaul communities life |
|
microclimate conditions increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? during saxaul communities life |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
forests area and output of fuel increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? during saxauls plantings life (40-50) years |
|
field-dust carrying out is prevented How can they be sustained / enhanced? during communities vitual activity |
|
environmental and sanitary-epidemiological contitions improves How can they be sustained / enhanced? during technology SWC existence |
|
Additional work places are created How can they be sustained / enhanced? in period technology SWC application |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| absence of enough qvantity of enough quantity of technique | by means of cooperative association of facilities |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| high rent payment for technique | additional purchase of the mechanised means |
| Low interest of local social institutions | to pay big attention for ecological education |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
"to study process of overgroving and to develop offers on assistance to natural reneval of saxaul black on the grounds of Aral Sea's naked bottom"
Disponível de onde? Custos?
RGP,SPC of forest facility. Kirov str.,58 city Schuchinsk, Akmola region
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos