Jatropha curcas hedge [Etiópia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Simon Bach
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
Agulo Keter
technologies_1524 - Etiópia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Ayele Habtamu
+251 92 592 0594
Haramaya University
Haramaya University, P.O. Box 138, Dire Dawa, Ethiopia
Etiópia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Haramaya University (HU) - Etiópia1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
30/04/2011
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
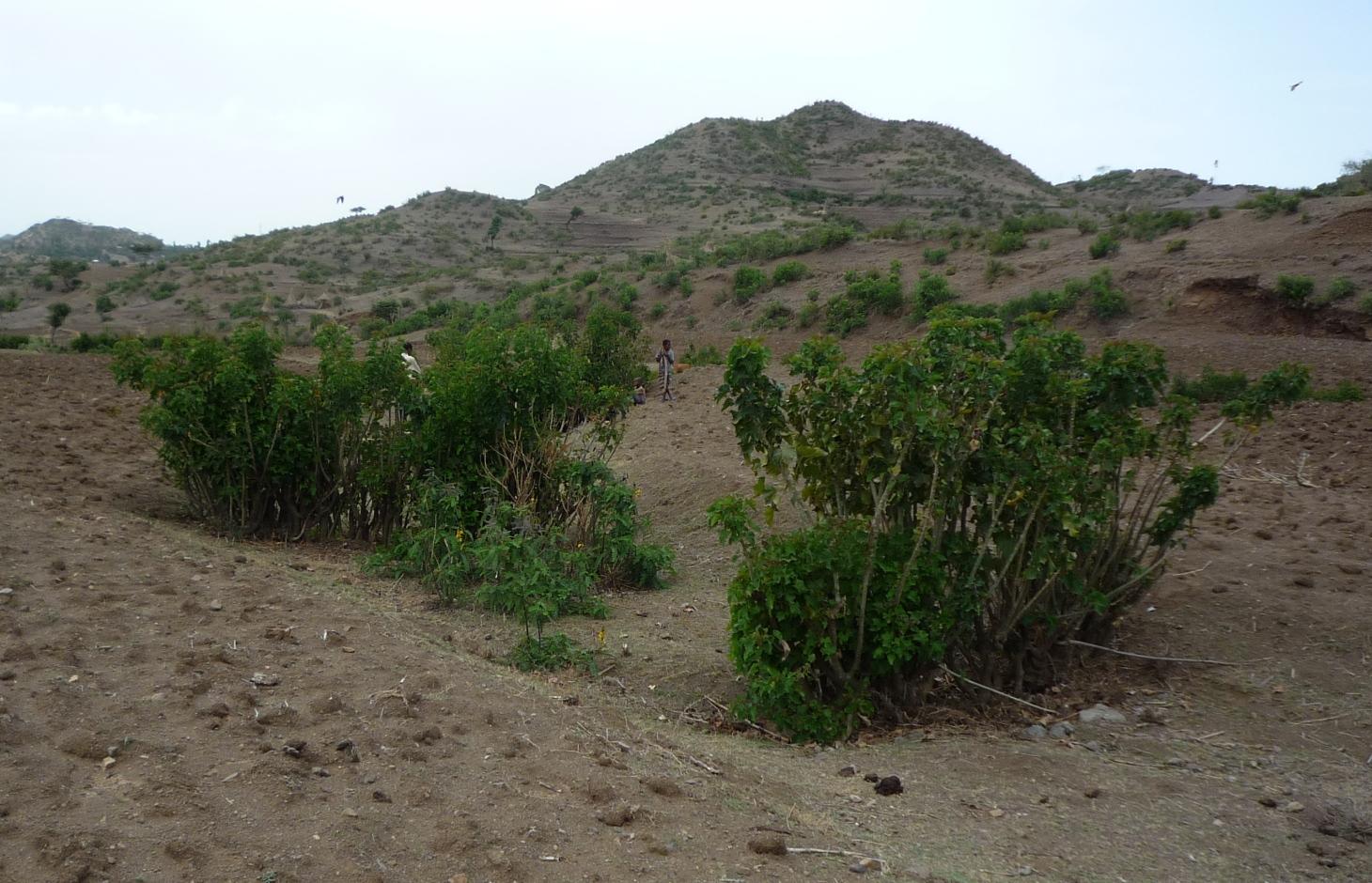
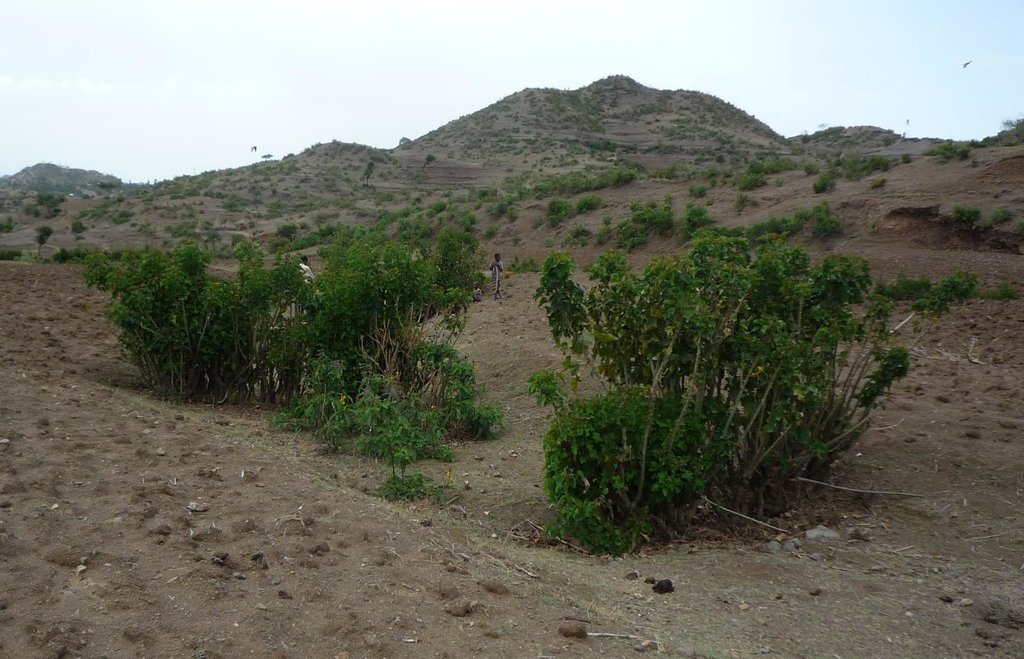
Gully rehabilitation and hill stabilization with Jatropha hedges.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
In the area around Bati in Ethiopia, Jatropha is used to stabilize hills ore to rehabilitate gullies. The technology was introduced during the last decade by local farmers on their plots. The advantage of Jatropha against other shrubs is that it is poisonous and therefore not browsed by animals. Additionally the seeds can be collected by household members and sold on the local market. The seed's oil can be used as a lamp oil or even for the production of bio-fuel.
Purpose of the Technology: Besides hedges and living fences, Jatropha is used for combating sheet or gully erosion. To stop erosion processes the Jatropha cuttings are planted across a gully or along hill sides to stabilize them in the same manner as check dams or terraces do. The plant is chosen because of its very tolerant character, rather high accessibility in the area and because it is easy to propagate by cuttings. Often Jatropha is used in combination with traditional stone check dams or terraces aiming for an increased stability of the technology itself. For that purpose Jatropha is planted in front of the stone walls or also on top of them.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In earlier times Jatropha was planted by seeds but nowadays, since there are a lot of plants in the area, propagation by cuttings is the more prominent form. Since the plants are pruned every year anyway, the cuttings are accessible almost in any case for free. At markets further away, the cuttings cost around one cent per piece. In order to rehabilitate a gully Jatropha cuttings are planted as near as possible in the selected area in a row across the gully. After rooting, the spaces between the plants are filled up with litter, shrubs or stones. In order to have a thick stem and avoid competition with crops, the plants are pruned every year. The thick main stems reach a height of approximately one meter which delineates the maximum height of possible soil collection. If the area behind the filled up gaps and the cuttings has silted up, the height is increased by adding new litter in the higher up gaps. In off farming season, the Jatropha seeds are collected and sold on the market to create additional income.
Natural / human environment: The case study site, Bati, lays in an semiarid climatic zone on 1600 m a.s.l. Rainfalls are erratic and the rain sum per year is between 500-1000 mm. The landscape is very hilly with rather steep slopes. The area has a high population density and growth. The agricultural sector is very dominant and lead by a lot of small scale farming with a lot of livestock and small plots of cropland.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Etiópia
Região/Estado/Província:
Ethiopia / Amhara Region
Especificação adicional de localização:
Bati
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Farmers are using Jatropha curcas since approximately 30 years in the research area in Bati mostly for fencing. Innovative farmers started using the plant for stabilizing existing physical structures (stone walls, terraces, gully check dams) or using it as a complete substitute for these physical structures.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Major food crop: Sorghum
Major other crop: Corn

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Silvipecuária
Principais produtos/serviços:
Major food product: Cattle, goat, sheep, camel
Major other product: Chicken
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Deforestation, overgrazing, cultivation of erosion-sensitive areas or steep slopes.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Too much soil loss and land degradation, no vegetation cover and poor soil moisture.
Grazingland comments: Livestock is not fenced in. Children herd the animals and watch out that they do not browse through crop fields. In off-farming season crop residues are collected from the field and stored next to the field. Animals are allowed to eat the still remaining residues on the field. After that, the animals are fed by the collected crop residues.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Type of grazing system comments: Livestock is not fenced in. Children herd the animals and watch out that they do not browse through crop fields. In off-farming season crop residues are collected from the field and stored next to the field. Animals are allowed to eat the still remaining residues on the field. After that, the animals are fed by the collected crop residues. Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Water supply: Also mixed rainfed - irrigated
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 90 Longest growing period from month to month: June until September
Densidade animal (se relevante):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.7 m2.
Size of the case study watershed.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços
- S6: Muros, barreiras, paliçadas, cercas
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation for the past 30 years.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Wood collection for cooking and construction.), overgrazing (60% of the watershed area are cultivated - big grazing pressure on remaining land), other human induced causes (specify) (Cultivation of very steep slopes.), change of seasonal rainfall (Erratic rainfall.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (If there is rain, it is intensive.), population pressure (High population pressure.), poverty / wealth (Poor facilities.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (Poor soil management practices and lack of awareness.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Annual cropping.), droughts (The research area is considered rather dry.), land tenure (If the land is rented, it is poorly managed.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Poor access to fertilizer. Bad infrastructures.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of awareness for soil degradation.), Low productivity of the land (As a consequence seeking for new/larger areas to increase production.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
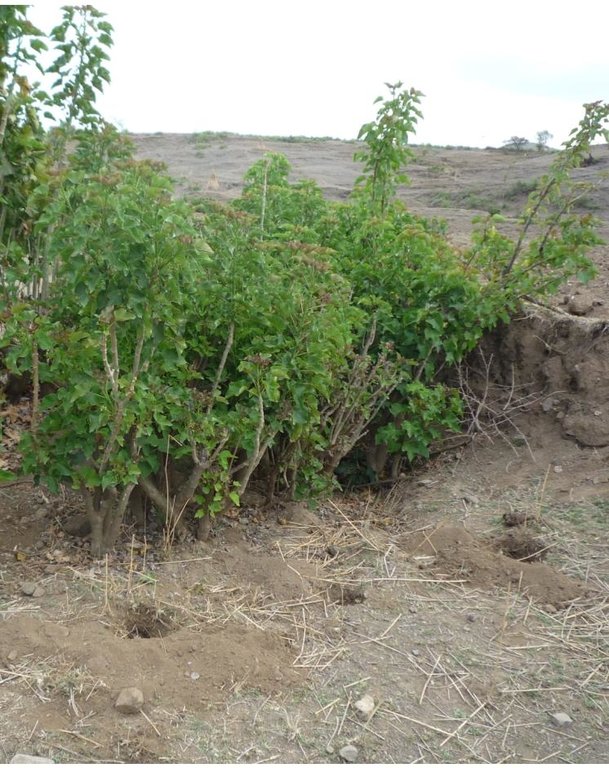
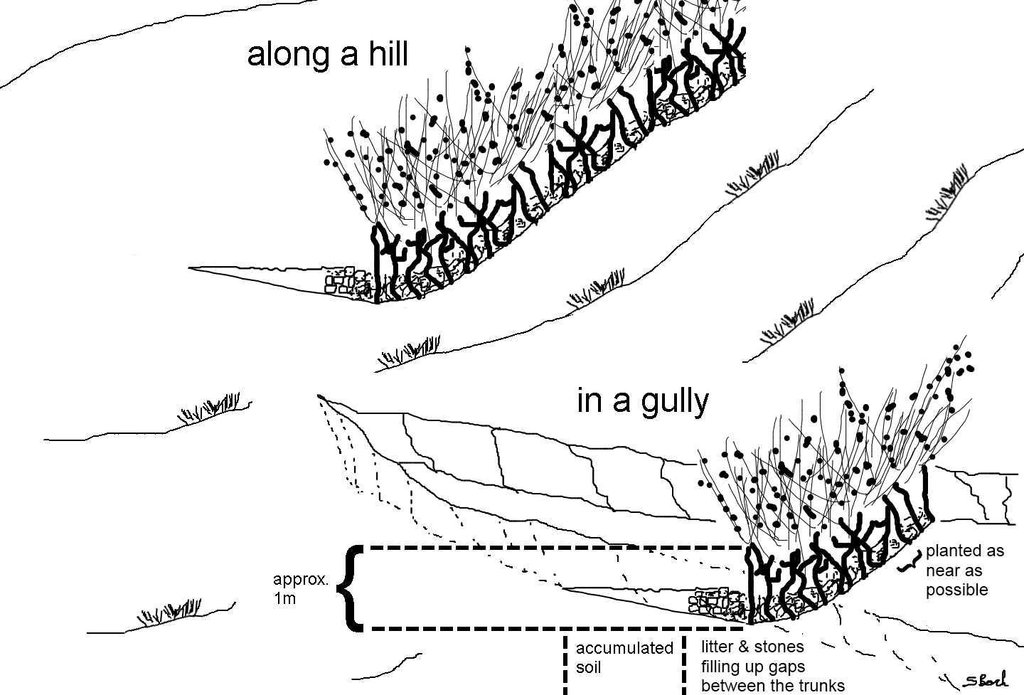
Jatropha hedges as they can be found in the region of Bati. Often the plant is used for gully rehabilitation. For that purpose it is planted (mostly by cuttings) with a minimal interval between each plant to create a barrier-like hedge. The gaps are filled up with litter or stones.
Approximately 1 m of soil can be collected by the trunk - above that height it is too thin. The Jatropha seed can create additional income besides the purpose of soil and water conservation. Often, the plant is used in combination with traditional technologies (terraces, stone walls) and planted on top or in front of these traditional structures to improve their stability.
Location: South of Bati. Bati Woreda, Amhara Region, Ethiopia
Date: 05.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Planting takes place rather randomly in places of needs.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 10 per m
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): ~1m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): ~20m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Vegetative measure: filling material
Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: O : other
Trees/ shrubs species: Jatropha curcas
Other species: Stones, shrubs, sticks - things that can be found and utilized to fill up gaps between each plant.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Ethiopian Birr
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
16,82
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
1.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | One time initial sawing of Jatropha seeds (30 years ago). | Vegetativo | Initial. Wet season. |
| 2. | Cutting of the Jatropha cuttings (12.5 person days needed). | Vegetativo | dry season |
| 3. | Planting of the Jatropha cuttings (12.5 person days needed). | Vegetativo | dry season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Seeding | person day | 1,0 | 1,0 | 1,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Cutting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12,5 | 1,0 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting of the Jatropha cuttings | person day | 12,5 | 1,0 | 12,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools for cutting | 500m | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | kg | 1,0 | 2,0 | 2,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 33,0 | |||||
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of Jatropha seeds (5 person days needed). | Vegetativo | Off farming season(Okt.) |
| 2. | Filling up the gaps with litter (5 person days needed). | Vegetativo | If necessary |
| 3. | Pruning of the Jatropha hedges (15 person days needed). | Vegetativo | Yearly before wet season. |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Collection of Jatropha seeds | Person days | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Filling up the gaps with litter | Person days | 5,0 | 1,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Pruning of the Jatropha | person days | 15,0 | 1,0 | 15,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | Person days | 15,0 | 0,333333333 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Wood | 500m | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Material de construção | Stone | 500m | 1,0 | 100,0 | ||
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 30,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: saw, axe
Total costs of a hectare are calculated for a hedge of 100 m length every 20 m (500 m total hedge) in the year 2011. Tool prices were estimated and labor costs were calculated with a daily wage of 1$.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Rough topology in the area, questionable availability of construction materials if they are not found nearby.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Erratic rainfall (rainseason from June until September)
751-1000 mm ranked 1
501-750 mm ranked 2
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: tropics
LGP shorter than 90 days.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (The study site is located at 1600m a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1) and valley floors (ranked 2)
Slopes on average: Hilly (ranked 1), rolling (ranked 2) and steep (ranked 3)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Very shallow (ranked 1), shallow (ranked 2)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage/infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table is unknown.
Availability of surface water: Only during rainy season
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, mostly groundwater)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Relative to other parts of Ethiopia.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 6%
1% of the land users are rich (Adopt the most of SWC technologies).
19% of the land users are average wealthy.
89% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Off-farm income has low importance.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (plowing by oxen, ranked 1) and manual work (ranked 2)
Market orientation: Mixed (subsistence and commercial) Goat/sheep are main meat source (in household or on market).
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
gullies are transformed to fields
Risco de falha de produção
Comentários/especificar:
improving soil moisture
Diversidade de produtos
Comentários/especificar:
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
gullies are transformed to fields. Structure needs space but also gains space
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
gully is now flat land and traversable, structure as a new obstacle
Geração de energia
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas seed oil as a biofuel
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
alluvial soil is relatively fertile
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
new fields lead to higher productivity
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
selling the Jatropha curcas seeds
Disparidades econômicas
Comentários/especificar:
additional income by selling Jatropha seeds
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
slightly labor increase, establishment and maintenance work
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
additional space for new fields
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
positive examples for other land users
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Comentários/especificar:
up -downstream problems may be solved
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Accumulation of soil leads to new space for fields and additional food security or even income (if crop surplus is sold). Collection of Jatropha curcas seeds - they can be sold (additional income) or processed to oil (lamp oil etc.)
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
increased soil moisture
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
increased infiltration, reduced flow velocity
Lençol freático/aquífero
Comentários/especificar:
increased infiltration
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
maybe due to the Jatropha curcas canopy
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas dam blocks water flow,. But additional groundwater may be logged
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas canopy
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
alluvial accumulation behind the structure
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Comentários/especificar:
increased rooting
Compactação do solo
Comentários/especificar:
increased rooting
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas leaves & litter
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas biomass
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
Diversidade animal
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
Espécies benéficas
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas new habitat for worms etc
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas as a new habitat
Controle de praga/doença
Comentários/especificar:
new habitat for rodents etc.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Comentários/especificar:
flood controll by Jatropha curcas dams
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
little effect by additional plants
Risco de incêndio
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas wood is a bad fire wood
Velocidade do vento
Comentários/especificar:
Jatropha curcas shrub as a wind breaker
Outros impactos ecológicos
Increased competition
Comentários/especificar:
Over water and sunlight
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
possibility of spring development
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Comentários/especificar:
if a spring can develop
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
increased infiltration/reduced flooding
Sedimentação a jusante
Comentários/especificar:
trapping of the sediments by the structure
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Comentários/especificar:
trapping of the sediments by the structure
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Comentários/especificar:
increased infiltration
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Comentários/especificar:
due to gully rehabilitation
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Comentários/especificar:
due to gully rehabilitation
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Establishment needs a little time, although not very much. Maintenance work is very little needed and can be done if needed or in off-farming season. Establishment and mainentance costs are none or very little.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Local technology spread from farmer to farmer.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Completely based on farmer's initiative.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: A lot of farmer are adopting (or already have adopted) Jatropha curcas as a SWC technology in the region.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Soil and water conservation are very important. Also the conservation of soil moisture. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create farmer's awareness that SWC is very important for a sustainable land management. |
|
In combination, Jatropha curcas can also be used to stabilize traditional stone structuress (terraces, dams). These physical structures are not consideret very stable and need a lot of work to establish and maintain. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Further research to improve physical structures, Jatropha curcas structures as well as their combination. |
|
The roots bind the soil and holding it together and help collecting additional soil that otherwise would be washed out. The root and the plant also help to slow down flowing water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Research on how tolerant is the plant on flooding etc. |
|
Jatropha curcas is also a very good life fence that animals do not browse through because the leaves are poisonous. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create awareness in the society that the plant is poisonous and should not be eaten. |
|
The seeds can be sold. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Creating and improving markets, infrastructures and technologies that need Jatropca curcas oil or biofuel. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Very low labor and money input for establishment and maintenance. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Keep the technology as simple as it is today. |
|
Easy to atopt in a wide range of environments (Jatroha curcas is a rather tolerant plant). How can they be sustained / enhanced? Additional research to improve knowledge of Jatropha curcas. |
|
Selling of the seeds is an additional income. If the seeds are crushed to oil it can substitute for example lamp oil that has to be bought. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve market situation and find technologies suitable to use Jatropha curcas oil or biofuel. |
|
The plant can be used in a wide range of rehabilitation purposes (gully rehabilitation, hill stabilization, improvment of micro climate etc.) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create and maintain awareness of the farmers. |
|
If plantet on bare land only, the plant does not compete with food production. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Sensitize the farmers that food is more important than gaining an extra income so they do not give up their fields for Jatropha seed production. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| If children eat the seeds they get sick. | Rise awareness that the plant is poisonous. |
| Plant competes for soil moisture. | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade as well as maximum soil moisture that can be taken by the plant to maximize yield. |
| Plant competes for sun light. | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade as well as maximum soil moisture that can be taken by the plant to maximize yield. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Jatropha curcas is an alien plant although it is used for more than 30 years in the region. | Research on the long term effects of Jatropha curcas in specific areas. |
| If the plant should reach maximum yields inputs have to be increased as well and it has to be planted on fertile soil (food competition). | Make shure people only use it as fence or as a SWC plant on bare land. |
| To avoid shading the plant is often pruned every year and the yield is therefore very small (economically irrelevant). | Find a good compromise betweeen pruning and maximum toleratet shade to maximize yield. |
| The plant is poisonous. People have to take care and children have to be sensitized. But acording to the farmers eating the leaves or the seeds leads to stomach ache and is not too dangerous. | Create awareness in the society that the plant is poisonous and should not be eaten. |
| Farmers plant and use Jatropha curcas quite randomly and without any specific approach. | The role of science: find the best practice. |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Bach S. (2012) Potentials and limitations of Jatropha curcas as a multipurpose crop for sustainable energy supply and soil and water conservation - a case study in Bati, Ethiopia, using the WOCAT approach. Unpublished master’s thesis, Centre for Development and Environment, University of Bern.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos