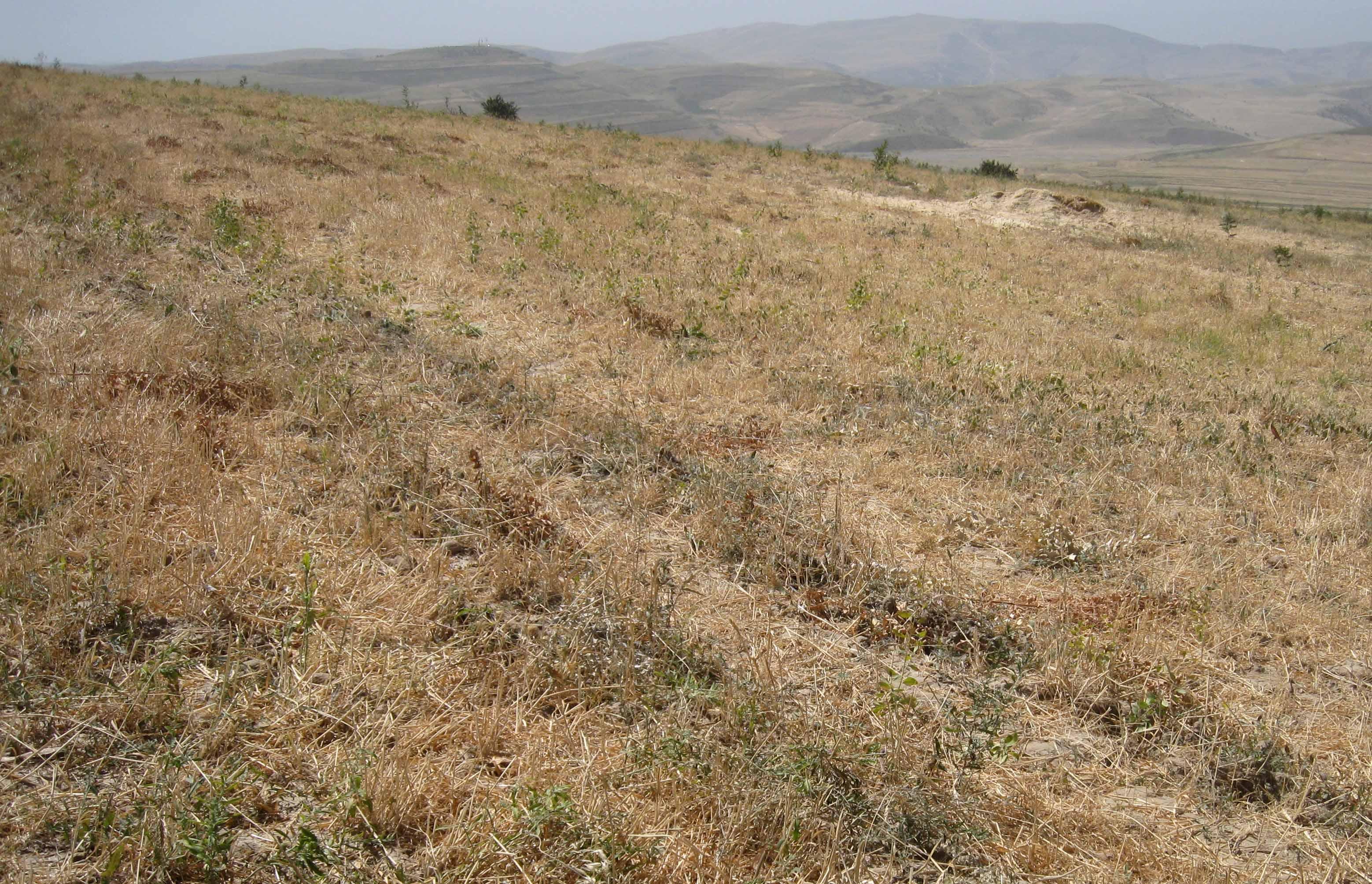
Current wheat crop in rotation with chickpea cultivation [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Malgorzata Conder
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1552 - Tajiquistão
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
06/09/2012
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Current wheat crop in yearly rotation with chickpea cultivation
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The rainfed crop of the farmer sizes around a hectare. He owns the crop since seven years and switches between chickpea and wheat every year. When he started to cultivate, soil properties were good, he did not use fertilizer. Because of the years of ploughing, the soil lost nutrients and moisture. The more rill building and slope instability is severe currently. The plot is over one hectare because it includes a narrow vegetation strip between his and the neighbours crop. The plot, as all the other crops are grazed by livestock, after harvest.
Purpose of the Technology: Chickpea cropping generates a satisfactory yield, whereas wheat production is rather variable and low. Nevertheless the farmer would not change the crop type because the main purpose is to get straw for feeding his cows. The farmer has over three hectares in total. Even though he claims the benefit to be low comparing to the input, he is content as long he can feed his family.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Ploughing, sowing and then harvesting were part of the establishment phase. The same activities count for maintenance. But as soil is gradually washed away, fertilizing became crucial. The farmer does not control and protect the crop from wild animals and grazing herds.
Natural / human environment: The crop lies on a foot slope not far from the riverbed. Neighbouring cultivations are of the same crop type, chickpea, wheat and food grain. It is less than one kilometre away from the farmers home in Doshmand village. Access to services is rather low, especially in winter, because of the bad condition of the road. Doctor, middle and higher school grades and market are in the village below.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Khatlon, Tajikistan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Muminabad
Map
×3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Major food crop: Wheat
Comentários:
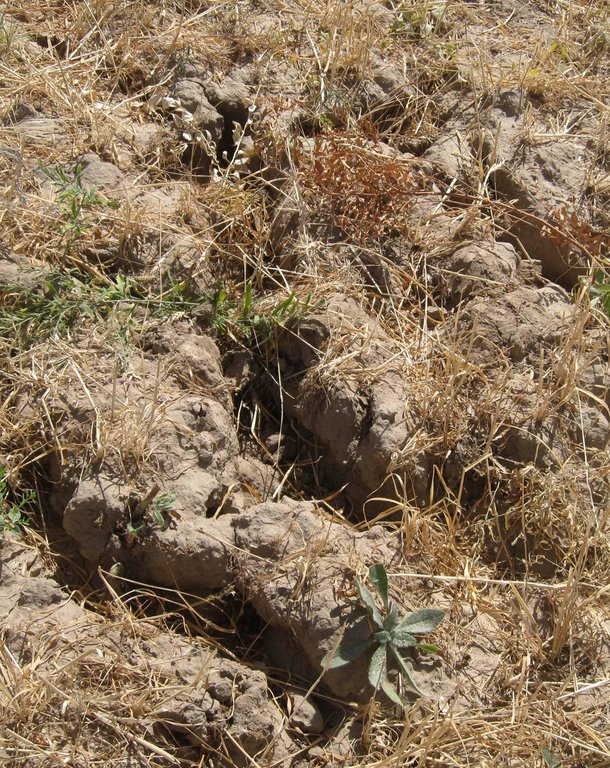
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Sealed and compacted topsoil, which hinders infiltration. Hardpan is propable due to plowing. Erosive processes with rill building are relatively widespread on the crop. A lot of plowing rills aggrandize by runoff. A lot of licorish plant grow on the crop, which is a indicator for degraded soil. Soil shows a low level of organic matter, nutrients and moisture.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Increasing soil wash out with simultaneos augmentation of fertilizer input over years. Rills destroy crop growth, reason why yield quantity and quality is decreasing.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Farmer doesn't try hard to get a better yield. As long as he can feed his family he doesn't see the real need to do that.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180 Longest growing period from month to month: March to September
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- sistema rotativo (rotação de culturas, pousios, cultivo itinerante)
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.01 km2.
Crop counts around 1 ha. Total plot is over 1 ha, because of a narrow vegative strip underneath the crop.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pk: quebra e ressecamento

Degradação da água
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pk: sealing and crusting, Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Main causes of degradation: soil management, crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), land tenure (For private cropping and communal grazing)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing, disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Contour lined plot, with a vegetation strip of < 1m width, between this and the underneath plot. A lot of rills visible.
Location: Doshmand, Chukurak Watershed. Muminabad, Khatlon, Tajikistan
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase / maintain water stored in soil
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Somoni
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
4,83
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
12.40
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Sowing | Person days | 0,25 | 12,4 | 3,1 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Applying fertilizer | Person days | 0,25 | 12,4 | 3,1 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Cutting wheat | Person days | 18,0 | 12,422 | 223,6 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Plowing | Person days | 0,4375 | 12,4 | 5,42 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine use | Hours | 3,5 | 5,914 | 20,7 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Petrol | Liters | 40,0 | 1,1375 | 45,5 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | 150,0 | 0,414 | 62,1 | ||
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | Bucks | 2,0 | 31,05 | 62,1 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 425,62 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.125 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plowing, 3.5 hours, 1 person | Agronômico | every year, spring |
| 2. | Sowing wheat, 1 hour, 2 persons | Agronômico | every year, spring |
| 3. | Applying fertilizer (not in the first year), 1 hour, 2 persons | Agronômico | only once a year in spring, more year by year |
| 4. | Cutting wheat, 6 days (à 8 hours), 3 persons | Agronômico | once a year, around semptember |
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Establishment and maintenance cost are similar. Agricultural inputs as seeds and fertilizer are the highest expenditures. As soil nutrients are washed out, the fertilizer input rises gradually.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Totally 800 mm: 700mm in winter-spring, July-Sept dry season
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: temperate, LPG from end of March until September
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (1600 m asl)
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility: Low
Soil drainage/infiltration: Poor (sealing and probably hard pan)
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Off-farm income specification: The farmer has in total over 3 ha of crop. The output of straw of this one hectare makes 40% of his total income.
Level of mechanization: Manual labour (harvesting wheat) and mechanised (plowing)
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
2.06 ha (household 7.7 members)
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
Land ownership is based on the Land user's certificate
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Risco de falha de produção
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
demand on fertilizers is increasing
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
gradually increasing
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Only on long term according to the farmer
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Many rills
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Velocidade do vento
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
Comentários:
The crop would be less sensitive to heavy (seasonal) rainfalls or droughts if vegetation cover or mulching would be improved.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Comentários:
Farmer knows that there is no real benefit when looking at the input. Over the years it got slightly negative because more fertilizer is needed and yield is decreasing.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Vegetation strip underneath the crop is an idea to develop as it reduces the negative offsite effects. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Knowledge transfer about how to reduce offsite effects. Soil cover could rise in that strip, thanks do what soil erosion woul be stopped. Enhance communication between above and below vegetation strip cultivating farmers. |
|
Maintain and develop crop rotation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Knowledge transfer and field studies on other plots with crop rotation (e.g. perennial crops). |
| Plowing horizontally. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Too much soil erosion causes rills. | Another crop type according to the steepness of the plot. Change plowing deepness or do human-powered tillage. |
| Development of soil crust, sealing and hardpan. | Enhance crop rotation and "soft" and horizontal tillage practices. |
| Observed trampling and grazing of the plot. | Guarding or fencing of the plot. Guarding could be organized by several farmers in rotation. |
| Poor pecentage of organic matter. | Introduce mulching. |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos