Calliandra contour hedges [Uganda]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Wilson Bamwerinde
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Alexandra Gavilano
Orugo rwa Calliandra (Rukiga)
technologies_1178 - Uganda
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ItáliaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Kabale District Local Government (Kabale District Local Government) - Uganda1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
20/01/2014
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
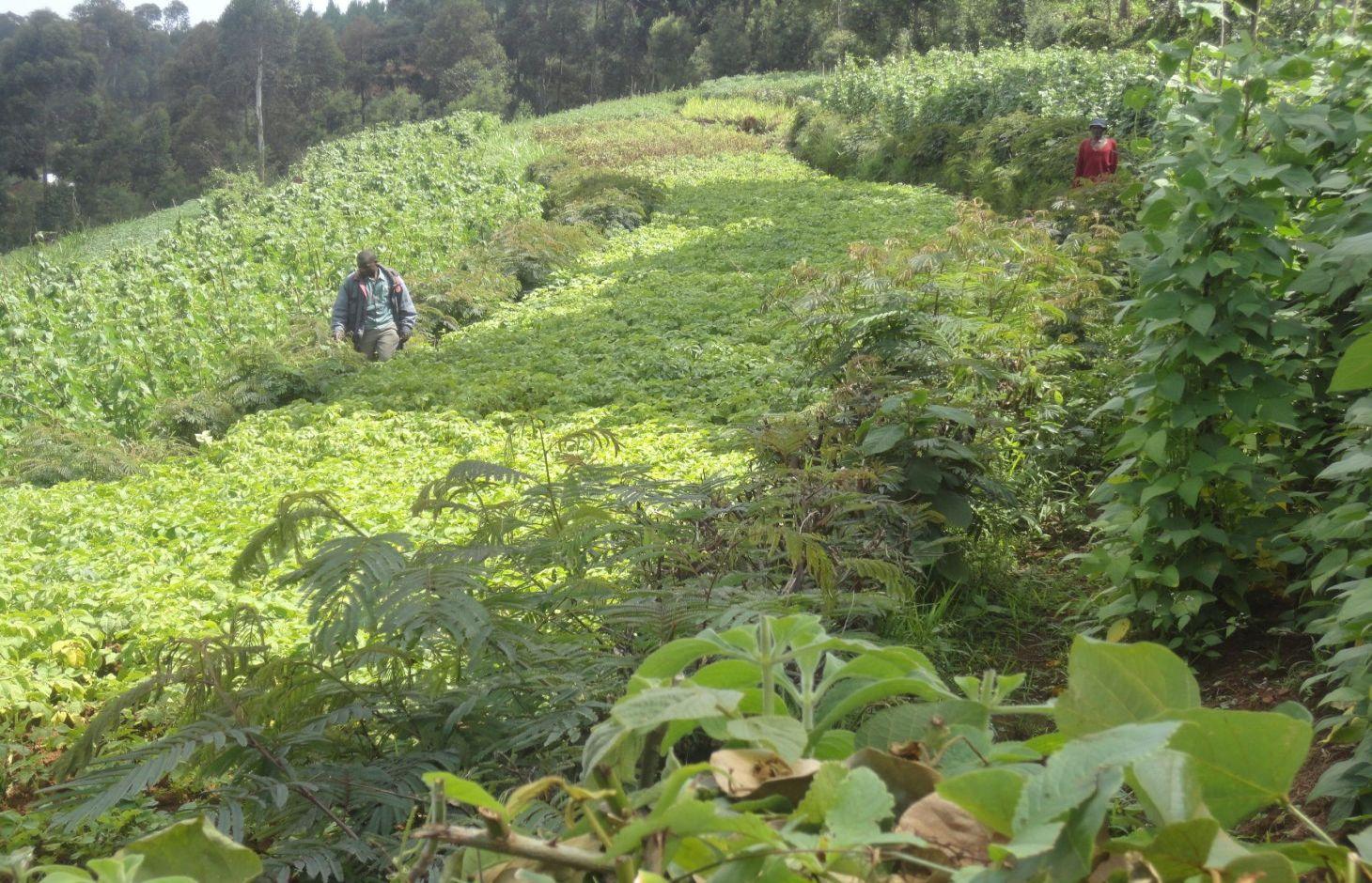
Contour hedges of Calliandra planted on very steep slopes to combat soil erosion by decreasing surface runoff and increasing infiltration.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Calliandra Calothyrsus trees are closely planted along the contours on hilly and steep slopes to create natural and effective barriers for reduction of the surface runoff and retention of eroded sediment. Calliandra hedge barriers are a fairly cheap, effective, and sustainable way of controlling soil erosion and landslides on vulnerable steep slopes, especially where trash lines and Napier grass strips were inadequate to mitigate dispersed and concentrated soil and water runoff. Once established, the living barrier is durable with minimal additional maintenance cost to the farmer apart from pruning. The average length of a hedgerow is 50 to 70 m, corresponding to the width of a single terrace. The height varies according to intended use of the mature shoots. To use the stems as stakes, the hedgerow is allowed to reach a height of 4 to 6 m at maturity while a height of 1 to 2 m is sufficient for harvesting foliage as livestock fodder. The hedge barrier reaches its mature, maintenance level after 12 to 18 months.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of the Calliandra hedge barrier is to reduce soil and water runoff.Calliandra is a leguminous shrub with deep roots that provids additional benefits such as soil stabilization and soil fertility improvement through nitrogen fixing. Calliandra is a source of fodder and its flowers attract bees.
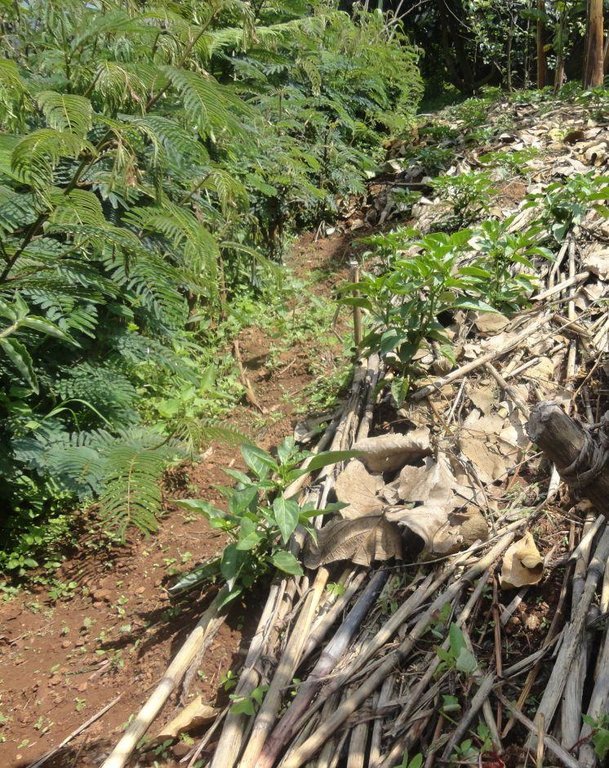
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: At the beginning of the rainy season, calliandra seedlings are transplanted from the nursery (0.2m to 0.3m height) and planted in a row (0.3m spacing). In the early stages, gap-filling with more seedlings may be necessary as some fail to get established. A mixture of top soil and manure is applied in the spaces between the seedlings and watering is done to improve the seedling survival rate. The distance between rows is 10 to 15 m and depends on the gradient of the slope. Establishment of hedges starts with construction of an earth banked terrace, creating a trench at the lower end of the terrace. Calliandra seedlings are planted on the higher side of the trench. Measuring off 10 m lengths upwards into the terrace, other rows of Calliandra seedlings are planted along the contour in order to achieve the inter-row spacing. Establishment is manual labor intensive and therefore the community, organized as Farmer Field Schools, participates in the planting, one field at a time. Simple tools such as hand hoes, sokajembe (pick-axe) and shovels are used. Maintenance is achieved by weeding, mulching and cutting back. For it to establish well, Calliandra needs to be weeded to minimize competition with weeds for water and nutrients . The weeds also harbour pests. It may also be necessary to mulch the area around each seedling during the dry season. Where mulching is done, the mulch is placed at least 0.05m away from the plant to reduce pest attacks. Calliandra calothyrsus trees are cut back at a height of 2m to between 0.15m and 1m to improve foliage which is used as fodder for livestock. The hedge is then maintained at a height of 1 to 6 m depending on the intended additional uses. The branches removed can be used as fuel wood or stakes, while leaves can be used as fodder.
Natural / human environment: The hedge barrier may be attacked by pests. Scales are white, powdery insects that attack Calliandra stems. Scales can be controlled using washing detergents such as ‘Omo’ dissolved in water and sprinkled on affected plants using leafy branches or a knapsack sprayer. Black ants can seriously damage trees. They can be controlled by spraying. Other likely pests are crickets and grass hoppers which affect seedlings in nurseries, and Armillaria mellea, a fungus that attacks roots of Calliandra plant causing root rot and eventual death. Affected plants are uprooted and burnt. In addition, calliandra is affected by hot, dry weather. During the hot, dry weather, the hedge barrier becomes weak. However during the wet season it sprouts again, and, if well managed, becomes healthy again. A well-maintained hedge barriers can last well over 20 years.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Uganda
Região/Estado/Província:
Uganda
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kabale District
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -1.29294, 29.96006
-1.29336, 29.96027
-1.29327, 29.96084
-1.29371, 29.96095
-1.29345, 29.96091
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology was introduced by ICRAF in 2006 and scaled-up Kagera TAMP project 2 years ago.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
The landuser majorly grows beans (climbing ) as food and cash crop.

Pastagem
Principais espécies animais e produtos:
The animals reared depend on improved pasture such as calliandra
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The slopes are steep >30% to very steep >60%), with very high precipitation (>1440 mm). Severe surface erosion and landslides may occur at the beginning of the rains, before sufficient vegetation covers the soil. Continuous cultivation with little external inputs and nutrient transfer affects negatively soil fertility and in results reduces crops growth/vegetation cover, leading to erosion on steep slopes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Floods are common in the valleys over the past ten years.
Improved pasture: Diary hiefers,pigs(largewhite and layers)pasture include calliandra,stellia and elephant grass.
Constraints of settlement / urban: floods invade houses
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): transport problem
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: February to MaySecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: September to November
Densidade animal (se relevante):
1-10 LU /km2
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.03 m2.
The documented case study area is around 3ha
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
Comentários:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Poor vegetative cover/no trees to bind soil particles.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Rainfall intensifying in september and April.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (steep slopes (extreme topography)), population pressure (Population increase/no of people increased per sq km), poverty / wealth (lack of resources to implement known natural resources degradation mitigation measures)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
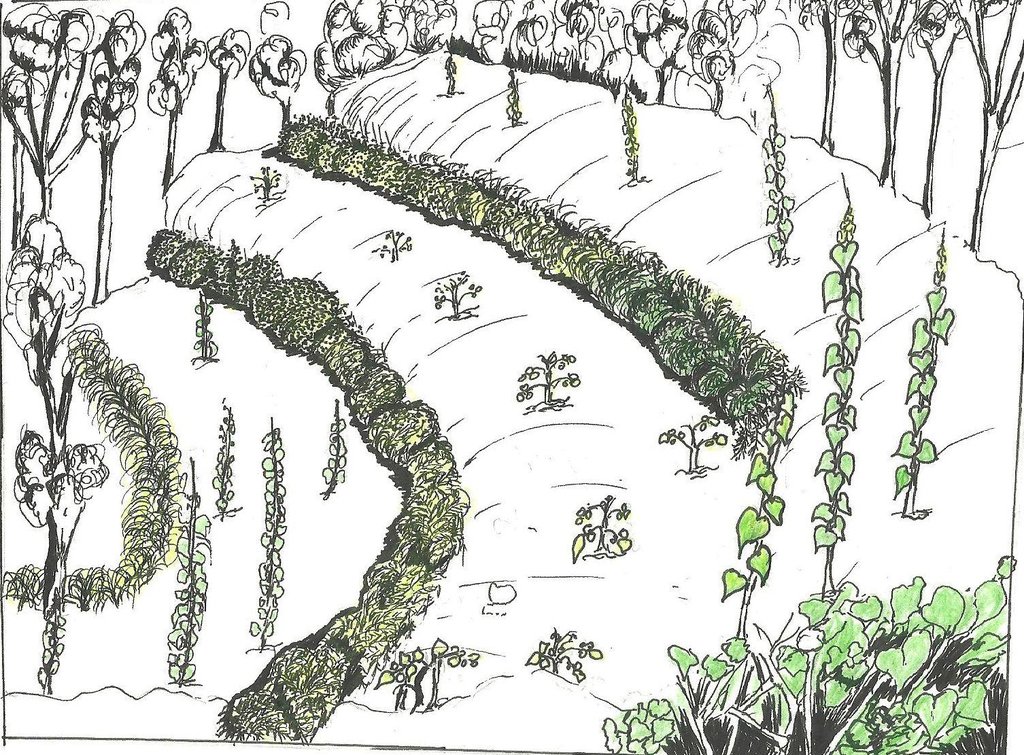
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Calliandra trees are planted in rows along the contour. Cutting back is done between 12 and 18 months to a height of 0.5 m. The trees are allowed to grow to between 1 and 6 m and the hedge is maintained at that height. Gap-filling, weeding and trimming are critical for a productive hedge.
Location: Bukoora, Kabale. Kabale/Uganda
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Such knowledge as is required to manage the Calliandra nursery, transplant and maintain the plants especially until the first coppice.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (The land user is responsible for maintaining the technology on his or her land and a good hedge requires diligence)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, increase of infiltration, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 670 to 720
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.4
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.7
Trees/ shrubs species: Calliandra was planted
Fruit trees / shrubs species: n/a
Perennial crops species: n/a
Grass species: n/a
Other species: n/a
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 40%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): n/a%
Gradient along the rows / strips: <3%
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
UGX
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
2602,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
3.80
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Establishment of Calliandra nursery | Vegetativo | Dry season |
| 2. | Plantation of Calliandra seedling on the higher side of the trench | Vegetativo | Wet season |
| 3. | Weeding | Vegetativo |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | 1,0 | 44,6 | 44,6 | 100,0 | |
| Equipamento | tools | 1,0 | 16,2 | 16,2 | 100,0 | |
| Material vegetal | seedlings | 1,0 | 30,4 | 30,4 | 100,0 | |
| Material vegetal | seeds | 1,0 | 9,6 | 9,6 | 100,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 100,8 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 18 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prunning and triming the hedge barriers | Vegetativo | wet/dry season |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | labour | 1,0 | 20,8 | 20,8 | 100,0 | |
| Equipamento | tools | 1,0 | 16,2 | 16,2 | 100,0 | |
| Material vegetal | seedlings | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 | |
| Outros | 100,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 38,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: I panga,1 watering can, 1hoe.
The cost assesment above refers to steep slopes.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The cost of seedlings (0.20 US$ each) and their transport up along steep slopes are the key factors affecting costs and hindering spontaneous adoption of the technology. Otherwise, the technology is acceptable to farmers as benefits are easily visible in the short run.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: tropics. at the Equator
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Maintenance such as pruning trimming is mostly done by the men, but the other activities are done by both men and women.
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%; 3%
5% of the land users are rich and own 40% of the land.
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (meets basic needs/necesities).
45% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Crop and animal production greatly increased for land users implementing conservation measures , compared to those who do not implement.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
The land belongs to an individual with no title but has all the rights over it.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
n/an/an/an/a:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
150
Quantidade posterior à GST:
700
Qualidade da forragem
Quantidade anterior à GST:
-
Quantidade posterior à GST:
-
Produção animal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
-
Quantidade posterior à GST:
25
Área de produção
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
1.5 million
Quantidade posterior à GST:
3.5million
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Quantidade anterior à GST:
-
Quantidade posterior à GST:
-
Atenuação de conflitos
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Outros impactos ecológicos
increased pests
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
-
Quantidade posterior à GST:
-
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Quantidade anterior à GST:
-
Quantidade posterior à GST:
-
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
| n/a |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
Benefits are high compared to establishment and maintenance cost
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
88% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
45 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
12% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The technology is appreciated by most farmers but adoption is limited by cost of seedlings and transportation up steep slopes
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Calliandra binds the soil, thus reduces landslides. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It should be maintained through proper management |
|
Adds scenic beauty on a plot How can they be sustained / enhanced? By regular trimming |
|
Calliandra is good and attractive to bees How can they be sustained / enhanced? Leave every second or third row to flower |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
It is easy to establish and maintain How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote education campaign and spread information |
|
It has helped to increase crop and animal production How can they be sustained / enhanced? By proper management and not overgrazing animals |
|
Stabilize the soil and strenghtening resistance to intensive rainfall and fast runoff How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote technology through increased community mobilization |
|
Very effective to reduce soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine with other practicies e.g. mulching |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The hedge barrier is ineffective before 12 months | Combine with trash lines before establishment |
| Technology harbors nesting birds | Ensure regular trimming of Calliandra to reasonable height and use scarecrows |
| Needs at least 2 seasons to establish | Apply manure and water to the seedlings to ensure accelerated growth |
| May reduce the amount of sunlight available to young crops if left untrimmed | Trim regularly |
| Extra cost in protecting from damage by livestock | Inter-crop with other fodder species to act as alternative fodder for livestock |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Kagera TAMP Project website
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos