Tree row and grass strip to sustain filtering and productive function of the riparian zone [Quênia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Manuel Fischer
- Editor: –
- Revisor: David Streiff
technologies_1559 - Quênia
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Tree row and grass strip to sustain filtering and productive function of the riparian zone: 28 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Tree row and grass strip to sustain filtering and productive function of the riparian zone: 28 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Tree row and grass strip to sustain filtering and productive function of the riparian zone: 30 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Tree row and grass strip to sustain filtering and productive function of the riparian zone: 9 de Maio de 2019 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
usuário de terra:
Muthoni Mary Njagy
0727 906 945
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - Suíça1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
08/11/2012
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
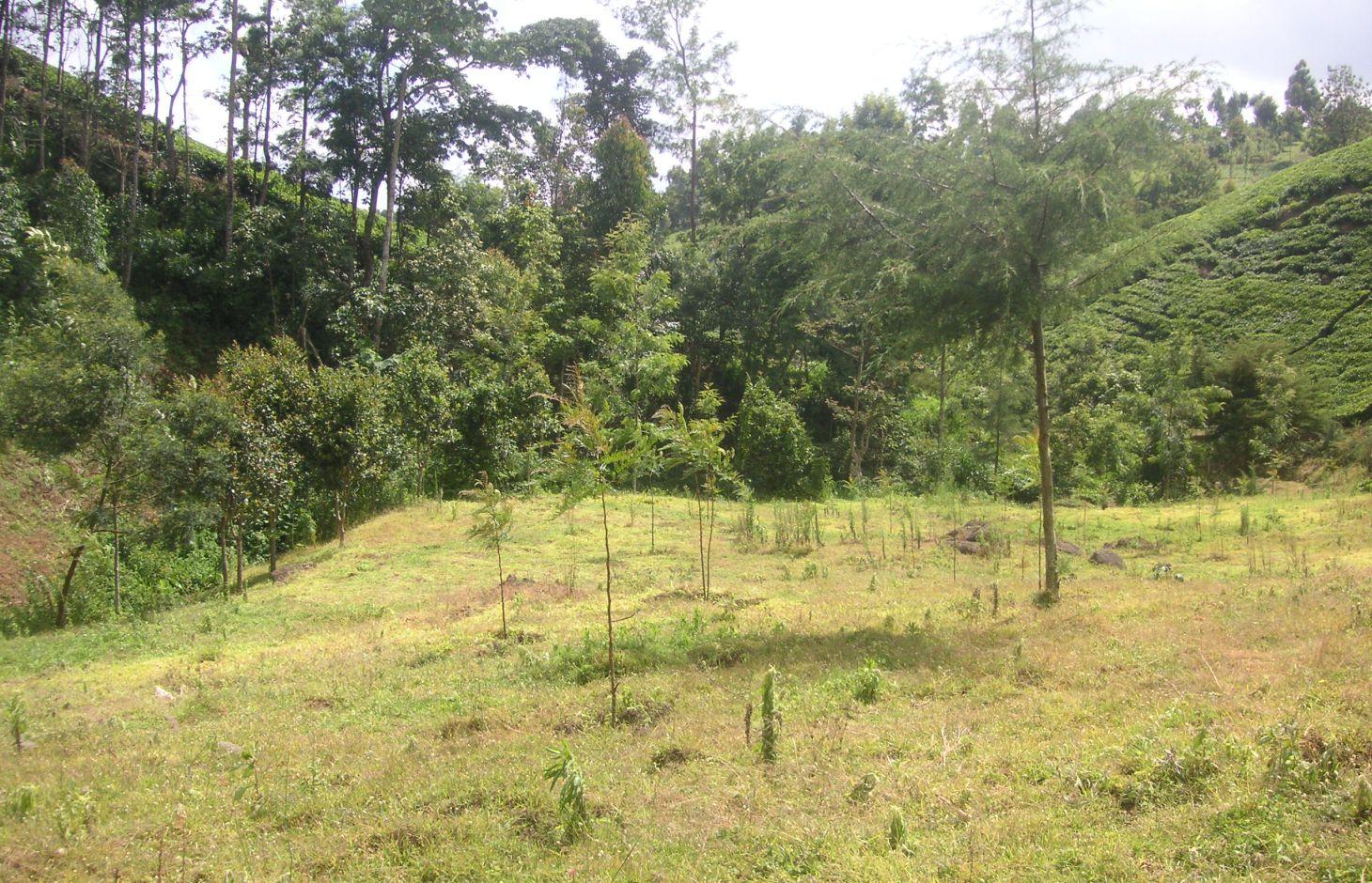
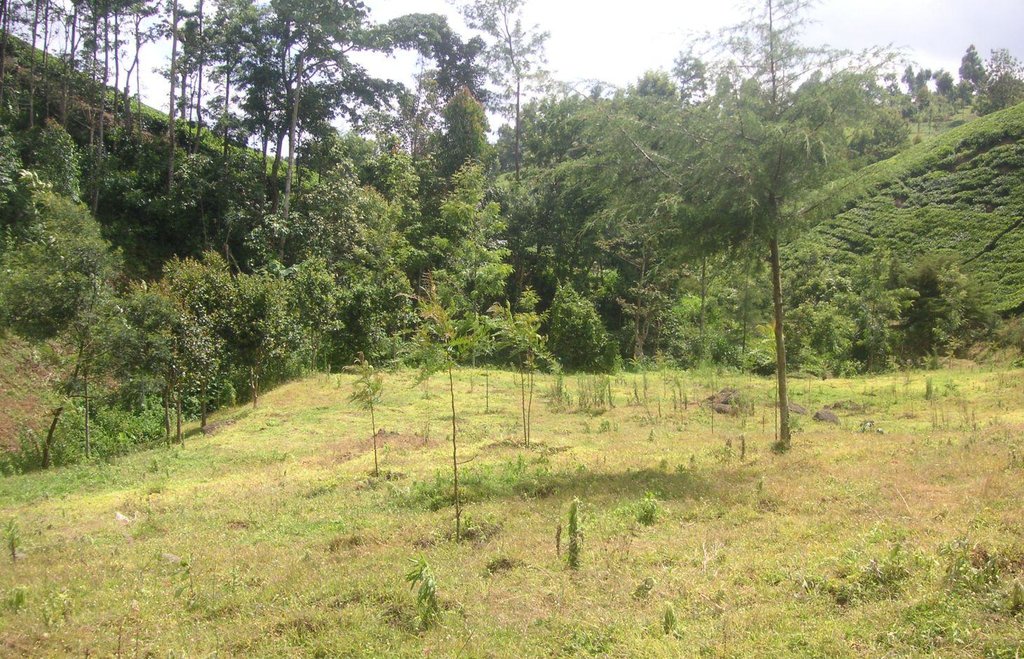
Tree line with adjacent grass strips as example of a productive and protective riparian area at Kapingazi River
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
On the south-eastern slopes of Mt. Kenya, the conditions are ideal for agricultural activities. There is plenty of rainfall (2100 mm/year) which is usually reliable. However in the year 2000, the river Kapingazi dried up for the first time since many decades during a dry spell. This led to community activities that finally came up with a system of vegetative interventions to strengthen the riparian zones. The intervention consists of tree planting and establishment of grass strips along the river. Napier grass is planted to stabilize steep slopes and to supply material for the construction of tea baskets.
Purpose of the Technology: The goals of this technology are manifold. Firstly, the vegetation prevents surface water and eroded soil flowing from the agricultural fields directly into the river. Therefore, sediments and chemicals used on the field are retained in the riparian soils and do not pollute the river. Surface water flow from runoff during heavy storms is slowed down and infiltration on soils covered by grass and trees is increased. As a result more groundwater is recharged during the wet seasons, which can be released during the dry season. Thus peak or flood flows are reduced and low flows are improved. Damage during flood flows on the riverbank (through erosion and destabilizing the riparian vegetation) as well as damages of floods downstream can be reduced or avoided.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Before planting the indigenous trees, water guzzlers like eucalyptus trees were cut down. Indigenous seedlings were planted right along the river at a distance of 2m. Between the trees and the tea plantation a grass strip of up to 10m is established. Some trees were planted scattered on the grass strip. The young trees are surrounded by grasses which are cut regularly every 2 weeks. This reduces competition and enhances growth of the trees. As soon as the trees are big enough, they function as a source of firewood, they can be pruned every 5 months.
Natural / human environment: The studied plot is situated right below the natural mountain forest of Mt. Kenya at the south-eastern slope. The source of Kapingazi River can be found at 1.5 km of walking distance upslope of the plot. Agricultural circumstances are good because of the fertile, volcanic plots and the abundant precipitations. However, the terrain is quite steep.
The zone which is used for tea production reaches from an elevation of 1700 m.a.s.l to 2000 m.a.s.l. Most tea farmers own between 4 and 20 acres. The area of the riparian zone covers 6 m from the river edge and belongs to the government. Since the harvest of the tea leaves requires a high labour input, local workers are hired. Most of the harvest is done during the rainy season because the tea plants are growing fast in this period. For the tea production only the youngest leaves are used, transported in a basket on the worker’s back to the tea factory in the evening.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Quênia
Região/Estado/Província:
Kenya/Eastern Province
Especificação adicional de localização:
Embu
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
In the year 2002 the new constitution obliged the government to take care of the water resources. The instrument for this were the WRUA (Water Resource Users Associations), local initiatives of land users that promote protective measures along the rivers.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
major cash crop: Tea
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The main land use problems are pollution of the riverwater, low rainwater storage that provokes floods, too few water during the dry season and riverbank erosion.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The main problem is the few water in the dry season that prevents irrigation.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Additionally, few food crops are planted in a relatively small homegarden.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 60 Longest growing period from month to month: april to may Second longest growing period in days: 60 Second longest growing period from month to month: november to december
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
Since the technology is only used by one farmer at a single spot, it does not make sense to indicate the area. Furthermore, the length along the river is more important than the area.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade

Degradação da água
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
- Hw: redução da capacidade de tamponamento de zonas úmidas
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hp: decline of surface water quality, Hw: reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland areas
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline, Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Riparian trees were chopped down.), education, access to knowledge and support services (People didn't know about the consequences of the deforestation.), planting directly next to river
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
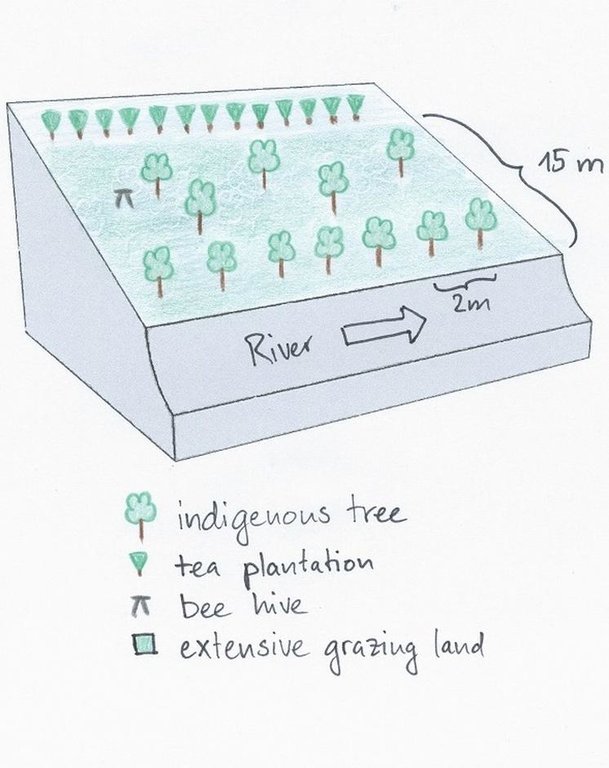
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
The area between the river and the tea plantation is used to establish a riparian habitat. Trees are planted along the river and also on the adjacent grazing land. The grass is cut regularly and used as fodder. A bee hive was installed to generate additional income.
Location: Manyatta. Embu / Eastern Province
Date: 28.12.2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 30
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: indigenous trees, Napier grass
Grass species: normal grass
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
3.33
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tree planting | Vegetativo | During rainy season |
| 2. | Replanting of seedlings which dried up | Vegetativo | |
| 3. | Planting trees | Gestão | At the beginning of the rainy season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Tree planting during rain season | Persons/day | 6,0 | 3,3333333 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Replanting of seedlings | Persons/day | 2,0 | 3,333333 | 6,67 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting trees before rain season | Persons/day | 8,0 | 3,333333 | 26,67 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings | pieces | 70,0 | 0,111 | 7,77 | |
| Material vegetal | Seedlings for replanting | pieces | 20,0 | 0,111 | 2,22 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Riparian seedlings | pieces | 90,0 | 0,034555 | 3,11 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 66,44 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding the area around the trees to get fodder and boost the tree growth | Vegetativo | every 2 weeks for 4 years |
| 2. | Weeding the lawns for better growth of the trees and for fodder | Gestão | every 2 weeks during raining season |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Weeding the area around the trees | Persons/day | 16,0 | 3,33333 | 53,33 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Weeding the lawns | Persons/day | 64,0 | 3,33333 | 213,33 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 266,66 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Jembe (Machete)
The costs were calculated for a riparian area with a length of 100m and a width of 10m, since hectares are difficult to apply on a riparian context. The determinant factor for the costs is labour. In this case, the costs are very low because the trees were only planted every 10 metres along the riparian. The seedlings have to be bought in a nursery. Most of the bushes regrow naturally and do not need any management.
Some of the seedlings had to be replanted, because they dried up. The required equipment like a spade is available on nearly every farm or can be borrowed from neighbours and is thus not added to the costs.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
2100,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Most of the rain falls during the rainy seasons from April-May and Oct-Nov.
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: subtropics. http://www.mappedplanet.com/klima/klimadiagramm-39729-Nanyuki,Kenia
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is very high
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
< 5 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water: Also excess and poor/none
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- >50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Empregado (empresa, governo)
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly Leaders / privileged
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
Off-farm income specification: Owner is a member of the parliament.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
Land user was a former member of parliament
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Produção de madeira
Comentários/especificar:
Pruning of trees
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
Grass for basket production.
Fuelwood
Comentários/especificar:
Pruning the trees
Impactos socioculturais
Oportunidades culturais
Comentários/especificar:
aesthetics
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Through the increase of the water quality, the technology improves the access to clean water.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Diversidade animal
Diversidade de habitat
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Sedimentação a jusante
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não conhecido |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
levemente positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
10% of all the riparian land users have adopted the technology
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 10-50%
Comentários:
70% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: 10% of all the riparian land users have adopted the technology. The external support was the provision of seedlings.
30% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Through the action of several organisations, the attention of the land users is drawn to a proper riparian management.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
The river does not dry up easily during dry seasons. The grass yield can be used for fodder purposes. How can they be sustained / enhanced? disseminating the knowledge among the farmers. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
A vivid and stable riparian ecosystem is the key to ensure biodiversity and stability of the riverbanks. This leads to a smaller vulnerability to floods or droughts and combats degradation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? continuous awareness raising among the land users. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Labour input for weeding is high | cutting grass at a bigger height |
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos