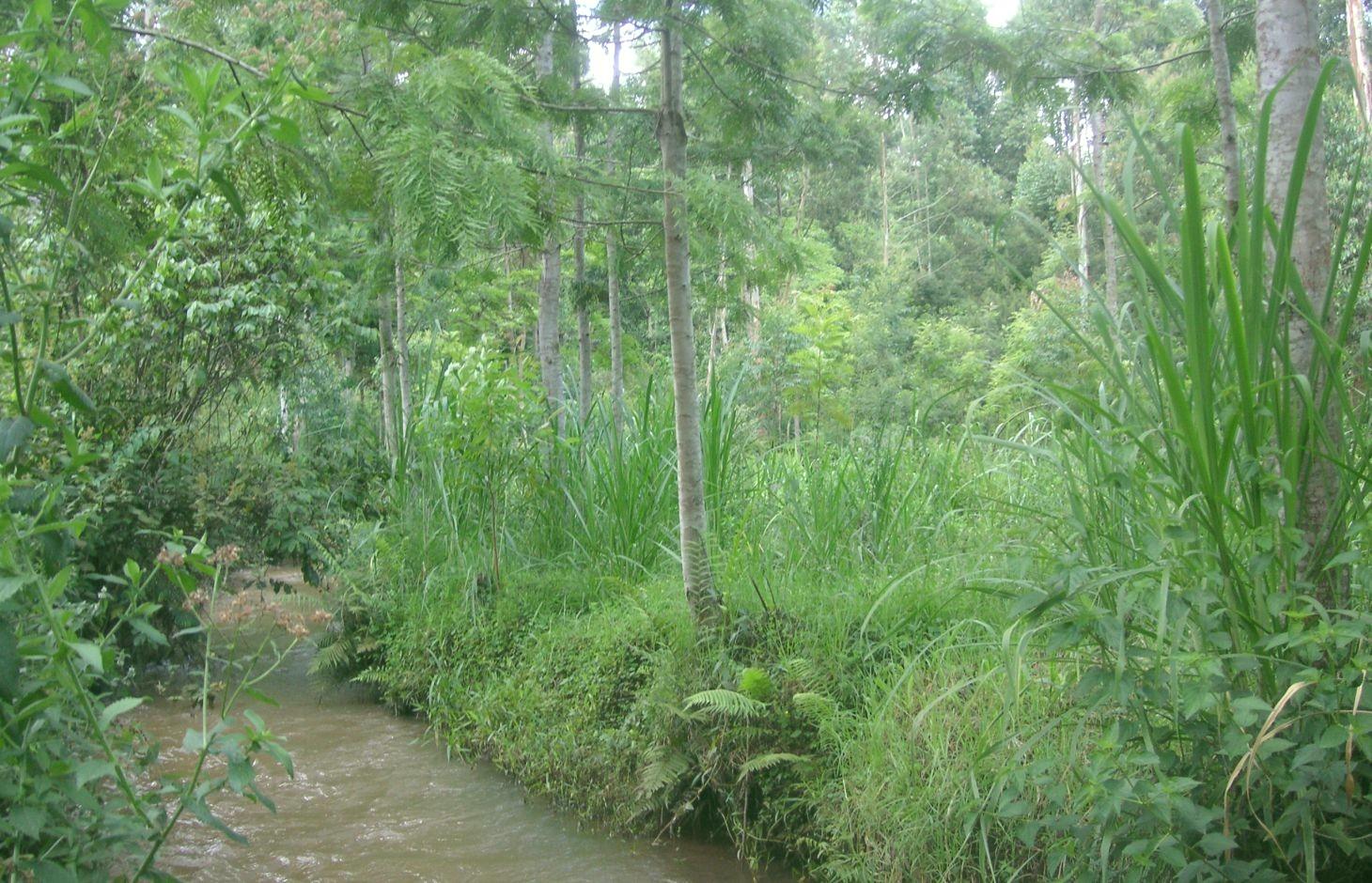
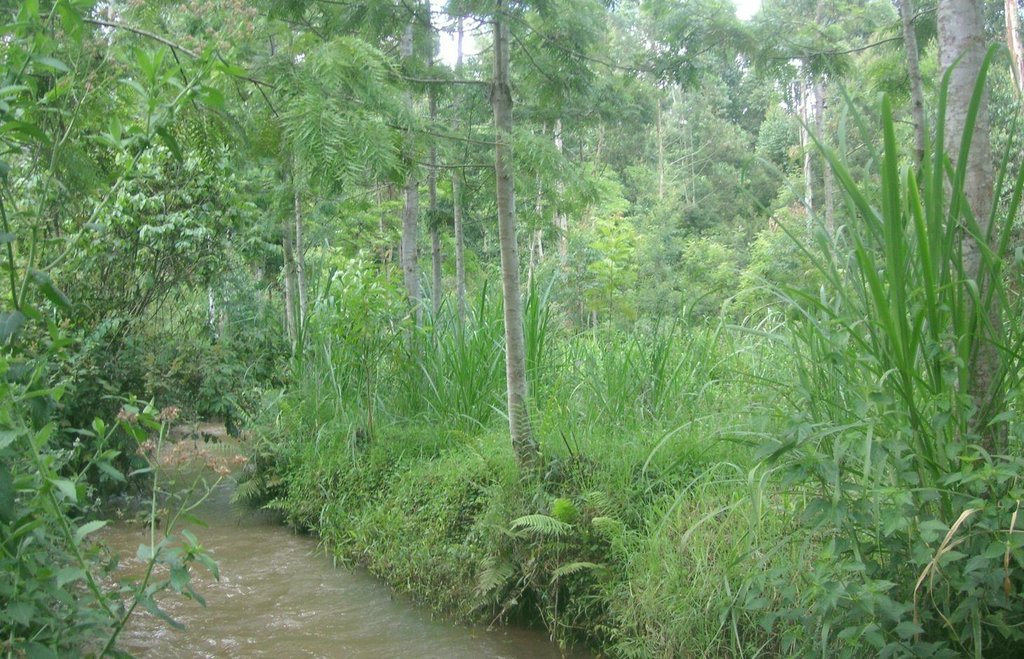
Productive use of the riparian area using Napier grass and protection of the riverbank with indigenous trees at Kapingazi River [Quênia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Manuel Fischer
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
technologies_1558 - Quênia
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Productive use of the riparian area using Napier grass and protection of the riverbank with indigenous trees at Kapingazi River: 28 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Productive use of the riparian area using Napier grass and protection of the riverbank with indigenous trees at Kapingazi River: 4 de Setembro de 2019 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
usuário de terra:
Nyaga Robinson
0726 408 839
Quênia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
16/11/2012
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
A riparian area that is frequently flooded requires a special treatment because conventional agriculture is not possible. Trees along the riverbank and Napier grass on the remaining space still allow a productive use despite the difficult circumstances.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
On the southeastern slopes of Mt. Kenya, the circumstances are ideal for agricultural activities, the rains are plenty and normally reliable. The plot owner started realizing a problem of riverbank degradation 17 years ago. But still he continued the traditional way of agriculture, planting beans and maize. Since his plot is on the slip-off slope only few metres above the river level, it experienced regular floods in case of heavy rainfalls, destroying the plants and leading to crop failures. Conventional plants like maize and beans do not resist such an excess of water. To fight the land loss and the bad harvest, the farmer introduced indigenous trees along the river and Napier fighting the riverbank degradation. Behind that, several rows of the flood resistant Napier grass were planted to still use the area in a productive way.
Purpose of the Technology: Above all, the goal of this technology is to get a high grass production. As a side effect results a quite good protection of the riparian area. The vegetation prevents rainwater from running directly from the fields into the water. Therefore, the chemicals from the field get stuck in the riparian soils and don't pollute the river. In the same way the infiltration in the riparian enlarges the total infiltration since the water would go to the river directly. Especially the raw surface of the riparian allows more infiltration and interception storage of water. This surplus of stored water is able to provide river water for a longer period, when rains are humble for a longer period. In case of floods, the increased infiltration potential can cut the peak flow and thus prevent damages. The grass yield is used as a fodder for the cows.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Before planting the indigenous trees, water guzzlers like eucalyptus trees were cut down. Indigenous seedlings were planted right along the river at a distance of 1 m. Behind the tree row, Napier grass is planted and harvested twice a year. The cutting and harvesting of the grass is done regularly such that animals can be provided with fodder every day. As soon as the trees are big enough, they function as a source of fire wood, they can be pruned every 5 months.
Natural / human environment: The studied plot is situated between the tea and the coffee zone at an elevation of 1663 m.a.s.l. This small-scale farm does not produce tea nor coffee, there is mainly subsistence agricultural production and some few products are sold on the market. Rainfall is reliable and ensures a regular production.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Quênia
Região/Estado/Província:
Kenya/Eastern Province
Especificação adicional de localização:
Embu
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Farmer asked neighbours for advice.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Pastagem
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
Principais espécies animais e produtos:
Cows are living on the farm. The farmer carries the fodder to the stall.
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The excessive water on the plot hinders conventional agriculture and the floods lead to riverbank degradation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The land plot is situated right beside the river and is less than a metre above the river. Flood destroyed regularly the harvest of maize or french beans. Parts of the riparian have been removed.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Comentários:
Water supply: Also post-flooding
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 90 Longest growing period from month to month: march to may Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: october to december
Densidade animal (se relevante):
> 100 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- variedades vegetal/raças de animais melhoradas
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
The area along the river is very small, namely 750m2.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wr: erosão das margens

Degradação biológica
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade

Degradação da água
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wr: riverbank erosion, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, floods (The floods are mostly responsible for the riverbank degradation and destroy conventionally cultivated crops.)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), population pressure, land tenure (By law the riparian should be protected. The land owner uses it in a productive way.), poverty / wealth
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
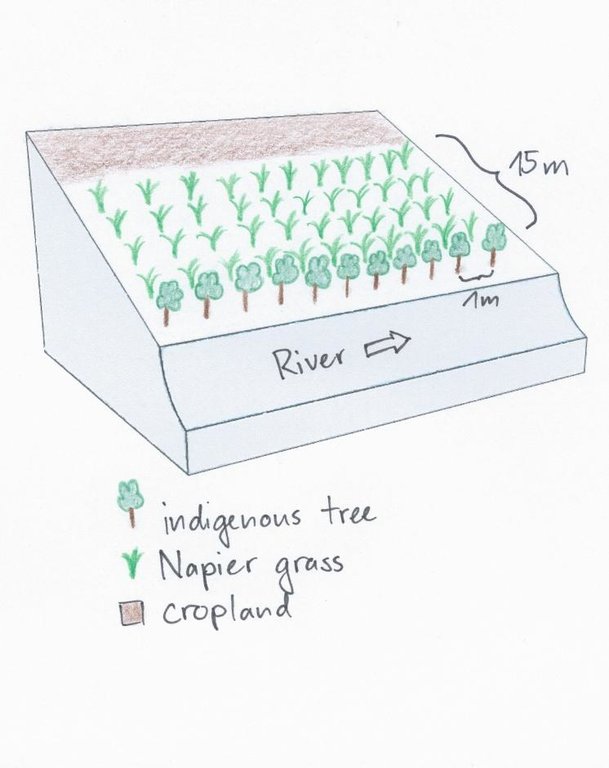
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
A tree row is aligned directly beside the riverbed with a spacing of 1m. Directly behind the trees, Napier grass is planted up to a width of 15m. Adjacent to the Napier grass, there is cropland.
Location: Manyatta. Embu West / Eastern Province
Date: 28.12.2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of biomass (quantity)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.8
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.8
Trees/ shrubs species: Grevillea, Mutundu, Miburu, Mulinga, Mugumo
Grass species: Napier Grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0%
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
3.33
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Chopping bad trees | Vegetativo | anytime |
| 2. | Tree planting | Vegetativo | rainy season |
| 3. | Planting of Napier grass | Vegetativo | Beginning of rainy season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Chopping bad trees | Persons/day | 2,5 | 3,2 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Tree planting | Persons/day | 5,0 | 3,6 | 18,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting of Napier grass | Persons/day | 2,0 | 2,75 | 5,5 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seedling | Pieces | 70,0 | 0,114285 | 8,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 39,5 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.3 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Adding manure | Vegetativo | 2 times a month |
| 2. | Harvest of Napier | Vegetativo | 2 times per year after rainy season |
| 3. | Pruning | Vegetativo |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Adding manure | Persons/day | 0,2 | 2,25 | 0,45 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Harvest of Napier | Persons/day | 2,0 | 3,3333 | 6,67 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Prunning | Persons/day | 2,0 | 3,25 | 6,5 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 13,62 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Jembe (Hacke), Panga (Machete)
The plot is situated right at the riverside and gets flooded regularly. 70 trees were planted along the river in one row. The area of the Napier grass is approximately 750m2 big, harvest is two times a year. Costs were calculated in 2012.
The costs per hectare were calculated for a riparian area with a length of 100m and a width of 10m, since hectares are difficult to apply on a riparian context. The determinant factor for the costs is labour and the area of the plot. The required equipment like a spade is available on nearly every farm or can be borrowed from neighbours and is thus not added to the costs.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1703,00
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
source: http://www.wri.org/publication/content/9291
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: tropics. http://www.levoyageur.net/weather-city-EMBU.html
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: 1668 m a.s.l., source: aster gdem
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture (topsoil): It is called Murram
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Species diversity: Also low
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Market orientation of production system: Family of 10 children
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
Abstractions are controlled by the local Water Resource Users association (WRUA), but everybody can take water by hand.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Produção animal
Risco de falha de produção
Renda e custos
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Fuelwood production through pruning
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Qualidade de água
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade de habitat
Outros impactos ecológicos
Stabilization of riverbank
Infiltration
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Sedimentação a jusante
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
Establishment and maintenance costs are quite low.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
15% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The knowledge is spreading and people acknowledge the benefits.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Protection of the riverbank and reduced riverbank erosion. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Regular management of riparian trees by replacing dead trees with new ones. |
|
Productive function of the Napier grass in terms of fodder and of the trees in terms of pruning for fire wood. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Careful use of the trees and the grass enables a sustainable use of the plants. |
|
No more crop failures. How can they be sustained / enhanced? One should only cultivate plants that can cope with the local excess or scarcity of water. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Riverbank stabilisation due to the plantation of trees. How can they be sustained / enhanced? A good idea would be to establish a second row of trees along the river and thus enlarging the number of trees and their positive effects on riverbank stabilisation and filtering of the runoff. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| After the harvest of the Napier, the land is bare and vulnerable to erosion. | Instead of cutting the whole plot at once, only a quarter of the Napier grass should be cut at once. So that the land is not completely vulnerable to rain. |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos