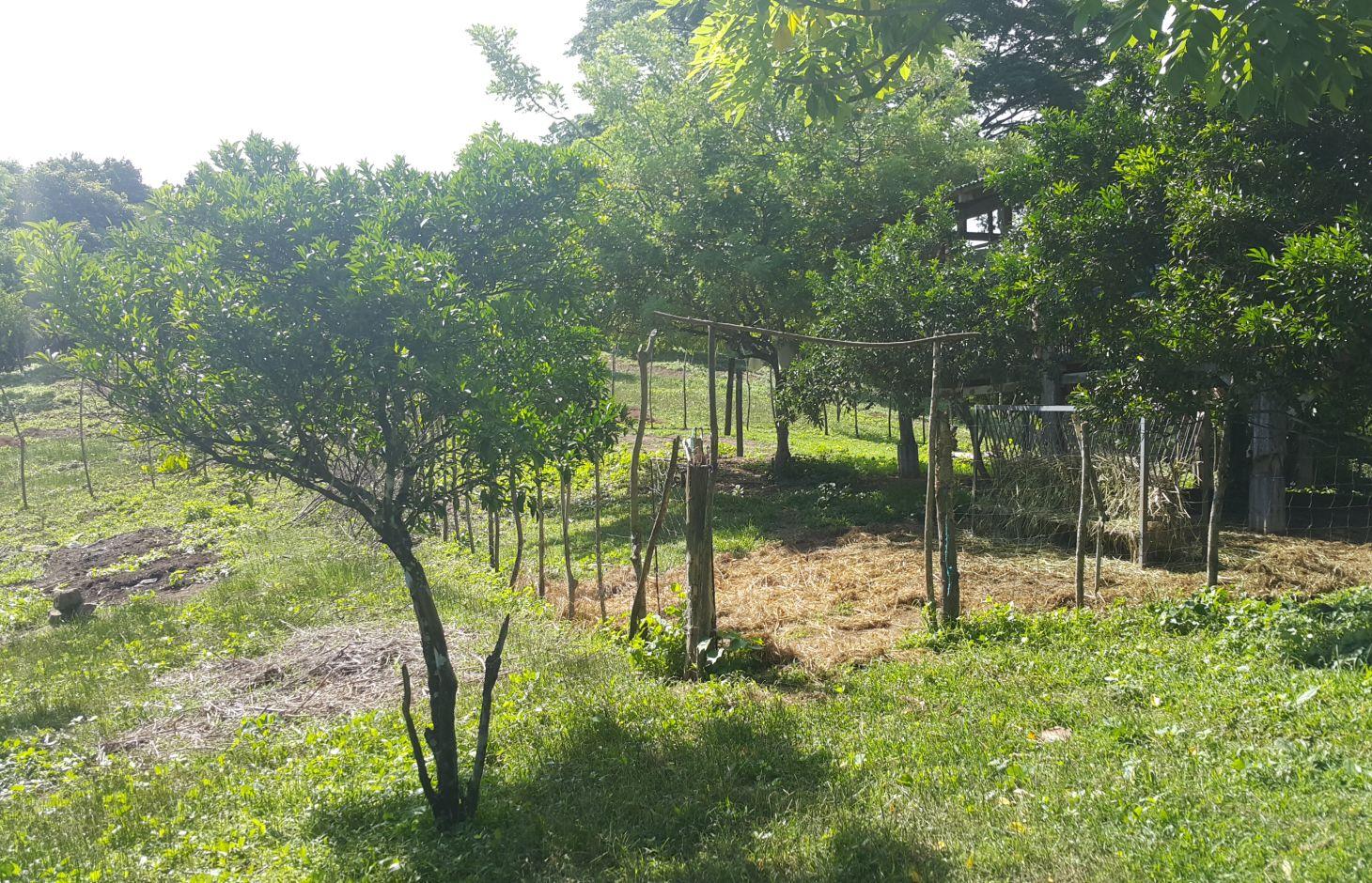
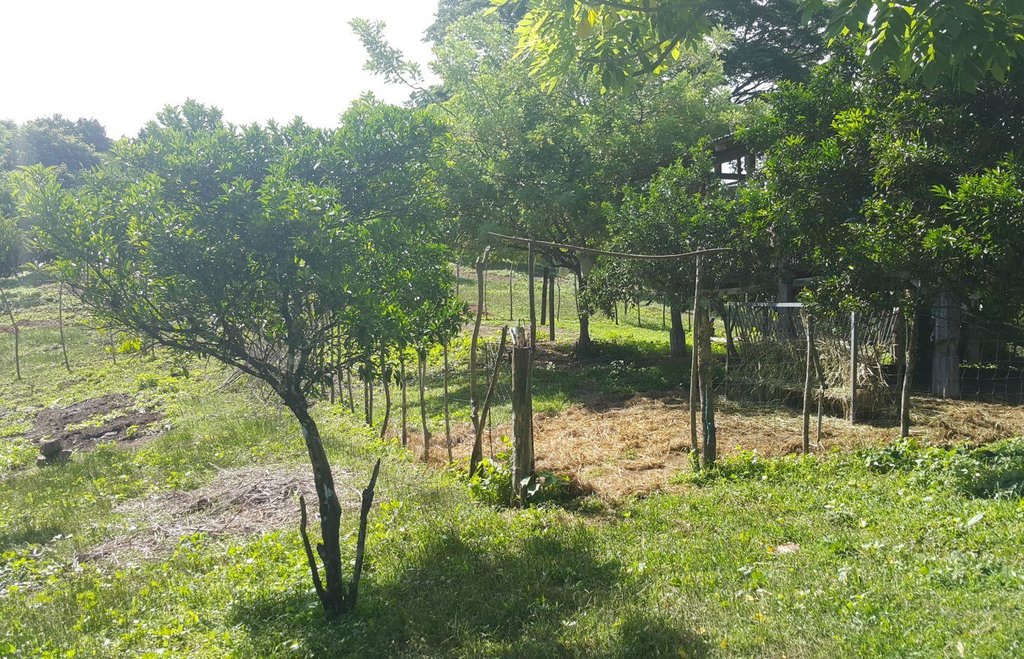
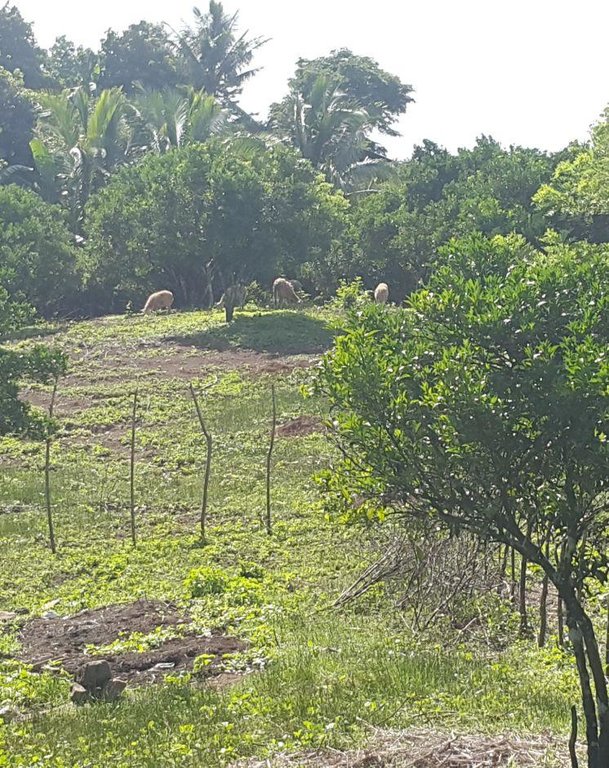
Improved pasture under citrus [Filipinas]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Pastulan sa ilalim ng dalanghitaan (Filipino)
technologies_1321 - Filipinas
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Rojales Jose
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Calonge Arsenio
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Millare Kirby
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Quinto Jasmin
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Gultiano Wilfredo
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Cornes Jennelyn Mae
(632)9230459
Departement of Agriculture - Bureau of Soils and Water Management
Quezon City Elliptical Road corner Visayas Avenue, Diliman, Quezon City
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - Filipinas1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
29/06/2016
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST

Soil Conservation Guided Farm System [Filipinas]
Soil Conservation Guided Farming System (SCGFS) is a land use management approach that integrates technologies: terracing, agro-pastoral technology, multi-storey cropping, and contouring within the socio-economic and bio-physical limitations of upland areas for optimum development of soil and water resource in a sustainable manner.
- Compilador/a: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
It is a farming system that integrates the growing of fodder crops under plantation crops.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
It is an integration of livestock and agronomic crop production of incorporating small ruminants in an existing citrus plantation. This technology was based on the private initiative of the farmer where he adapted it from other land users. He further improved it through study of reading materials and ad hoc monitoring of his environment.
Purpose of the Technology: After the adaption of the technology, the land user observed a decrease in the infestation of aphids. The land user observed and concluded that the decline in the aphids infestation was due to the presence of the small ruminants in the area. The small ruminants forage on grasses that were continuously growing, year-round, in the plantation area. The foraging of grasses improved the micro-environment of the plantation crop, which contributed to the decline and almost total eradication of aphids in the area, as observed by the land user. This promoted natural farming and improved the biodiversity.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The area was first established as a citrus plantation inter-cropped with Vigna unguiculata, Cucurbita maxima, and Ipomoea batatas, as cash crop during the vegetative stage of the citrus crop. As the small ruminants increased in number, the land user decided to do “controlled grazing” by dividing the area into 3 paddocks. During lean days of forage grasses, the land user practices “cut-and-carry” system of feeding. In addition, the manure of the small ruminants serves as a source of organic fertilizer for the citrus and other crops grown by the land user.
Natural / human environment: Aside from the eradication of the aphids on the citrus crop, the technology aided in the financial needs of the land user. It increased the land user’s income by an increase in the fruits bore by the crop and the increase in the number of the small ruminants. The land user sells or sometimes suppliers of citrus fruit and goat meat would go to the area to do wholesale buying. As for the community near the area, they to benefit from the area, by wholesale buying the citrus fruit and be the one selling it to the market. The technology does not only contribute to the livelihood improvement of the land user but also to the community.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Filipinas
Região/Estado/Província:
Bulacan
Especificação adicional de localização:
City of San Jose Del Monte
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- experience from other farm land user
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
8 years
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Major cash crop:
Citrus

Pastagem
- Silvo-pastoralism
Principais espécies animais e produtos:
Goat and sheep grazing in combination
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Possibility of pollution in the area. The land user might have applied pesticide to the citrus crops to control the pest, but the land user did not mention of it. Application of herbicide to control the growth of grasses within and outside the area.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Without land conservation, there was an occurrence of pest in the citrus plants.
Mixed: (eg agro-pastoralism, silvo-pastoralism): silvo-pastoralism, goat and sheep grazing in combination
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Ms: Silvo-pastoralism
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Water supply: rainfed, rainfed
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: July to November
Densidade animal (se relevante):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão integrada plantação-criação de animais
- Gestão integrada de pragas e doenças (inclusive agricultura orgânica)
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.08 m2.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes
Comentários:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bp: aumento de pragas/doenças, perda de predadores
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (intercropping planting), droughts (time frame of drought)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (grazing of small ruminants), overgrazing (no. of small ruminants), change in temperature (dry season time frame)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Third goal: prevention of land degradation, rehabilitation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
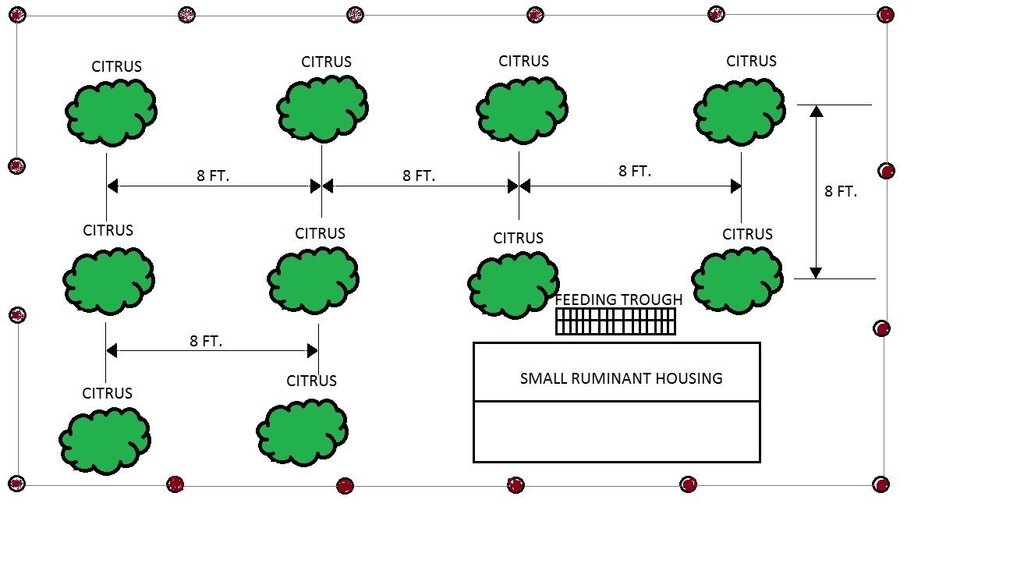
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Citrus plants are evenly distributed in the area, with a planting distance of 8 feet by 8 feet. The ground cover are forage grasses for the small ruminants.
Location: Barangay San Roque. San Jose Del Monte, Bulacan
Date: 06/29/2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (technical assistance from agricultural advisory from other aspect in land degradation)
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (land user is open minded with the technology introduced)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, increase of surface roughness, increase of infiltration, reduction in wind speed, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: pole sitao-squash-sweet potato/citrus
Agronomic measure: intercropping (1st Year)
Material/ species: pole sitao/citrus
Quantity/ density: 2,000/188
Agronomic measure: intercropping (2nd year)
Material/ species: squash/ citrus
Quantity/ density: 2,000/188
Agronomic measure: intercropping (3rd year)
Material/ species: sweet potato/ citrus
Quantity/ density: 8,800/188
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: goat manure
Quantity/ density: 5,000 kg
Remarks: .5 per square meter
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Philippine Peso
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
47,5
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5.26
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | rotational grazing | Vegetativo | rainy season |
| 2. | cut-and-carry feeding system | Vegetativo | dry season |
| 3. | Buying pole sitao | Agronômico | |
| 4. | Buying sqaush | Agronômico | |
| 5. | Buying citrus | Agronômico |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,52 | 10,52 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 3160,0 | 3160,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 48,0 | 48,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Hog wire | ha | 1,0 | 397,89 | 397,89 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 3616,41 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
Life span of products:
Pole Sitao - 1 year
Squash - 1 year
Citrus - 50 years
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 10,52 | 10,52 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 10,52 | |||||
Comentários:
The above costs usually occurs during the dry season when forage grasses are scarce. Lean months of availability of forages grasses are from the months April to June. This is the time the cut-and-carry method is applied and the start of the maintenance/recurrent cost.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Cut-and-carry method of feeding the small ruminants during lean months of forage grasses.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
2382,00
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Landforms: Ridges (concave)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is: Good
Soil water storage is: High
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: It is the countries socio-cultural model, where men is the one working and the women stay at home. According to the land user it is the women who is record keeper.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: off-farm income provides additional income to the land user during the dry season.
Market orientation: Subsistence (small ruminants are bought by the land user)
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
3,000 kilograms
Quantidade posterior à GST:
8,000 kilograms
Produção animal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
5
Quantidade posterior à GST:
5
Diversidade de produtos
Gestão de terra
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
30,000
Quantidade posterior à GST:
80,000
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
It gave an opportunity to the neighbors of the land user to work at the field, with pay. Thus, an added income to the neighbor of the land user. According to the land user, he was able to send his children to a decent school for a quality education. It also gave the land user another source of income by purchasing a jeepney used as a public transportation through the increased income from the SLM technogy he adapted.
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
The increased in the income of the land user contributes to the food security of the family
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Daily chores of herding the small ruminants contributes to the good over health of the land user
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Rotational grazing and "cut-and-carry" style of feeding contributed to the possible overgrazing which is contributor to erosion
Atenuação de conflitos
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Comentários/especificar:
The land user allows the member of his community to harvest some fruits and sell them to the market without the land user asking for something in return.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Rotational grazing and "cut-and carry" style of feeding contributes to the reduction in surface runoff, grasses are maintained on the soil surface
Drenagem de excesso de água
Lençol freático/aquífero
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface reduced soil in any form
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Manure of the small ruminants contributes to nutrient recycling
Salinidade
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Manure of the small ruminants contributes to the increased in soil organic matter content
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Espécies exóticas invasoras
Comentários/especificar:
Incorporation of small ruminants in the farming system which aid in the maintenance of grasses within the plantation area, helps improve the microclimatic condition inside the plantation area that further reduced alien species invasion
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
Incorporation of small ruminants in the farming system which aid in the maintenance of grasses within the plantation area, helps improve the microclimatic condition inside the plantation area that further increased biological pest/disease control
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Risco de incêndio
Velocidade do vento
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface improves soil tilth which further improves infiltration capacity
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários/especificar:
Manure of the small ruminants improves the soil tilth, an improved soil tilth improves the buffering/filtering capacity of the soil
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Comentários/especificar:
Maintenance of grasses on the soil surface reduces erosion due to wind
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não conhecido |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Decreased in occurrence of pest |
| Increased land user's income |
| Helped the land user's neighbor by profit sharing during harvest of the citrus fruits |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Less labor input How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the varietal species of the forage grass |
|
Decreased in occurrence of pest How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain the existing micro environment |
| Rotational grazing |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| There was an inbreeding of the small ruminants | Putting another small ruminants of good genetic quality |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Variety of forage grass is of low quality in terms of crude protein content | Planting of improved variety with a high crude protein content |
| Species of small ruminants are not of good genetic quality in terms of meat quality | Putting of species with a good genetic quality in terms of meat produce |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Soil Conservation Guided Farm System [Filipinas]
Soil Conservation Guided Farming System (SCGFS) is a land use management approach that integrates technologies: terracing, agro-pastoral technology, multi-storey cropping, and contouring within the socio-economic and bio-physical limitations of upland areas for optimum development of soil and water resource in a sustainable manner.
- Compilador/a: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
Módulos
Não há módulos