Mobile cultivation beds [Alemanha]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Peter Kirch
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Fabian Ottiger
technologies_1678 - Alemanha
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Shaw Robert
+49(0)17624332297
rs@prinzessinnengarten.net
Nomadisch Grün gemeinnützige GmbH
Forster Str. 5, 10999 Berlin, HRB 121043 B 3
Alemanha
Bärich Christian
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Nomadisch grün GmbH - AlemanhaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Humboldt Universität zu Berlin (HU Berlin) - Alemanha1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
08/05/2015
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
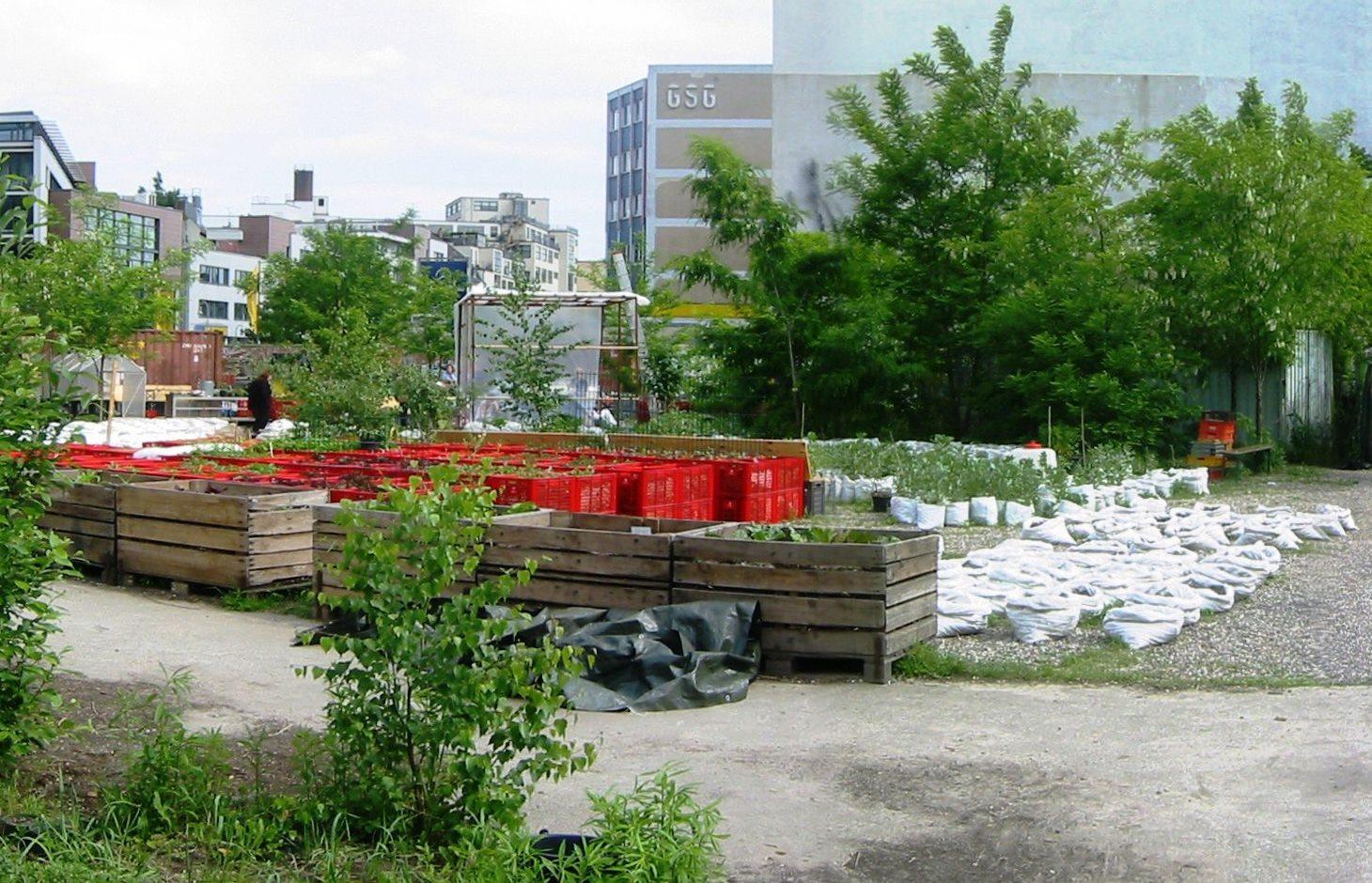
Mobile vegetable cultivation system for urban areas with "baker boxes" as main elements.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The main technology applied in the urban gardening project "Princess gardens" can be described as mobile vegetable culitivation system based on the use of "baker boxes".
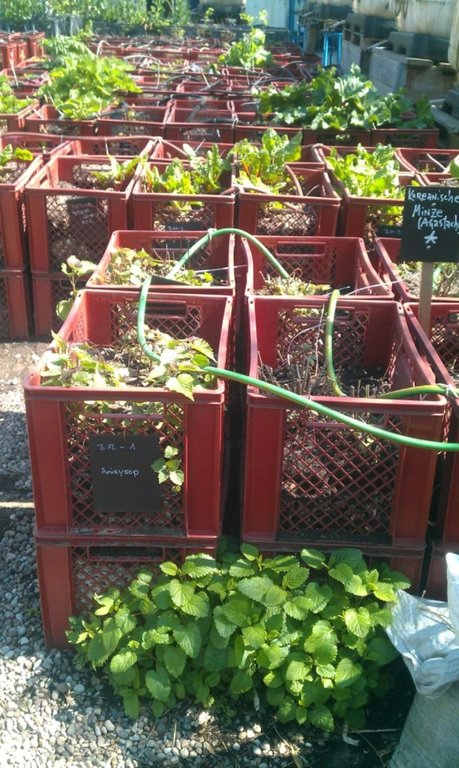
"Baker boxes" are plastic boxes (size: average area of 40 cm x 60 cm x 35 cm) made out of heat-resistant materials, which do not contain softeners. The bottom part as well as the side parts are formed in a grid pattern (holes of 1cm³ size).
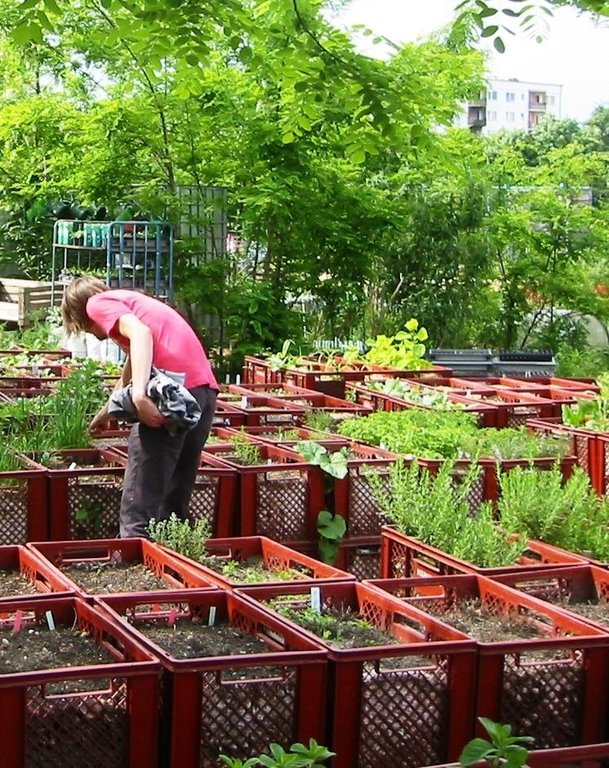
For the vegetable production, cultivation units ("box towers" ) are built out of two boxes by placing them on top of each other. The lower box is filled with organic material (composition of the material like in a compost) and the upper box is filled with garden mould (or other earth material suitable for cultivation). To prevent the washing out of earth material through the grid pattern, carton is put on the bottom as well as on the side walls of the upper box.
During a period of time (length can vary from 1 to 3 years) the upper box can be cultivated according to the principles of "good practise" (e.g. crop rotation). During this time, the lower box serves as compost. In the course of each year this box is checked if the ongoing decomposition processes have lead to the creation of free space in the box. In this case, organic material needs to be refilled.
In the end of the 1-3 years-cultivation period the upper box is emptied and the contained earth material can be used for purposes such as landscaping. The box is then filled with organic material and switched with the lower box, which should contain "ready to cultivate"-compost material. The cultivation can then be restarted.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is to allow cultivation on sealed or contaminated soils. Through the use of the box towers as cultivation units the roots of the plants never get in touch with the soil. While the main rooting zone is to be found in the upper box, deeper rooting plants can grow down to 70 cm into the lower box without reaching the soil in place.
Another purpose of the technology is to create a mobile cultivation system. If needed, the boxes can be easily moved away even during the vegeation period.
Last but not least, the technology has the purpose to create a space, where knowledge sharing on a practical basis regarding the topics e.g. agriculture, sustainability and health can take place.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of the technology first and foremost a sufficient number (depending on the size of the gardening area) of "baker boxes" is needed.
Maintenance activities consist of refilling the lower box with organic material.
This is also true for the required inputs.
Natural / human environment: The environment is strongly influenced by humans, as the first urban structures in this area already were established about 200 years ago. Regarding the topic soil this led to the conversion of the natural soils in place to Technosols.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Alemanha
Região/Estado/Província:
Berlin
Map
×3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Assentamentos, infraestrutura
- Assentamentos, edificações
- Tráfego: estradas, ferrovias
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The major land use problem can be addressed as a lack of cultivation plots within the urban areas. This is due to the fact that the soils are to a great extent sealed or contaminated.
As a result in the urban area there is also a lack of pratical learning areas which relate to the topics agriculture and soils.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): As major land use problems the cultivation circumstances are regarded. This inculdes the topics of destroyed natural soil fertility and a lack of water infiltration into the ground.
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 200Longest growing period from month to month: April to October
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Cultivation on sealed or contaminated soils
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0,006 m2.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros

Medidas de gestão
- M6: Gestão de resíduos (reciclagem, reuso ou redução)
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures, management measures
Specification of other structural measures: creation of cultivation plots
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pk: quebra e ressecamento
- Pu: perda da função bioprodutiva devido a outras atividades
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Pk: sealing and crusting, Pu: loss of bio-productive function due to other activities
Main causes of degradation: urbanisation and infrastructure development (1 sealing (foundations of buildings were constructed in the area))
Secondary causes of degradation: population pressure (as a main cause for urbanisation), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (need for public services in the city), governance / institutional (urban planning in the city)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
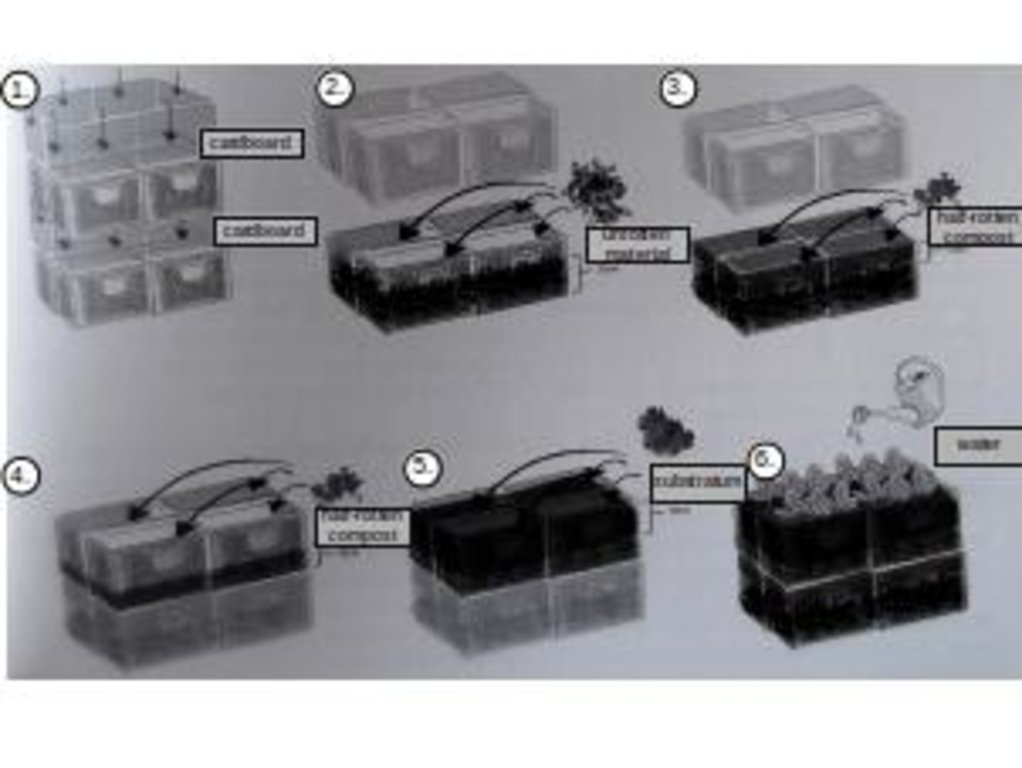
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
edited by Peter Kirch on the basis of Daniel Müller/dkmnews in „Prinzessinengärten- Anders gärtnern in der Stadt“, Nomadisch Grün (Hg.),Dumont Buchverlag, Köln, 2012, page. 115
Location: Berlin. Germany
Date: 08.10.2015
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Structural measure: boxes
Spacing between structures (m): various
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,35
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,4
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0,6
Construction material (other): plastic (food-safe)
Change of land use type: urban area to urban gardening area
Layout change according to natural and human environment: area is limited through infrastructure elements (roads) and buildings.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Euro
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
0,9
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | putting boxes in place | Estrutural |
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Costs are affected by the wages for the employees and the rent of the plot
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is very low
Soil drainage/infiltration is poor
Soil water sotrage capacity is very low
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Seasonality of water quality and source of pollution: for agricultural use only (rainwater)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2%
Relative level of wealth: very rich, rich, very poor
1% of the land users are very rich.
5% of the land users are rich.
50% of the land users are average wealthy.
40% of the land users are poor.
4% of the land users are poor.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
100
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
100
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Oportunidades culturais
Oportunidades de lazer
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
The "Prinzessinnengarten" is more than just a place to grow vegetables in the city. It is a space for diverse activities. Through the opportunity to contribute and to participate in open workshops, through the garden café and a variety of cultural events, the "Prinzessinnengarten" has become a lively meeting place far beyond the neighborhood.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade animal
Diversidade de habitat
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não conhecido |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não conhecido |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Comentários:
An economic analysis is hard to make, as the main goal of the project is not economical profit. In the interviews it was stated, that each year about 50.000 people visit the garden. To have an outreach to such a high number of people with a budget of about 500.000 € is regarded as "benefical" by the project members.
Only looking at the financing part it was stated in the interview that the garden is one of the very few urban gardening projects that can provide for its recurrent costs itself.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
Comments on adoption trend: The members of the "Prinzessinnengarten" are supporting other land users to implement urban gardening projects through giving them advise. Up to 100 urban gardening projects were supported this way. The support is often funded by foundations. How to receive such funding is communicated by the Prinzessinnengarten to the ones seeking their advise.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| light and long-lasting production units |
| a great part of the needed material has been recylced |
| standardized format of the production units (fitting even to international cargo norms) |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| mobile, flexible cultivation system |
| allows cultivation on sealed or polluted soils |
| open access technology |
| knowledge sharing as key priority |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| limited productivity | |
| are highly dependent on irrigation, as the boxes dry-out fast (high evaporation/ surface area) | |
| Soil can be easily lost/washed out throught the grid pattern (especially in the long term, when the erosion measures are reduced (decomposition of carton) | |
| The spacing in between the boxes serves as habitat for snails. | |
| The carton sometimes rots away in the course of the cultivation period. This leads to a loss of soil material out of the boxes. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| dependent on a high supply of "baker boxes" | |
| dependent on external inputs (especially organic material) | |
| allows only for hand labour |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Urban Gardening. Über die Rückkehr der Gärten in die Stadt. Christa Müller, 2011.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
ISBN 3-86581-244-9
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Prinzessinnengärten. Anders gärtnern in der Stadt. Marco Clausen, 2012
Disponível de onde? Custos?
DuMont,ISBN 3-8321-9436-3
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos