Grass strips [Níger]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Dieter Nill
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Deborah Niggli
Bandes enherbées (French)
technologies_1621 - Níger
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Mamadou Abdou Gaoh Sani
mamadou.sani@giz.de
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP), Niamey, Niger
Níger
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation - A contribution to adaptation and farmers ́ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel (GIZ)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH (GIZ) - Alemanha1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
01/07/2012
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
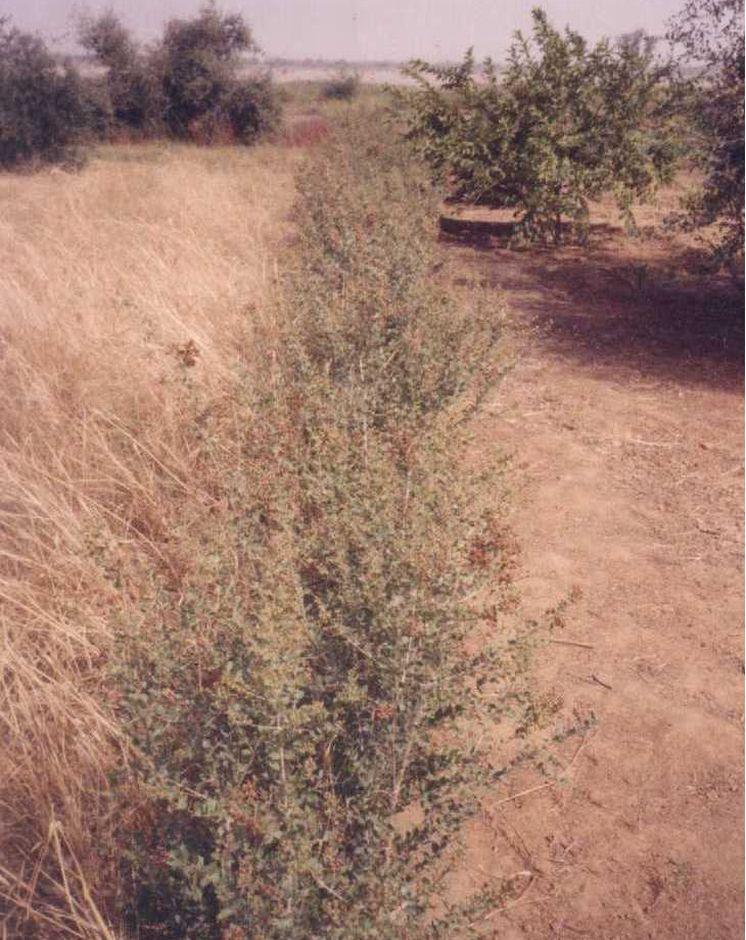
Grass strips slow down runoff, increase infiltration and retain sediment, thus increasing crop production.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Grass strips measuring 0.80 m to 1 m wide are planted 20 to 80 m apart on low-gradient terrain. Local grasses (for example, Andropogon gayanus, Cymbopogon schoenateus and Vetivera nigritiana) are sown or planted (plantlets) at the start of the rainy season. Like stone bunds, grass strips are planted along the natural contour of the land to slow down runoff, increase infiltration and retain sediment. Grass strips get bigger as sediment builds up, which maintains their capacity to retain water, unlike mechanical structures (stone bunds and dikes).
The species of grass are chosen according to what the farmers want to use them for (straw, hay, mat weaving, roofing, construction of straw granaries, brooms, etc.). In cattle and sheep raising areas, the use of fodder plants can increase interest in this technique and ensure wider acceptance. It is recommended that the development of grass strips be combined with assisted natural regeneration (woody species) or the planting of trees.
Designed as an erosion control measure, grass strips slow down runoff in the event of heavy rain. They distribute rainwater more evenly over the land and improve infiltration which is particularly important when there are dry spells in the rainy season. Sediment builds up behind the grass strips, thereby reducing the erosion of fertile soil layers. The roots of the plants bind the soil and hold it in place. Although the vegetation growing in the strips competes with the crops to some extent for water, the overall effect on yields is positive. Crops are also protected from wind erosion. Thanks to the vegetation cover they provide, grass strips contribute to lowering soil temperature.
Like contour stone bunds, grass strips reduce the harmful effects of heavy rain and violent downpours, events that are expected to increase as a result of climate change.
Compared with plots without grass strips, millet yields were 50 kg per hectare per year higher, and straw yields 125 kg higher on plots with grass strips. Yields can be substantially improved by combining grass strips with the application of organic fertiliser, mulch or pen manure. The best results, an average increase of 280 kg of millet grain per hectare (370 kg of straw per hectare), were achieved by combining them with mulching and pen manuring. Grass strips therefore improve yields of cereals and forage for livestock (straw and grass growing on the strips).
Increased crop output increases household food security and improves livestock feeding. The straw cut on the grass strips can also be used for other purposes (fencing and roofing). It is also a source of income, as traditional products made with straw, such as woven mats, can be sold.
Grass growth tends to be patchy, and resowing is required several times to fill in the gaps in the strip. In order to protect the grass strips from grazing animals during the first year, it is recommended that the area be monitored, which requires strict control over the village herds and flocks and those of nomadic livestock keepers.
Some grasses tend to invade crop fields. It is therefore important to control them by cutting them down before they flower and to tend the strips regularly, straightening and cutting back the edges.
Any dead plants in the grass strips must be regularly replaced. Grass strips are more likely to be maintained if they are economically profitable, for example, if they produce hay for livestock or their output can be sold as forage or construction material.
It is a technique designed mainly for cropland, but can also be used on rangeland, provided that the plants are protected when the grass strips are put in place. Grass strips are suitable for areas in the Sahel and the Sudan with rainfall ranging between 400 and 1,000 mm/year and gently sloping terrain (< 2%). Ecological units that benefit from the implementation of this measure include dune land, pediments and plains (highland pediments). Grass strips are particularly appropriate for non-stony land in areas with higher rainfall levels.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Níger
Região/Estado/Província:
Niger
Especificação adicional de localização:
Filingué, Ouallam, Tillabéri, Tera
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by GIZ (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation), PDRT (Projet de développement rural de Tahoua - Tahoua Rural Development Project), PASP (Projet de protection intégrée des ressources agro-sylvo-pastorales Tillabéri-Nord - Project for the Integrated Protection of Agricultural, Forest and Rangeland Resources in Tillabéri-Nord), and PATECORE (project for land development and resource conservation in Plateau Central Burkina Faso)
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Seminomadismo/pastoralismo
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Semiestabulação/sem pastagem
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil erosion by water and wind, fertility decline
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: August to October
Densidade animal (se relevante):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de pastoralismo e pastagem
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 10-100 km2
Comentários:
After three seasons of promoting this technique, grass strips had been established on a total area of 4674 hectares (sometimes in combination with other measures). Over half of the improved land is located in the Filingué area (2587 hectares), followed by Ouallam with 1042 hectares. However, only small areas were improved with grass strips in Tillabéri and Tera (228 hectares and 817 hectares respectively), where acceptance of this technique was low
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes
Comentários:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Neglect of fallow periods and crop rotation), droughts (due to heat waves), population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land and collectively managed communal land), poverty / wealth (very poor population)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (deforestation through overgrazing and fire wood collection), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (firewood collection), overgrazing (cattle, sheep and goats), change in temperature (Climate change: heat waves), change of seasonal rainfall (more variable onset of rain), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (more variable and intensive rains), wind storms / dust storms (frequent storms), floods (due to intensive rain storms), labour availability (some migration of men to nearby cities), education, access to knowledge and support services (high level of illiteracy)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
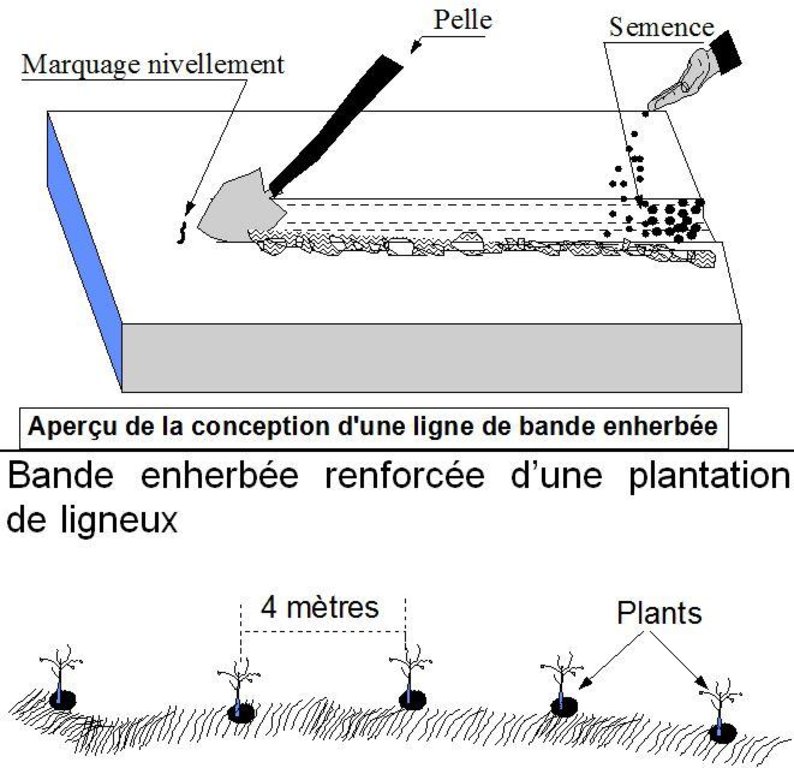
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Grass strips measuring 0.80 m to 1 m wide are planted 20 to 80 m apart on low-gradient terrain. Local grasses (for example, Andropogon gayanus, Cymbopogon schoenateus and Vetivera nigritiana) are sown or planted (plantlets) along the natural contour at the start of the rainy season.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 20-80
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.8-1
Grass species: Andropogon gayanus, Cymbopogon schoenateus and Vetivera nigritiana
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
CFA Franc
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | marking out the contour lines | Vegetativo | |
| 2. | making 10-15 cm deep furrows in which to plant the seeds or seedlings | Vegetativo | |
| 3. | sowing or planting 1 to 4 rows per strip. | Vegetativo |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | labour | ha | 1,0 | 46,7 | 46,7 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | seeds | ha | 1,0 | 3,3 | 3,3 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 50,0 | |||||
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | resowing is required several times. Any dead plants in the grass strips must be regularly replaced. | Vegetativo | |
| 2. | Cutting down grasses which invade crop fields. | Vegetativo | |
| 3. | straightening and cutting back the edges | Vegetativo |
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour: 6 man-days per ha
• marking out the contour lines
• making 10-15 cm deep furrows in which to plant the seeds or seedlings
• sowing or planting 1 to 4 rows per strip. Upkeep: 2.5 man-days per year.
Other costs:
• grass seeds or seedlings
• equipment: water-tube level.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
- Pobre
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4% (mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income, women and men seasonally carry out paid farm work
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Comentários:
traditional land use rights prevail. On fields individual land use rights, communal rights on pasture and forest land (collection of wood and other products (fruits, medicinal plants))
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Produção animal
Risco de falha de produção
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Part of the plot is taken up by the grass strips, reducing the area left for growing crops
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
competition of grasses with crops
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Atenuação de conflitos
contribution to human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Increased crop output increases household food security and improves livestock feeding. The straw cut on the grass strips can also be used for other purposes (fencing and roofing). It is also a source of income, as traditional products made with straw, such as woven mats, can be sold.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Velocidade do vento
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
In the Tillabéri area, in northern Niger, the adoption of grass strips varies greatly from one place to another. After three seasons of promoting this technique, grass strips had been established on a total area of 4,674 hectares (sometimes in combination with other measures). Over half of the improved land is located in the Filingué area (2,587 hectares), followed by Ouallam with 1,042 hectares.
However, only small areas were improved with grass strips in Tillabéri and Tera (228 hectares and 817 hectares respectively), where acceptance of this technique was low.
In spite of good results in terms of increased production and soil improvement, grass strips have only been widely accepted in southern Niger (Maradi and Zinder). Farmers are of the view that grass strips could be confused with plot boundaries.
The availability of land in southern Niger may be another factor that facilitates acceptance of the measure is this area. Part of the plot is taken up by the grass strips, reducing the area left for growing crops. This hinders acceptance in areas where land is limited. The reduced crop-growing area is offset by better per-hectare grain, straw and hay yields. Certain grasses (such as Andropogon gayanus) have a harmful effect on nearby crops. The systematic exploitation of the grass strips as a source of straw or hay improves acceptance of the technique. In the Tillabéri area, in Niger, the adoption of grass strips varies greatly from one place to another. After three seasons of promoting this technique, grass strips had been established on a total area of 4,674 hectares (sometimes in combination with other measures). Over half of the improved land is located in the Filingué area (2,587 hectares), followed by Ouallam with 1,042 hectares. However, only small areas were improved with grass strips in Tillabéri and Tera (228 hectares and 817 hectares respectively), where acceptance of this technique was low. In spite of good results in terms of increased production and soil improvement, grass strips have only been widely accepted in southern Niger (Maradi and Zinder). Farmers are of the view that grass strips could be confused with plot boundaries. The availability of land in southern Niger may be another factor that facilitates acceptance of the measure is this area. Part of the plot is taken up by the grass strips, reducing the area left for growing crops. This hinders acceptance in areas where land is limited. The reduced crop-growing area is offset by better per-hectare grain, straw and hay yields. Certain grasses (such as Andropogon gayanus) have a harmful effect on nearby crops. The systematic exploitation of the grass strips as a source of straw or hay improves acceptance of the technique. At first, people living in the areas covered by the PDRT project were reluctant to establish grass strips. They considered them to be weeds with no place on their farmland. With time and exchange visits within the country, they began to accept the technique.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| reduce the harmful effects of heavy rain and violent downpours, events that are expected to increase as a result of climate change |
| improve rainwater harvesting and water retention in the soil |
| contribute to creating vegetation cover, which provides a habitat for biodiversity |
| contribute to lowering soil temperature and are also effective in reducing wind erosion. As the vegetation provides shelter from the wind, fine particles of soil accumulate behind the strips. |
| Increased crop output increases household food security and improves livestock feeding. The straw cut on the grass strips can also be used for other purposes (fencing and roofing). It is also a source of income, as traditional products made with straw, such as woven mats, can be sold. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Grass growth tends to be patchy, and resowing is required several times to fill in the gaps in the strip. Strips with bare patches are not effective in retaining water, and rilling can be caused by water gushing through the gaps. | The clumps must therefore be arranged in staggered rows and the strips made wide enough to prevent this problem. |
| With the use of certain types of grasses that grow in clumps, such as Andropogon grass, gaps are left between the tufts, and water spurting through these gaps can cause rilling. | |
| In spite of good results in terms of increased production and soil improvement, grass strips have only been widely accepted in southern Niger (Maradi and Zinder). Farmers are of the view that grass strips could be confused with plot boundaries. | |
| Certain grasses (such as Andropogon gayanus) have a harmful effect on nearby crops. | |
| Part of the plot is taken up by the grass strips, reducing the area left for growing crops. This hinders acceptance in areas where land is limited. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos