Check Dam [China]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Haiyan WEI
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Lan Sha Ba
technologies_1365 - China
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
20/05/2002
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST

Check Dam [China]
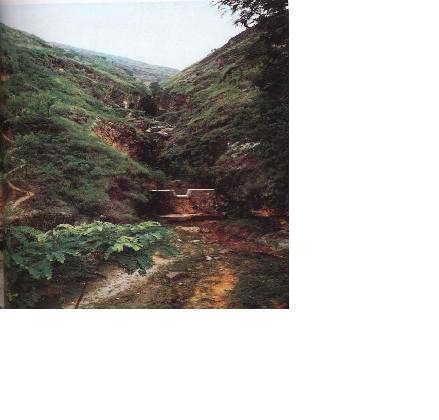
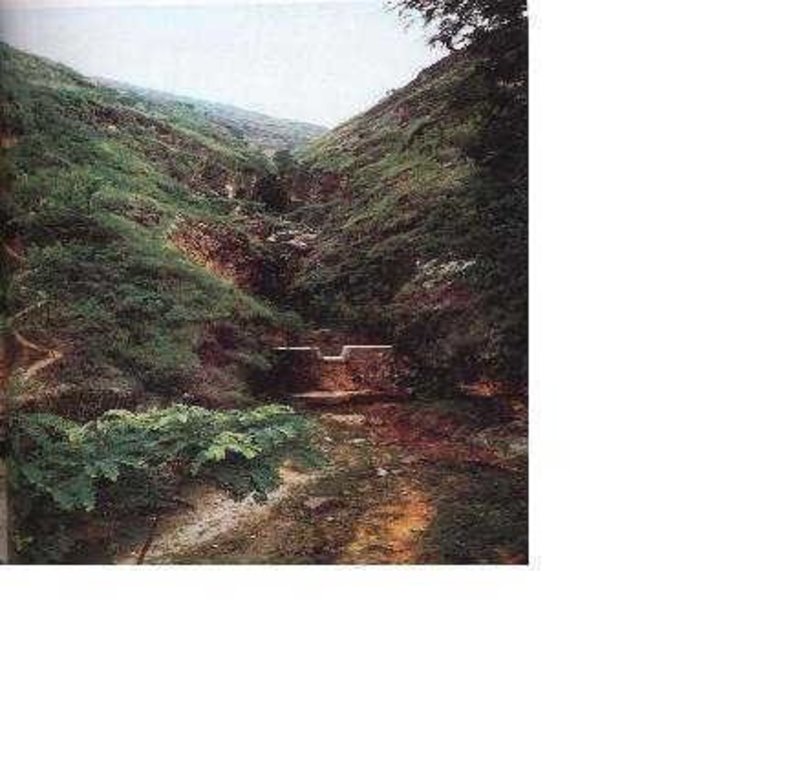
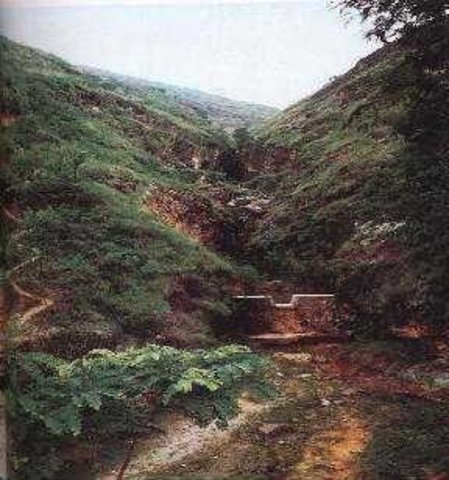
Check dam is a kind of sediment storage dam of 5m below and is built in channels to control the down cutting of channel bed.
- Compilador/a: Haiyan WEI
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Check dam refers to dam that constructed in the gullies or river ways and the height of the dam is often lower than 5m.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Check dams are built in the gully systems to harvest water and sediment. Usually many check dams are built in a gully or waterway to control the gully erosion. Check dams can be classified into "masonry dam", "check dam of earth", "check dam with willow" according to materials. Some strong masonry can last more than 10 years. As willow pegs in the "check dam with willow" can grow into timber after years.
Maintenance work should be done before rainy seasons every year so as to prevent the dam from destruction.
Following are the building procedures:
Masonry dam & check dam using earth:
1. Preparation---Removing grass, roots and surface soil; Digging a channel along an axis of a check dam in order to combine the dam and the bed firmly.
2. Construction---If a dam is planned to be made of earth, do scarification first, then adding earth (about 0.3m thick) and ramming it into 0.2m layer by layer. Building the dam with stones and/or rocks.
3. Base---If a bed of a gully consists of earth or sand, "base" should be built at the downstream feet of the dam. Length of the base should be twice as that of the dam and thickness should be 50-70cm.
4. Building a spillway at the top of the dam.
Check dam with willow:
1. Removing grass, roots and surface soil.
2. Cutting branches from willow; chopping the branches into pegs with the thick ends wedge.
3. Inserting the pegs into the ground.
4. Entwining wattles from willows around the pegs compactly.
5. Filling the space between two rows of pegs with stones, bricks, treetops etc. Making the stuff surface 10cm lower than the pegtop.
6. Combining the dam into a whole with iron chains.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
China
Região/Estado/Província:
Shanxi, Beijing
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Experiences from the local people's many SWC practice.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
corn or winter wheat.

Pastagem
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Serious gully erosion by water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gullies were widened and deepened greatly in the rainy season and crop land area is decreasing above the gully edges.
Constraints of urban land use
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Sep
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de água de superfície (nascente, rio, lagos, mar)
- reduce loss of cropland
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 100-1.000 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 145 m2.
As a traditional SWC technology, check dams have been used widely in China.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), poverty / wealth (Lack of captial)
Secondary causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge), Lack of enforcement of legislat./authority
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Description of Building Check Dam Procedures
Location: the Loess Plateau. Shanxi, Beijing
Date: 2000
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading
Secondary technical functions: increase / maintain water stored in soil
Construction material (earth): Loessial earth
Construction material (stone): if available
Construction material (wood): willow pegs
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 16%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 90%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:30
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
RMB Yuan
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
8,27
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
2.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation | Estrutural | |
| 2. | Construction | Estrutural | Before rainy season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 120 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | reparing after rainstorm. | Estrutural |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Length, width and height of check dams.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Sizes and materials of the check dams.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
580,00
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Slopes on average also gentle, moderate and rolling
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: low
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Nível de mecanização:
- Tração animal
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land (No difference).
Off-farm income specification: The land users who made the check dams can own more "deposited land". Generally these deposited land is fertile and produces high yield.
Level of mechanization: animal traction: on steep slope
Level of mechanization: mechanized/motorized: plateau or gully flat.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
48
Quantidade posterior à GST:
30
Solo
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
180
Quantidade posterior à GST:
110
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
180 household are using the technology and represent 65 percent of the poeple living in the stated area
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 10-50%
Comentários:
55% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
150 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
30 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: In the past (planning economy)SWC activities are administrative action to call local land users to carry out, but nowadays in the market economic conditions, if no or little benefits obtained, land users would not like to do any more.
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
How to design the dry masonry dam in the Hanjiachuan watershed. Tianyuzhu, Wangzuliang. Beijing. Water conservation in Beijing.. 2000.3.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Consideration about the check dam design and application. Liu shunzong. Soil and water conservation in China.. 1990.6.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Special Planning of Soil and Water Conservation in Xinzhou Region, Shanxi Province. 1986-2000.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
The application of the Check dam with willow in controlling gully erosion.Tu xingwen. Soil and water conservation in China.. 1986.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Library of the Resource and Environmental Department of the Beijing Normal Univ.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Check Dam [China]
Check dam is a kind of sediment storage dam of 5m below and is built in channels to control the down cutting of channel bed.
- Compilador/a: Haiyan WEI
Módulos
Não há módulos