Unexpected flood risk control in village [Nepal]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Sabita Aryal
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Bhelbadi Niyantran
technologies_1590 - Nepal
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Koirala Pratiksha
Nepal
Gautam Bibhu
Nepal
Mulmi Anjuli
Nepal
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Kathmandu University (KU) - Nepal1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
It is a technology used to control and reduce the effects of downstream flood by physical interventions like construction of spillway, ditch and stone dam on the wall of ditch.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
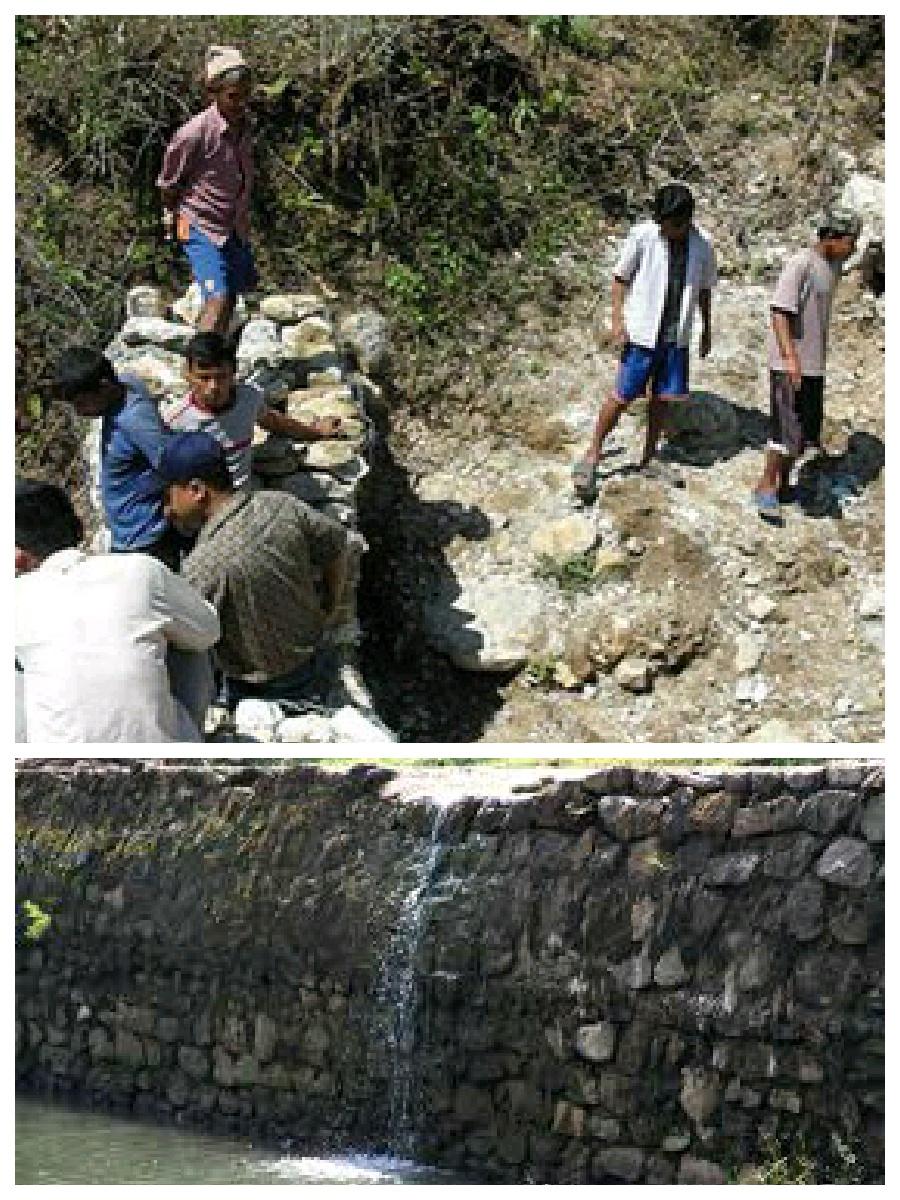
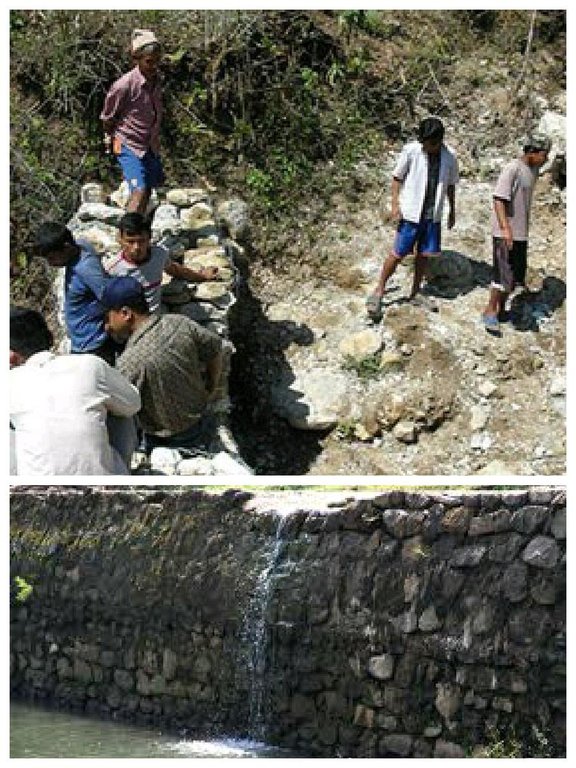
Hilly areas are prone to flash flood that occur with little warning. During rainy season, level of water rises in the stream due to which land mass field of around area was degraded. This technology is used to control the land mass and water flowing from upper region to the lower region of the hill. The natural stream was modified to deep and more sloppy. And surrounding walls were made by piling up stones dams and tighten them by metal wires. These dams decrease the slope gradient and reduce the velocity of water flow and promote the deposition of eroded materials.
Purpose of the Technology: There was no problem of landslide and downstream flood before. But after the road construction, soil became loose resulting in the occurrence of downstream flood. It caused massive destruction of agricultural fields and disturbed settlement areas. Also, stone and gravel during landslide and stream flood used to be deposited and block the flow of the water. So land user invented by this technology to control and reduce the effects of downstream flood.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Land users and other villagers took the initiative to carry out the technology. Stones were abundantly found in the stream that were utilized to make the dams on lining the stream. Dozer was used to deepen the stream and increase the slope of stream. Stones were piled up and tied by iron wires on the bank of stream by local farmers themselves with their own investment.
Natural / human environment: The area where this technology has been used is a hilly area. Soil fertility in that area is low or medium which differs according to the place. Due to landslide and downstream flood, sand and gravel get deposited in the cropland, so its fertility is very low. No crops can be grown in there. This technology helps to control further degradation of land but could't help to restore natural quality of land.
This area is semi arid area. Due to the proper supply of water the area is prevented from drying. People living in that area are mainly farmers and depend on agriculture for livelihood. Also the area is developing more after the road construction. People are now being more aware about health, education and development.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Nepal
Região/Estado/Província:
Nepal
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kavre
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The problem of downstream flood was caused before two years after the construction of road. so technology was also developed before 2 years.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Reduzir riscos de desastre
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Vias navegáveis, corpo d'água, zonas úmidas
- Waterway, ditch
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Cropland destruction
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Cropland destruction, vegetation destruction, decreased soil fertility.
Constraints of waterway/ditch (Ditch for the flow of water): Big stone which block the water ways.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 3
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 150; Longest growing period from month to month: june-november; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: march-june
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de água de superfície (nascente, rio, lagos, mar)
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
Comentários:
The area occupied by SLM technology is approximately 28 km2. It includes area occupied by conversation measures and the additional area protected by them.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S3: Valas graduadas, canais, vias navegáveis
- S6: Muros, barreiras, paliçadas, cercas
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: urbanisation and infrastructure development (Construction of road i.e infrastructure development), floods (Downstream flood during rainy season.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Road construction)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Heavy rainfall during rainy season cause downstream flooding.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
Comentários:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Autor:
Bibhu Gautam, KUGH,Kavre
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
This technical drawing shows the constructed dam and gully which allow proper flow of downstream flood.
Location: Chyamrangbes. Kavre
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Technical knowledge required for labour: high (Through their experience to construct in a useful way.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing)
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Vertical interval between structures (m): n'a
Spacing between structures (m): n'a
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2.13
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1000
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.8
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 1000
Construction material (earth): Soil excavate from the ditches is used to build bank.
Construction material (stone): the cut off ditch is lined with stones, embankment with stones.
Construction material (other): iron wire was used to bind the stone together.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 12%
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land user increased the width and slope of existing ditch for easy flow of water. | Estrutural | dry seasonm |
| 2. | Land user embanked the bank with stones on either side. | Estrutural | dry season |
| 3. | Stones are bind together by wires in some places. | Estrutural | dry season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Increase the width and slope of ditch | ha | 1,0 | 941,17 | 941,17 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 941,17 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: dozer, Dozer
The above mentioned cost is not given per unit/hectar. It is the total cost used for that technology.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The most determinate factor affecting the cost is land structure. Land contains loamy soil which made it difficult for construction of ditch.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
monsoon rain, dry winter
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições côncavas
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Slopes on average: The average slope is about 15%.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil texture: Sandy and graveled land
Soil fertility is medium - low and varies according to soil texture
Soil drainage / infiltration is poor
Soil water storage capacity is low, soil is sandy and contains gravel. So it cannot store water
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
Na superfície
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Excesso
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Inutilizável
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table: Infiltration is very low. Water only flow on surface.
Availability of surface water: During rainy season excess water flow through the steam.
Water quality (untreated): Some portion water is used in agriculture
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Soil is very infertile. So it is poor in biodiversity.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: More male because women cannot do such type of heavy labor work.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
(living standard is more than average).
(average life standard).
Off-farm income specification: Their land is protected from further degradation
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
The land where SLM technology is applied belongs to individual, but it land use right belongs to community.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Risco de falha de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
n/a
Quantidade posterior à GST:
n/a
Comentários/especificar:
protected the cropland from flood
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Quantidade anterior à GST:
n/a
Quantidade posterior à GST:
n/a
Comentários/especificar:
active participating people on land conservation.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
water travel in fixed path
Drenagem de excesso de água
Comentários/especificar:
improved water way for passage of excess water
Solo
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
soil loss due to flooding is reduced
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
the main benefits of this technology
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Comentários:
Dame can be made more tolerant again flash flood by using wire to tighten the stone walls or making the concrete wall.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente negativo
Comentários:
This technology is not a investment purpose. People used their own money to construct it.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
14 households in an area of 10 - 100 sq km (50 - 100 persons per sq km)
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
14 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Iron wire was provided by Bagmati watershed.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: People have well accepted this technology.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Risk of downstream flood and landslide is reduced. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If they had been more donation from government or any other projects, they would construct concrete or more flood resistance dams. As some parts are still unconstructed they would complete them with some more external support. |
| Agriculture land get protected so they can plant the crop without being at risk. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Proper water drainage system and water can get collected in the river following the fix path. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Fodder plant could be grown on the stream banks which is now left and unused. This could be used to feed the animals and would also help to control flood and landslide. |
|
It reduced the risk of further land degradation by downstream flood. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Dams can be made more strong by making concrete walls |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| N/A |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| N/A | N/A |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos