Plastic film technology [Nepal]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Shreedip Sigdel
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
Plastic proyog gari kheti garne prabidhi (Main Contributor: Samden Sherpa, ICIMOD)
technologies_1687 - Nepal
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Sherpa Samden Lama
+977 1 5003222
ssherpa@icimod.org
ICIMOD
P.O.Box 3226, Kathmandu, Nepal
Nepal
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - Nepal1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
01/03/2013
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
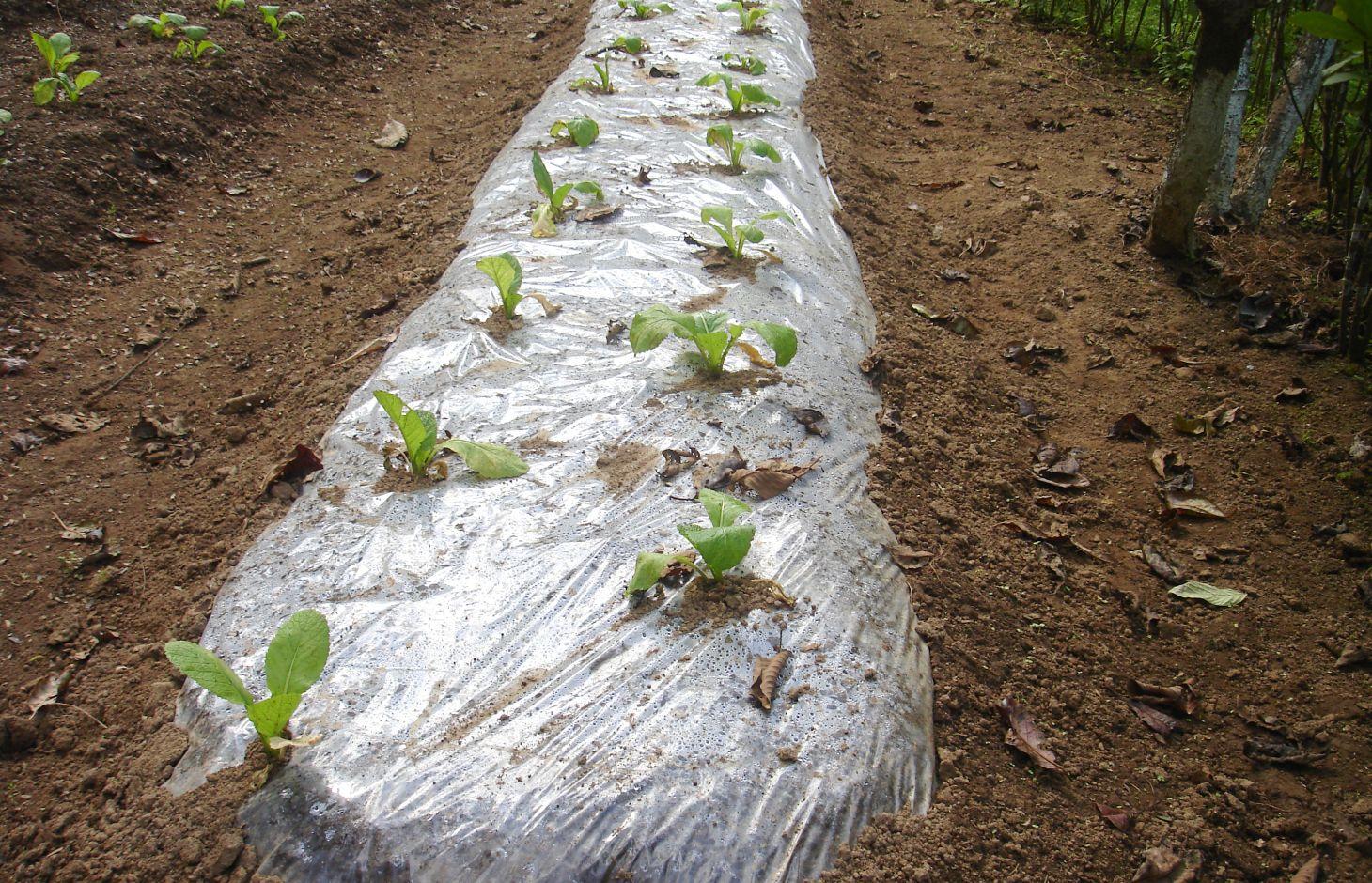
Plastic film technology, sometimes called plastic mulching, is an important breakthrough that can transform traditional agriculture into modern agriculture by helping to circumvent many of the limitations of temperature and moisture. Plastic film is used to cover the surface of the soil in order to increase the temperature, to retain moisture, and to promote the germination of seeds.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Agricultural production by traditional methods is constrained by extremes in temperature and by extremes in the availability of water; freezing temperatures as well as droughts and waterlogging have long daunted farmers. When plastic film is used on the soil, the solar energy absorbed by the soil during the day is retained at night since the plastic film prevents water from evaporating. Higher night time temperatures and higher levels of moisture in the ground promote active micro-organisms, which diminish the need for fertilizer and improve the physical properties of the soil.
Purpose of the Technology: Plastic film can be used in one of two ways. In the first method, the plastic film is spread on ridges of soil, the plastic is perforated at regular intervals, and the seedlings are planted through these openings. In the other method, seeds are planted on the ridges as in the traditional method, and when the seedlings have grown to a reasonable size, the ridge is covered by a plastic film and holes are cut at the position of the seedlings to allow them to pass through the film. Depending on the condition of the film after the crops are harvested, the covered ridges can be used to grow another crop.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Experiments at ICIMOD show that the use of plastic film can, on average, double the crop yield as compared to traditional methods. Previous studies by Lu Rongsen (1994) showed that the plastic film method can increase chilli production by 74%, tomato production by 52%, and the production of garden peas by 31%.
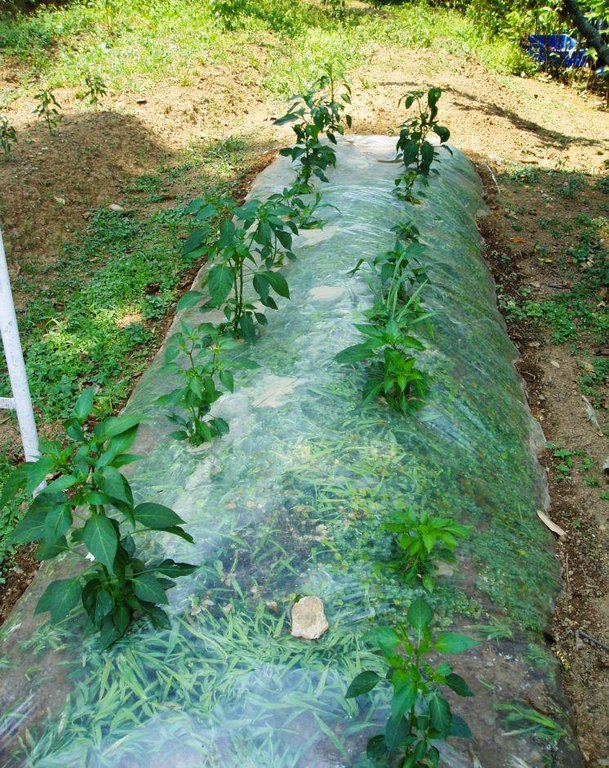
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Nepal
Especificação adicional de localização:
Lalitpur District
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Farmers have traditionally used mulching to retain moisture in the soil and to help plants withstand ground frost. Mulching is useful but has many limitations. Recently, plastic film technology has been successfully introduced to help retain moisture in the soil and to promote seed germination. Since moisture is retained, the temperature of the soil does not drop as low as it would otherwise; this accelerates the growth and the development of both the roots and the whole plant, resulting in good crops and high yields.
Forest products and services: fuelwood
Other forest products and services: Fodder
Constraints of Scrubland
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Comentários:
It was done in demonstration plote
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas de gestão
- M7: Outros
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
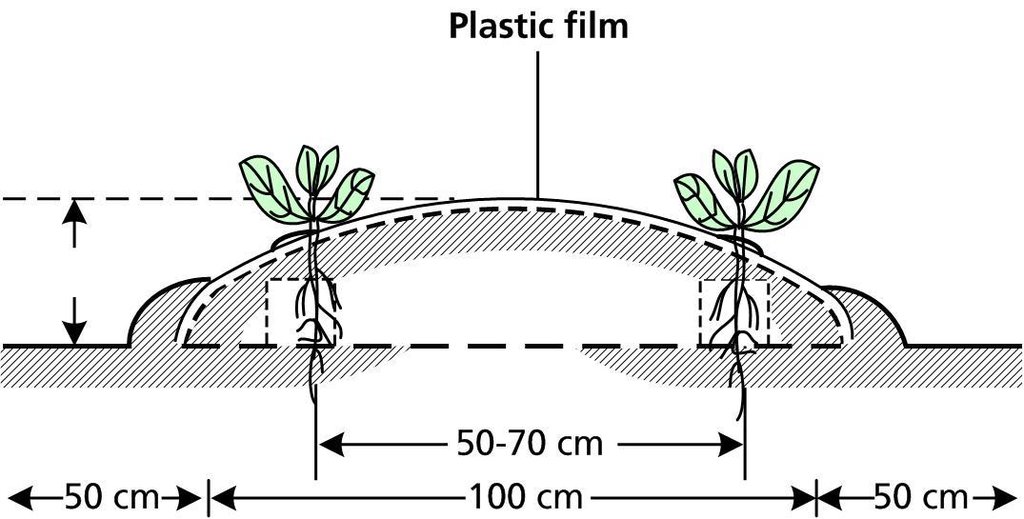
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
The diagram shows a cross-section of a ridge planted using plastic film technology. The plants grow through holes punched in the plastic. The plastic helps to retain moisture in the soil and, in so doing, also helps to increase the soil temperature. Weeds trapped below the plastic are inhibited from interfering with the crop.
The ridges (or beds) are typically 20 m long, 1 m wide and spaced 1 m apart (for access); they are usually 10–20 cm high. The distances shown in the diagram are averages for crops such as chillies where the row-to-row distance is 50–70 cm and the plant-to plant distance is 40–50 cm. These distances vary according to the crop.
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: Increase the temperature of the soil and promote seed germination and emergence, Retain soil moisture and reduce soil erosion
Secondary technical functions: Accelerates the growth and development of roots and plants in areas where the temperature is low dur, Hastens maturation of crops and increase yield and promote good quality crop
Change of land use practices / intensity level
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
ha
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | The plot of land to be planted is prepared by first fertilizing it with a mixture of soil, compost, and/or farmyard manure. The soil is gathered into parallel ridges, typically 20 m long, 1 m wide, and 10–20 cm high; the distance between two ridges is usually 40–50 cm. For many crops the seedlings are spaced 50–70 cm apart. | Gestão | |
| 2. | Method #1 Plastic film (approx. thickness 0.014–0.003 mm) is used to cover the ridges and anchored into the ground. Round holes are punched in the film at regular intervals. Some soil is excavated through the holes and the seedlings are planted through the holes and thoroughly watered. The holes in the plastic are sealed using soil. | Gestão | |
| 3. | Method#2 Seeds are sown on the ridges and seedlings are allowed to develop. The ridge is covered in plastic film and the film is anchored. Holes are punched into the plastic at the position of the seedlings so that they pass through. | Gestão | |
| 4. | For either method, when the crops are harvested all residue should be removed. Depending on local conditions and on whether the plastic film is still viable, the plastic covered ridges can be reused to grow another crop without replacing the film. | Gestão |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Preparing land plot | persons/day/ha | 80,0 | 3,875 | 310,0 | |
| Equipamento | Spade, secateurs | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | |
| Equipamento | Plastic film | kg/ha | 48,0 | 1,0 | 48,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 250,0 | 250,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 618,0 | |||||
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Provide crop support such as staking and removal of excess leaves as required | Gestão |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Support the crops | persons/day/ha | 30,0 | 3,6668 | 110,0 | |
| Equipamento | Bamboo poles | ha | 1,0 | 20,0 | 20,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 130,0 | |||||
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
This was a demonstration project conducted by ICIMOD.
All costs and amounts are rough estimates by the technicians and authors.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Water quality (untreated): Also for agricultural use (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Empregado (empresa, governo)
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Labour:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
in areas with a long winter season
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
less time is spent weeding
Impactos socioculturais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
improved crops and higher yields benefit the entire community because more food is available and the harvest brings in cash income.
Impactos ecológicos
Solo
Umidade do solo
Outros impactos ecológicos
soil erosion and nutrient loss
soil temperature
weeds are controlled
discarded plastic
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Downstream farmers benefit because soil is conserved and runoff is reduced
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| long spell of low temperature, frost and snowfall | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Acceptance/adoption:
This demonstration of plastic film technology was used mainly to show that it is viable both in the mid-hills and at higher elevations where temperatures can be very low during the winter season. Plastic film technology can be used to cultivate high-value horticultural crops such as vegetables, strawberries, and melons. In China, it has been successfully used to cultivate more than 80 species (Lu Rongsen 1994).
Driver for adoption:
Improved income for farmers and less time is spent weeding. Greater awareness among farmers is being spread through participatory research and development in rural areas.
Constraints
Plastic film is not always available in rural areas
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Plastic film technology can increase the yield of some crops by as much as 100% as compared to conventional farming. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Since this technology is still relatively new, it will be necessary to continue sharing experiences and to promote awareness. |
|
Plastic film technology can be used to grow crops in hilly areas where the long winter season is usually too cold to support crops. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Need to create greater awareness of the benefits of using plastic film technology in mountain areas |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| As farmers begin to use plastic film technology more plastic is being discarded in rural areas. | Plastic film needs to be retrieved and recycled. In China it has been shown that this is possible. |
| Discarded plastic film can pollute agricultural lands | Farmers need to be made aware of hazards and encouraged to form networks for collection and recycling the used plastic. |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
The application of plastic film technology in China: Plastic film technology data collected and analyzed in ICIMOD D&T Centre, Godavari. Kathmandu, Nepal: ICIMOD, Rongsen, L (1994)
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos