Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China [China]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Christian Rumbaur
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
膜下滴灌 (Chinese)
technologies_1305 - China
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 9 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 9 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 4 de Abril de 2018 (inactive)
- Drip irrigation under plastic mulch for cotton production in Xinjiang province, China: 13 de Março de 2019 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Müller Joachim
+49 711 459-22490
joachim.mueller@uni-hohenheim.de
University of Hohenheim
Alemanha
Especialista em GST:
Zia-Kahn Shamaila
+49 711 459-23119
shamaila.zia@uni-hohenheim.de
University of Hohenheim
Alemanha
Especialista em GST:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Sustainable Management of River Oases along the Tarim River, China (SuMaRiO / GLUES)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Universität Hohenheim - Alemanha1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
14/05/2015
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Drip irrigation under plastic mulch, associated with drainage, to reduce water demand and improve cotton yields in Xinjiang Province, China.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
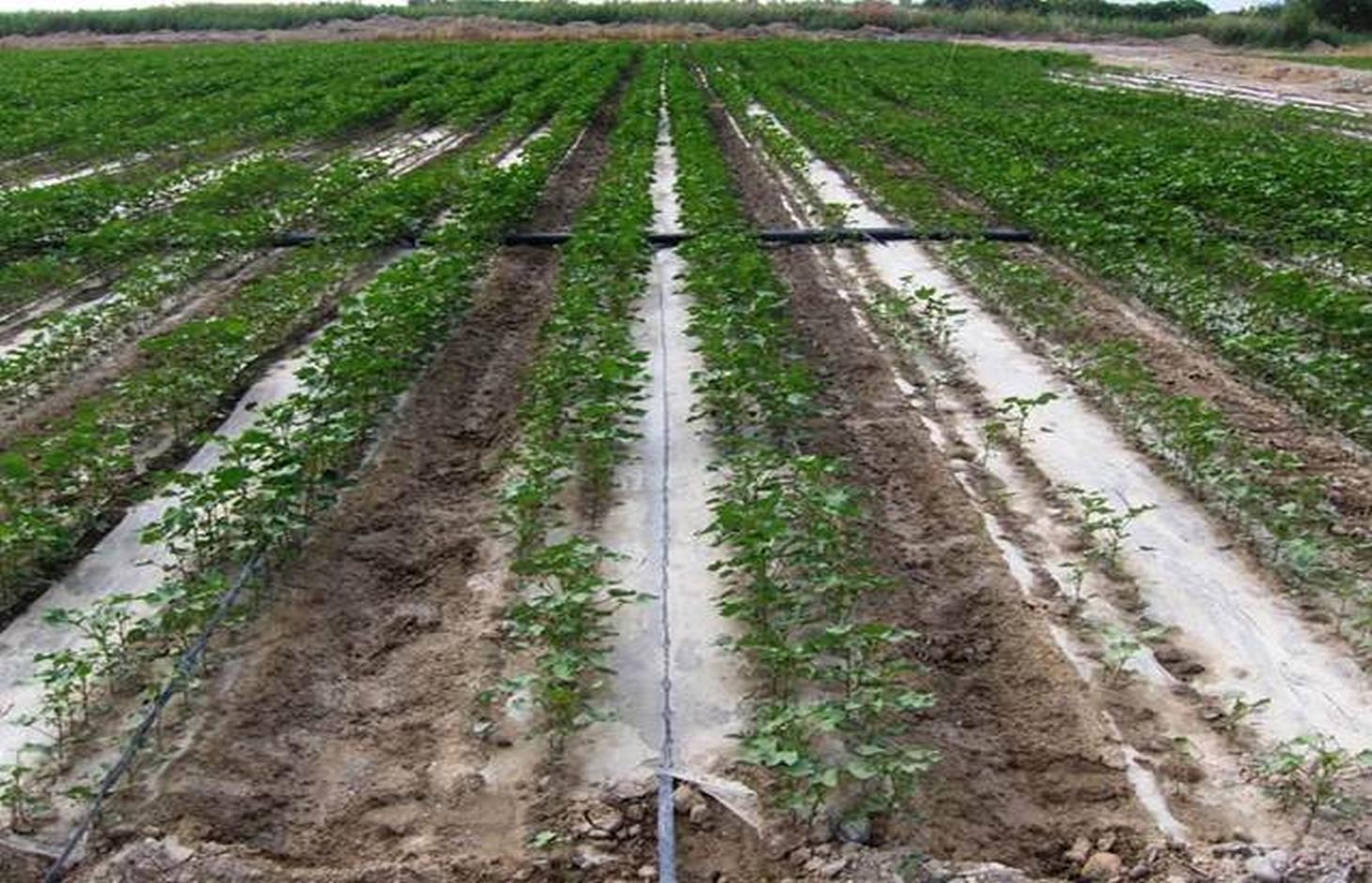
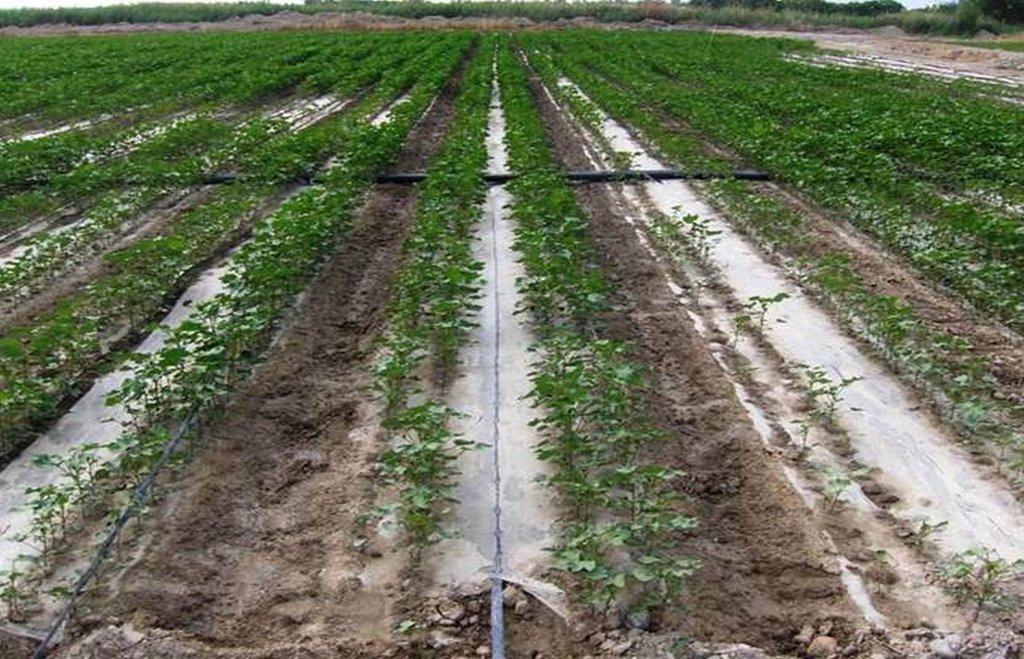
The dry climate and the long hours of sunshine make Xinjiang especially suitable for production of high quality cotton, and as a result some 40% of China’s cotton is grown here. But there are two main problems: shortage of water and salinization of the soil. Farmers who use the traditional flood irrigation method, and don’t have a drainage system, tend to abandon their fields when they become too saline - and then they look for new land to cultivate. A combination of mulching and drip irrigation can be very effective but still needs careful management. Drip irrigation helps to save water for farmers - and for the environment. But it is still very important to install a drainage system to dispose of surplus water in order to reduce the risk of salinization of the soils. Every four cotton rows are covered with transparent polyethylene film and as a result approximately 80% of the ground surface is covered by the plastic mulch. Plastic mulch and drip lines are placed with a specially equipped tractor.
Purpose of the Technology: Low temperatures and dry soil at sowing, in combination with soil salinity, hinder early plant growth. Plastic mulching increases soil temperature, reduces the need for irrigation, and also helps control salinity in the root zone and suppresses weeds, thereby increasing yields by 10–30% (and improving quality also) (Wang, R. et al., 2011). In the first stages after sowing the climate is particularly cold. With plastic mulching the cotton plants can be sown earlier, because the soil will not cool down during the night as much as without plastic mulch.
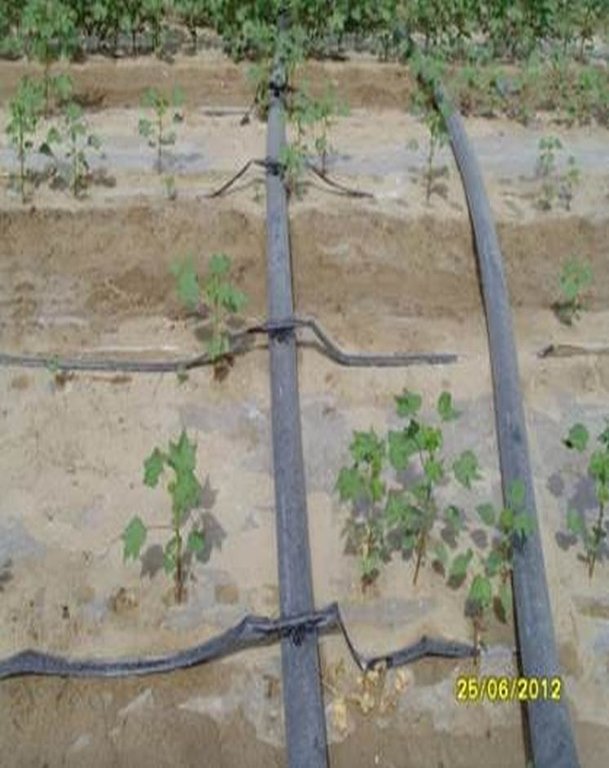
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of the new technology of drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is simultaneously essential to install a drainage system to avoid raising the groundwater level and causing salinity. For the installation of the drip lines, the transparent plastic film and the seeding, a tractor and a special tool for the installationis needed: one acre can be installed in a day. After the emerging of the cotton plants, holes must be cut in the plastic film so that the cotton plants can emerge. After harvesting, the drip lines and the plastic film must be collected and recycled. If the plastic is left behind it will pollute the soils and injure livestock if they eat it. Furthermore plastic residues in the soil can reduce subsequent yields, as roots are physically inhibited. After the collection of the plastic residues, if there is no adequate drainage system, the field needs to be flooded to flush the salt layer, which has accumulated below the root zone, deeper into the soil. If the field is not flooded the salt will negatively affect the next years’ cotton plantation.
Natural / human environment: Southern Xinjiang is an arid region with 50 to 90 mm per year. Most precipitation occurs between June and August. It is classified as a temperate cold desert climate. For drip irrigation under plastic mulch, it is principally surface water that is used, which is delivered to the field via channels from reservoirs to the fields. The reservoirs are filled in summer with the floods along the Tarim River. The untreated surface water is of poor quality - for agricultural use only. For drip irrigation, the water needs to be treated to avoid blocking the drip outlets. The overall technology is expensive, and only land user groups and communities can afford the machines and the materials.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
China
Região/Estado/Província:
China / Xinjiang Province
Especificação adicional de localização:
Tarim River Basin
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
It is not clear how the technology was invented.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
major cash crop: cotton
major food crop: wheat
other: fruit trees
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water use conflicts between agriculture and natural vegetation, soil salinization, desertification.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil salinization and water shortage.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Ca: Annual cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps: water availability, evaporation
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Forests / woodlands: Fn: Natural
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Irrigação completa
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 220Longest growing period from month to month: March to October with irrigation
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Desvio e drenagem de água
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- > 10.000 km2
Comentários:
It might be used also in other provinces. But this not known to the author.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
- M4: Principal mudança no calendário de atividades
- M6: Gestão de resíduos (reciclagem, reuso ou redução)
Comentários:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cs: salinização/alcalinização

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pw: estagnação hídrica

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Pw: waterlogging
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Most fields have no drainage - Increase of groundwater - salinization of soils), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (cotton monoculture), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation to gain new arable land), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), wind storms / dust storms (Dust storms, blow out of top soil), droughts (It is an arid climate), population pressure (Doubling of population during the last thirty years.), land tenure (Land belongs to the state), poverty / wealth (Family farmers are poorer than city dwellers), education, access to knowledge and support services (Poorer farmers have less access to extension services.)
Secondary causes of degradation: industrial activities and mining (There is oil production in the region, but it was not studied), discharges (point contamination of water) (Non-point source pollution and drainage water discharge from the fields.), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (use of surface and ground water for large scale irrigation), floods (Floods are necessary for the region (riparian forests))
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
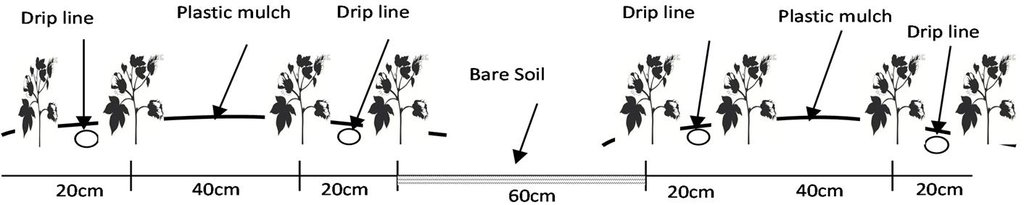
There are double rows of cotton 20 cm apart, with a drip line between. 40 cm then separates each double row. Two double rows are covered by one length of plastic mulch. There is a small strip of bare soil between each length of plastic mulch. Mulch covers around 80% of the soil surface.
Location: Korla City. Xinjiang Province / China
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (For the easy and fast installation a tractor is needed)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of biomass (quantity), increase of water use efficiency
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase / maintain water stored in soil
Mulching
Material/ species: transparent plastic (Polyethylene), thickness: 0.08 mm
Quantity/ density: 7100 m/ha
Remarks: 1.4 m width in lines with spacing of 20 cm between lines
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Change from flood irrigation to drip irrigation
Major change in timing of activities: Plastic mulch enables early sowing of cotton
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
1
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tractor | ||
| 2. | Drip line installation, plastic mulch and seeding tool | Agronômico | At sowing |
| 3. | Making holes for the (cotton) plants in the plastic mulch.Maintaining hoses | Agronômico | After emerging |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Drip line installation | ha | 1,0 | 3,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Machine use | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tractor | Piece | 1,0 | 5000,0 | 5000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | seeds | kg | 30,0 | 3,0 | 90,0 | |
| Material de construção | Plastic mulch | 1,0 | 32,0 | 32,0 | 50,0 | |
| Material de construção | Black dripe lines | Set | 1,0 | 380,0 | 380,0 | 50,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 5510,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.33 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing and leveling of field. | Agronômico | Before sowing |
| 2. | Irrigation | ||
| 3. | Removal of the drip lines and the plastic mulch |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Collecting mulch | ha | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 98,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Irrigation and flooding water | 1,0 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 100,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 13,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: tractor with installation tool for the drip irrigation under plastic mulch, other tools: hoe
The costs for the machine, the plastic hoses and the plastic mulch are calculated above are for 1 ha and were calculated on the basis of 2013 (subsequently costs have risen). Water price: 0.019 CNY/m3. Farmers need 3000 m3 per ha.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
90 mm per year. Jan, Feb, Apr and May: 3 mm; Mar, Sept: 5 mm; Jun: 33 mm; Jul: 18 mm; Oct: 0 mm; Dec: 8 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Árido
Thermal climate class: temperate. cold desert climate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: altitudes of 800 to 1300 meters
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility: low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration: medium
Soil water storage capacity: medium high
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table: also < 5 m and the installation of drip irrigation under plastic mulch should be installed with a drainage system. If the groundwater table is too high salinisation of the soil will be the result
Availability of surface water: For the drip irrigation under plastic mulch mostly surface water is used. It is diverted by channels to the agricultural fields. There must be a good water availability at the fields.
Water quality (untreated): For the drip irrigation under plastic mulch the water quality must be quite high, otherwise the small holes of the drip lines will be blocked soon.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
- Muito rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Man are doing the earth works in the fields, women do more the harvesting
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 7%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land (income from large fields of cash crops).
20% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land (income from cash crops (fruits, cotton)).
40% of the land users are average wealthy and own 30% of the land (income from cash crops (fruits, cotton)).
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Farmers who have not implemented the drip irrigation under plastic mulch also generate off-farm income.
Manual labour: harvesting
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
Comentários:
5-15 ha: state farms
< 0.5 ha: family farmers
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Arrendado
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Arrendado
Comentários:
All the land belongs to the state. Farmers have the right to use the land for 70 years.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
15% of more cotton yield
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Demanda por água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Impactos socioculturais
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Evaporação
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Salinidade
Outros impactos ecológicos
salinization below root zone
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Sedimentos transportados pelo vento
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
No number on households
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The government gives subsidies to the farmers who are installing the drip irrigation under plastic mulch.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The government want to spread the technology in the whole region by giving subsidies to the farmers.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
helps to save water thus saves costs. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It is subsidies by the government. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
It helps to save water during the vegetation period and thus helps to reduce the conflicts between the upstream and downstream farmers. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology (drip + mulch) needs to be supplemented by installing a drainage system in the fields otherwise there will be a build-up of salinity and farmers will abandon land and move on. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Salinization of the soils is increasing The consequence is that the fields are flooded after harvest in November/December to leach out the salt. The water used for drip irrigation plus the water to flush the salts to lower soil layers add up to almost the same amount as if farmers were using the original flood irrigation technology. | drainage system in the fields required. |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Zia-Khan,S., Spreer, W., et al. Effect of dust deposition on stomatal conductance and leaf temperature of cotton in Northwest China.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Water 2015, 7, 116-131; doi: 10.3390/w7010116. www.mdpi.com/journal/water open access.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos