Closed Pipe-conduit [China]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Mei Zhao
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Deborah Niggli
Rat tunnel tillage
technologies_1556 - China
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Lingqin Meng
Division of water and soil conservation, Songliao water resources commission, ministry of water resources P.R. China
China
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Songliao Water Resources Commission (Songliao Water Resources Commission) - China1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
28/02/2013
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
A Rat tunnel is a kind of subdrainage. It is a drainage duct formed through extrusion or oscillation in soil layer by pulling a mole plough with a tractor. The rat tunnels in a field should be used together with a concealed conduit drainage system in order to safely and quickly drains the water in the rat tunnels and avoid field collapses incurred by poor drainage and washings on the rat tunnels.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
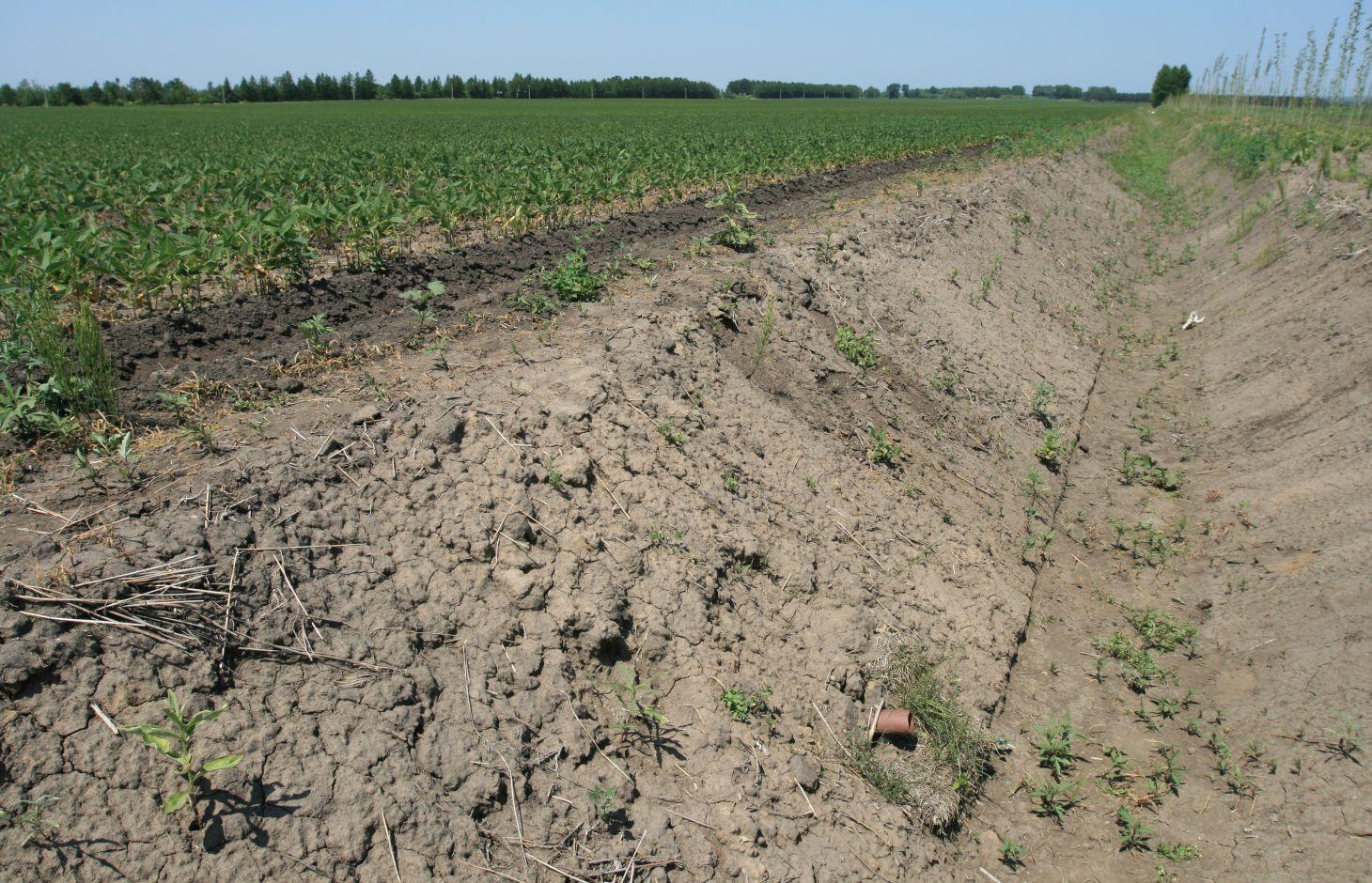
Rat tunnels are suitable for the regions with sticky and heavy soil, thick soil layer, and lower infiltration rates, high underground water level and where waterlogs are very likely to happen. By applying the rat tunnels, infiltration can be increased, soil salinization can be prevented without affecting the growth of the crops and occupying croplands. Good effect can be achieved by combining rat tunnels with closed conduits in application. Closed drainage refers to burying the drain pipes underground and letting the underground water flow along the fissures between the pipes and penetrate into the tubes and drained. In a field, if rat tunnels and closed conduits are combined for use, the rat tunnels constitute the first-grade drainage system, the closed conduits constitute the second-grade drainage system; the stagnant water in the plough layer penetrates through the soil and rat fissures and converges into the rat tunnels; While draining the water inside themselves to the outside, the rat tunnels collect the inside stagnant water and guide the water into the closed conduits, through which the water is discharged. In this way, the surface water can be discharged in a relatively thorough way.
Increase of soil infiltration, rapid discharge of direct surface runoffs, prevention of soil salinization.
In building such a project, the closed conduits should be built first, followed by the building of the rat tunnels; the closed conduits should be under the rat tunnels, the included angle between a closed conduit and a rat tunnel should be 90°.
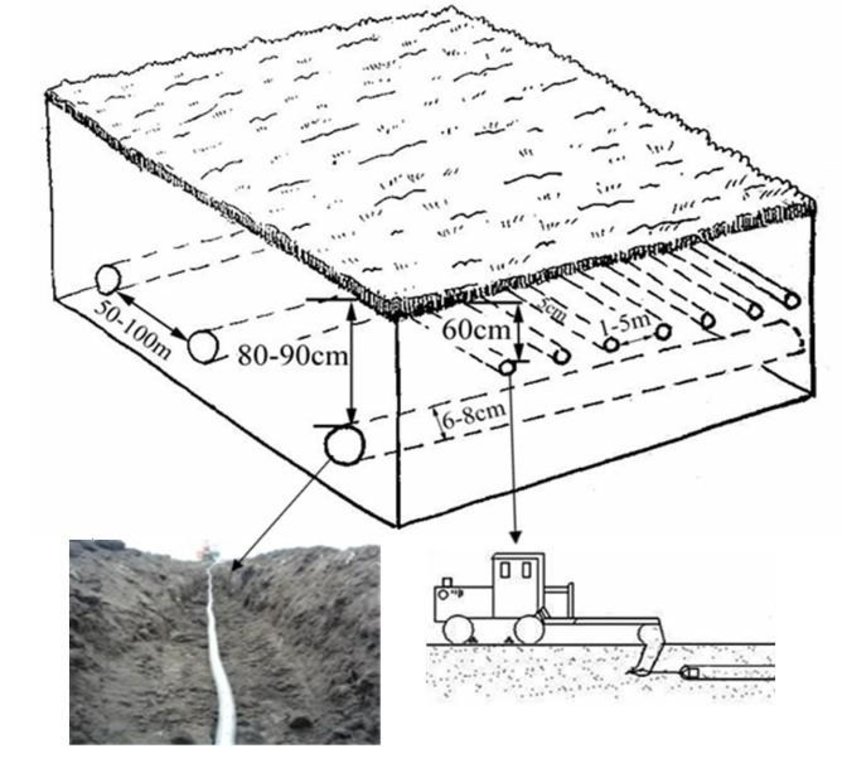
The gap between two neighboring laid closed conduits should be 50m-100m. The burying depth of a closed conduit should be 80cm-90cm, the area around the closed conduit should be evenly laid with a layer of coarse gravels 5-8cm in thickness. After the project on the closed conduits in a field is accomplished, restore the flatness of the field surface, then undertake the operation on the rat tunnels.
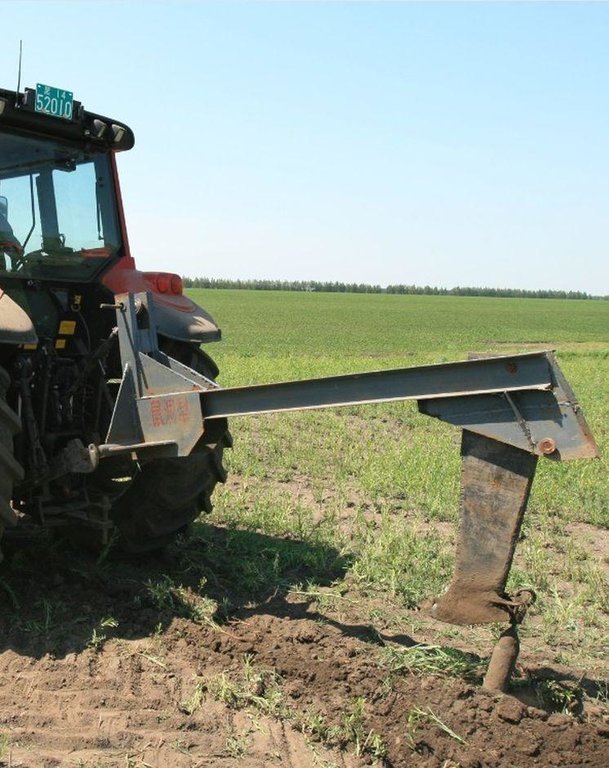
In building the rat tunnels, a tractor is directly applied to pull the mole plough in accordance with the designed distances. When the tractor moves forward, the mole plough goes deep into a specified depth(generally 60cm) of soil layer and generates through piercing the soil along the direction of the forward motion of the tractor a tunnel(rat tunnels) whose diameter is equal to bullet diameter and which is in parallel with the ground surface. The separation distance between two neighboring rat tunnels is 1-5m. The service life is generally 2-5 years. If the rate of flow of a field obviously decreases, new rat tunnels should be built by averting the original routes.
After a rainfall, check whether the rat tunnels have collapsed. The service life of the newly laid closed conduits is over 20, however, new rat tunnels should be built every two years.
Rat tunnels are mainly distributed on the Three River Plain, which is the largest marsh distribution area. It has a total population of about 8.625, with the population density being about 79/km2. With the annual average temperature being 1℃-4℃,being warm in summer with the average temperature being over 22℃, having an annual amount of precipitation of 500-600 mm with the rainfall seasons mainly concentrated in the hot seasons from June to August, the Three River Plain is suitable for the growth of crops. The area is affluent in water resources, with the total quantity reaching about 18.764 billion/m3. In this area, the per capita cultivated land area is about 5 times of the average level in China. There are also about 2.52 millions of theropencedrymion distributed in the terrains with low mountains and hills.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
China
Região/Estado/Província:
Hei Longjiang
Especificação adicional de localização:
San Jiang Plain
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): high underground water level, lower infiltration rates,Soil salinization
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): It's hard to drainage excess water. Lower soil fertility
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150, Longest growing period from month to month: From April to September
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Desvio e drenagem de água
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- > 10.000 km2
Comentários:
This technology is widely used in San Jiang Plain.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação
Comentários:
Causes of degradation: soil management (Backward management modes), change of seasonal rainfall (The rainy seasons mainly focus on summer), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (The land can't drainge the excess water after downpours), population pressure (Population pressure makes extensive cultivation in this region), land tenure (As the lands are owned by country or by peasant communities, the peasants will not protect their land initiatively.), education, access to knowledge and support services (The channels for the local peasants get knowledge are few, and they will not learn knowledge initiatively.), governance / institutional
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Diameter of closed conduit: 6-8cm, separation distance between two neighboring closed conduits: 50-100m, burying depth: 80-90cm: Diameter of rat tunnel: 5cm, separation between two neighboring rat tunnels: 1-5m, depth: 35-100cm(generally being 60cm). If the depth of the rat tunnels is >60cm, the depth of the closed conduit should be adequately increased.
Location: Hong Xing Farm. Hei Longjiang Province
Date: 2012-7-19
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (It's complicate to constructe this technology)
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Structural measure: Closed conduit
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0
Spacing between structures (m): 50-100
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 8-9
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.06-0.08
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): >50
Structural measure: Rat tunnel
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0
Spacing between structures (m): 1-5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.05
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): >50
Construction material (other): A closed conduit is a kind of corrugated plastic conduit with the diameter generally being 6-8cm and
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0%
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Ren Min Bi
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
6,25
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
60.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Layout the line of Closed Conduit | Estrutural | Spring |
| 2. | Laid closed conduits | Estrutural | Spring |
| 3. | Build rat tunnels.The tractor is directly applied to pull the mole plough in accordance with the designed distances. | Estrutural | Spring |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | labour | ha | 1,0 | 64,0 | 64,0 | |
| Equipamento | first machine | ha | 1,0 | 224,0 | 224,0 | |
| Equipamento | second machine | ha | 1,0 | 24,0 | 24,0 | |
| Material de construção | corrugated plastic conduit | ha | 1,0 | 640,0 | 640,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 952,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Build rat tunnels. | Estrutural | every two years |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipamento | second machine | ha | 1,0 | 24,0 | 24,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 24,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Mole Plough, refer to the photo of technical drawing.
The accounted costs for each hectare are as follows: Depth, diameter and spacing on closed conduit: being 90cm, 8cm and 80m respectively, the closed conduits with a total length of 200m are required for each hectare. 1. Costs of closed conduit laying: Tractor cost is 224$US ; Expense of the conduit materials is 640$US; Labor expense is 64$US. 2. Costs of rat tunnel building: Machinery cost: 24$US/hectare (the operation efficiency: 30 hectare/day). No maintenance cost. However, new rate tunnels should be built with the same costs(24$US) every 2 years. The service life of the closed conduits is over 20 years.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The most determinate factors is the cost of corrugated plastic conduit.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate, boreal
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Excesso
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
10% of the land users are very rich.
45% of the land users are rich.
35% of the land users are average wealthy.
10% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Apart from farming, the main works of the local people involve doing works for others in cities and towns or doing business.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Grande escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
The lands are owned by country or by peasant communities.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Produção animal
Produção de madeira
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Disparidades econômicas
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Oportunidades culturais
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Atenuação de conflitos
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
contribution to human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Local peasants learn some knowledges of soil and water conservation though this technology.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Drenagem de excesso de água
Lençol freático/aquífero
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Salinidade
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
95% of all households
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
This technology only be implemented by farmers, because it's too expensive for peasant to afford it. If farmers implement the technology, the local government will organization peasants to help farmers, the government pay for the wages.
A few of land users will implement the technology without any external material support.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Fast drainage of surface water |
| Prevention of soil salination |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| New rat tunnels should be built every two years |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Complicated in construction, big investment | seeking other substitutes |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Techniques standard for comprehensive control of soil erosion in the black soil region, Author: Shen Bo; Meng Lingqin, Years: 2009
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Internal book
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos