Improved terraces [Nepal]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Madhav Dhakal
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
GARA SUDHAR- Nepali
technologies_1499 - Nepal
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Shreshta Bhubhan
977015525313
bhshreshta@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Nepal
Especialista em GST:
Nakarmi Gopal
977015525313
gnakarmi@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Nepal
Especialista em GST:
Merz Juerg
977015525313
jmerz@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Suíça
Especialista em GST:
Shrestha Smriti
977015525313
smshrestha@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Nepal
Especialista em GST:
Adhikari Krishna.Raj
977015525313
mdhakal@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Nepal
Especialista em GST:
Shah P.B.
977015525313
pshah@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Nepal
Especialista em GST:
Bhuchar Sanjeev
977015525313
sbhuchar@icimod.org.np
PARDYP/ICIMOD
GPO Box. 3226 Kathmandu Nepal
Nepal
Especialista em GST:
Singh Bijendra K
bijendra@hotmail.com
District Soil Conservation Office Dhulikhel
Kavrepalanchowk, Nepal
Nepal
usuário de terra:
Thapa Kalpana
Hokse VDC, Kubinde
Nepal
usuário de terra:
Thapa Gore
Hokse VDC, Kubinde
Nepal
usuário de terra:
Thapa Leela
Hokse VDC, Kubinde
Nepal
usuário de terra:
Tamang Indra
Hokse VDC, Kubinde
Nepal
Especialista em GST:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
People and Resource Dynamics Project, Nepal (PARDYP)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - NepalNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
District Soil Conservation Office (DSCO) - Nepal1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
07/02/2003
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Hillside forward-sloping terracing and stabilisation using structural and vegetative measures
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
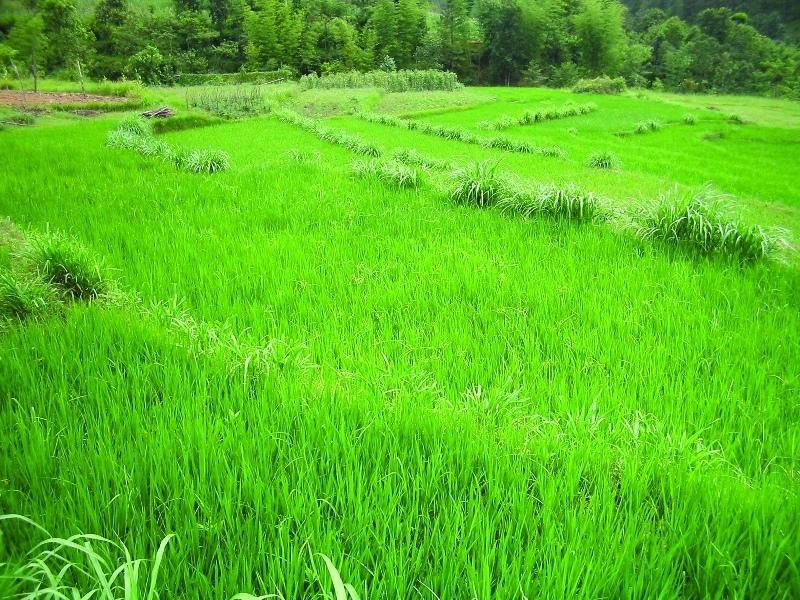
This technology addresses the soil erosion and water runoff problems associated with traditional outward-sloping terraces by reshaping the land into a series of level or gently sloping platforms across the slope. This technology is a variant of sloping land agricultural technology (SALT) or contour hedgerow technology. Nitrogen-fixing hedgerow species and quality fodder grass species, which bind the soil, are cultivated along terrace riser margins to improve terrace stability. This also enhances soil fertility and increases fodder availability. The plants are grown in either single or multiple layers. The practice is applied under rainfed conditions and is culturally acceptable and affordable. After establishment, the technology also addresses the problems of fodder scarcity making it easier and less time consuming for women and
girls to gather fodder.
The hedgerow and grass species are established between January and June. Complete establishment of this technology may take one year. The first step in creating the terraces is to build retaining walls using cement bags filled with soil which are then supported with bamboo cuttings along the contour (= future terrace risers). This divides the land into the planned terrace sections. The length and width of the terraces depends on the size and shape of the original field. Secondly, the soil is excavated from the upper part of the terraces and is used to build up the lower part above and behind the terrace riser wall to create a level bed. The fertile top soil must be kept aside and later spread over the newly terraced fields. The final step is to plant grass and hedgerow species on the outermost margins of the terrace above the risers.
Maintenance involves slicing the terrace risers once or twice a year with a spade, and smoothing off rills that appear on the surface of terraces after the premonsoon and monsoon periods. Hedgerows should be cut regularly but not more than twice a year, normally to a height of about 50 cm. Grasses should be cut about once to twice a month depending on their rate of growth.
The technology is applied under humid subtropical climate conditions (1300 mm annual rainfall with about 80% of it falling in the monsoon months of June - September). The case study area has hill slopes of 16-30% that are mostly highly erodible red soils (FAO classification: luvisols).
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Nepal
Especificação adicional de localização:
Hokse VDC ward no2
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
It is a combination of traditional knowledge and practice along with new scientific research findings from within the region and elsewhere, e.g., N-fixing fodder species related information from Phillipines.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
major cash crop: Potato and tomato
major food crop: Maize and wheat
other: Beans and chilli
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problem in the area documented is the small per capita cropping landholding size. The fields are mostly rainfed and have low soil fertility and acidity problems and are susceptible to erosion. The high intensity of rainfall leads to considerable soil loss (rill and gully erosion) at the beginning of rainy seasons.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The production of the cultivable land is declining. Management of slopes is inappropriate, the farmers experience serious constraints in terms of adopting better farming options, e.g., cash crops (due to fertility / erosion and soil moisture problems).
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Rice Premonsoon and monsoon( March- Novevember ) or Maize intercropped with Beans (April to August) ,Wheat and Potato ( September to January/ February) ,Tomato (January/February- April )
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 3
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Feb
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
- Desvio e drenagem de água
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.0126 km2.
The technology has been evaluated on the bases of village as a unit. Therefore the values calculated in terms of land use percentages is on the bases of village( Kubinde) data.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Soil erosion due to high intensity rainfall during rainy season and uneven distribution of rainfall during lean season.), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge - with regards to SWC measures)
Secondary causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes - lack of improved farming options), poverty / wealth (lack of captial - realted to inmproved seeds, technologies etc.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
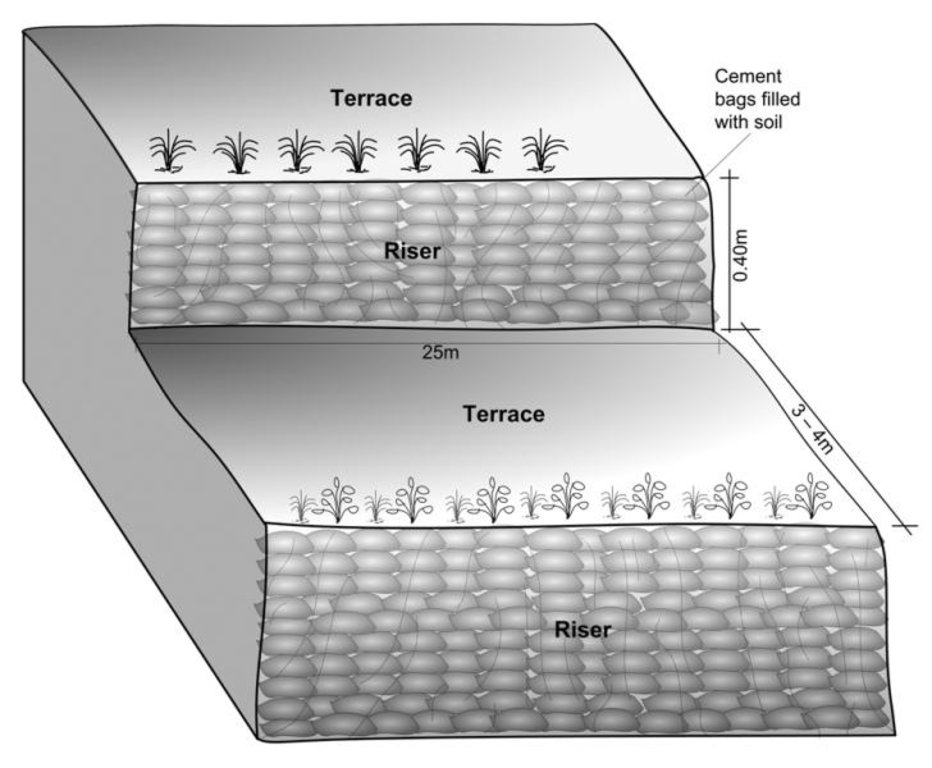
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Schematric view after intervention
[terracing and vegetative measures]
Riser slope: 75 degree
Terrace slope: ~ 2 degree
Location: Kubinde
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase in soil fertility
Vegetative measure: on risers
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 2500
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3 to 4
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.25
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: Sunhemp(Crotalaria juncea),Tephrosia (Tephrosia candida) and Flemingia (Flemingia microphylla)
Grass species: Napier(Pennisetum purpureum),Molasses (Melinis minutiflora) and Stylo(Stylosanthes guianensis)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 5.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 5.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 75.00%
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3-4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10-15
Construction material (earth): Cement bag filled with soil, Bamboo nets were used to make risers.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 5%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
-1,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
1.40
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Area estimation ( for vegetative measures) | Vegetativo | before rainy seasonn/lean period (February) |
| 2. | Selection of fodder grass species | Vegetativo | Before rainy season (Feb) |
| 3. | Planting of grasses and hedgerow species on the outward margins | Vegetativo | During rainy season. |
| 4. | Establishment of riser, using cement bags (filled with soil) and bamboo culms for terrace stabilisation | Estrutural | Beginning of rainy season(May) |
| 5. | Terrace leveling:The length and width of the terraces depends on the size and shape of the field. Excavate soil from the upper part of the terrace field and use it to build up the lower part behind the terrace riser wallt creat a level plateform/bed. | Estrutural | Beginning of rainy season(May) |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 970,0 | 970,0 | 50,0 |
| Equipamento | Total costs | ha | 1,0 | 92,0 | 92,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 25,0 | 25,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 30,0 | 30,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Bamboo | culms | 80,0 | 1,0 | 80,0 | 50,0 |
| Material de construção | Cement bags | ha | 1,0 | 80,0 | 80,0 | 50,0 |
| Outros | Supervision charge | ha | 1,0 | 10,5 | 10,5 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 1287,5 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hedgerow/grass maintenance: Hedgerows are cut regularly but not | Vegetativo | Grass is cut once or twice a month. |
| 2. | (Re)plantation of hedge species if necessary | Vegetativo | Before monsoon /1*/year |
| 3. | Surface and riser maintenance: smooth the surface/rills on the | Estrutural | after pre monsoon and after monsoon/2 */ year ,Jun |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | ha | 1,0 | 310,0 | 310,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools total costs | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 6,0 | 6,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 342,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Spade, Shovel, spade
All costs and amounts... are very roughly estimated by the technicians and authors.
Costs for structural measures are calculated considering the volume of excavated earth. 1 cubic meter excavated earth = 0.69 USD (labour cost). For vegetative measures it is normally based on daily wage = 1.4 USD as in 2006.
Labour cost is the major expenditure in the initial stage.
costs for tools for establishment are representative for the situation when tools for implementation of the SWC technology are not available (normally they are since the technology does not require very specific tools).
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
In case of projects interested in promoting this technology in the region, the labour cost is the major expenditure in the initial stage.The labour charges are decided by the district soil conservation office.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1304,00
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture (topsoil): Clay loam
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good but when rigid surface, then low infiltration
Soil water storage capacity is low - medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water: Sloping land , water available at downstream
Water quality (untreated): More in rainy season (June- September), less in April/May; source: natural spring
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
2% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
3% of the land users are average wealthy and own 15% of the land (off farm employment).
95% of the land users are poor and own 75% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily
Market orientation of production system: For subsistence there is: Rice, maize and wheat. Potato and tomato are for market or subsitence as well.
Level of mechanization: Land preparaion, planting,weeding and harvest is manual labour, but land preparation can also happen with animal traction.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
Land fragmentation due to poulation growth, mostly of rainfed type
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
maize crop by 100%
Produção de forragens
Comentários/especificar:
households of neighbouring village benefitted.
Qualidade da forragem
Área de produção
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
by >100% due to higher
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
terrace improvement group was formed
Livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Cropping pattern changed due to which, land users were able to produce more. Farm income and price of land increased.
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
nearby hedgerows
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
along risers
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
due to levelled surface and hedgerow barrier
Outros impactos ecológicos
Appearance of pests like rats due to introduction of planted
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Bigger area needs swc measures
Sedimentação a jusante
Fodder grass seed distribution
Comentários/especificar:
through farmer to farmer dissemination
Nutrients downstream
Comentários/especificar:
due to reduced nutrients leaching on-site
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
The initial investment is high, but can be recovered within a short period
due to yield increment and cash crop production.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
16 households in an area of 0.0126 sq km
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 50-90%
Comentários:
6 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The number of farmers applying the technology is increasing without further incentives being provided. Others have shown increasing interest in the technology without implementing it due to lack of incentives.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
The price of land increased considerably from NRs 30,000 in 2001 (for 1 ropani – 508.5 sq. m) to between NRs 100, 000 and NRs 150,000 per ropani after the technology was established How can they be sustained / enhanced? The price would increase further if irrigation facilities were installed |
| Pedicels of Tephosia and Sunhemp can be used for firewood. |
| Instead of planting only maize a farmer started planting rice (primary crop) and cash crops like potato / tomato (secondary crops). |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
The area of levelled terraces nearly doubled in Kubinde village from 2001 to 2003, which is an indicator of increased awareness of the benefi ts of soil and water conservation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Experience sharing would help expand the area under improved terraces. |
|
Land productivity increased, maize, potato and bean production increased, vegetables and rice production started. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Irrigation facility could increase the production capacity of the terraces. |
|
Availability of grass/fodder (nitrogen fixing) increased. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting horticultural fruits could increase farm incomes and so it should be promoted and more nitrogen fi xing species (preferably local) should be tried out |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| In the fi rst year of implementation, maize production was reduced due to soil amendment |
a phenomenon which is likely to occur with new terrace formation |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Presently the vegetative technology is confined to terrace margins | it should be extended to the risers also. |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
ICIMOD (2002) Hydro-meteorological Year Book of Jhikhu Khola Watershed. Kathmandu: ICIMOD
Disponível de onde? Custos?
ICIMOD
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Mathema, P.; Singh, B.K. (2003) Soil ErosionStudies in Nepal: Results and Implications. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Mathema, P. (2003) Watershed Managementin South Asia. Kathmandu: Government of Nepal, Department of Soil Conservation and Watershed Management
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos