Terrace [China]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Meili WEN
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Terrace
technologies_1367 - China
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University (Department of Resources and Environmental Science, Beijing Normal University) - China1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
18/05/2002
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
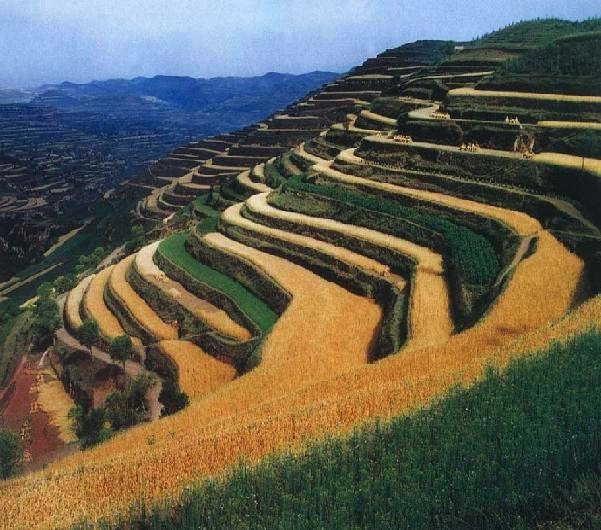
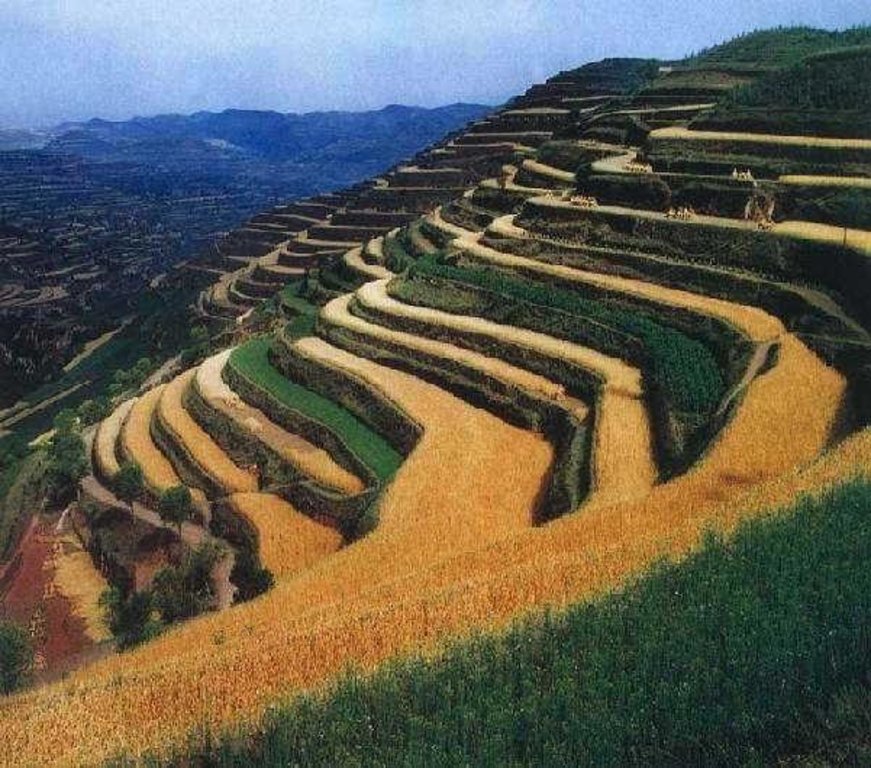
A terrace is a kind of measure to change the slope, which has a raised bank of earth or stone with vertical or sloping sides and a approximately flat top.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
A terrace has a raised bank of earth or stone with vertical or sloping sides and a approximately flat top. It can reduce slope angle and length, retain runoff, increase infiltration and reduce the soil loss. Crops can grow well because water increases in soils. Meanwhile, ground cover is improved. Terrace can be constructed by manual labor or machine. Firstly, determining the width of the field according to the slope angle and soil texture. Secondly, putting the topsoil aside. Thirdly, leveling up the slope and constructing banks. At last, putting the topsoil to the top of the flat surface.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
China
Região/Estado/Província:
Shaanxi, Shanxi, Inner Mongolia, Henan, Gansu
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Summary from farmers' long term experience in SWC, later being innovated.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
maize, Pease
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil and water lose seriously, soil degrades, soil fertility decreases and crop yield declines.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): crop yield declines, weak ability of resisting drought
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Water supply also mixed rainfed - irrigated
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 160Longest growing period from month to month: May-Sep
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- > 10.000 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 26666.7 m2.
Terrace is one of the most outstanding achievements in SWC in China. It can prevent soil and water loss so that slope land can be sustainable development. There are about 26.7 million ha of terrace in China, of which more than 13.3
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
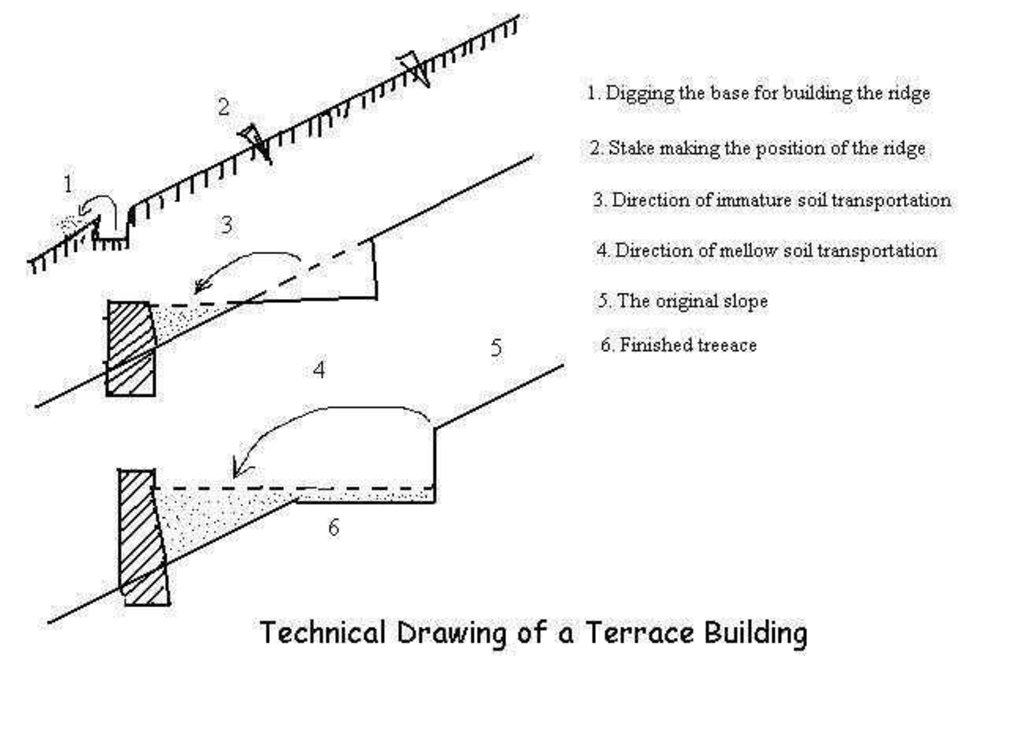
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Drawings of a terrace building in the Loess Plateau
Location: the Loess Plateau. Shaanxi, Shanxi, Henan, Gansu, Inner Mongolia
Date: 2002
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Construction material (earth): Construct ridge of terrace
Construction material (stone): Construct ridge of terrace
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 10%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 80%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:6
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
3.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | survey | Estrutural | After harvesting crop |
| 2. | constructing terrace: determine the excavation line which should make the excavation and the filling equal and the least workload | Estrutural | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 3. | constructing terrace: pilling mellow soil up to the middle of a bench | Estrutural | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 4. | constructing terrace: moving the immature soil of lower part to fill the upper part or moving the soil from inside to fill up outside | Estrutural | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 5. | constructing terrace: building the ridge | Estrutural | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
| 6. | constructing terrace: spreading the mellow soil on the surface | Estrutural | After harvesting crop, before raining season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | periodically inspecting | Estrutural | After a storm/About 1 year |
| 2. | repairing where terrace is collapsed | Estrutural | Whenever finding it is destroyed/timely |
| 3. | level up the field | Estrutural | after harvesting crops/timely |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Terrace section, building by bulldozer.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The factors are topography, soil texture, means of construction. The section of terrace is the most important factor.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
449,00
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Slopes on average also rolling
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility: low
Soil drainage / infiltration: good
Soil water storage capacity: low
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Rico
Nível de mecanização:
- Tração animal
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
Relative level of wealth: all selected
Relative level of wealth: very rich, rich, average, poor, very poor
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
10% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: estimate
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Comunitário/rural
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
10
Quantidade posterior à GST:
4
Solo
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
180
Quantidade posterior à GST:
58
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
80% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
20% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: If they have enough money, they would like to do, because they have known the benefits from terraces.
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
(inner resources) Suide Water and Soil Conservation examination station of Yellow River Water Resources Committee.. 1981.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
orpus of Test Research of Water and Soil Conservation (the second volume), p130~185.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
(inner resources) Water and Soil Conservation Department of Yellow River Water Resources Committee of Ministry of Water Resources and Electric Power.. 1987.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Corpus of economic benefits of water and soil measures, p77~102 ,510~514
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Dongyinglin,Changpiguang ,Wangzhihua. Discussion on the several questions on increasing production of the terrace with two banks.. 1990.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.1, p36~37
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Jiangdingsheng. Discussion on section design of the terrace on the Loess Plateau.. 1987.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
ACTA CONSERVATIONIS SOLI ET AQUAE SINICA, Vol.1, No.2,p28~35.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Liangqichun, Changfushuang , Liming. A study on drawing up budgetary estimate quota of terraced field.. 2001.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, Vol.21,No.5, p41~44.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Liumingquan, Zhangaiqin, Liyouhua. Pattern engineering of reconstruction the slope cropland.. 1992.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.3, p18~21.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Lixuelian,Qiaojiping. Synthetic technology of fertilizing and improving production on the new terrace.. 1998.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Soil and Water Conservation Science and Technology in Shanxi, No.3, p13~14.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Ministry of Water Resources of China. Terraces in China.. 1989.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
The press of Jilin science & technology.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Wangxilong,Caiqiangguo,Wangzhongke. The consolidating function and economic benefit analysis of the terrace hedgerows in the hilly loess region of northwest Hebei Province.. 2000.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Journal of Natural Resources,Vol.15, No.1, p74~79.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Xuyuanxu.The surveying report of the terrace benefits in yanbian autonomous prefecture. 1995.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Water and Soil Conservation,No.4, p50~52.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Zhujianqiang,Lijing. Experimental study on soil compact characteristics and its shearing strength in changing slope field into terrace on south shaanxi province.. 2000.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
ransaction of the CSAE,Vol.16, No.2, p36~40.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos