Lining geomembrane plastics for water harvesting and storage [Ruanda]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Iwona Piechowiak
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Ibidamu
technologies_1551 - Ruanda
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Muligirwa Emmanuel
+250 078 84 78 645 / +250 788 383040
Emmanuel.muligirwa@fao.org
FAO
P.O. BOX 1502 Bld of the Umuganda, Kigali
Ruanda
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - ItáliaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Rwanda Agriculture Board (Rwanda Agriculture Board) - Ruanda1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
29/01/2014
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST

Participatory approach [Ruanda]
This approach is a contribution of different stakeholders and land users in the identification and resolution of a particular crop land problems, which implicate at the end different stage of intervention by all stakeholders to resolve the problem.
- Compilador/a: Desire Kagabo
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
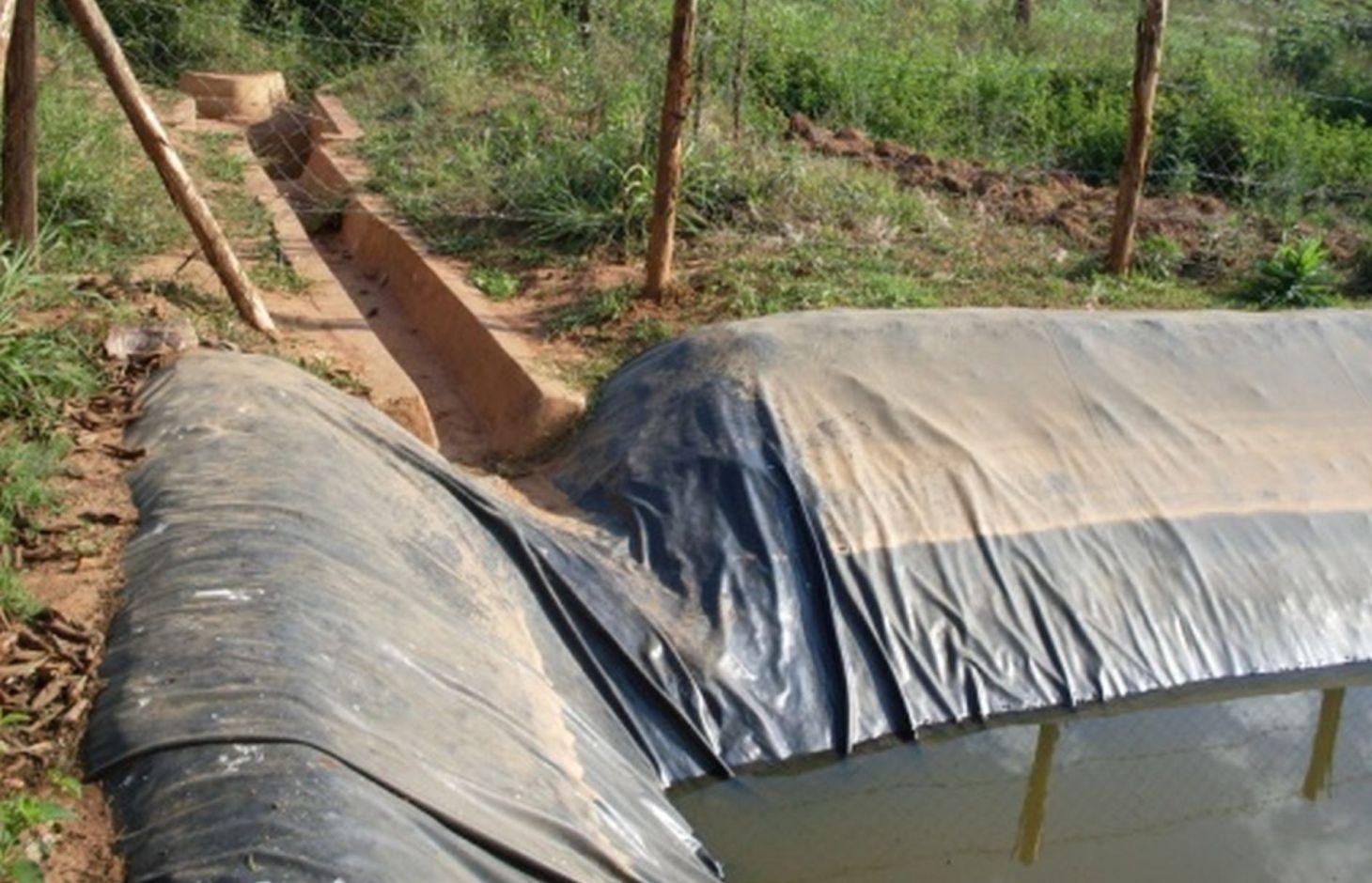
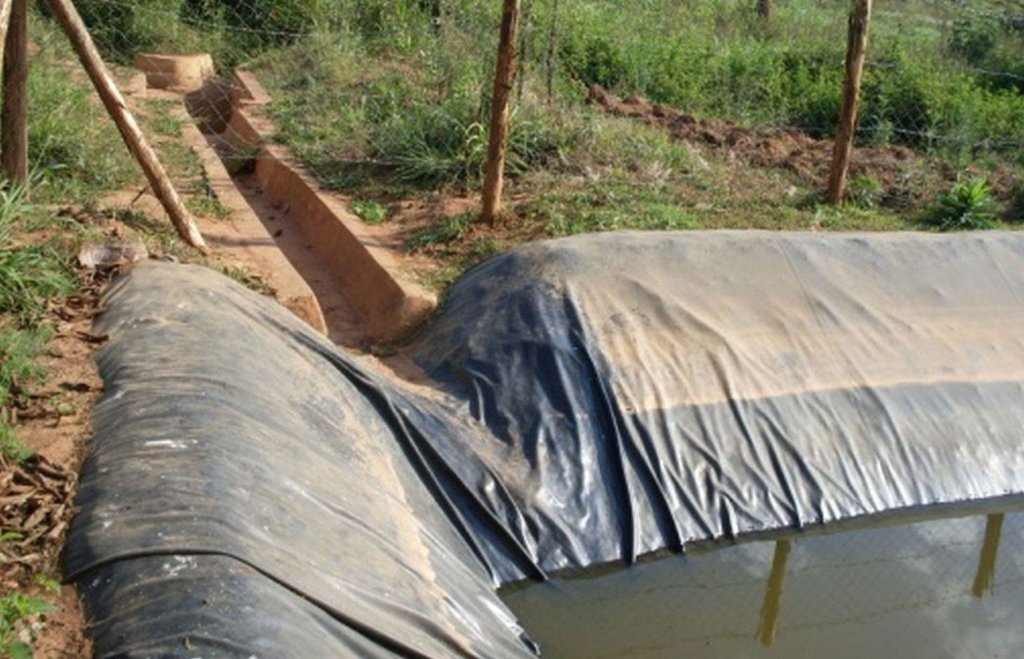
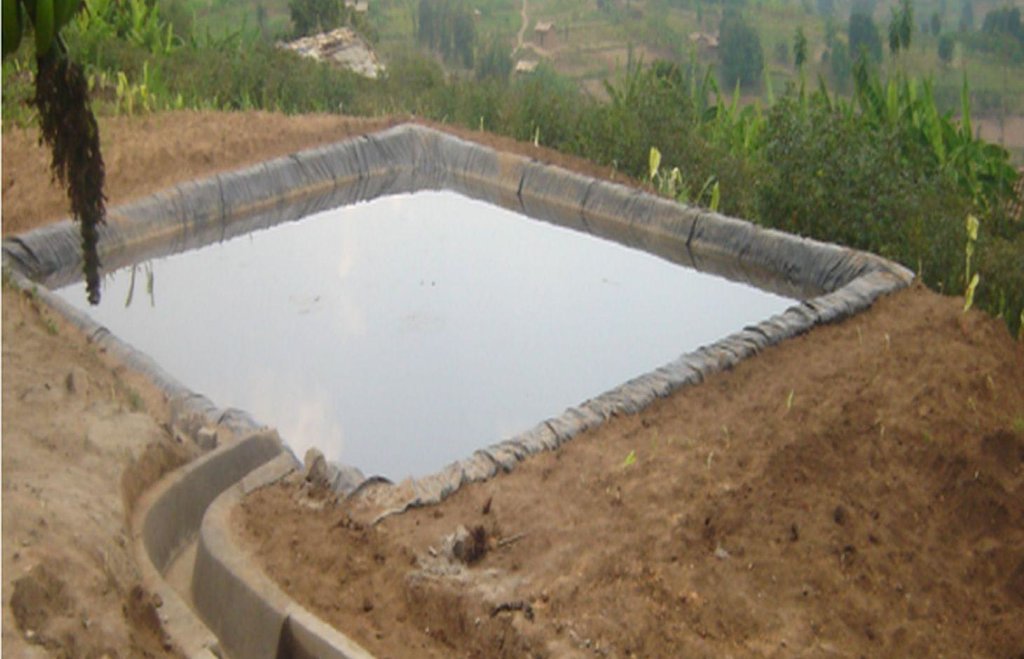
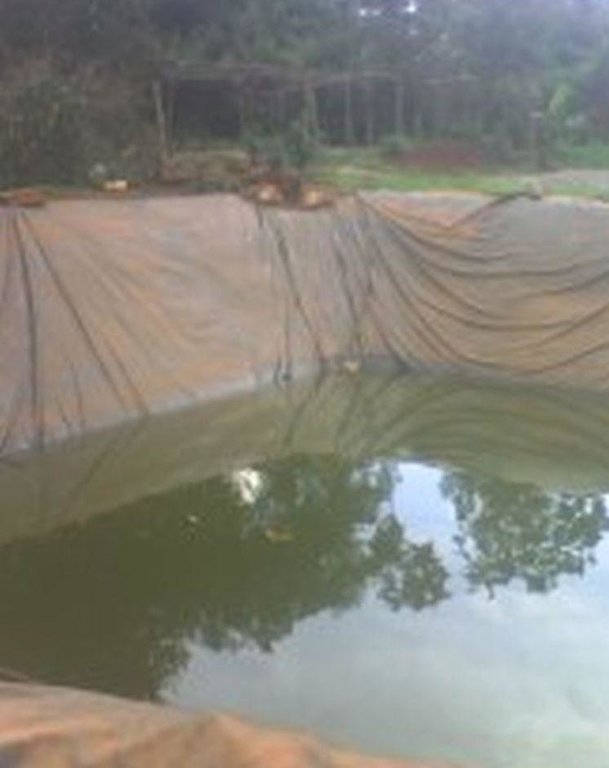
Lining geomembrane plastic for water harvesting and storage is a rainwater harvesting technique used by land users to collect rain water or runoff from a concave watershed to a common well-structured plastic-lined pond for agricultural, domestic and other use.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Rainwater harvesting initiatives were introduced in Rwanda in 2007, through a government-supported project on a pilot basis in three districts (Ruhango, Bugesera and Kirehe). By 2011, the technology had expanded at exponential rates such that the demand has exceeded the supply. Now the supply policy has shifted from government to private still there is a shortage of plastic lining. The typical design of each pond is trapezoidal in shape, measuring 10.5 by 9 meters top-width, 6.5 by 5 meters bottom width and 2 meters depth and a total storage volume about 120 m3. The plastic lining is factory–manufactured with standard shape and size to fit these dimensions. The ponds are made with this standard design to enable bulk purchase and supply of geo-membranes, to make use of economies of scale. The cost of the geo-membranes was subsidized by up to 100% by the government until 2010 but now only 20% are provided by the government. When this project was initiated, activities related to soil excavation was done by the government. However, with time the government pulled out and farmers are now covering the total cost of excavation and the government intervenes only for the technical compliance. The government provides technicians to train farmers on the safety and management of ponds. The volume of water harvested and stored in the ponds is on average 90 m3. However, water retention within the ponds over time differs with from farm to farm as affected by usage, evaporation and seepage losses. Treadle pumps are sometimes used to lift water by some of the farmers. Among most households, the water from the pond is used for domestic, livestock and supplemental irrigation, especially of horticultural crops. About 20% of the water is used for seedling and fruit production, 75% for livestock watering and 5% for domestic use. When the excavation of the pond is complete, the beds as well as sides of the pond have to be leveled and prepared for laying the lining plastic. Any rocks, large stones or other projections, which might damage the lining plastic, should be removed from the beds and sides of the excavated ponds.
Purpose of the Technology: Lining geomembrane plastic for water storage is designed to reduce seepage losses in ponds. This water is used by smallholder farmers to cope with the beginning of dry season and enhance crops to reach the maturity stage safely.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A periodical inspection is required for better life of the pond, thus timely maintenance hold the key of success for longer time. The maintenance includes inspection, repairing damages. Regular investigations are required on the pond sides, bottom, the inlet and the emergency outlet. In addition, the pond should be protected from intrusion of animals by constructing a fence around the pond. It is also important to remove aquatic vegetation, silt and sediment periodically that accumulate on the bottom of the pond.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Ruanda
Região/Estado/Província:
Rwanda
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kayonza District (East provice)
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
- Government
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
the technology was initiated in 2008
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- access to water
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
major cash crop: Vegetables
major food crop: Beans
other: Maize
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): There were poor yields of crops caused by elongation of dry season and increase of runoff soil erosion (intensive rain during rainy seasons) at the previous season.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low crop production, soil erosion
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: September – February; Second longest growing period in days: 120; Second longest growing period from month to month: March – July
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Coleta de água
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
The area was estimated.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Steep slopes in many cases over 60%), population pressure (Rwanda’s natural resource is subject to a high density of population with an average of 400 people per ha)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing, urbanisation and infrastructure development, poverty / wealth (Farmers have low income and have less access to off farm income or remittances), education, access to knowledge and support services (High rate of irriteracy)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
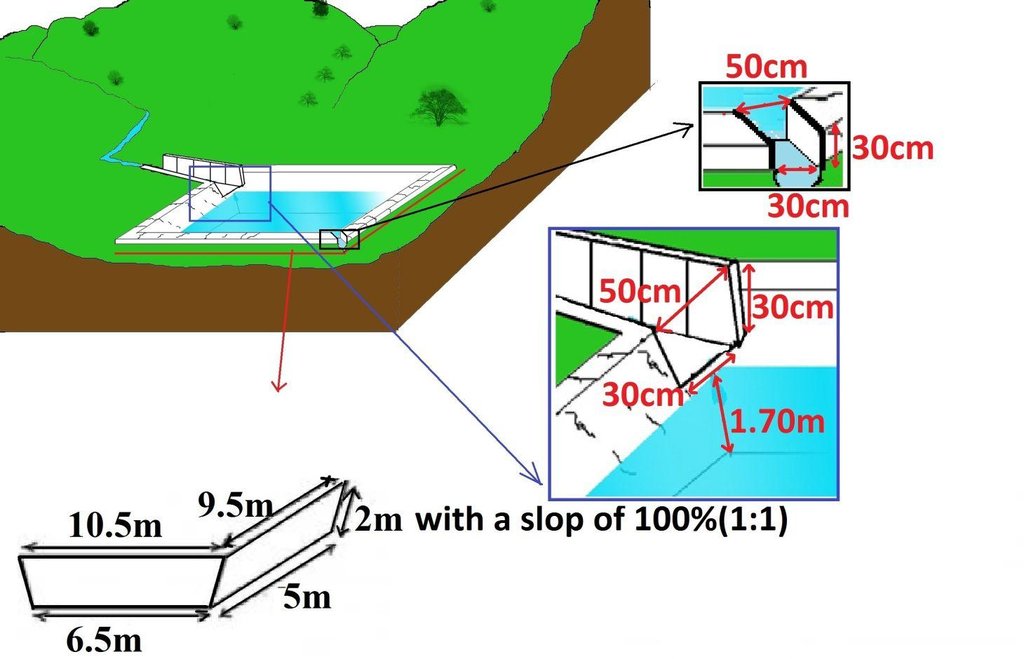
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Surface runoff water storage pond have got a reservoir of 10.5m x 9.5m at top and 6.5m x 5m at bottom and a depth of 2m with side slope of 1:1.5. The capacity of one pond is estimated about 120m3.
Location: Kabarondo. Kayonza/West/Rwanda
Date: 2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (The technology need skilled engineers)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (It need moderately skilled labor to construct the technology under supervision of engineers.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply
Secondary technical functions: water spreading
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 2
Spacing between structures (m): 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 9.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 10.5
Construction material (earth): the original land is digging
Construction material (stone): stones are used to concrete the pond inlet and outlet
Construction material (concrete): Cements, sand
Construction material (other): fencing wire and waterproof steering(plastic sheet)
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 120m3
Catchment area: 6ham2
Beneficial area: valleym2
Slope of dam wall inside: 50%;
Slope of dam wall outside: 50%
Dimensions of spillways: 0.8m x0.6mm
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:0.25
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Rwandan francs
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
640,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
1000
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Surveying | Estrutural | any time |
| 2. | Buying materials | Estrutural | Any time after surveying |
| 3. | Construction of pond | Estrutural | Dry season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Surveying | persons/day/ha | 4,0 | 45000,0 | 180000,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of pond | persons/day/ha | 180,0 | 1000,0 | 180000,0 | 80,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | pieces/ha | 100,0 | 3000,0 | 300000,0 | 20,0 |
| Material de construção | Cements | kg | 300,0 | 200,0 | 60000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Plastic sheet | m2 | 24,0 | 2500,0 | 60000,0 | |
| Material de construção | Stone | m3 | 8,0 | 562,5 | 4500,0 | |
| Material de construção | Sand | m3 | 8,0 | 390,625 | 3125,0 | |
| Material de construção | Fencing wire | m2 | 24,0 | 625,0 | 15000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 802625,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | regular maintenance of Channels and all around the pond. | Estrutural | Rainy season |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Regular maintenance | persons/day/ha | 10,0 | 1000,0 | 10000,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 10000,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: hoes, meter, clinomrter, ect....
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The most factors that affects the cost is the construction materials and labor.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is medium - high
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is very high - high
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4%
55% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
45% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land.
Market orientation of production system: (Begetables)
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
200 kg
Quantidade posterior à GST:
800 kg
Risco de falha de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
50%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
10%
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
40%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
80%
Comentários/especificar:
40% of income increases due to increase of agriculture
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
The technology improved the productivity so that farmers had means to take health insurance
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Increases up to 15%
livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
It has increased income of household hence enhance life.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Comentários/especificar:
60% improved
Solo
Perda de solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Controle de praga/doença
Quantidade anterior à GST:
20%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
50%
Comentários/especificar:
It increases the predominance of mosquito
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Sedimentação a jusante
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
neutro/balanceado
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
It require light labor during the maintenance activities
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
260 household covering 90 percent of stated area
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
250 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
10 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Income generation How can they be sustained / enhanced? More financial support and trainings |
|
Improvement of production How can they be sustained / enhanced? To make a regular maintenance of ponds |
|
Soil erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Divert more runoff to mitigate the soil erosion downstream and always clean the conveying channel. |
|
Impermeable material How can they be sustained / enhanced? Acquisition of high quality plastics that can last many years |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Occasional accidents | To maintain fences around the pond and increase awareness about accidents around a pond, especially for parents (high risk for small kids) |
| Pond attract various insects and diseases (habitat for Mosquitoes) | Mosquito nets are needed |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Participatory approach [Ruanda]
This approach is a contribution of different stakeholders and land users in the identification and resolution of a particular crop land problems, which implicate at the end different stage of intervention by all stakeholders to resolve the problem.
- Compilador/a: Desire Kagabo
Módulos
Não há módulos