Almond and Apple sapling plantation [República Islâmica do Irã]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Unknown User
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
تبدیل دیمزارهای کم بازده (گندم و جو) به باغات سیب و بادام (arab)
technologies_1742 - República Islâmica do Irã
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Majid Soufi
Especialista em GST:
Hasan Ahmadi Shiraz
1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
01/05/2010
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
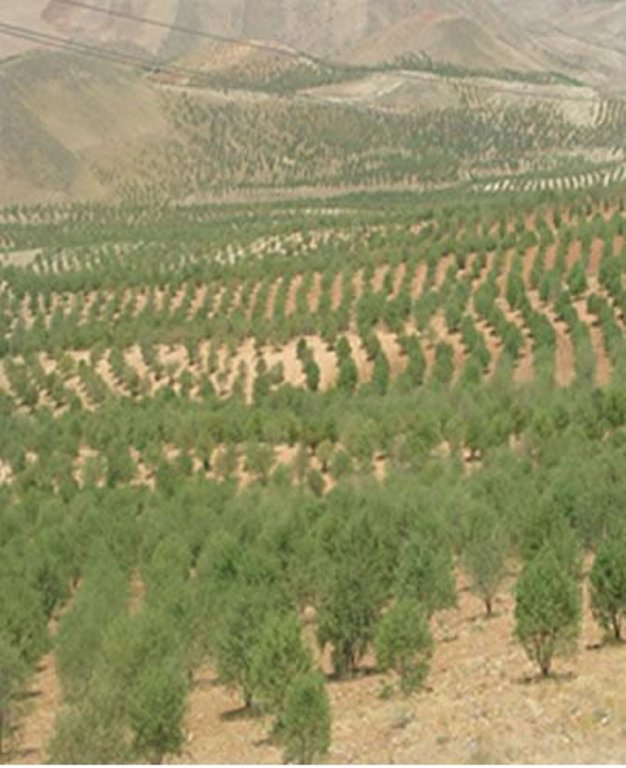
Plantation of almond and apple trees on the contour lines instead of annual rainfed crops such as wheat and barley on hills with 8 to 30% slope.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
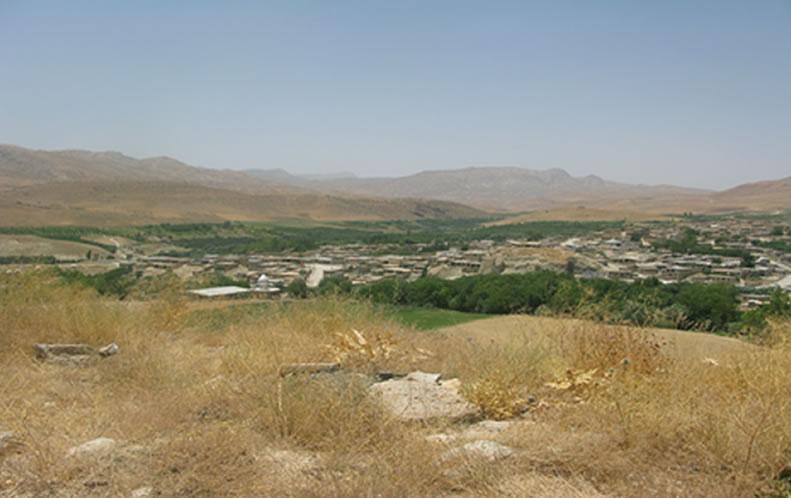
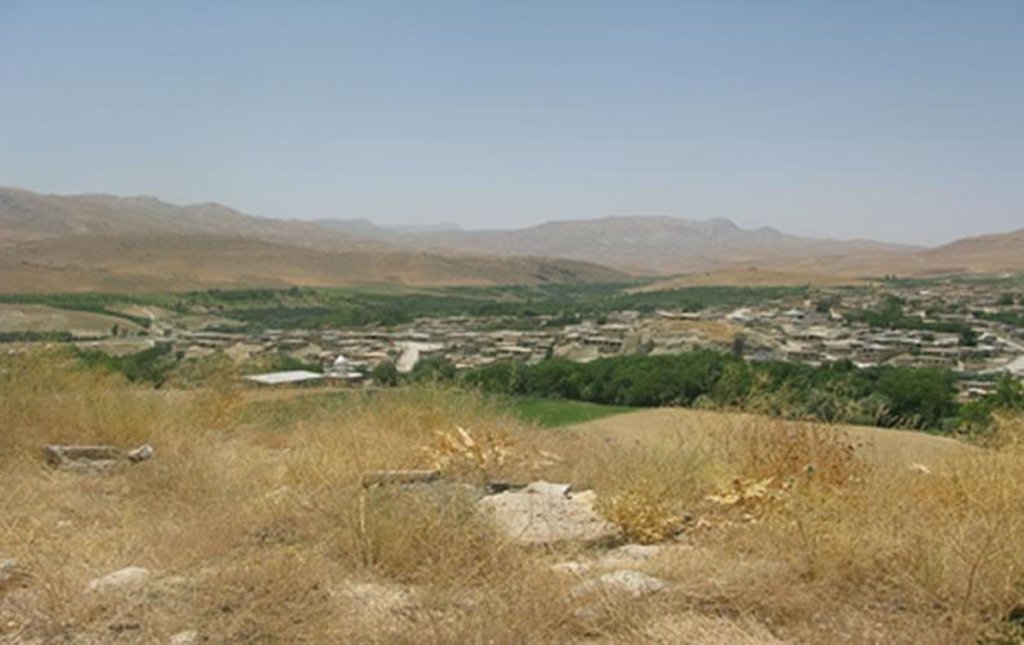
Dejkord village is located in north – west of Fars province and west of Eghlid dis-trict. This village is located on hilly steep land with 390 families. Climate of the village, according to Demarton classification, is situated in the Mediterranean temperate zone. The long-term mean annual temperature is 13.5ºc and long-term mean annual rainfall is 510 mm. The landforms of the study area are generally rolling (with slope 8-16%) and medium mountain ridges (with slope 16-30%). The site study is located between 2000 and 2700m above sea level. The average depth of the soil in this region is 50cm. Dominant top soil textures are sandy loam, loam, and sandy clay loam and are commonly shallow with low amounts of organic matter (usually below1% ). The results of soil analysis showed that silt decreases and sand and clay increase with soil depth. The range of clay, silt, and sand is respectively 16 to 35 %, 9 to 33 %, and 47 to 73%. EC (Soil Electrical con-ductivity) is less than 1(dS/m). The main problems in this area are poverty and soil erosion that reduce crops yield. Ploughing in slope aspect increased soil erosion in this area.
The impact of this technology depends on establish pits on contour line that caused to keep runoff and reduce velocity of rain water and also canopy cover of trees caused to prevent of rain splash and provides adequate soil cover, protect-ing the land from Erosion and roots of trees enhanced infiltration. Otherwise this system increased farmer income rather than before implementation technology.
Watershed Cooperative of Dejkord started its activities since 1998 with 548 mem-ber and covering 8 villages but today this watershed cooperative have 8000 members . In order to build capacity for the watershed resident, the Fars province office of natural resource started to give lands for non – irrigated plantation which are suitable for improving the watershed. The mentioned office gives US$ 800 loan as a very cheap facility against 1 hectare of the land to the members of watershed cooperative, and the time of paying back is 5 years after they get the loan. Nowadays 15000 hectares of those lands are converted to non – irrigated gardens of Almond and Apple trees. Out of 15000 hectares, 10000 include productive Almond garden, and 5000 hectares include Apple garden .As an average, for 1 hectare about 4.5 to 5 kg seed with the value of 1.5 US$ are needed. There are 270 to 300 saplings in 1 hectare and the distance between the saplings is 6 meter. Before the watershed program, the income of resident was US$ 80 per hectare per year, however after the project their income increased to US$ 1000 to 1200.per hectare per year. For maintenance of the project some measure like fertilizing, recession, spraying, cropping and etc will be done.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
República Islâmica do Irã
Região/Estado/Província:
Fars Province, Iran
Especificação adicional de localização:
Eghlid District, Dejkord Village
2.6 Data da implementação
Indique o ano de implementação:
1998
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): There are several problems in this area, including: land degradation because of inter-rill, rill and gully erosion, lack of income economic resources for stockholders before implementation. income of resident was US$ 80 per hectare per year from annual crops but after the implementation, their income increased to US$ 1000 to 1200, plowing the lands by farmers along with slope in land with more than 10% slope topographical status, soil fertility decline.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ct: Tree and shrub cropping
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 150 km2.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal

Degradação da água
- Hq: declínio da qualidade do lençol freático
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing, industrial activities and mining, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), floods, population pressure, poverty / wealth, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
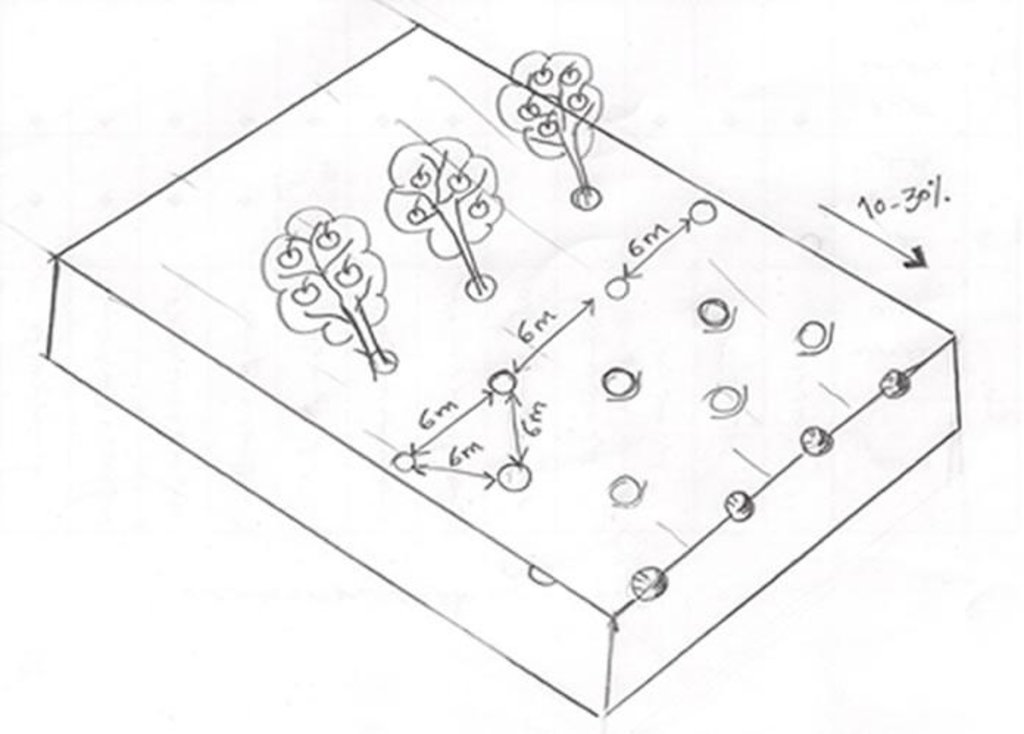
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Fruit trees cultivated on slope (10 - 30%) with a spacing of 6 between.
Location: Dejkord Village. Eghlid District, Fars Province, Iran
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, increase in organic matter, increase of infiltration, increase in soil fertility
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Vegetative measure: Vegetative Measure
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Change of land use type: Change from grazing land and annual rainfed crops to tree crops.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging Pits carried out by labor on hilly steep land (approximately 270-300 pits per ha) | Vegetativo | before rainy season |
| 2. | Planting of fruit tree seeds (Almond and Apple) by hand | Vegetativo | spring |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Digging Pits and planting of fruit trees | ha | 1,0 | 90,0 | 90,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 40,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds | ha | 1,0 | 7,5 | 7,5 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 137,5 | |||||
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plugging of land with tractor in contrast to the slope. | Vegetativo | |
| 2. | Digging pits at the foot of the tree for water harvesting. | Vegetativo | |
| 3. | Pest management with chemicals. | Vegetativo | two or three times a year |
| 4. | Trees pruning. | Vegetativo | every year |
| 5. | Create a slot for fertilizers/manuring | Vegetativo | |
| 6. | Manuring. | Vegetativo | after one year |
| 7. | Irrigation of new seedlings. | Vegetativo | |
| 8. | Harversting of fruits. | Vegetativo | |
| 9. | Pest control for trees and their fruits. | Vegetativo |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | All the labour | ha | 1,0 | 410,0 | 410,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 45,0 | 45,0 | |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 70,0 | 70,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Toxin for pets | ha | 1,0 | 45,0 | 45,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 570,0 | |||||
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate. Mediterranean
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
Na superfície
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Excesso
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table: Near ground
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
There were many wild birds before, now there are only few.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Cooperativa
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Off-farm income specification: Most farmers depend economically entirely on their own crop production.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de madeira
Risco de falha de produção
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Oportunidades culturais
Oportunidades de lazer
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
livelihood and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Escoamento superficial
Drenagem de excesso de água
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Controle de praga/doença
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Velocidade do vento
Outros impactos ecológicos
competition
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
Danos em áreas vizinhas
wind velocity
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Establishment costs are high in the first year, but after 5 years the system becomes very profitable.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Comentários:
Comments on adoption trend: At the first stage most of the land users who accepted the technology did so with incentives, but there was no spontaneous adoption.
- The project gives educational assistance, training, technical assistance in the field.
- Spontaneous adoption is growing in neighboring villages.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Different fruit harvested at different periods How can they be sustained / enhanced? gives better income in 1 year and therefore encourage family members participation |
|
Improved conservation/ erosion knowledge How can they be sustained / enhanced? This project has caused the resident acceptance and therefore caused to the extension of the technologies to the neighbor region |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Rehabilitation of degraded areas How can they be sustained / enhanced? reduced soil erosion and increased productivity |
|
Production increase and good fruit yields How can they be sustained / enhanced? Introduce low input demanding and fast producing tree species and varieties. |
|
Increased food security How can they be sustained / enhanced? with production and generation of different kind of fruits |
|
Reduction of erosion processes How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve the soil cover through implementation of planted trees |
|
Increased crop production and diversity (fruit, timber) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Apple and Almond |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Fruit trees consume more water (but they also help in drainage) these trees with consuming water and waste it to transpiration caused to Reduction in stream flow in downstream | through lowering the ground water table. Appropriate tree species need to be selected and bred. |
| Pest and diseases | pests on apples reduced the price of products (pets controlled by toxin and natural hunters). |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos