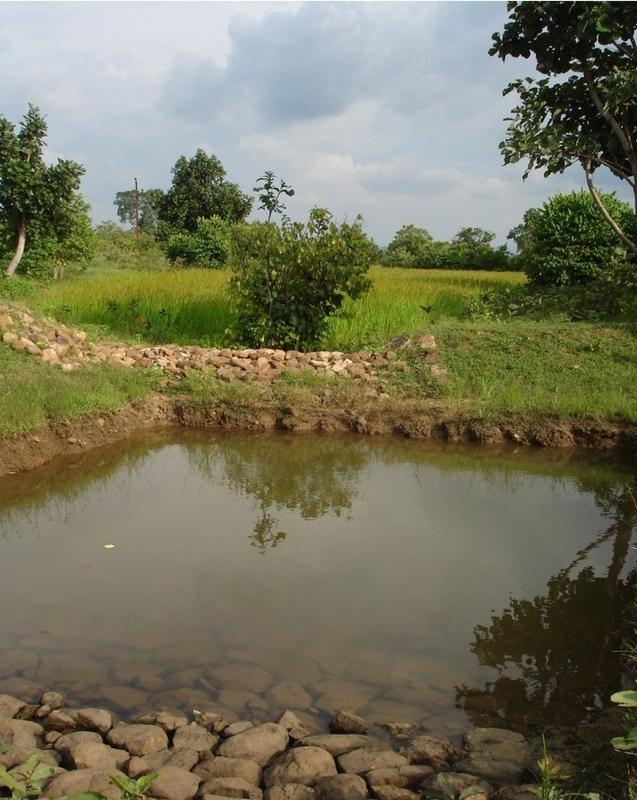
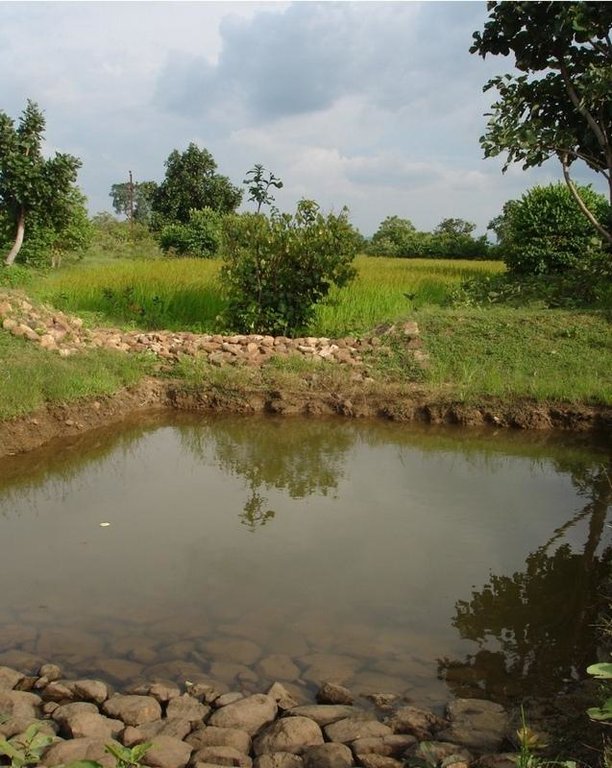
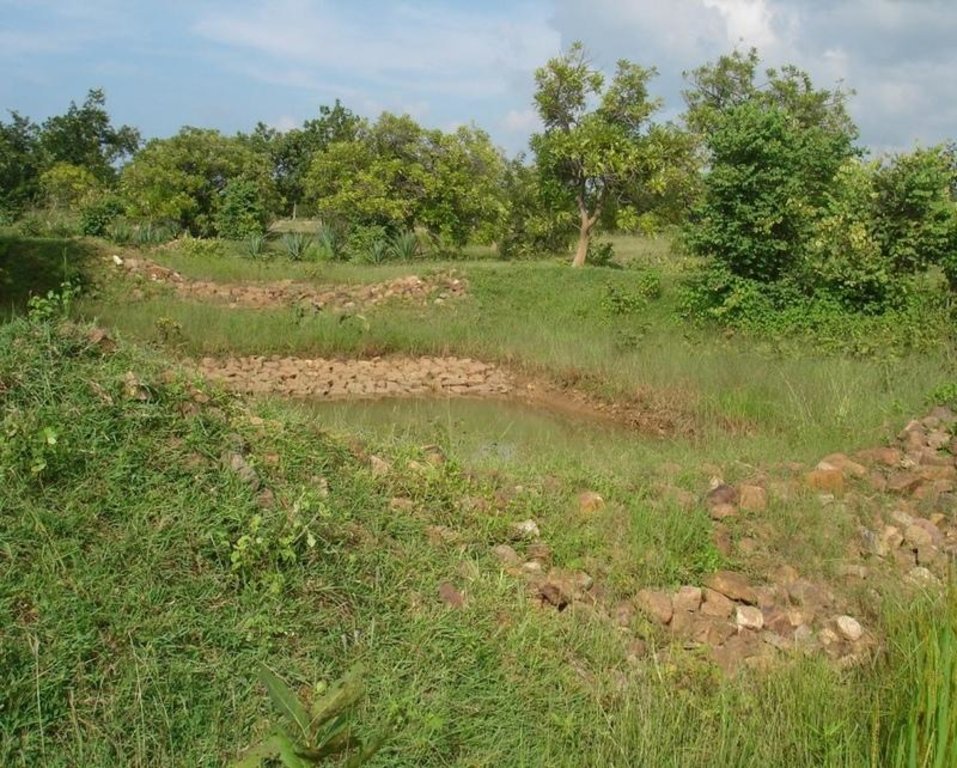
Sunken gully pits [Índia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: SATYANARAYANA SAHU
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
khancha, Dhuda
technologies_1479 - Índia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Nayak Pradeep Kumar
Nuapada, Orissa, India
Índia
1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
10/10/2006
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST

Participatory Watershed Development Approach [Índia]
Livelihood asset base development through participatory watershed developemnt keeping people at the center stage of development and promoting village level institutions.
- Compilador/a: Narendra Kumar Panigrahi
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Runoff management pit in the gully with provision of waterway for excess runoff water.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Adopted in 4-8% sloped gully at an interval varying from 20 M to 30 M . Pits are dug on the upsteam of the bund with graded slope or the upsteam of the pits. Also having provision of safe water disposal. Purpose: 1. Reduction in flow velocity 2. Withheld and impound the flow water 3. Ground water recharge 4. Increase in soil moisture regime 5. For supplemental irrigation by the middle and lower reach structure. Establishment/maintenance: Turfing, Placing in position of displaced boulder. Excavation of deposited earth from the pit. Environment: User friendly, Low maintenance, Promotes vegetation,Eco-friendly
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Índia
Região/Estado/Província:
ORISSA
Especificação adicional de localização:
ORISSA/NUAPADA/MAHANADI/CHAKAPADA
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
ANDHRA PRADESH By Hanumant Rao based upon Four- Water concept.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Silvipecuária
Principais produtos/serviços:
Shrubs, trees and fodder cultivation. Also: fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.), nature conservation / protection, recreation / tourism
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Formation and development of gully in course of time.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Problem of sand casting in crop land and graduallly coverted into unproductive lands.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Animals reside in the Watershed area
Grazingland comments: Trend increasing towards livestock production. Trend to have stall feeding. Trend to produce better and improved quality fodder.
Plantation forestry: Yes
Other type of forest: Natural forest
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Management and protection of existing forest and species are increasing by providing watch and ward by the Watershed members through Vana Surakhya Samiti(Forest Protection Committee)
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct Second longest growing period in days: 75 Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Jan
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Coleta de água
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Gestão do lençol freático
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 0,1-1 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.4 m2.
Technology adopted following T.Hanumanth Rao's four- Water concept.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wo: offsite degradation effects
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
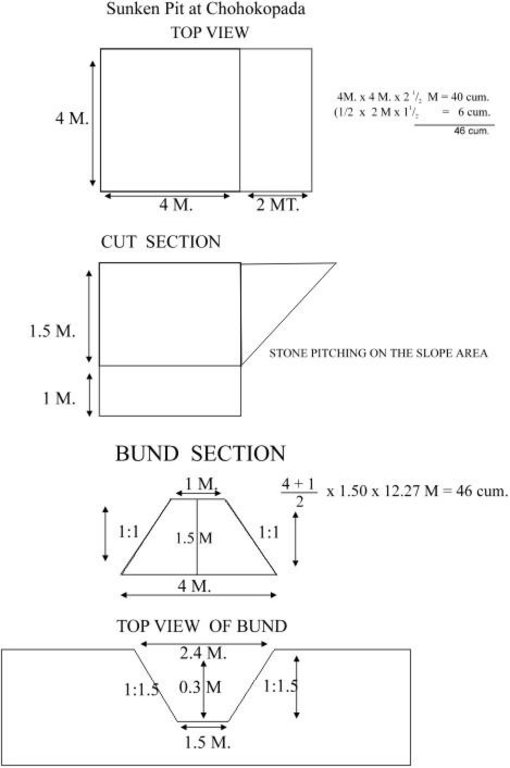
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Sunken pit technical drawing
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase in soil fertility
Vegetative measure: Turf on bund
Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: G : grass
Grass species: Local grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 2.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.00%
Structural measure: Sunken gully pit
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3
Construction material (earth): Excavated earth over 4.5 cum is utilised for construction of down stream bund
Construction material (stone): 1.08 cum of stone is used in upstream pit slope
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Rupees
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
50,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
1.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Local grass collection | Vegetativo | Onset of monsoon(Jun-july) |
| 2. | Putting the turf on the bund | Vegetativo | Onset of monsoon(Jun-july) |
| 3. | Establishment of grass | Vegetativo | During monsoon |
| 4. | Survey and layout | Estrutural | before onset of rain. |
| 5. | digging of pit & construction of earthen bund | Estrutural | pre-monsoon |
| 6. | stone pitching on upstream slope of pit | Estrutural | pre-monsoon |
| 7. | grass turffing | Estrutural | monsoon |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 37,0 | 37,0 | |
| Material de construção | Stone | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 40,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replanting of grass in the dried out patches | Vegetativo | During rainy season(July-Sept) /When required. |
| 2. | stabilisatioin of bund with grass | Estrutural | during rain/annual |
| 3. | de-silting of pit | Estrutural | Before onset of monsoon/annual |
| 4. | Maintaing upstream & down stream bund slope | Estrutural | Before onset of rain/annual |
| 5. | Re-arrangement of displaced stones | Estrutural | before onset of rain/annual |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Length of structure , deapth of gully , stone availability
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour availability, stone transportation.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1250,00
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (ranked 1) and high (ranked 2)
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 40% of the land.
5% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
30% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land.
40% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Income from offl farm activities like stone cutting, stone transporation, dry stone pitching
Market orientation of grazing land: Mixed (ranked 1, shrubs, trees and fodder cultivation) and subsistence (self-supply, ranked 2, to supplement the fodder requirements of watershed)
Market orientation of forest land: Commercial/market (ranked 1, sale of oil producing seeds), mixed (ranked 2, supply of excess fodder to nearby area/watershed) and self subsistence (ranked 3, trend increasing towards livestock production. Trend to have stall feeding. Trend to produce better and improved quality fodder.)
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Low fertile and degraded soil
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
Cowpea, Stylo
Qualidade da forragem
Comentários/especificar:
Cowpea, Stylo
Produção de madeira
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Private land
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Rs. 400/- per ha
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Crop area increased.
Awareness and willingness for maintenance required needs to develop
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
On farm employment
Comentários/especificar:
Farm production
Off farm employment
Comentários/especificar:
Stone cutting and T.C. of stone and dry packing
Input constraints
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
User group formation
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
Communitymobilization is required to restore the conflicts.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
60
Quantidade posterior à GST:
25
Drenagem de excesso de água
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Retention of water in pit. But might lead to waterlogging
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Plantation of fodder crops
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
20
Quantidade posterior à GST:
18
Outros impactos ecológicos
Soil fertility
Comentários/especificar:
Top soil loss checked
Biodiversity
Comentários/especificar:
Ecological changes/Eco. Dev./benefits to environment not assesed in short period of time.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Recharge to ground water
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
13
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
25% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
2% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
3 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Because this technology shows successful result in moisture retention, check soil erosioin and prevents sand casting.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Low cost & affordable. |
| Maintainable based upon traditional practices with some additional techniques. |
| Farmers friendly. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Best upon traditional practices, reducing runoff and soil loss How can they be sustained / enhanced? proper planning Water disposal at higher elevation Regular maintenance Adoption of proper cropping pattern depending on water availability Water disposal at higher alevation Regular maintenance Adoption of proper cropping pattern depending upon water availability. Water disposal at higher elevation Regular maintenance Adoption of proper cropping pattern depending upon water availability. water disposal at higher elevatioin regular maintenance Adoptioin of proper cropping pattern depending upon water availability. |
| low cost |
| Farmers can maintain and very less area is lost |
| Efficient soil & moisture conservation. |
| Protection of top soil, Increase Productivity and production of land |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Expected conflicts from adjecent farmers | Community mobilisation |
| Contribution mobilisation to have their ownership | Participatory planning |
| To be liable for its future care & maintenance | Awareness among the community |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Participatory Watershed Development Approach [Índia]
Livelihood asset base development through participatory watershed developemnt keeping people at the center stage of development and promoting village level institutions.
- Compilador/a: Narendra Kumar Panigrahi
Módulos
Não há módulos