Alternate Wetting and Drying [Filipinas]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
technologies_1725 - Filipinas
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Dinamling Djolly Ma
DA-BSWM
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Raquid Jemar G.
DA-BSWM
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Martinez Mamerto F.
DA-BSWM
Especialista em GST:
Pascual Kristine
Philrice
Filipinas
Especialista em GST:
Sibayan Evangeline B.
Philrice
Filipinas
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Bureau of Soils and Water Management (Bureau of Soils and Water Management) - FilipinasNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice) - Filipinas1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
11/02/2016
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre as abordagens da GST

Palayamanan: Climate Change Adaptation Strategy for Lowland Ecosystem [Filipinas]
Synergistic mix of farming ventures implemented by the farm family based on the existing environment and their resources to address food security, income instability, and sustainability.
- Compilador/a: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Alternate Wetting and Drying is a water-use management technique wherein irrigation water input could be substantially reduced to as much as 35% without significantly affecting rice yields.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
It was observed that most of the farmer’s irrigation practice of continuously flooding their rice fields is wasteful and uneconomical. The imbalance amount of water, either in deficit or excess, might affect the development and productivity of the crops.
With this inefficient water use and coupled by the increasing frequency of drought, vulnerability to water scarcity is inevitable. Furthermore, it has been recognized that poor water management practices contributed to the process of land degradation. Hence, there is a need to practice proper water management in rice cultivation. As an integral part of the Palayamanan system, the Philippine Rice Research Institute (PhilRice) introduced a water saving technology to the farmers called Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD).
The AWD modifies the irrigation scheduling and application and eventually the amount of water to be use in the field. Irrigation water is applied a few days after the disappearance of the ponded water in the so-called “observation well”. Hence, the field is alternately flooded and non-flooded.
Purpose of the Technology: The following are the purpose of this technology: (1)reducing water use for irrigation so that it can be used for other purposes, (2) reducing the use of irrigation water because there is less of it, and (3) reducing the use of irrigation water to reduce the cost. Emission of greenhouse gas (GHG) specifically on methane is reduced since this is caused by flooding of ricefields.
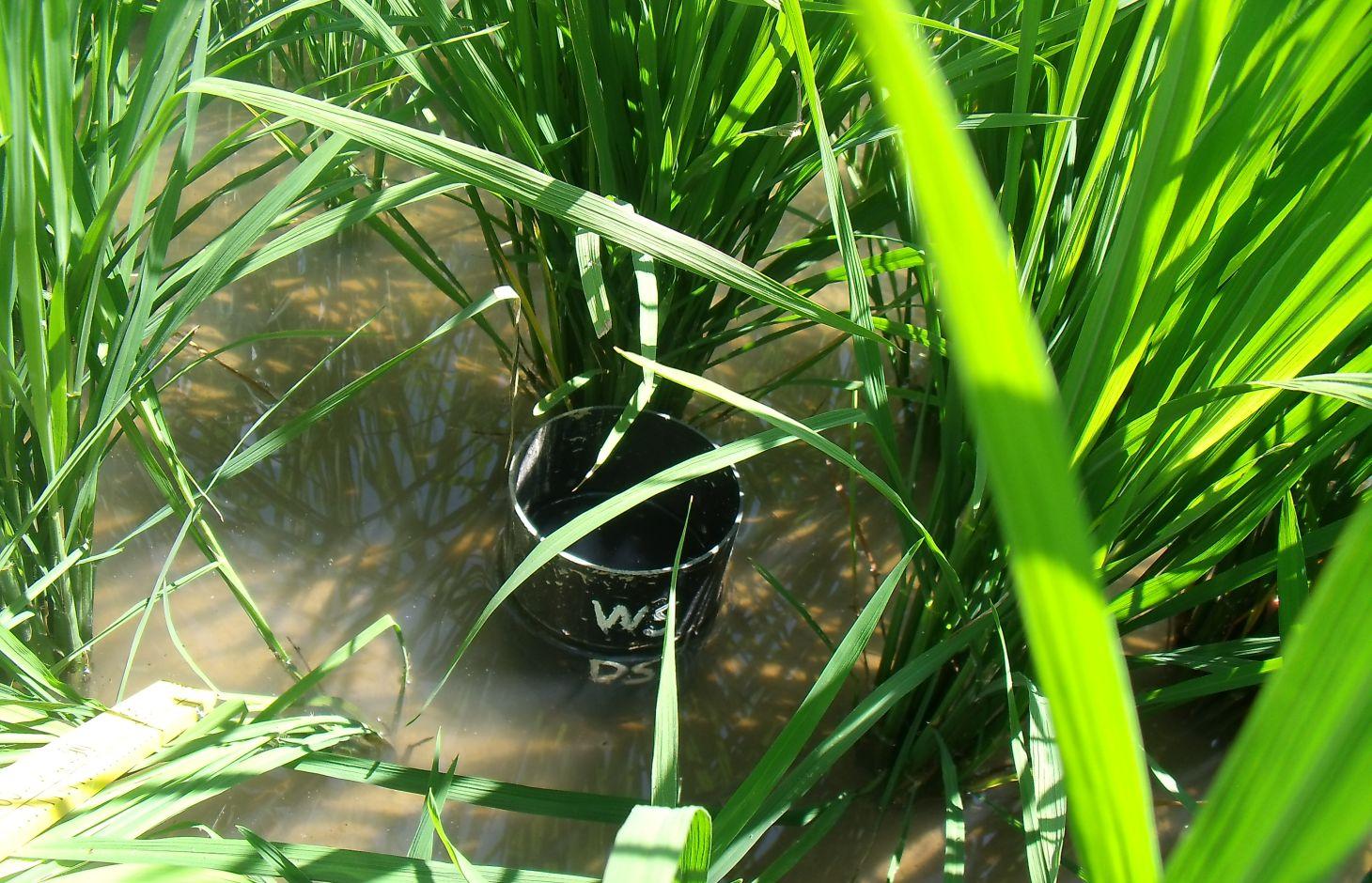
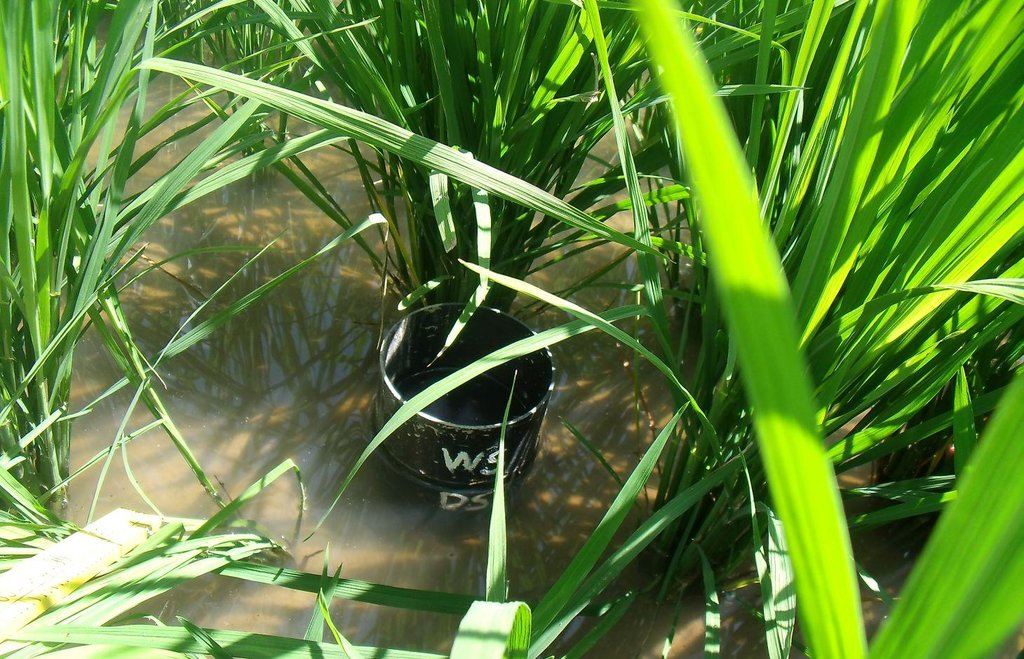
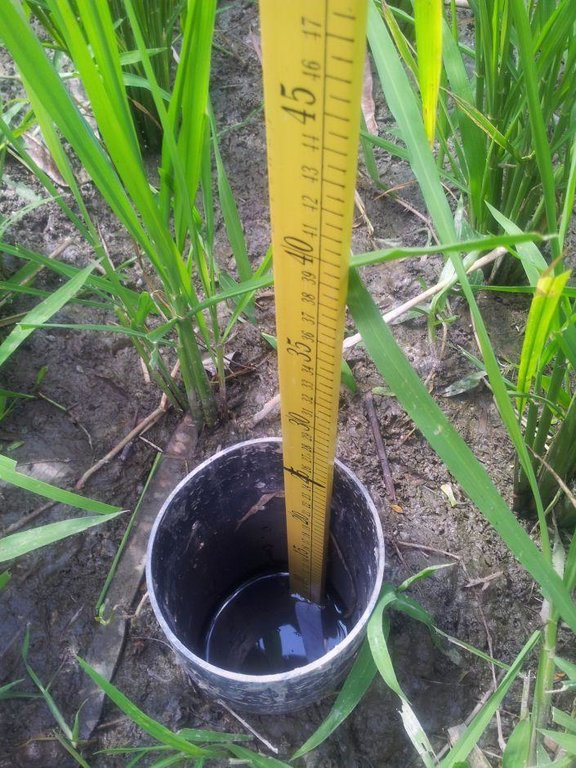
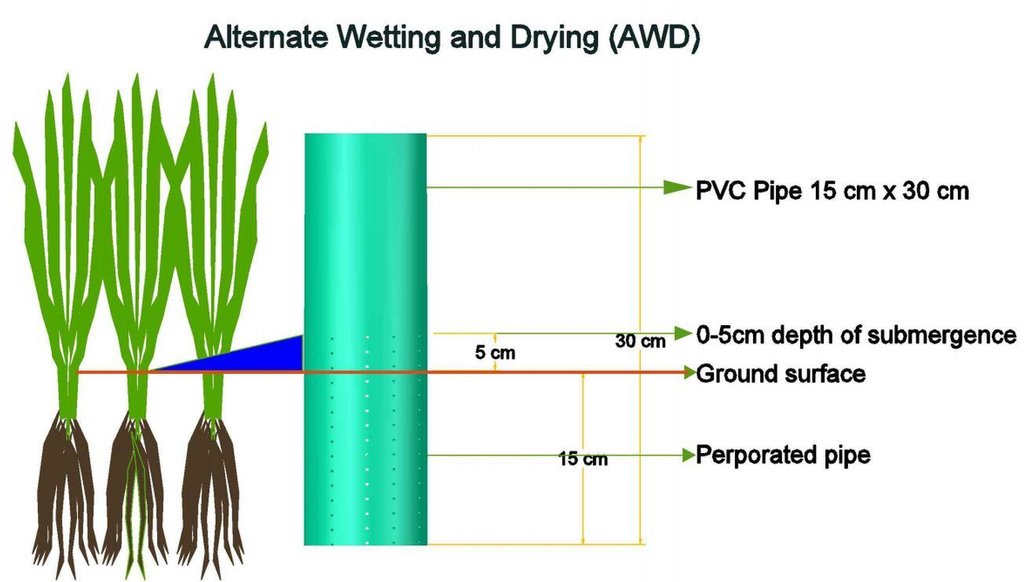
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Practical implementation of AWD is facilitated using a simple tool called a 'field water tube' as observation well, used in monitoring the water level in the field.It is made of a 25 cm long PVC pipe with a diameter of 10 to 15 cm. In some instances, bamboo can be used instead of the PVC pipe. The pipe is perforated with many holes on all sides to allow lateral movement of water in the root zone. It is installed into the soil by ensuring that 10 (dry season) or 5 (wet season) cm protrudes above the soil surface. Soil must be removed inside the tube so that the bottom is visible. During the first 21 to 30 days after direct seeding or transplanting, 2 to 3 cm of water is maintained to control weeds and to ensure that the crop has already
recovered from transplanting shock. AWD is imposed after 21 to 30 days where the water in the tube is monitored. Once the water inside the tube disappears, irrigation is applied to a water depth of 5 cm above soil surface. It is noted that during fertilizer application and flowering stage, sufficient water is maintained to avoid spikelet sterility. Terminal drainage from one to two weeks before the expected time of harvest is also done to promote uniform maturity of the crop and to facilitate easement of post-harvest operations in the field.
Natural / human environment: The area is under a humid climate experiencing wet and dry season with an annual average rainfall ranging from 1000-1500 mm per year. The technology was applied to irrigated rice field in flat and plain areas.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Filipinas
Região/Estado/Província:
San Nicolas, Dingras
Especificação adicional de localização:
Ilocos Norte
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
major cash crop: rice
major food crop: rice
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): lack of irrigation water
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Outros (p. ex. pós-inundação):
- controlled flooding
Comentários:
The field is alternately flooded and non-flooded.
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
This is practiced in most of the "Palayamanan" sites in Ilocos Norte.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas de gestão
- M4: Principal mudança no calendário de atividades
- M7: Outros
Comentários:
Main measures: management measures
Specification of other management measures: water use management
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação da água
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), other human induced causes (specify) (water use management)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
PVC pipe used for the technology.
Location: Ilocos Norte
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: more efficient water use
Major change in timing of activities: AWD modifies the irrigation scheduling and application
Other type of management: Water use management on irrigation water is applied a few days after the disappearance of ponded water in the field water tube.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
3.33
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of the PVC/bamboo pipes | Gestão | |
| 2. | Perforation with many holes on all sides of the PVC/bamboo pipe | Gestão |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Perforation with many holes on all sides of the PVC/bamboo pipe | Person/day | 1,0 | 3,33 | 3,33 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Preparation of the PVC/bamboo pipes | piece | 1,0 | 4,44 | 4,44 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 7,77 | |||||
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Installation of the PVC/bamboo pipe into the soil | Gestão |
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Market orientation: Rice produced are intended for market and food consumption for the family
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%; 1%
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha and1-2 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Demanda por água para irrigação
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
weed growth during dry period
Comentários/especificar:
seen as disadvantage
Impactos socioculturais
Atenuação de conflitos
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Drenagem de excesso de água
Evaporação
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: No exact data is available to determine the numbers of land user who adopted the technology but most of the "Palayamanan" farmer partners in the irrigated areas adopted and practiced it.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: No exact data is available to determine the numbers of land user who adopted the technology but most of the "Palayamanan" farmer partners in the irrigated areas adopted and practiced it.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Most of the land users practicing "Palayamanan" in the municipality and province of Ilocos Norte is adopting the technology.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Positive outcome primarily in water savings without significant yield difference from the usual practice. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Simplicity of the technology's method. |
| AWD leads to firmer soil conditions at harvest, which is beneficial to operating machines in the field. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Prone to weed growth during the period when the soil is dry. | Proper weed management |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Palayamanan: Climate Change Adaptation Strategy for Lowland Ecosystem [Filipinas]
Synergistic mix of farming ventures implemented by the farm family based on the existing environment and their resources to address food security, income instability, and sustainability.
- Compilador/a: Philippine Overview of Conservation Approaches and Technologies
Módulos
Não há módulos