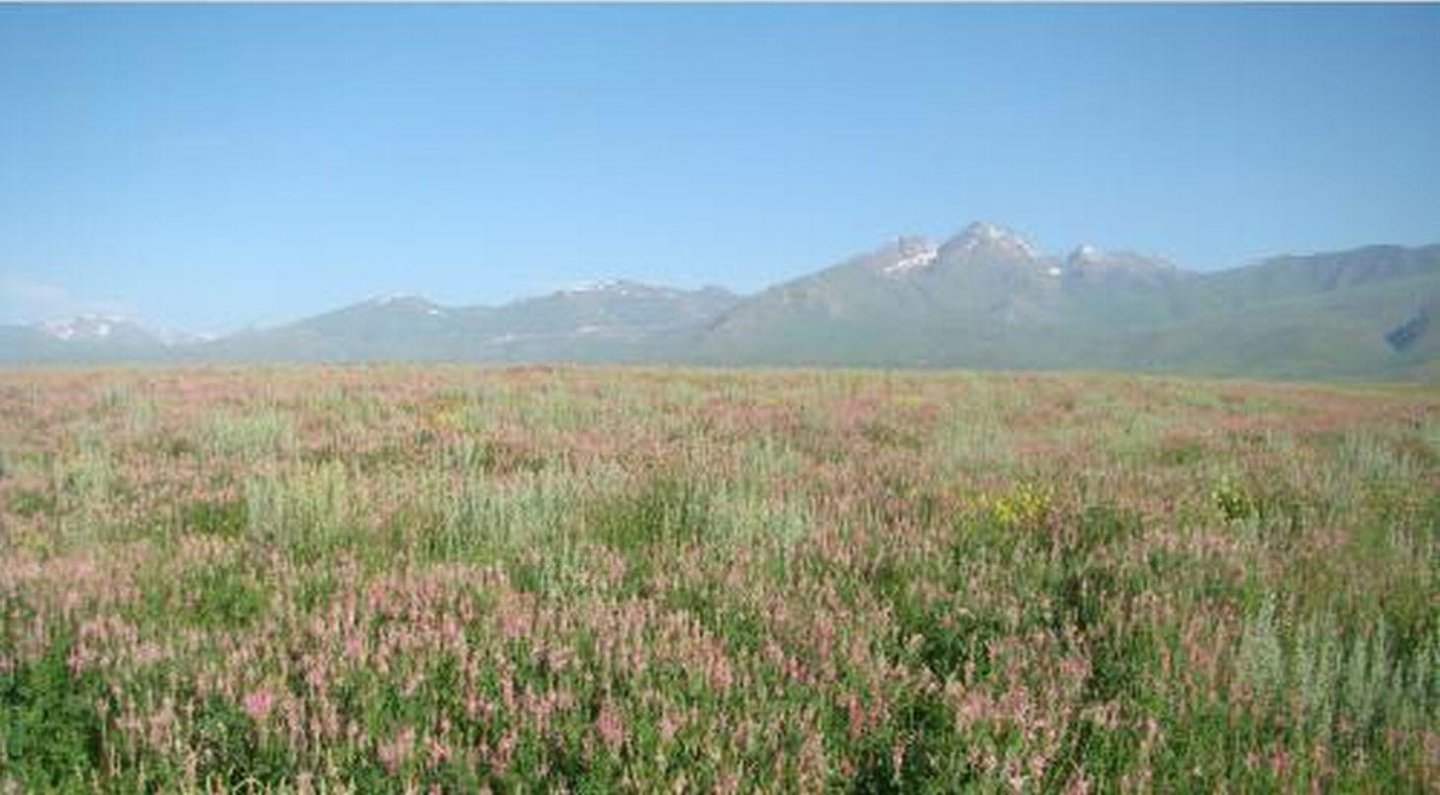
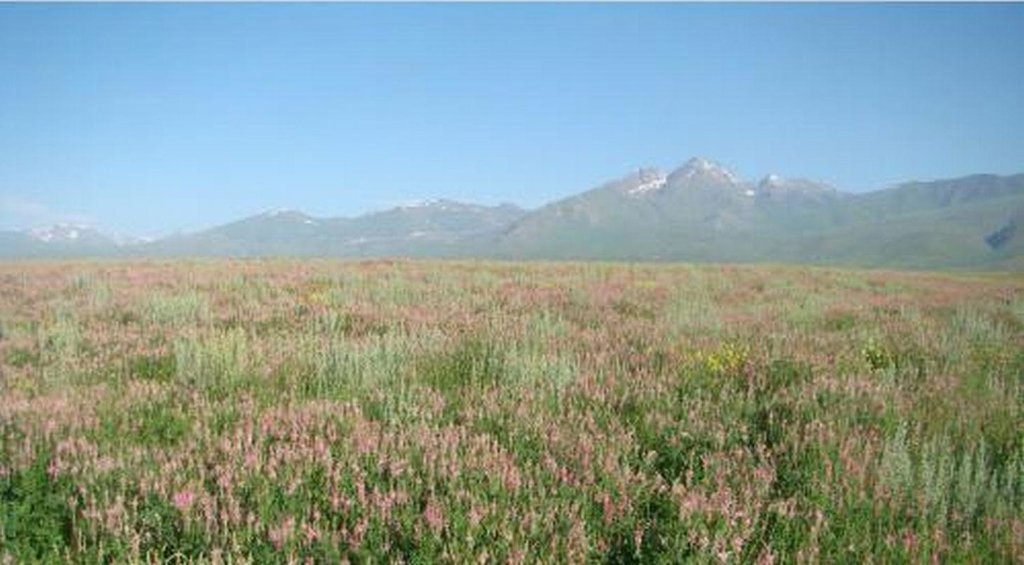
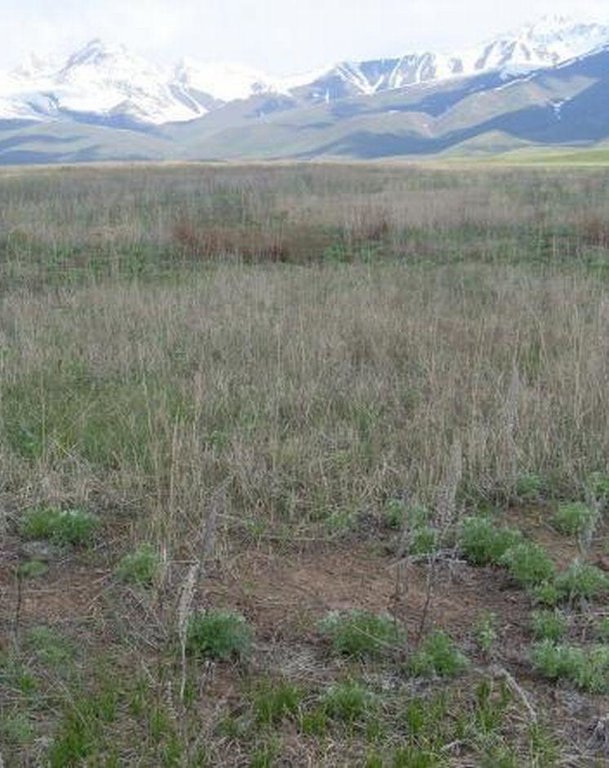
Cultivation of sainfoin on high mountain pastures – Suusamyr Valley (in the frame of CACILM) [Quirguizistão]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Abdybek Asanaliev
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Kyrgyzstan - Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM/ИСЦАУЗР)
technologies_963 - Quirguizistão
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Cultivation of sainfoin on high mountain pastures – Suusamyr Valley (in the frame of CACILM): 27 de Dezembro de 2016 (inactive)
- Cultivation of sainfoin on high mountain pastures – Suusamyr Valley (in the frame of CACILM): 21 de Março de 2017 (inactive)
- Cultivation of sainfoin on high mountain pastures – Suusamyr Valley (in the frame of CACILM): 3 de Agosto de 2017 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
usuário de terra:
Ibraimov Azimjan
Farmer in Susamyr valley
Quirguizistão
usuário de terra:
Usubaliev Baibek
996 (312) 566 318
b.usubaliev@up.elcat.kg
ELCAT
Toktanaliev Street, # 4 A, room # 212,
Quirguizistão
usuário de terra:
Duishenaaly uulu Urmat
Suusamyr Village
Quirguizistão
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM I)1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
14/01/2011
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Conservation of soil fertility through the cultivation of sainfoin (perennial legume plants)
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The Suusamyr Plain is located in the South-West of Chui Valley. Generally, this zone, located at 2000-3800 meters above sea level is used by farmers as summer pastures. Farmers are practicing agro-pastoralism by grazing animals and at the same time producing winter fodder for their livestock. They cultivate mainly barley and sometimes perennial grass.
The territory of the local administration of the Aiyl Okrug “Suusamyr” includes 6645 hectares of arable land. In 2009 about 2500 hectares were cultivated with cereals (including 1950 ha of barley) and 250 ha with sainfoin. As a result of the monoculture of cereals, weeds, pests, and insects accumulate on the fields and the soil fertility is declining. These are direct and indirect indicators of soil degradation.
The main cultivated perennial legume is sainfoin. However,farmers are short of sainfoin seeds. Most of them cultivate sainfoin for hay making and consider the seed production as non profitable.
Fallow is maintained free from weed during the vegetation season. As fallow is weed free and accumulates the soil moisture it has synergy effect to harvest high yield of barley grain. This fallow is kept during one vegetation season and applied by other farmers during next season. Crop rotation cycle is 5 years including 1 year-fallow period (1year-fallow period, 1year for barley planting and 3 years for sainfoin planting). Barley is planted into the fallow.
Sainfoin improves the soil structure as a result of high rizo-biomasses (237-333 kg/ha). Sainfoin is able to accumulate 194 -178 kg/ha of biological nitrogen providing sufficient nitrogen fertilization for two consecutive cropping seasons. Sainfoin can be cultivated at altitudes from 700 to 3400 m above sea level (G. Balian, 2004). Sainfoin is a high nectar producting crop, allowing farmers to produce 150 kg of honey from 1 hectare of sainfoin during a vegetation period. As the result of insect pollination, an increase in seed production of between 100 and 200 kg/ha has been observed.
Purpose of the Technology: Soil fertility conservation through crop rotation of barley with the perennial grass sainfoin (Onobrichis sativa).
Farmer Ibraimov Azimjan has 25 hectares of private land and rents other land from neighboring farmers. UNDP’s project procured seeds of sainfoin and covered expenditures for tillage and planting. The farmer’s responsibility is to distribute produced seeds among other farmers which are able to expand their areas under sainfoin cultivation. The farmers maintains crop rotation.
Fields are located in the foothills at an elevation of 2038-2200 m above sea level. Plowing is conducted along the slope. But planting is done across to the tilling direction, horizontally along the field (contour planting drilling). This technology increases vegetation cover and after harvesting stubbles remain
Agriculture in Suusamyr Valley is based on animal husbandry which is kept on pastures during three seasons (spring, summer and autumn). But farmers practice agro-pastorals. They have private arable land and produce cereals and forage crops. The Local Government “Suusamyr” has 6645 hectares of arable land including 561 hectares from the Distribution Found (state regulated land). Farmers are not subsidized by the Government.
The farmer Ibraimov Azimjan has 25 hectares of private land and rents other land from the neighboring farmers. In 2009 UNDP’s project procured basic seeds of sainfoin and covered the expenditures for tillage and planting. UNDP’s project organized several workshops for farmers on technology of cereals and forage crops cultivation. Project manager also had finance support in field inspection of sainfoin seed and barley.
Farmer’s responsibility is to distribute seed among other farmers which able to expand their areas under sainfoin. Farmer has resources to guard the field from grazing of animals during the vegetation period, harvest and transportation of seed. Azimjan also organized the seed cleaning and storage. Project’s management developed the rules on seed distributions and sale.
The farmer should produce sainfoin and barley in order to get benefit. Farmer’s responsibility is to distribute seed to other farmers which able to expand the area under sainfoin and barley. Name of sainfoin variety is “Belek”, barley variety is “Kylym”, they are developed in research centers of Kyrgyz Republic.
The population of the Aiyl Okrug “Suusamyr” is 6400. The Local Government has no human resources for field activities. There are six villages at the territory of this Local Government. All fields and villages are connected by dirt roads. The electricity is supplied on regularly basis. People have drinking water supplies.
Farmer’s fields are located at foothills of 2038-2200 m above sea level. The type of land use is rainfed. Some irrigated channels which were developed in Soviet time are destroyed now. The fields are infested mainly with wild Oat, Couch-grass, spp. pigweed, wormwood and others.
The farmers cultivate cereals as monoculture. Some of them plant the sainfoin. Additionally, farmers cultivate potato on a total area of 180-200 hectares. The varieties are from local breeders (Nevsky, Cardinal) and introduced varieties from seed Firm “Agrico” and “NZPC” (Picasso, Sante and Mondial).
The main type of soil is chestnut (light chestnut soil and dark chestnut soil). The potential fertility of these soils is high but due to the lack of crop rotation, plant protection activities, fertilizer application, soil degradation is going on. There are no soil maps in the office of local administration except for those which were developed during the Soviet time.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Quirguizistão
Região/Estado/Província:
Kyrgyz Republic, Chui oblast
Especificação adicional de localização:
Jayl district
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: The sainfoin is cultivated on mountain pastures from 800 meters to 3000 meters above sea level
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The Technology was developed by the Kyrgyz Livestock and Pasture Research Institute and applied by the UNDP Project "Demonstration Sustainable Mountain Pasture Management in Suusamyr Valley, Kyrgyzstan"
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Seminomadismo/pastoralismo
- Fazenda pecuária
Pastagem intensiva/produção de forragem:
- Pastos melhorados
- agro-pastoralism
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Decline of soil fertility due to longstanding cultivation of barley on the field. Annual conventional plowing is affecting the mineralization of soil humus.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Decline of barley yield. The quality of barley grain also is declining.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: April - August
Densidade animal (se relevante):
25-50 LU /km2
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 0,1-1 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0,24 m2.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A3: Tratamento da superfície do solo

Medidas vegetativas
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal
- Bh: perda dos habitats
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Lack of fertilizes), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Usually in dry weather plants have a vertical appearance. After heavy gales they lose their vetical standing and they droop. This is lodging. During lodginh of plants the yield of seed is decreasing.), land tenure
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (As a result of the monoculture of cereals, weeds, pests, and insects accumulate on the fields and the soil fertility is declining.), other human induced causes (specify) (inappropriate soil management)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
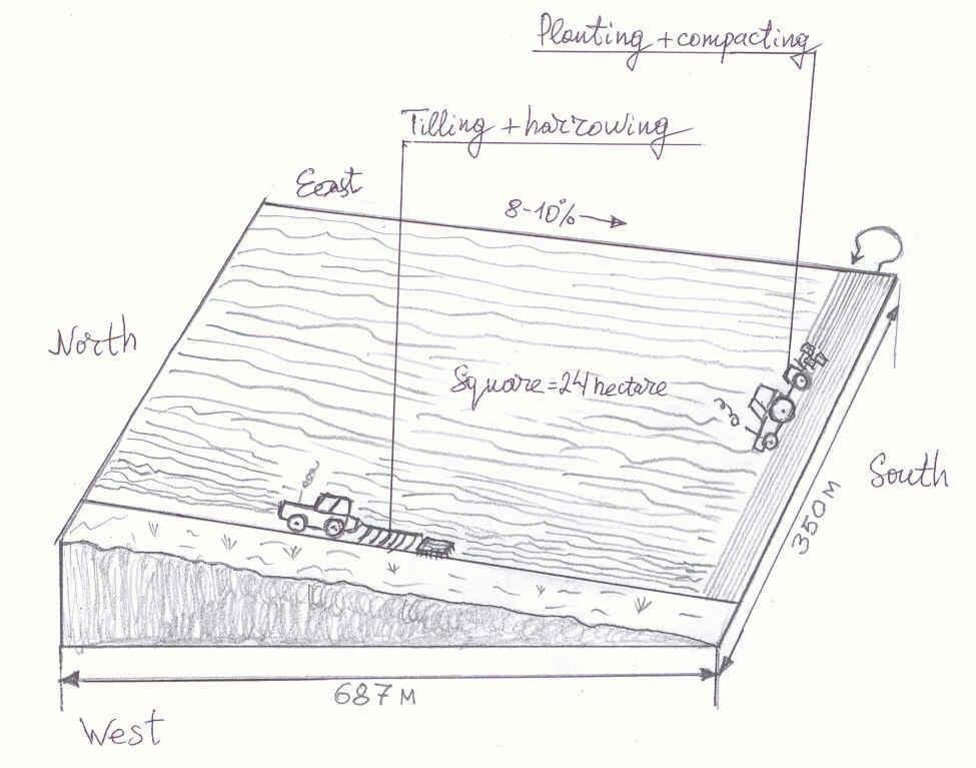
Fields are located on South exposition of the foothills of the Kyrgyz Ala-Too Mountains in the Northern part of the Suusamyr valley. The length of the sainfoin field is 687 meters, and its width is 350 meters. Slope steepness is 8-10 %.
Tilling is conducted along the slope by a tractor K-700, with harrowing being conducted at the same time. The depth of tilling is 20-22 cm. Planting is conducted across to plowing direction. The date for sainfoin sowing is the first ten days of May. The seeds required are 80 kg/ha. Depth of sowing is 4 cm. This field is situated 8 kilometers from central Suusamyr village, reachable on a bad dirt road.
Location: Suusamyr Valley. Jaiyl raion / Chui oblast / Kyrgyzstan
Date: 11.01.2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Special training is requested)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Field demonstration is needed)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of subsoil structure (hardpan)
Vegetative measure: field planted by perennual grass
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 3000000
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.15
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.15
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Perennial crops species: Sainfoin os sowed with planting machine C3-3.6. The distance between colters is 15 cm.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
KGS
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
45,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
8.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Tilling | Vegetativo | End of April. Once in 3 years |
| 2. | Planting | Vegetativo | End of April. Once in 3 years |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | establishment costs | hectare | 1,0 | 187,0 | 187,0 | |
| Mão-de-obra | labour | person/hour | 0,8 | 128,0 | 102,4 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | seeds | hecatre | 1,0 | 108,0 | 108,0 | |
| Material vegetal | seeds | kg | 75,0 | 2600,0 | 195000,0 | |
| Outros | fuel | liter | 58,0 | 321,0 | 18618,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 214015,4 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Harvesting | Vegetativo | annually |
| 2. | Cleaning of seed | Vegetativo | annually |
| 3. | Cleaning of seed | Vegetativo |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor MTZ-80, Self-Proppeled Combine Enisey-600, Seed Cleaning Machine SM-4
The above costs were affected by the length of the field and number of turn points during tilling and planting.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The price of sainfoin seeds is very high. The slope is increasing the fuel consumption of the tractor, and prices for fuel are raising. Contour tilling (also planting) by big tractor (K-700) is further increasing fuel consumption, because the number of turning-points are increased. Soil depth is not increasing cost in a major way, because soil structure in the area is comparatively good and the tractor is powerful.
All costs are calculated for 1 hectare of sainfoin. National currency is KGS. Exchange rate was approximately 45 KGS for 1 US Dollar in 2009 and 2010.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Alto (>3%)
- Médio (1-3%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
medium-high soil fertility, soil water storage = medium, soil drainage = good
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Diversidade de habitat:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Earthworms and gnawing animals inhabit on the field
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Semi-nômade
- Nômade
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Muito rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Nível de mecanização:
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: This technology is very strongly supported by Pasture Users Association, who is interesting in improving forage quantity and quality. Sainfoin's hay has high protein content in comparison with natural hay. Therefore the association is interested in expansion of sainfoin fields.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
Off-farm income specification: Some farmers sell agricultural and processing products in the shops located along the highway Bishkek-Osh and in the villages. Some of the villagers provide taxi services from Suusamyr to Bishkek.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Extension Service:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
19 c/ha
Quantidade posterior à GST:
23 c/ha
Produção de forragens
Quantidade anterior à GST:
500 bales
Quantidade posterior à GST:
550 bales
Qualidade da forragem
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
24 ha
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Oportunidades culturais
Instituições comunitárias
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1
Atenuação de conflitos
Quantidade anterior à GST:
0
Quantidade posterior à GST:
2 training
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
80%
Quantidade posterior à GST:
95%
Compactação do solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade de habitat
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Quantidade posterior à GST:
5ha
Comentários/especificar:
Project recruts a security guard to protect sainfoin field since May. And at the same time he watches the neighbours fields.Therefore damage on it is reduced.
Honey collection is improved
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | não bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
1 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Saifoin seed was provided to farmers with lower price than commercially available seeds.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: There is little trend towards (growing) spontaneous adoption of the technology.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Some farmers are aware about the production of high quality forage and want to be ready to be protected from drought. During drought periods the yield of natural vegetation is less, but the yield of sainfoin’ is constant.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Keeping the fields as fallow is not profitable for ordinary farmers. It can be done by rich farmers. |
| There is need in subsidies from the Government in order to distribute cereals and perennial legume seed. |
| If there is enough fuel and seed farmers can cultivate sainfoin everywhere, it is very good technology. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| The winter is very hard in Suusamyr Valley and livestock need enough and quality forage. Sainfoin hay contains high level of protein. |
| Natural vegetation yields for hay making is not so big particularly in drought period. Sainfoin is very productive crop. |
| Rizo biomass of sainfoin is big and it accumulates the nitrogen. Sainfoin improves the soil fertility. |
| Sainfoin is income generating crop because after harvesting of seed sainfoin the straw can be also sold by farmers at the price of 50 som for one hay bale |
| This Technology also protects the soil surface from the erosion in the result of strong density of plants. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Poor farmer is not interested in the Conservation Technology | Awareness raising of the poor farmers is necessary |
| We are having not enough knowledge about the soil conservation possibility legumes | To organize the training of farmers. |
| State legislation about soil protection is not maintained by Local Government and farmers | To monitor the observation of legislation by land users and local authorities |
| There should be Soil fertility protection service. | The Government should finance the establishment of service on soil fertility protection. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Lack of good credit system for farmers SWCT. | To lower interest rates of credits while lending farmers for implementation of the Conservation Technology |
| Comparatively high price of certified sainfoin seeds are not available for farmers | Usage of not certified seed by farmers leads to poor yields of sainfoin and cereals. To ensure the supply of high quality seed through distributers’ centers |
| Farmers need special knowledge in order to produce sainfoin seed | To conduct trainings for farmers on seed production technologies. |
|
To consolidate farmers about the effect of sainfoin cultivation for soil fertility some scientists have to do on farm demonstration plots |
Extension services should organize demonstration fields in villages. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Usubaliev B. Annual project activity’s report. “Demonstration sustainable mountains pasture management in the Suusamyr Valley. Kyrgyzstan”. UNDP.- Kyrgyzsran., 2010. Bishkek.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Project office
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Duishenaaly uulu Urmat.- Report of land management specialist of the “Local Gogernment Suusamyr”, 2010
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Suusamyr Village
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Bekganov Nurkan.- Report of local mobilization specialist of the UNDP project.- 2010
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Suusamyr Village.
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Amankulov Kubanychbek.- Report of statistics specialist of the “Local Gogernment Suusamyr”, 2010
Disponível de onde? Custos?
.Suusamyr Village
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos