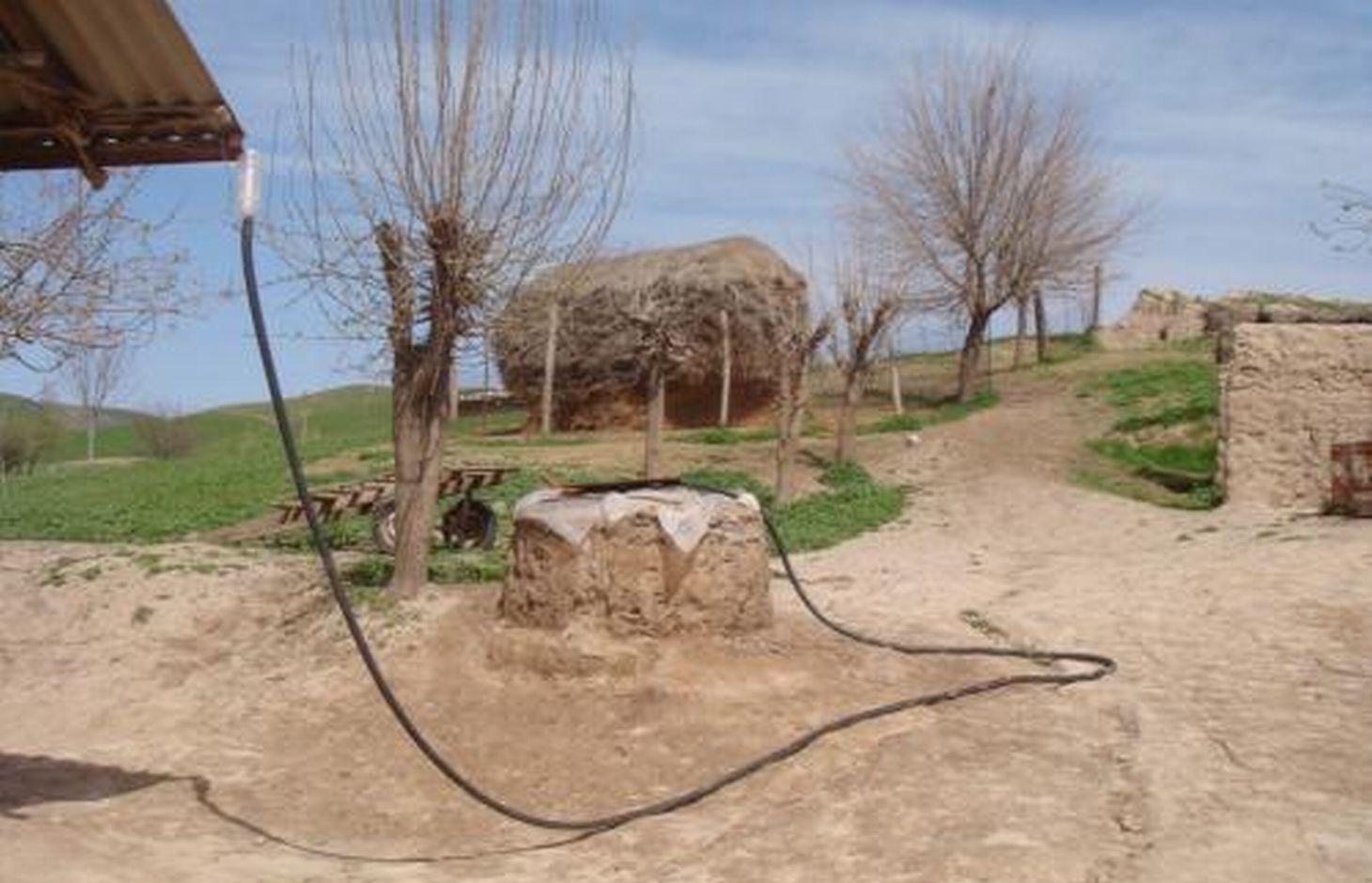
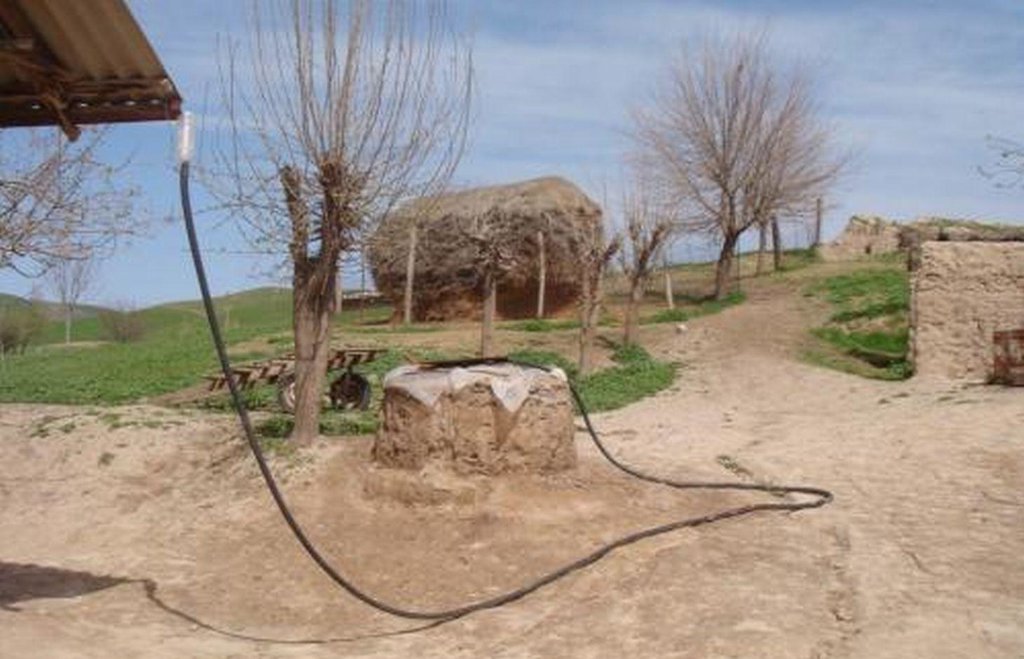
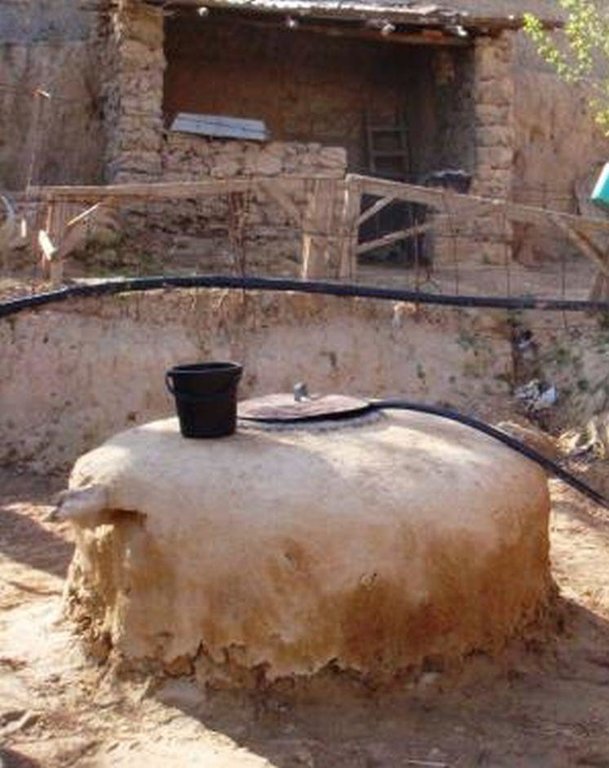
Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank. [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Daler Domullojonov
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Чамъоварии оби борон аз руи боми хона
technologies_1446 - Tajiquistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 2 de Novembro de 2021 (public)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 4 de Abril de 2018 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 15 de Agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 19 de Julho de 2017 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 6 de Maio de 2017 (inactive)
- Roof top rainwater harvesting stored in a polythene lined earth retention tank.: 14 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe (Welthungerhilfe) - TajiquistãoNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience Tajikistan (PPCR Tajikistan) - Tajiquistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
06/04/2011
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
The use of an earth tank lined with a polyethylene sheet to retain rainwater collected from the roof of the house.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
An earth retention tank is a simple low cost structure that can be used to retain rain water from the rooftop. A hole is prepared and lined with a polyethylene sheet to prevent leakage. The top of the hole is covered with a metal lid for access. The roof of the house is fitted with a plastic guttering that captures the rainwater and funnels the water via a plastic pipe into the earth tank. The water in the earth tank then can be utilised for the irrigation of crops (especially during the hot dry summer months), sanitation, and potentially drinking water.
Purpose of the Technology: The population in Southern Tajikistan consists largely of subsistance farmers and are thus highly reliant upon their kitchen garden plots. As the population in the area continues to expand, the pressure on the land increases. The latter is already in a poor state, because it is becoming degraded through deforestation, overgrazing and general over exploitation. There is much precipitation during the rainy season from autumn until spring in Southern Tajikistan, but the scarcity of water from late spring to the end of autumn poses a problem with water shortages.
During the rainy season, a lot of water is lost as surface runoff, this water can be saved in a retention tank to be utilised during the dry season. It can be used to water crops to help increase yields as well as crop diversity and quality. The additional water can also be used for sanitation, drinking water and watering of livestock.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For the establishment of such a retention tank several steps are needed. In preparation, a rough estimation of the potential volume of harvested rainwater needs to be calculated. Thereafter, a location for the tank needs to be selected so that expenses are minimised and it is easy to access. The establishment of ponds near big trees is not recommended, because the polyethylene layer might be punctured by the roots.
Natural / human environment: The actual steps of constructing the tank involve:
(1) digging the pond, (2) plastering the inside walls with a fine soil and water mixture to smooth them, (3) lining the pond’s walls with double polyethylene layer, (4) connecting the inside polyethylene sheets with the pond coverage through a piece of cord, so that it can be taken out of the pond any time to be cleaned of sediments, (5) covering the pond with any available material such as a soil, water and straw mixture, reinforced by several poles, leaving an opening of 0.25 x 0.25m to extract water, (6) finally connecting the roof to the pond with a plastic pipe. To avoid dirty water flowing from the roof into the pond, the pipe should only be connected to the pond some time after the rainfall has started.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Khatlon province
Especificação adicional de localização:
Temurmalik, Baljuvon
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology was developed through a Welthunger Hilfe Project and promotion in the local communities started in 2008.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Assentamentos, infraestrutura
- Assentamentos, edificações
Observações:
Kitchen garden
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Inefficient natural resource management, which is mainly visual because people throw potential organic fertilisers away instead of spreading them on the fields. Incorrect ploughing techniques which leads to the acceleration of erosion, deforestation and waste of fuel materials in inefficient stoves and ovens. Overgrazing leading to pasture degradation.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): lack of water
Constraints of settlement / urban
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: March - November
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Coleta de água
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 10-100 km2
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification, Hs: change in quantity of surface water, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Inproper land management), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Cutting trees and shrubs), overgrazing, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (poor water supply)
Secondary causes of degradation: population pressure (the population is increasing over time.), poverty / wealth (lack of funds)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Autor:
Daler Domullojonov, 14, Giprozem str., Dushanbe, Tajikistan
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Harvesting water from the household roof to an earth built retention pond with plastic sheet lining. The retention pond is covered with a removable metal plate for access.
Location: Davad village, Vatan jamoat, Temurmalik district,. Khatlon province, Tajikistan
Date: June 2009
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low (No special knowledge is needed for implementation)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Any farmer can implement, once they understand the basic concept.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, water harvesting / increase water supply
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2
Construction material (earth): digging in earth, plastering and cover
Construction material (wood): pole for cover
Construction material (other): polyethelene sheets, plastic pipe
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 3.96m3
Catchment area: 72 m2m2
Beneficial area: 0.2h.am2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:0.5
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
TJSomoni
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
4,5
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
6.60
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Manual digging of pond;smoothing and plastering;covering pond | Estrutural | once in the beginning |
| 2. | polyethylene sheet and pipe procurement, preparation and placement; | Estrutural | once in the beginning |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Manual digging of pond | Persons/day | 2,0 | 30,0 | 60,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Placing sheet | Persons/day | 0,1 | 30,0 | 3,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Wooden poles for pond | poles | 4,0 | 5,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Earth | tons | 0,1 | 45,0 | 4,5 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Polyethylene sheet | square meters | 10,0 | 2,3 | 23,0 | 50,0 |
| Material de construção | Cord | meter | 20,0 | 0,025 | 0,5 | 50,0 |
| Material de construção | Plastic pipe | meter | 5,0 | 2,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Bucket | pieces | 1,0 | 4,5 | 4,5 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 125,5 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cleaning of pond (washing out sediments) | Estrutural | once every year |
| 2. | Changing polyethylene sheet;covering | Estrutural | once every 2 years |
| 3. | Changing polyethylene sheet;covering | Gestão | once per 2 years |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Cleaning of pond (washing out sediments) | Persons/day | 0,1 | 45,0 | 4,5 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Changing polyethylene sheet (every 2 years) | Persons/day | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Polyethylene sheet | square meters | 10,0 | 2,3 | 23,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Cord | square meters | 1,13 | 8,85 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Earth | tons | 0,05 | 45,0 | 2,25 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 49,75 | |||||
Comentários:
The above costs were calculated for the building of one retention tank. One household could have several ponds in one kitchen garden.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The type of earth in Tajikistan is very good for making the retention ponds, the labour is provided by the land user, and the plastic pipes can be manufactured out of empty plastic bottles. The polythene sheet and cord have to be purchased from the shop.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Average annual precipitation is 575 mm (according to data from the last 15 years), most of which falls between late autumn and spring time.
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate. 3 months below 5 degrees, 7 months above 10 degrees
Continental conditions
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: Mainly communities in this range
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is medium and if it is not overused the fertility can be increased.
Topsoil organic matter: Usually locals collect cow dung and use it as fuel.
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium because the loess material contains clay material
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Ground water table can also be below 50 m.
Availability of surface water is so poor du to deforestation the natural water balance is disturbed.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: In this example the farmer's son has migrated to Russia.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Produção animal
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Quantidade anterior à GST:
120 litres
Quantidade posterior à GST:
12000 litres
Comentários/especificar:
Water storing capacity of household increased
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
100
Comentários/especificar:
vegetables and greens are available for own consumption
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
no need to carry water
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
more water available
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Comentários/especificar:
more water available
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
only in kitchen garden
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | não bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
Comentários:
To minimise the damage to the polyethylene waterproofing layers and, reduce evaporation rates, pond is covered. As the pond is dug into earth the temperature remains fairly stable. If precipitation decreases less water can be harvested.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Before the implementation of this technology, one family would spend an avarage of $44.5 on one truck of water per month. A pond costs around $25 to build, and should provide families with around 4 months worth of water after the rainy season.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
600 households (in an area of 10-100km^2)
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 10-50%
Comentários:
58% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
350 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: In the initial stages of the project, they were provided with 50% of the costs of the polyethylene sheets and cord only.
42% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: After observing the benefits of the technology and the high cost benefit ratio, many people in the community and surrounding villages have replicated this technology themselves.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Easy and quick to establish, and maintain. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
It is a low cost technology and can be made from many locally available materials. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To disseminate these ideas in areas with water scarcity through local Extension Service providers / NGOs or local inhabitants. |
|
It reduces the time and effort to collect water and also the cost to buy water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promotion of different water saving methods and technologies by interested and line departments. |
| More water available for gardening and household purposes |
|
Increases access to water for drinking and sanitation purposes. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Construction of larger and/or more tanks. |
|
Provides water for irrigation during the hot dry months, therefore improving crop diversity and yields. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Training and education on kitchen garden farming techniques to optimise the use of the extra water supply. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The polyethylene only lasts for 2-4 years. | To increase the number of layers or use a thicker polyethylene sheet |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The plastic layers have a limited lifespan. | To find thicker and more hardy materials, or apply multiple layers. |
| Th waterproof layer can easily be degraded by mice and large insects. | |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Brochure - Converting drought prone areas into productive gardens! Low cost options to improve rainwater harvesting in Southern Tajikistan rain fed areas …. and beyond! 2009
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Welthungerhilfe, Temurmalik office,
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Training film - Simple ways to improve management of kitchen gardens in Southern Tajikistan rain fed areas …. and beyond. 2009
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Welthungerhilfe, Temurmalik office
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Welthungerhilfe project final narrative report (144-912) - 2010
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Welthungerhilfe, Temurmalik office
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos