Integrated stone wall and poplar tree perimeter fencing [Tajiquistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Habib Kamolidinov
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1107 - Tajiquistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Integrated stone wall and poplar tree perimeter fencing: 21 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Integrated stone wall and poplar tree perimeter fencing: 23 de Julho de 2017 (inactive)
- Integrated stone wall and poplar tree perimeter fencing: 14 de Agosto de 2019 (inactive)
- Integrated stone wall and poplar tree perimeter fencing: 2 de Novembro de 2021 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
GITEC/ADB/DMC Rural Development Project Land Management Institute - Tajiquistão1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
28/04/2011
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
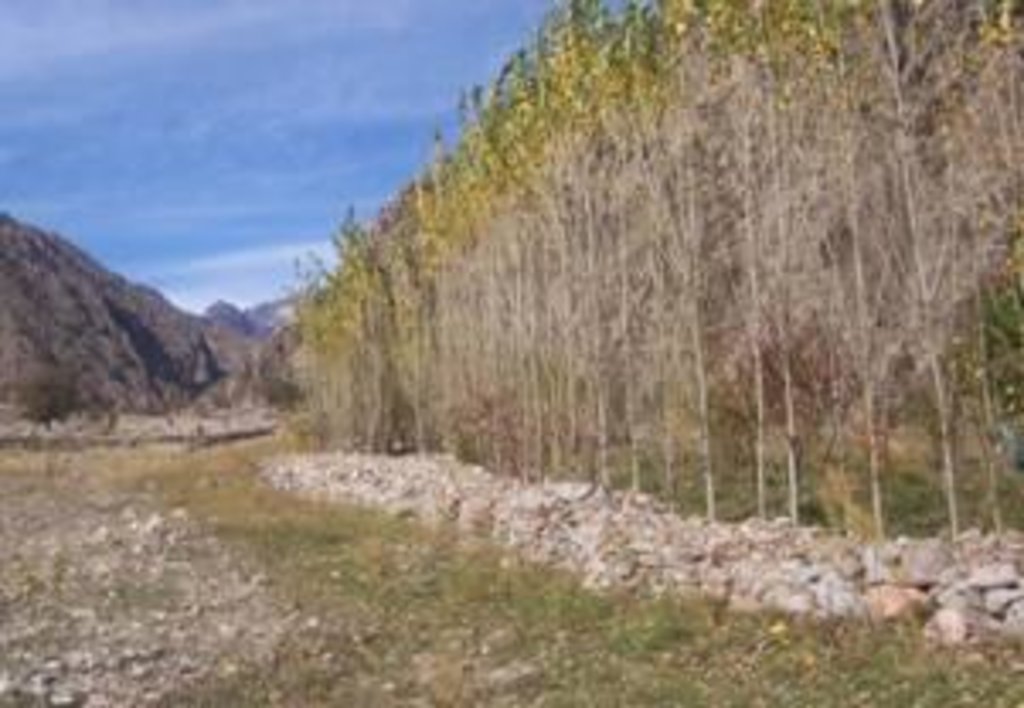
Stones cleared from land within a narrow valley floor where flat land is at a premium, was used to construct a perimeter stone wall which was subsequently supplemented with a row of poplar tree to protect an agro-forestry area with small scale supplementary irrigation.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
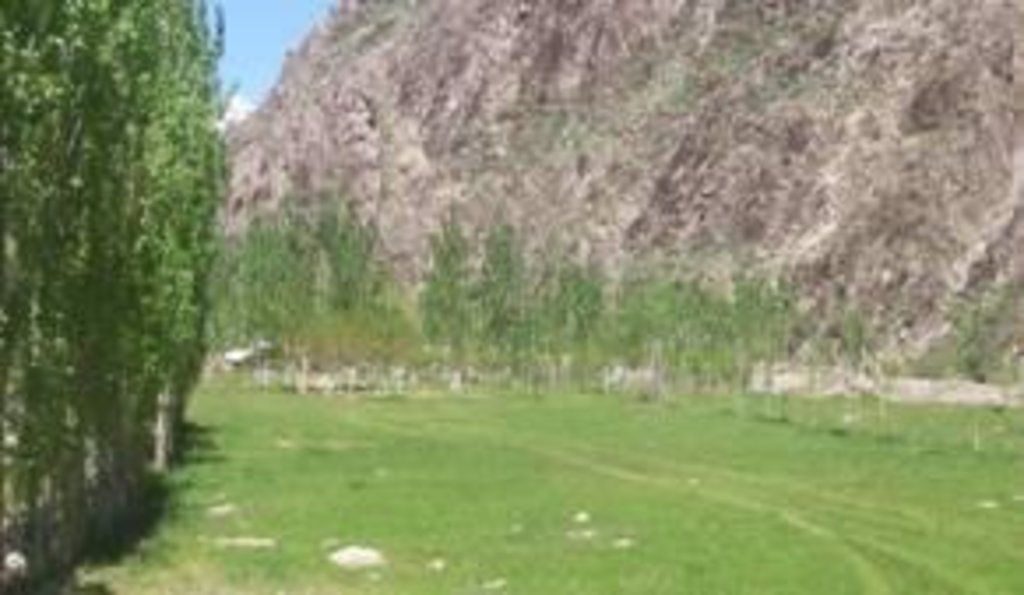
The area in question is a very narrow, flat valley floor, 95% of which was covered in stones and boulders, and devoid of vegetation, both grass and trees/shrubs. The stones in the area were cleared and used to build a protecting, perimeter wall (approx. 1.5 m high). This was then supplemented by an inner row of fast growing poplar trees. The stone clearing has resulted in deeper soil within the protected area that has led to far greater vegetation coverage, such as grass (that can be cut and used as fodder), forest and orchard trees and vegetable gardens. Irrigation was provided to the area by a small diameter poly pipe from a permanent spring. The area is now being extended to almost double the size of the initial walled agro-forest area.
Purpose of the Technology: The farmer’s primary aim, in initiating and continuing this SLM approach, was to “leave a legacy of improved land” for future generations, recognising how little flat and potentially productive land there is in this high, narrow valley location. Clearing the land of stones and building a walled enclosure that was irrigated greatly assured the quantity and quality of fodder for his animals, as they remain fenced in beside his village home almost all year. Fruit and vegetable production was also greatly improved.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The family commenced stone clearing and wall construction in 2005. The next task was tree planting; poplar trees were planted around the wall's perimeter. The irrigation source was tapped into using a poly pipe. The vegetable gardens are seasonal and their plants change with the seasons and the family’s needs. Stone removal continues even now, to improve the soil in the walled area. The farmer hopes to extend the walled area in the future.
Natural / human environment: Before the family began clearing stones and building the wall, this land had almost zero productivity. This area has a shortage of cultivated land and with increases in popluation and continued food insecurity, cultivated land is at a premium.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Tajiquistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Central District of Tajikistan
Especificação adicional de localização:
Kushon village, Romit Jamoat, Vahdat
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The initiative began in 2005 and has been ongoing ever since, it continues to improve, at least up to 2010 when reviewed.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- increase size of agrictultural land
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Major food crop: Fruit, vegetables, grass for fodder and orchard fruits.

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
Principais produtos/serviços:
Apple, apricot, cherry, firewood and construction materials
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): This area is strongly dependent on the extremely limited flat, valley bottom land for the production of pasture, 'cut and carry' fodder, orchards and vegetable production. 95% of this land is covered in stones that require removal before any productive capacity can be achieved. Even when cleared of stones the soil is still very shallow (< 20cm) and requires irrigation to ensure plants survive the hot summer months
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Same – the above words were used by him in the on-farm interview
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: sheep/cattle
Plantation forestry: The Poplar trees they planted are pruned and thinned for firewood and construction materials
Other type of forest: orchard species: Apple, Apricot, Cherry
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
Other: Oo: Other: wastelands, deserts, glaciers, swamps, recreation areas, etc
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: April to September
Densidade animal (se relevante):
< 1 LU/km2
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Agrofloresta
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
A small area was all that the family could manage as there was an initial large workload, clearing stones and fence building, etc
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas estruturais
- S6: Muros, barreiras, paliçadas, cercas

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
- M3: Disposição de acordo com o ambiente natural e humano
- M4: Principal mudança no calendário de atividades
- M5: Controle/mudança de composição de espécies
Comentários:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping, cover cropping, retaining more vegetation cover, furrows (drainage, irrigation)
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, in blocks
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bl: perda da vida do solo
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bl: loss of soil life
Secondary causes of degradation: land tenure (The lack of good quality available land puts pressure on the lower grade land.), poverty / wealth (People still need land to harvest to survive.)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
Comentários:
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
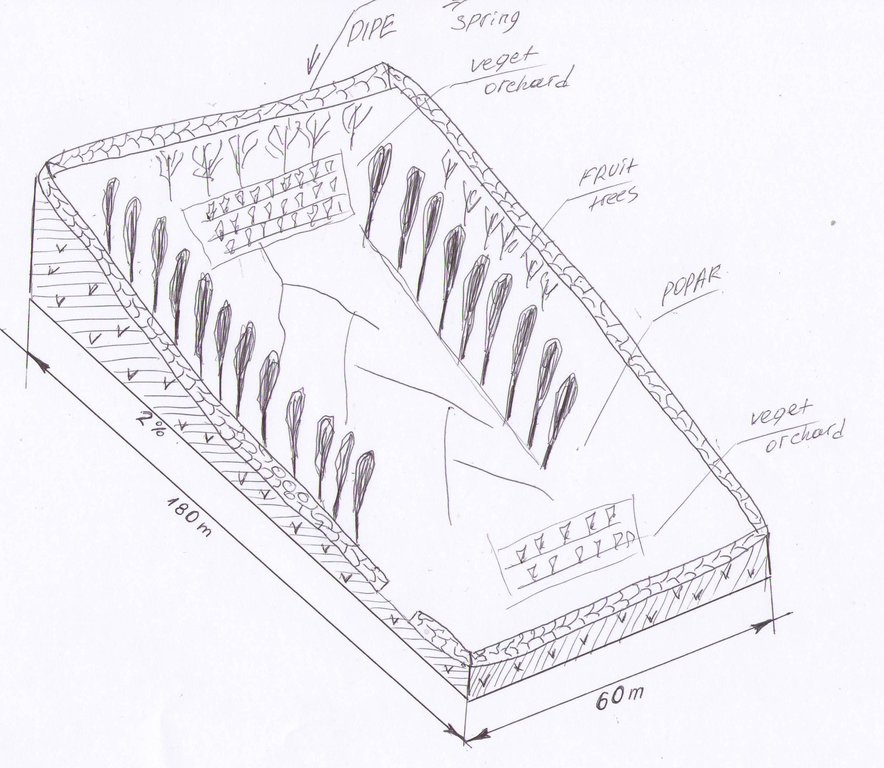
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
The drawing shows a 1.5m high stone wall, lined with poplar trees on a gentle slope. The site is located in the valley floor and has access to a naturally occuring spring. The enclosed land is now used mainly for fodder production, intercropped with fruit trees and vegetable patches.
Location: Khatlon province. Kushon village, Romit jamoat, Vahdat raion
Date: 21.04.2011
Technical knowledge required for land users: high (The farmer has a good understanding of farming techniques.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length, improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, reduction in wind speed, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Perennial pasture (grass) for fodder
Quantity/ density: 100 %
Remarks: covers 1.3 ha
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Forest and orchard trees with fodder grasses and vegetable gardens
Quantity/ density: 100
Remarks: dramatically increased
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Perennial grass is the cover crop
Quantity/ density: 100
Remarks: dramatically increased
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: Land previously bare and stony
Quantity/ density: 100
Remarks: vegetation cover increased
Furrows (drainage, irrigation)
Material/ species: Irrigation via hand cut 20cm cube ditches and poly pipe from nearby spring
Agronomic measure: Stone removal and clearance
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 1200
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
In blocks
Vegetative material: F : fruit trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 60% cover
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): About 0.5 ha planted
Trees/ shrubs species: Poplar trees - planted
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Apple, cherry, apricot - planted
Grass species: Grass - natural
Other species: Vegetable garden - planted
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 0.00%
Wall/ barrier
Vertical interval between structures (m): Wall around area
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.7
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 500
Construction material (stone): Stone wall – from stones removed from within area
Lateral gradient along the structure: 3 degrees%
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
somoni
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
4,5
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
4.50
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Stone clearing | Gestão | On initial set up |
| 2. | Wall building | Estrutural | On initial set up |
| 3. | Tree planting | Vegetativo | annually |
| 4. | Irrigation pipe | Estrutural | On initial set up |
| 5. | Vegetable garden | Vegetativo | annually |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Stone clearing | Persons/day | 15,0 | 50,0 | 750,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Wall building | Persons/day | 15,0 | 50,0 | 750,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Tree planting | Persons/day | 10,0 | 25,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Vegetable garden | Persons/day | 20,0 | 15,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | Pieces | 6,0 | 16,66666666 | 100,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Trees | Pieces | 100,0 | 10,0 | 1000,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Plants for vegetable garden | - | 1,0 | 450,0 | 450,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Irrigation pipe | meter | 700,0 | 3,0 | 2100,0 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Wall | meter | 500,0 | 7,0 | 3500,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 9200,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Stone clearing | Agronômico | Annually |
| 2. | Vegetable garden | Agronômico | Annually |
| 3. | Tree planting | Agronômico | Annually |
| 4. | Animal husbandry | Agronômico | Annually |
| 5. | Fertilising and cultivating (garden vegetables) | Agronômico | Annually |
| 6. | Tree planting | Vegetativo | Annually |
| 7. | Vegetable planting | Vegetativo | Seasonally |
| 8. | random stone removal | Estrutural | Annual |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Stone clearing | Persons/day | 10,0 | 25,0 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Vegetable garden | Persons/day | 50,0 | 25,0 | 1250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Tree planting | Persons/day | 20,0 | 15,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Animal husbandry | Persons/day | 40,0 | 15,0 | 600,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour: Fertilising and cultivating | Persons/day | 20,0 | 15,0 | 300,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour: Random stone removal | Persons/day | 10,0 | 15,0 | 150,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 2850,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: All works done manually., all done manually, All work done manually.
Wall – length; all money spent in first 1 or 2 years
Trees – per unit tree; initial start up and annual costs, now ongoing.
Vegetable seeds – per packet, annually
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The human labour costs involving the family were nothing as they willingly gave of their time to clear the land and build the wall, plant trees and create vegetable gardens. The real labour cost were the few days when the farmer paid 3 men to help build the wall.
The cost of the wall cost was also nothing as all materials came from on site.
Trees – there was an initial start up cost and the farmer said he tries to plant at least 20 new trees each year to maintain and enhance productivity
Grasses (fodder) – are self regenerating and local. The farmer has never bought grass seed or used fertiliser on the grass
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Dominate in Spring (March-May) The period June to September is very hot and dry (almost no rain).
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone: The centre of the site is at 1,305 meters a.s.l
Landforms: The site is slightly sloped, north to south.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: Before intervention the soil was <1cm in depth. Now 20-30cm average depth.
Soil texture: Loess soil – silty loam
Soil fertility is high and with proper management/intervention these soils are very fertile. Before the intervention they were virtually infertile.
Topsoil organic matter is medium with intervention (<1% before).
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium because loess soils are low in clay (high in silt) – so have moderate PAWC.
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water: Also medium
Water quality (untreated): The spring water is almost pure water
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Not a large difference. The farmer’s wife shares the workload but tends to focus more on the garden, fruit production, household duties and bee keeping. The farmer conducts hay cutting and gathering, stone removal, fence upkeep and animal tending (feeding and slaughtering when required).
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
100% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The issue is that the older and the very young family members (ie the farmer and his wife are in their late 50s ) stay on the farm. The rest (18 to 50 yrs ) have paid employment in Dushanbe and Russia, and only visit the farm, occasionally. However, it is believed they part-finance (contribute) to the upkeep of the family farm.
Market orientation of production system: All of the farm produce stays on the farm for home consumption, but they do eat well and very healthy (fresh and organic) food. Their cattle are also well fed and healthy .
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Is 1.5 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- This is jamoat land (local village land). The farmer has no certificate but is now applying for one
- This is jamoat land (local village land). The farmer has no certificate but is now applying for one
Comentários:
Not yet an issue – as he is the only one with access to the spring water
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Before the Technology this land was almost 95% covered in rocks with almost zero carrying capacity, no productivity and no water supply. So the % increase as a result of the Technology is all related to this increase from nothing.
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Produção animal
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2
Produção de madeira
Risco de falha de produção
Diversidade de produtos
Área de produção
Gestão de terra
Geração de energia
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
The primary aim of the farmer in introducing the technology was to improve the family’s lifestyle (livelihoods) and well being. He has easily achieved this and it seems to be getting better, year on year.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Drenagem de excesso de água
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Ressecamento/ selagem do solo
Compactação do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Outros impactos ecológicos
Hazard towards adverse events
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
Comentários:
The Technology (stone clearing, wall building, tree planting, vegetable production and grass (fodder) production) is vastly more tolerant to extremes of climate than what existed before.
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
The establishment and ongoing costs are very small compared to the returns both long and short term gained from introducing the Technology
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
1 household
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material suppor
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Unsure how many such walled agro-forests are in this region. Would need to consult with Jamoat leader. There are quite a few walled areas. But unsure about the number and content (ie technologies inside).
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There seem to be quite a few enclosures in this area – but we have not conducted a formal survey.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| As above, as these words were transcribed during the farmer interview, on site. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
The stone clearing and wall building underpins the whole SLM initiative. That it was achieved by only 3 or 4 people, in under a year and at such a low cost (with minimal paid labour) adds to the strengths. The wall is also critical to keep animals out of this now richly vegetated area, not only sheep and goats but also wild pigs and even wolves. The stone clearing “created” soil which is critical for all the vegetation growth within the walled area. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The farmer is in the process of expanding the stone cleared area, and is using the stone to build a larger perimeter fence, aiming for a larger plot of 2 or 3 ha. |
|
Bringing water to the site (at his own cost) by poly pipe was a critical part to the technology. The walled agro-forestry area would have struggled without this extra and constant water supply – as the soil is so shallow (all the rock remains below the soil surface). Now he can have good fodder grass, trees, orchard and vegetables with a guarenteed regular supply. Getting the plants and trees through the hot summer months is the key use of the water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The farmer wishes to source a 2nd spring to water the extended (2 - 3 ha) site. |
|
The rich mix of vegetation on the site (trees, perennial grasses and vegetable production) not only ensures the intervention remains viable but also ensures a continuous, rich, healthy food supply to the family and their animals year round. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The farmer has already started to plant new fruit trees outside the original walled area, in readiness for moving the fence to encompass a 2 -3 ha site. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| As above; as these were the sentiments of the farmer during the on site interview. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| None really. What the farmer has achieved is most impressive. Particularly as his Technologies were all self-financed and conducted slowly and carefully, hence with no financial burden to the family and no interruption or lessening of their food supply. | If costs / budget permit (unlikely) to bring some power-type assistance to stone removal (like a small tractor) or a solar powered pump to increase irrigation water pressure. However, the farmer may not wish to be reliant on such items, as if they breakdown, his whole enterprise (currently so successful) may suffer. |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
There is no relevant documentation
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos