Biogas [Botsuana]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Sebego Reuben
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Gase ya Boloko (Setswana)
technologies_1521 - Botsuana
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Mulale Kutlwano
P/bag UB 00704 Gaborone
Botsuana
Especialista em GST:
Chanda Raban
University of Botswana
P/bag UB 00704 Gaborone
Botsuana
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
University of Botswana (University of Botswana) - Botsuana1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
19/02/2009
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Production of methane gas from cow-dung for use in house-hold cooking, heating and lighting in order to reduce fire wood demand
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
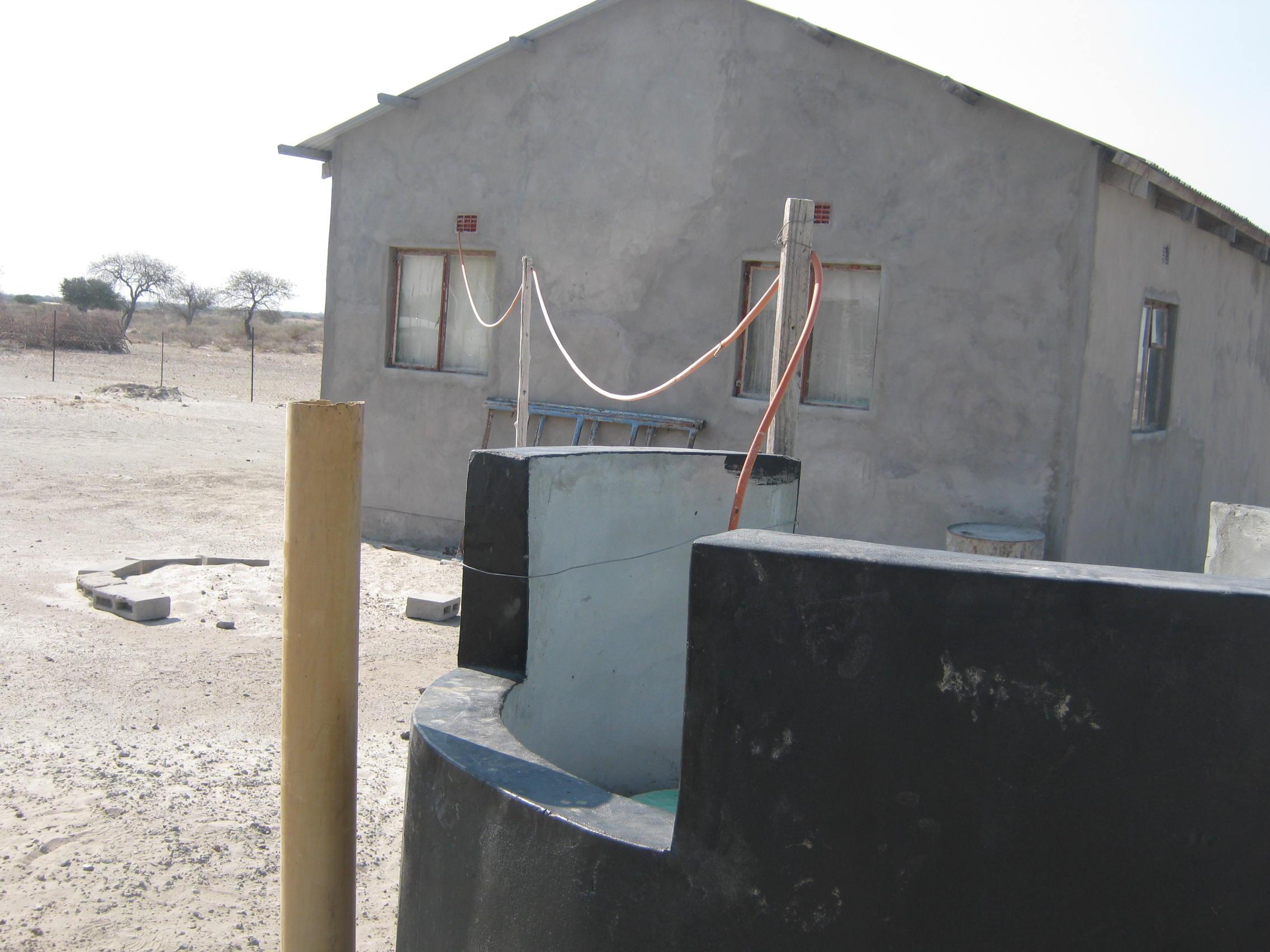
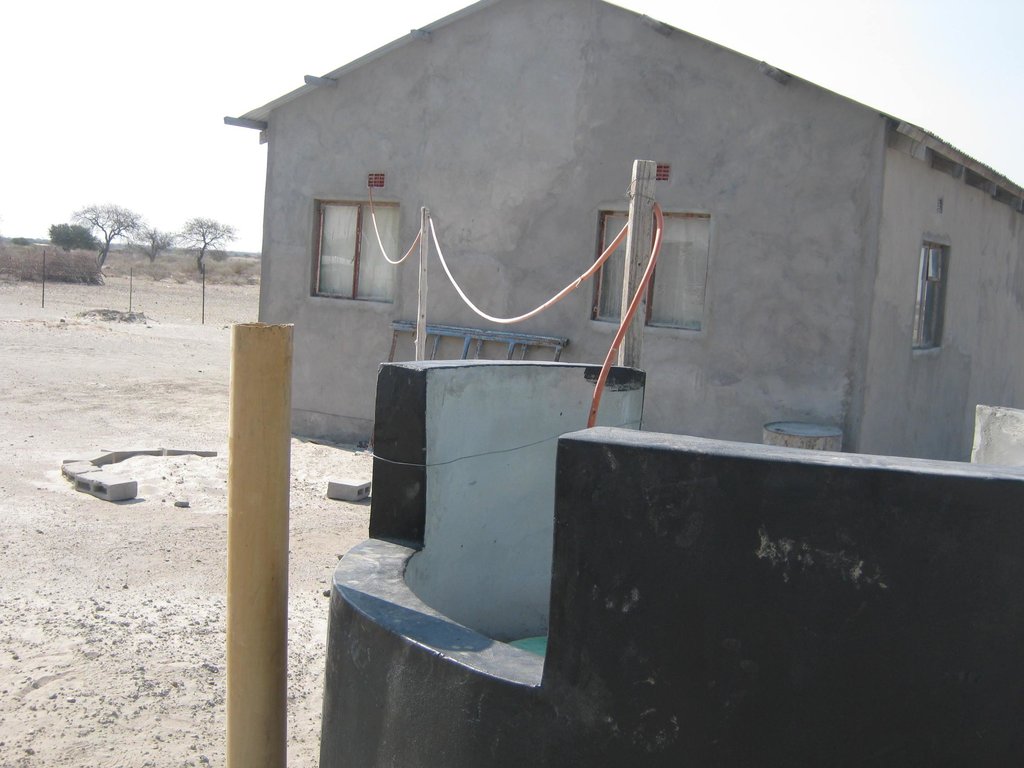
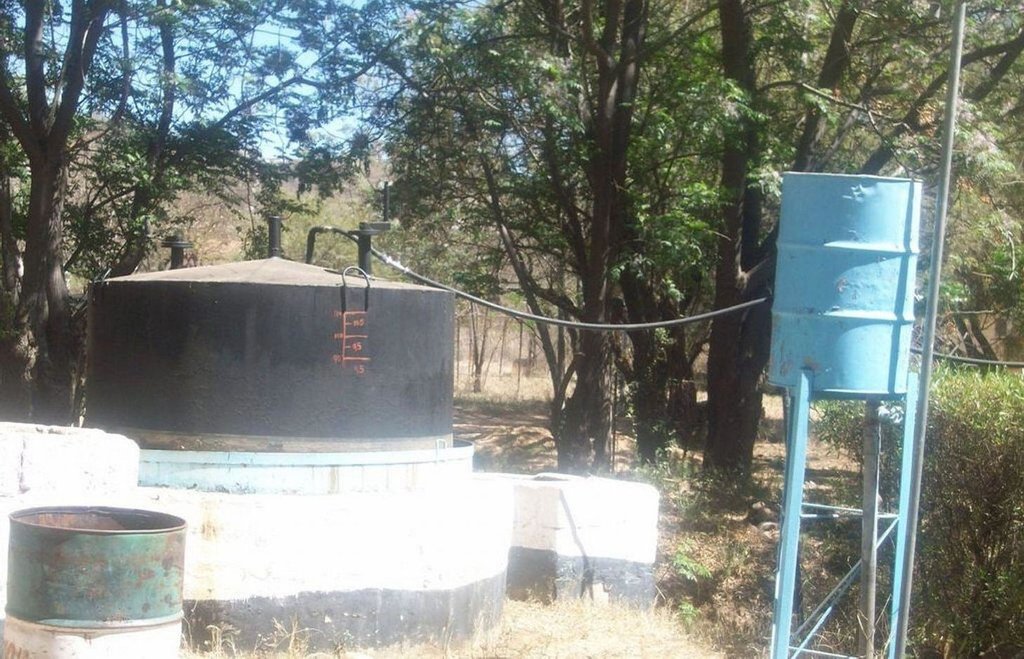
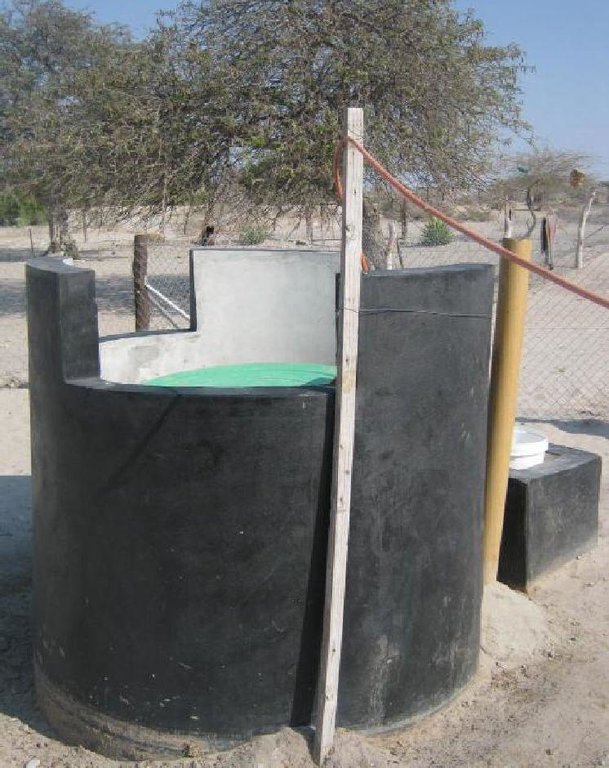
Biogas plant: The biogas plant can be constructed in several ways as long as it can provide a medium for the biological material be digested. Biogas is the name given to the gas that is produced during the decomposition of some organic waste specifically to produce methane gas. The gas is then captured in a storage tank (on site) to be used for household energy needs. In many parts of the world where this technology is used (including Botswana) the most common form of input material is cow dung making it more appropriate for rural environments.
Purpose of the Technology: Advantages: the technology offers two major advantages; first, at every level of use i.e. individual or institutional, savings in terms of energy is realized. The only costs that are borne are at installation, otherwise input of cow dung has a minimal cost of collection (if any at all). The second advantage is that there is reduced usage of fuel wood which translates into less cutting down of trees leading to reduced deforestation and degradation of land. A disadvantage is the initial investment which is significant for poor farmers.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Construction of the biogas plant: construction of the plant consists of three main chambers: namely, the Digester pit where all the microbiological reactions or decomposition of the material takes place. The digester has to be built to be air-tight with the released gas only escaping into the gas holder. The gas holder is connected to the digester by way of a pipe. Its main purpose is to collect all the gas that has been fermented. The mixing pit is the input chamber where the dung is mixed with water and fed into the digester. The amount and quality of water required for this is no constraint, even in this water stressed area. Construction the biogas plant has to be done according to specifications. A technical drawing of the plant is shown on page 3. The purpose of the technology is to use it for house-hold energy (for cooking, lighting and running appliances).
Natural / human environment: In Botswana the technology was introduced by the Rural Industries Innovation Center which is a government funded research institution. Despite the existence of this company for many years, the uptake has been very low due to poor marketing and extension services and lack of financial assistance to poor farmers.
Biogas is suitable either for a farm, cattle post or rural setting where the inputs (cow dung) are easily available. But there are possibilities of experimenting with other bio-degradable materials in major centres where cow dung is not readily available.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Botsuana
Região/Estado/Província:
Southern District
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kanye village
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology is promoted by a government funded NGO, but has its origins outside the country
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Preserva ecossistema
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Agrossilvipecuária
Principais produtos/serviços:
Major cash crop seasonal cropping:
Major food crop seasonal cropping:
Major other crops seasonal cropping:
Main products semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Beef cattle, goats, sheep, donkeys, chicken
Main products ranching: Beef cattle
Forest products and services: fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing of the commons, droughts, saline water and over-harvesting of fuelwood for cooking, heating leading to deforestation and land degradation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Overgrazing of the commons, droughts, saline water and over-harvesting of fuelwood for cooking, heating leading to deforestation and land degradation.
Grazingland comments: Biogass technology is not applied in the Boteti area at the moment, only at DESIRE test site.
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: specific tree species are felled for fuelwood even though people are supposed to take only fallen-dead wood
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Mixed cropping is the traditional practice but government extension advice promotes monocropping which the majority find expensive and risky.
Type of grazing system comments: Biogass technology is not applied in the Boteti area at the moment, only at DESIRE test site.
Constraints of settlement / urban
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Water supply: Also post-flooding
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 179 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
Densidade animal (se relevante):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Tecnologias de eficiência energética
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0 m2.
This technology is basically on a point location, even though it is to benefit a wider area in terms of conservation
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
Comentários:
Main measures: management measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (harvesting of fuelwood for cooking, sometimes live trees are harvested.), land tenure (Area is communal grazing land)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Trees are cut for bush fences), droughts (The study area is prone to droughts), poverty / wealth ((lack of alternative livelihood sources))
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
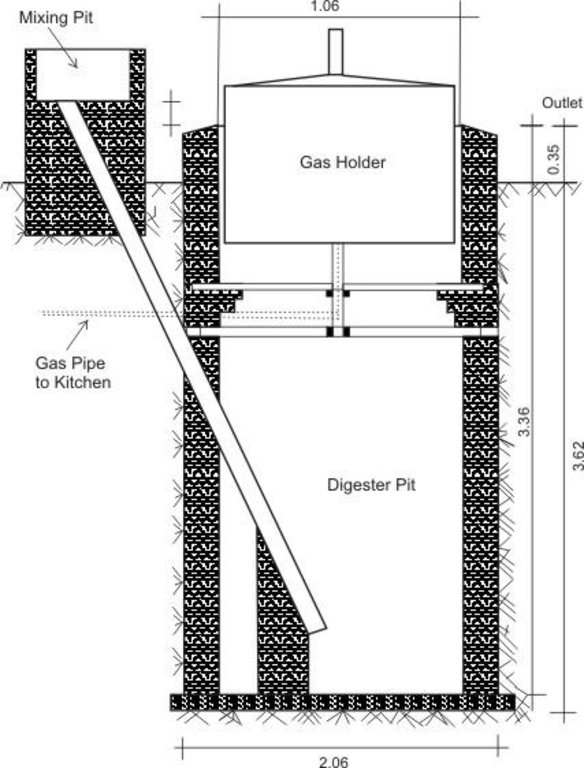
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
The diagram shows the technical layout of a biogas plant; showing the position of the main components: Digester, Gas holder, Mixing pit, and outlet. Cow dung & or kitchen waste (except bones) is mixed with water to form a sludge. This sludge is fed into the digester pit where decomposition and fermentation takes place. As the sludge ferments, methane gas is produced. Methane is a combustible gas and can therefore be used for cooking and lighting. Specially designed gas stoves and lanterns may be required as the gas would not be purified and hence ‚thicker‘ than commercially produced gasses. However, the design can include a water filled pipe bend (u shaped) between the gas holder and outlet pipe. The water in this pipe would help to purify the gas before it is fed to the household appliances. The gas holder tank floats in water, through which the gas bubbles escape and methane gas collects into the floating tank. An outlet through which decomposed material leaves the plant is necessary. Old sludge would float and be removed through this opening (Diagram drawn by G. Koorutwe, Department of Environmental Science, University of Botswana).
Location: Mopipi. Boteti Sub-District
Date: 05/10/11 (revised)
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Skilled technician is needed for installation)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: reduction of wood exploitation
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), enhancement of tree growth
Structural measure: Digestion pit
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.38
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2.06
Structural measure: Gas holder
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.6
Construction material (other): bricks, pipes, cement, iron sheets
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Use of biogass for cooking would lead to reduced cutting of wood for cooking
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Pula
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
6,5
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
1.08
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construction | Gestão | N/A |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | Tank | 1,0 | 198,0 | 198,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tank | Tank | 1,0 | 615,0 | 615,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Bricks | Tank | 1,0 | 77,0 | 77,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Cement | Tank | 1,0 | 123,0 | 123,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Plumbing material | Tank | 1,0 | 154,0 | 154,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Earth | Tank | 1,0 | 31,0 | 31,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 1198,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.5 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Filling up with cow dung and water | Gestão | 1 Day |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipamento | Cow dung | Tank | 1,0 | 33,0 | 33,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 33,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Costs were calculated for labour and material based on the real cost of construction at the Mopipi Site.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Material, labour and equipment used in construction are the most determining factors affecting the costs (installation cost is US$ 1198).
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Seasonal summer rains, approx six months dry (LPG = 75-179)
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: subtropics. Sub-tropical climate. Semi-arid with dry winters (LPG=75-179 days).
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 501-1000 m a.s.l. (Part of the Makgadikgadi basin)
Slopes on average: Flat (ranked 1, mainly low lying land of lucrustrine (pans) formation) and gentle (ranked 2, gently sloping (plains))
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Shallow (ranked 1, generally soils are 40cm deep, underneath is a calcrete layer at about 40cm deep) and deep (ranked 2, some sandy area away from pans e.g. the Gidikwe Ridge )
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1, away from pans/river/flood plain = main soil type) and fine/heavy (ranked 2, sticky when wet in the depression)
Soil fertility: Low (ranked 1, sandy areas (Arenosols)) and medium (ranked 2, in flood plains of the Boteti river)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (ranked 1, low on sandy areas/soils) and topsoil organic matter (ranked 2, on the flood plains for molapo farming)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1, very good on sandy soils) and medium (ranked 2, flood plains are medium)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low (ranked 1, on sandy soils) and medium (ranked 2, on flood plains)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table: >50m (ranked 1, for Boreholes) and 5-50 m (ranked 2, wells in the Boteti River bed)
Availability of surface water: poor/none (dry season-unreliable river flow/rainfall)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required, salty water in most areas, ranked 1) and unusable (sometimes too salty even for livestock consumption, ranked 2)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Biodiversity: High (several game reserves (protected areas) nearby, ranked 1) and low (grazing areas with arable agriculture, ranked 2)
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Muito rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Difference in the involvement of women and men: There is no difference, as this is mainly a family thing or institutioanal like in schools and community halls
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are very rich and own 50% of the land (Cattle farmers).
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (Most inhabitants).
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land (Subsistance farm).
Off-farm income specification: Saves money for buying commercial gas and electric power. Helps conserve the forests. Limited off-farm income opportunities for everyone including non-adopters of the technology.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (mostly donkeys for draught power)
Market orientation of annual cropping production system: Mixed (subsistence/commercial) Could be used/produced for domestic and commercial purposes.
Market orientation of grazing land production system: Subsistence and commercial/market
Market orientation of forest production system: Mixed (subsistence/commercial) in both cases use of biogas is approppriate
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Grande escala
Comentários:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology on grazing land
1000-10000 ha (ranked 1, cattle farmers in ranches and cattle posts)
15-50 ha (ranked 2, subsistence farmers)
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology on cropland:
50-100 ha (ranked 1)
2-5 ha (ranked 2, on average)
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
The SLM can be used by anybody - not specified to any group. Dual grazing rights is a problem (private ranchers can also use the commons).
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Assuming large scale removal of dung, there could be reduction in animal manure available for crop production
Geração de energia
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
As farmers would have to purchase fertilizer as animal manure becomes scarce
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
With biogas no labour for fuelwood collection. Time and effort previously used for firewood collection is freed
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
Future conflict over fuelwood resources would be averted. In case of no ownership of cattle.
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Comentários/especificar:
Less demand on the time and labour of women and the girl child who are the main collecters of fuelwood
Gender related issues
Comentários/especificar:
Where taboos exist for women harvesting dung from kraals (livestock enclosure); this could constrain adoption along gender lines
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Provides cheaper and alternative source of energy. Reduces workload for fuelwood collection for women and the girl child.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Due to reduced plant cover
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
More trees certaily provides soil cover. But problems possible when plant cover is reduced as a result of less manure
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced soil fertility with distance from water points/kraals
Salinidade
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Due to redused animal manure
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Trees would have more density or cover
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Wood collectors target specific species
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Large scale adoption of biogas production may introduce air pollution. Also unpleasent smell around the village.
Outros impactos ecológicos
Concentration of nutrients (dung)
Comentários/especificar:
Cow dung will be reduce around water points and kraals
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Danos em áreas vizinhas
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
| temperature decrease | não bem |
Comentários:
Biogas technology may be limited under extreme cold conditions whereby fermentation may be limited by cold temperatures.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
Very costly to set up, if no government aid. It is however very good for long term water provision.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
10
Comentários:
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: A very insignificant number of individual farmers have used this technology
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology has mostly been used where the Research institution has installed in farmers' properties. Only in very few instances around the country have individuals installed it for themselves.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There seems to be very little marketing of biogas in the country
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Problems of diminishing firewood species are reduced. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Because it is not every or all species that is used for firewood, the targeted species are quickly diminished |
|
Cost of getting firewood is reduced How can they be sustained / enhanced? Distance to wood collection places are ever increasing hence users have to buy from truck or donkey cart owners |
|
More time is freed How can they be sustained / enhanced? This especially applies to children (of school going age) in that they would have more time for their home works. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Low maintenance and inputs are required for this technology How can they be sustained / enhanced? There is need for promotion of the technology |
|
The structures to be put in place are very basic How can they be sustained / enhanced? There is need for the government to subsidize farmers in installing biogas plants, especially in the rual areas. |
|
Good for rural households where firewood is used extensively. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve income of rural families so that they could afford the technology |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Too expensive for poor farmers to adopt without assistance | Donor/government subsidies |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Brown, V. J., 2006. BIOGAS: A Bright Idea for Africa. Environ Health Perspectives. 114(5), pp. A300–A303.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
internet
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Dayal, M., Vimal, O.P., Singh, K.K., 1989. Biomass gasification in India — DNES activities. Biomass, Volume 18, issues 3-4,pp. 197-204
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.ganesha.co.uk/Articles/Biogas%20Technology%20in%20India.htm
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos