Minimum Tillage [Federação Russa]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Peter Liebelt
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Deborah Niggli
Минимальная обработка
technologies_1315 - Federação Russa
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Global Assessment of Land Use Dynamics, Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Ecosystem Services (GLUES)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
23/06/2016
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
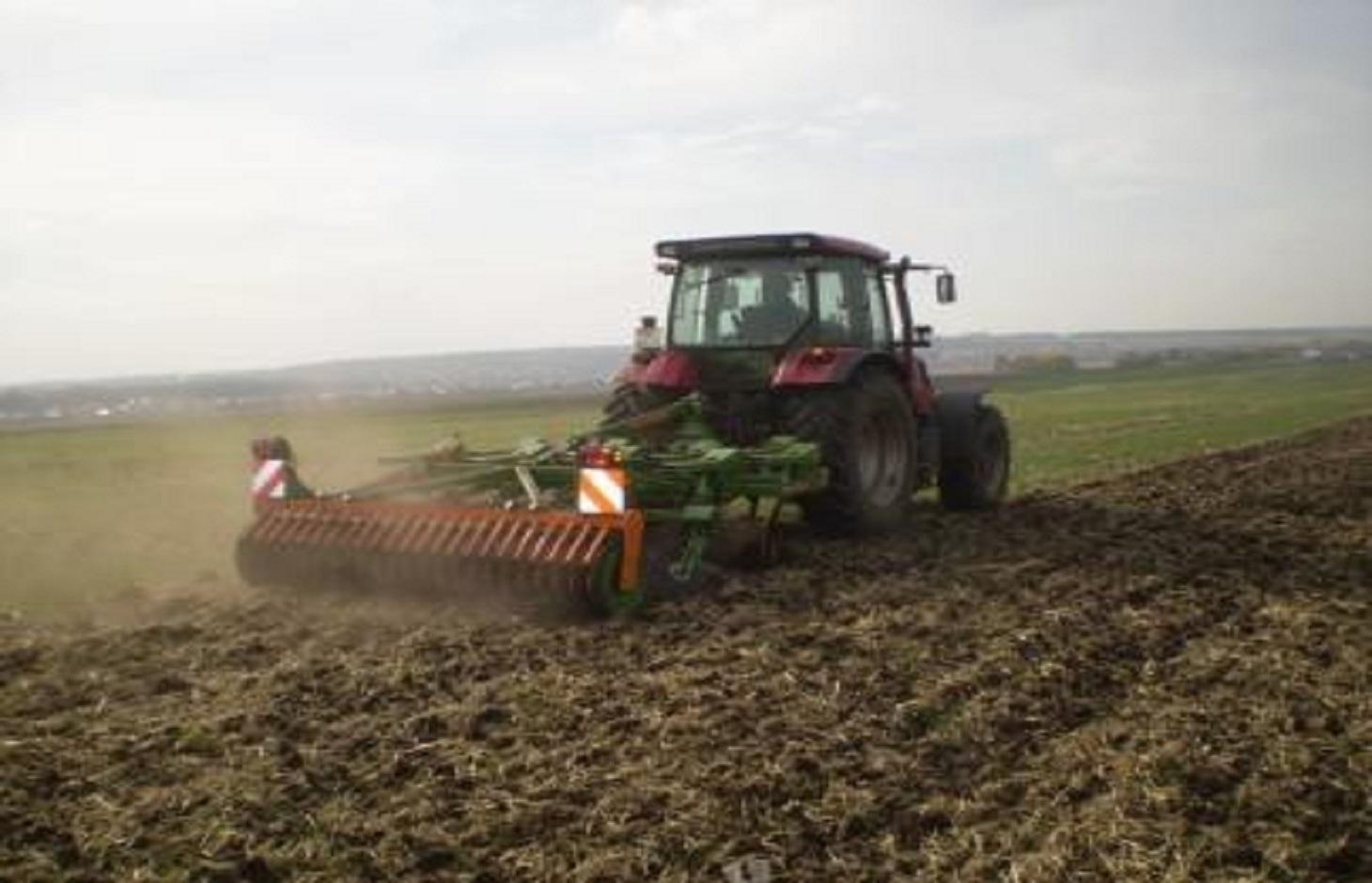
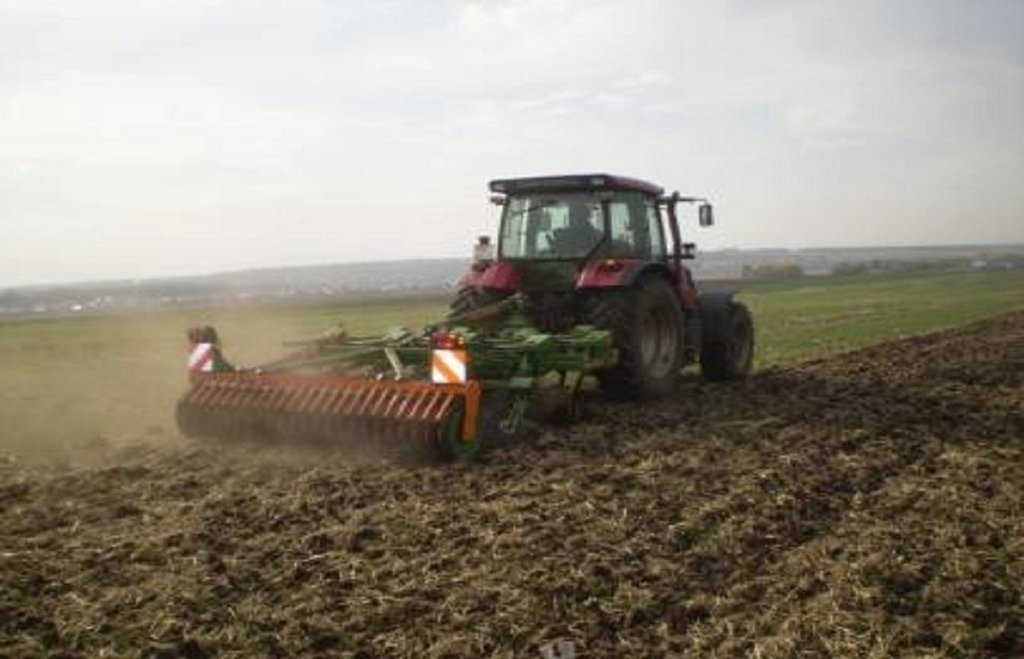
Minimum tillage is a one-pass operation combined with sowing, using a classic Russian seeder modified for seedbed preparation and soil mixing. It can include shallow stubble cultivation after harvesting.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Minimum tillage is a key element of the "adapted Soviet cropping system", which aims at more sustainable land use but based on predominantly local technologies. For successful implementation of minimum tillage, adaption of the whole cropping system is required, including crop rotation. Rotation includes a succession of cereal crops (e.g. spring wheat), legumes (peas), and oil seed crops. Stubble cultivation in autumn is best performed with the "Catros" compact disc harrow for a quick, shallow operation. Seedbed preparation is carried out using a classic Russian seeder modified with wing shares for shallow seedbed preparation including soil mixing. In general, the performance of this drill is very close to that of a cultivator.
Minimizing tillage, saves time and fuel, and also helps to reduce evaporation, as well as protecting the soil against erosion. Shallow tillage with disc harrows after harvest ensures better stubble mixing and stimulates the germination of weed seeds. The adapted seeder, SZS 2.1, works with wing shares that open the soil and place the seed. Thus traditional deep tillage operations for the preparation of the seedbed can are omitted: that helps to reduce costs. With respect to crop protection, the first and most important element is to implement a full crop rotation. To control late germinating weeds and seeds of the previous crop, a disc harrow is used for shallow cultivation – this can be supplemented by the application of a non-selective herbicide if there is germination - to avoid the risk of flowering before the hard frost sets in. Fertilization becomes more important, because of the decreased mineralization rate under minimized soil tillage, especially at the beginning of the conversion of the cropping system.
The Technology including crop rotation was tested in the field in 4 test plots with 4 repetitions at the test site in Poluyamki. Results showed that the intensity of soil tillage and seeding methods used had a great influence on crop establishment and expected yields. It was demonstrated that minimizing tillage leads to higher water use efficiency and highest yields. Positive effects were also observed regarding soil structure and soil fertility already after 3 years. Minimized soil disturbance led to higher aggregate stability, which leads to a lower risk of wind erosion, increased soil organic carbon storage and soil fertility as well as available soil water content. The adapted Soviet system is more profitable, due to higher gross margins.
The test site in Poluyamki is located in the dry steppe of the border region next to Kazakhstan, where, due to the climatic conditions, no natural afforestation occurs, and the planted windbreaks don’t grow vigorously due to the prevailing aridity. The annual precipitation is under 300 mm a year. Probably the greatest climatic influence factor is the precipitation - in terms of quantity and space/ time distribution and, due to high summer temperatures, the high rates of evapotranspiration. The total yearly precipitation rate is the primary yield-limiting factor in all steppe regions. The ratio between precipitation and evaporation is negative. In the late weeks of spring, prolonged droughts must be expected in 5-year cycles, limiting germination and crop establishment. The soils are classed among those of cool-tempered grasslands. Due to their physical and chemical characteristics, these soils (Chernozems and Kastanozems) have high agronomic potential.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Federação Russa
Região/Estado/Província:
Russian Federation/Altai Krai
Especificação adicional de localização:
Mikhaylovski district (Pavlovski district, Mamontovski district)
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: Centre latitude: _52° 4'3.00"N Centre longitude: 79°54'26.16"E Test site Poluyamki
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Already during the Soviet land use periode temporal,especially after the Virgin land campagne (1954-'63)efforts were made to minimize soil tillage intensity to obtain from conventional ploughing system. An important scientific thinker for this innovative farming systems was T. C. Malcev. But at this time the new approaches for minimized tillage systems were not seriously implemented in Russia. Only in the last decade a significant trend towards minimum soil tillage can be recodnized in the Russian agriculture
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The decrease of soil organic carbon content in the soils and loss of topsoil depth has led to a decrease in soil fertility. Additionally, the negative soil water balance due to the high summer temperatures and evaporation, and the high spatial and temporal variability of precipitation, is a serious problem relating to the lack of soil water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The land users who were involved in the studies and implemented the new farming practices have a similar opinion. But there are still a lot of farmers that underestimate the ecological risks of soil degradation resulting from conventional/ traditional soil management.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 110, Longest growing period from month to month: May-October
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Perturbação mínima ao solo
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 0,1-1 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.13 m2.
The total investigation area of the SLM Technology “Minimum Tillage” refers to the test site areas: 1. Poluyamki, Mikhaylovskiy Rayon: 13ha ; 2. Pervomayskiy, Mamontovskiy Rayon: 10ha and 3. Komsomolskiy, Pavlovskiy Rayon: 3ha all managed by Minimum Tillage. This questionnaire is related to the test site in Poluyamki, Mikhaylovskiy Rayon
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
Comentários:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mulching, green manure, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, rotations / fallows, minimum tillage, non-inversion tillage
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial
- Ed: deflação e deposição
- Eo: efeitos de degradação externa

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Conventional (intensive) soil tillage by phloughing), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Bare fallow (without any vegetation cover)), wind storms / dust storms (Strong wind and storm (local name: Sukhovey) from the south-western central-Asiatic semi-desert regions cause a higher risk of wind erosion especially on traditional cropland without plant cover), droughts (The frequently occurring early-summer drought periods are particularly problematic for agricultural production)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (The linkages between research, education, extension services and end users need to strengthened, for better knowledge creation and transfer. Need for more efficient and qualified advisory service), Capital for investments (Lack of capital for investment in modern adapted agricultural technologies)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
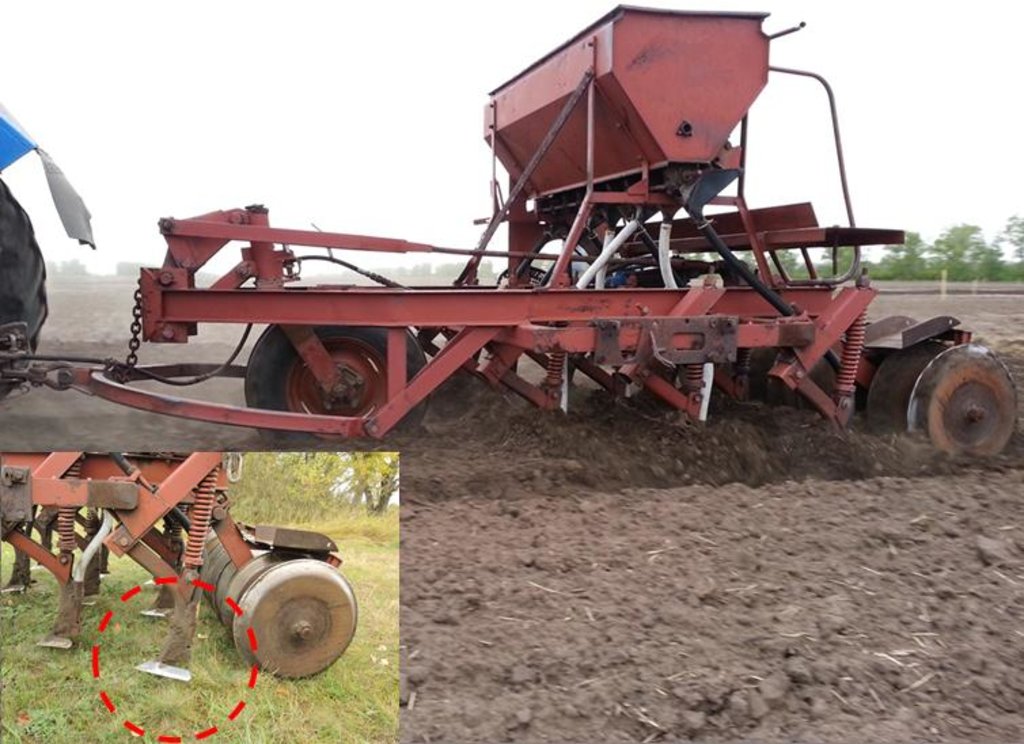
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Soviet Seeder SZS 2.1 with wing shares for shallow soil mixing and seed bed preparation.
Location: Poluyamki. Altai Krai
Date: 20.05.2015
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Crop rotation without bare fallow
Mulching
Material/ species: stubble cultivation with disc harrow or harrow weeder
Quantity/ density: 1/year
Green manure
Material/ species: pea
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: fertilization with calcium ammonium nitrate
Quantity/ density: yearly
Remarks: (100kg/ha (spring wheat and rape), 50kg (pea)
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: wheat-pea-wheat-raps
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Catros (disc harrow) and Seeder СЗС2.1 (wing shares)
Remarks: Catros (depth: 10 cm) after harvest (autumn) and Seeder in May)
Non-inversion tillage
Material/ species: Catros (disc harrow) and Seeder СЗС2.1 (wing shares)
Remarks: Catros (depth: 10 cm) after harvest (autumn) and Seeder in May)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Stubble cultivation | Agronômico | september |
| 2. | Seeding | Agronômico | late april/early may |
| 3. | Seeding (extension) | Agronômico | |
| 4. | Pest management | Agronômico | period of vegetation |
| 5. | Pest management (extension) | Agronômico | |
| 6. | Harvest | Agronômico | september |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | labour | ha | 1,0 | 4,34 | 4,34 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | machine use | ha | 1,0 | 37,4 | 37,4 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | fuel | ha | 1,0 | 47,34 | 47,34 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 25,3 | 25,3 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 30,83 | 30,83 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | pesticides | ha | 1,0 | 9,42 | 9,42 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 154,63 | |||||
Comentários:
The costs refers to 1ha land of the test field in Poluyamki.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The highest cost factors of minimum tillage are equipment, fuel, fertilizer and seeds. Compared to the conventional deep ploughing often without fertilizer application, fertilizer and pesticides are the main additional cost factors.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Muito rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Empregado (empresa, governo)
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
There are generally less woman than men in rural regions caused by rural-urban migration. Furthermore, jobs in the agricultural sector are not so attractive for woman.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Grande escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Arrendado
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Comentários:
state: 45%, the data refer to the Altai Krai
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
In the first years after the change of the cropping system, there is an increased risk of crop losses due not correct/suitable management of the new cropping system
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
mainly for initial investments and herbicides in the first years
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
but increase of costs for herbicides and fertilizer; decrease for fuel and labor
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Increase use of herbicide applications
Comentários/especificar:
particular necessary in the first years after the imlementation of the minimum tillage system
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
In general yes, but food security is not a problem in this region.
Atenuação de conflitos
contribution to human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Technology makes a contribution to the long-term productivity of the soil – the most important factors in the rural areas of the Kulunda region. Furthermore, it leads to an increase in efficiency and to an improvement of the economic situation of farms, which might lead to a decrease in out-migration of the youth.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Espécies benéficas
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Velocidade do vento
Outros impactos ecológicos
Increased use of herbicide application
Comentários/especificar:
Especially in the first years after the implementation of the minimum tillage system.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
there is a higher content of soil moisture under minimum tillage than under traditional ploughing especially in dry weather periods / drought periods.
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Danos em áreas vizinhas
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não bem |
Comentários:
The increase of air temperature and wind lead to an increase of the evapotransporation rate and consequently, as well as rainfall decrease and droughts, to a decrease of soil water content that is one of the most important limiting factor in crop production. The minimization of soil tillage intensity helps to reduce the evapotranspiration rate and thus leads to a higher soil water content. The stubble slow down the wind, that protect the soil against erosion and reduce the evapotranspiration rate.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
The 3 farms/ sites where minimum tillage was tested were already interested in conservation technologies and were able to invest in new machinery, which is not representative of the whole Kulunda region. There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors, like precipitation or the economic situation and financial power of the farmers.
There is a trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology, but this trend depends on different natural and socioeconomic factors like the precipitation or conditions an economic situation of the financial power of the farms. For example the drier the conditions, the more sense is to minimize the tillage. But there is a need to invest in new machinery. An advantage of the tested Adapted Soviet System in contrast to the Modern Soviet System is the less need for new machinery through the use of old Soviet machinery.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Increase of soil aggregate stability and improved soil structure thus better erosion control and protection of soil organic matter will improve soil fertility and water holding capacity |
| Minimization of evaporation losses through the mulch layer |
| Protection of soil organisms thus ensuring natural soil forming processes |
| Lower input costs (materials, fuel, labour, time) and quicker field operations. |
| A great advantage of the tested ‘minimum tillage’ in contrast to ‘no till‘ is that the former needs no new machinery because of the use and adaptation of old Soviet machinery. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Need for comprehensive system knowledge and risk of significant crop losses in case of incorrect implementation | Knowledge transfer, Capacity building and extension services, State support (subsidies for new technologies) |
| Application of chemical herbicides leads to higher costs and possible ecological risks | Selective spraying using the “Amaspot” system that is based on infrared detection of weeds. |
| Higher requirements for fertilizers, especially at the beginning, due to lower mineralization rates and less nutrient availability compared to conventional cultivation | Higher fertilizer application in the first years after conversion. |
| Challenging straw management that leads to higher risk of fungal infestation and poorer field crop emergence | Good straw management: effective straw chopping and spreading as well as stubble cultivation for an optimal straw/ soil ratio. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos