Controlling invasive species by physical removal and crop cultivation through open fallow irrigation [Quênia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Beatrice Otieno
- Editores: Urs Baumgartner, Christian Hergarten
- Revisores: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Rene Eschen
Cut, Burn, Uproot and Cultivate
technologies_3444 - Quênia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
14/03/2018
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
Comentários:
Cultivation through irrigation in Perkerra scheme begun in 1954, three decades before the introduction of Prosopis in Baringo. Despite the rapid and widespread expansion of the invasive species, it is evident that cultivated areas under the scheme are free from Prosopis, unlike their surrounding neighborhoods which are heavily invaded and rendered unproductive. This is an indication of its sustainability to control Prosopis spread to irrigated land.
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
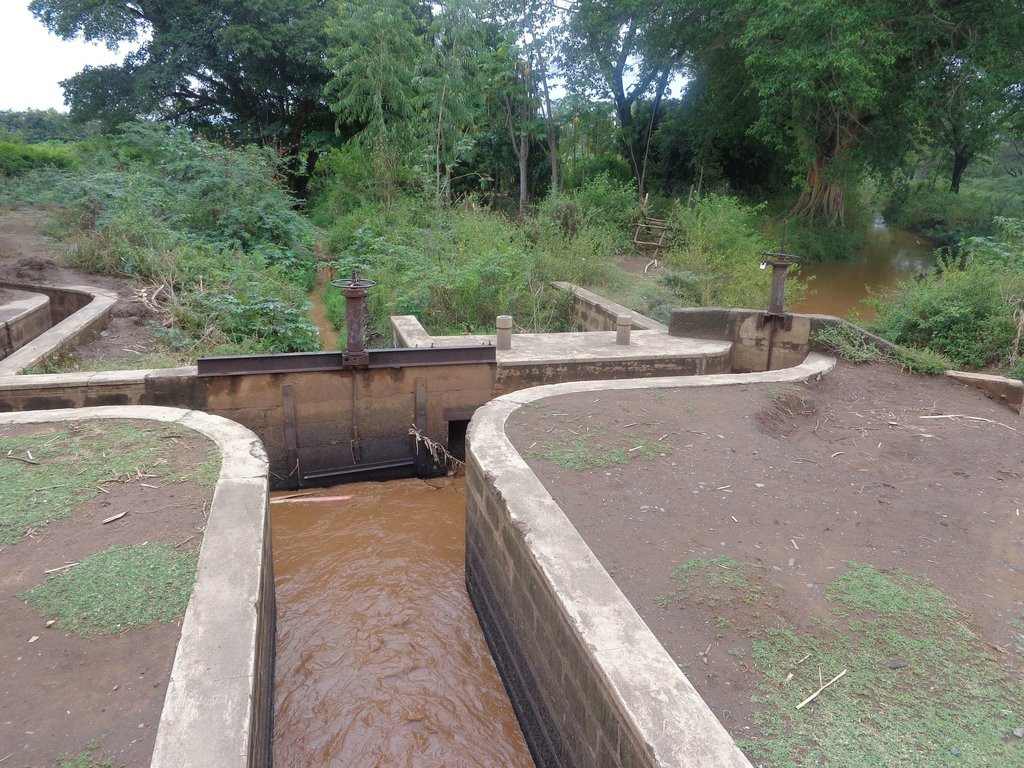
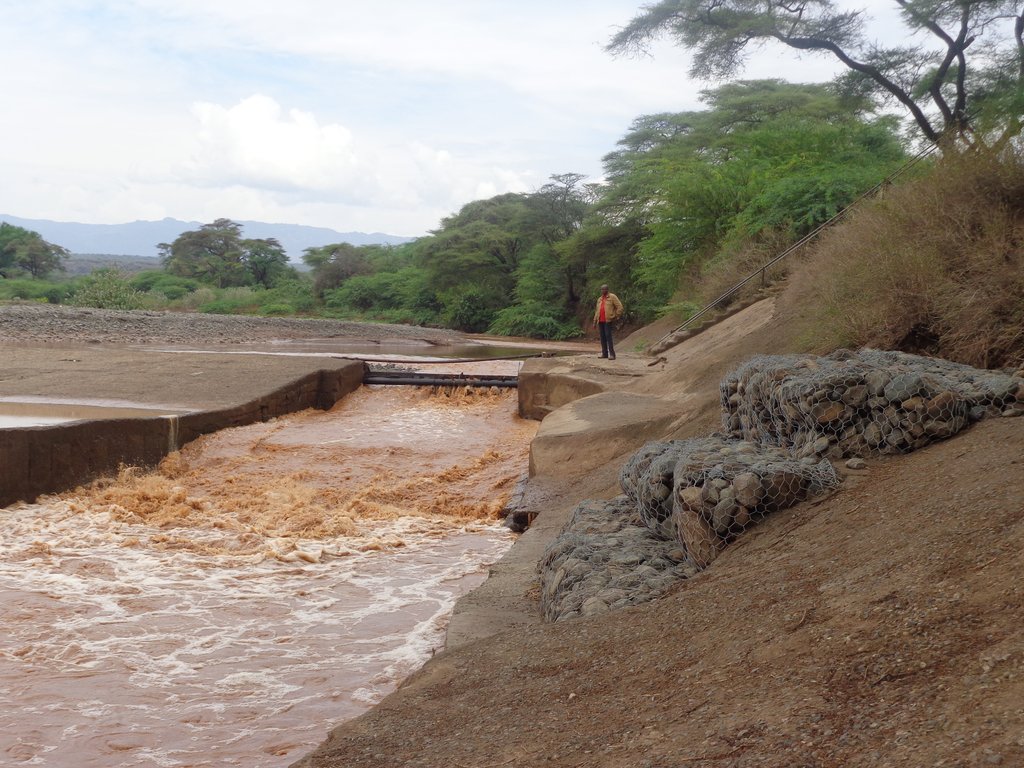
This is an open-furrow system consisting barriers constructed along a water source such as a river to direct water through a conveyance system by gravity into feeder channels to cultivated land. It is a simple method entailing control of water flow rate and direction to improve water utilization efficiency and enhance productivity of land.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Perkerra irrigation scheme was constructed by the colonial government in 1945 to ensure efficient water utilization, enhance soil productivity and food security. It is an open-furrow system consisting barriers constructed along a water source such as a river to direct water through a conveyance system by gravity into feeder channels to cultivated land. Water control system is constructed between the conveyance and the feeder channels to control the direction and speed of the water.
This technology is suitable on fairly flat, irrigable land with reliable water sources for irrigation. Consideration of population structure is crucial in ascertaining the availability labor force in farmlands. Depending on the size and market orientation of the production system, a stable market is also an important consideration.
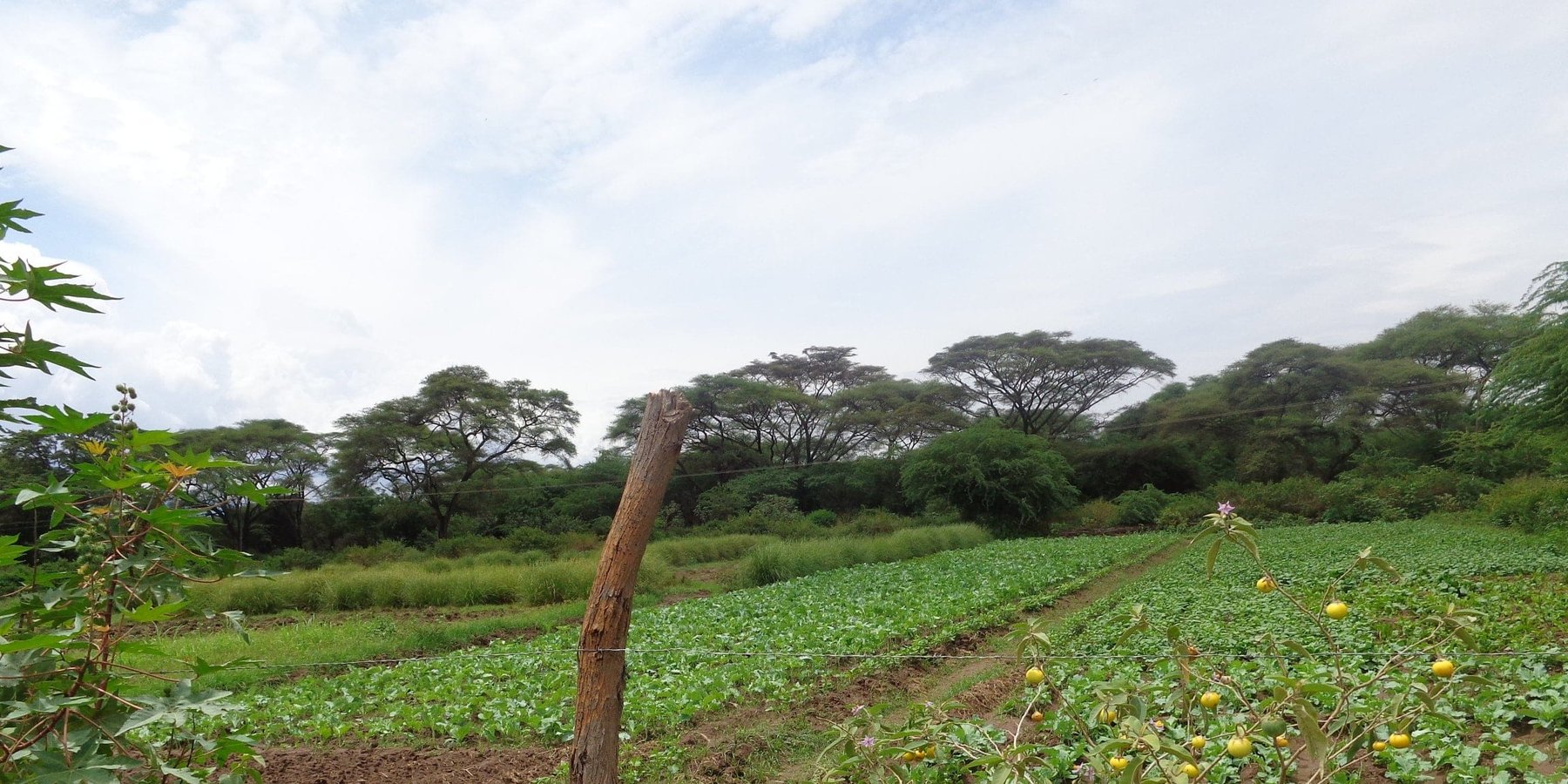
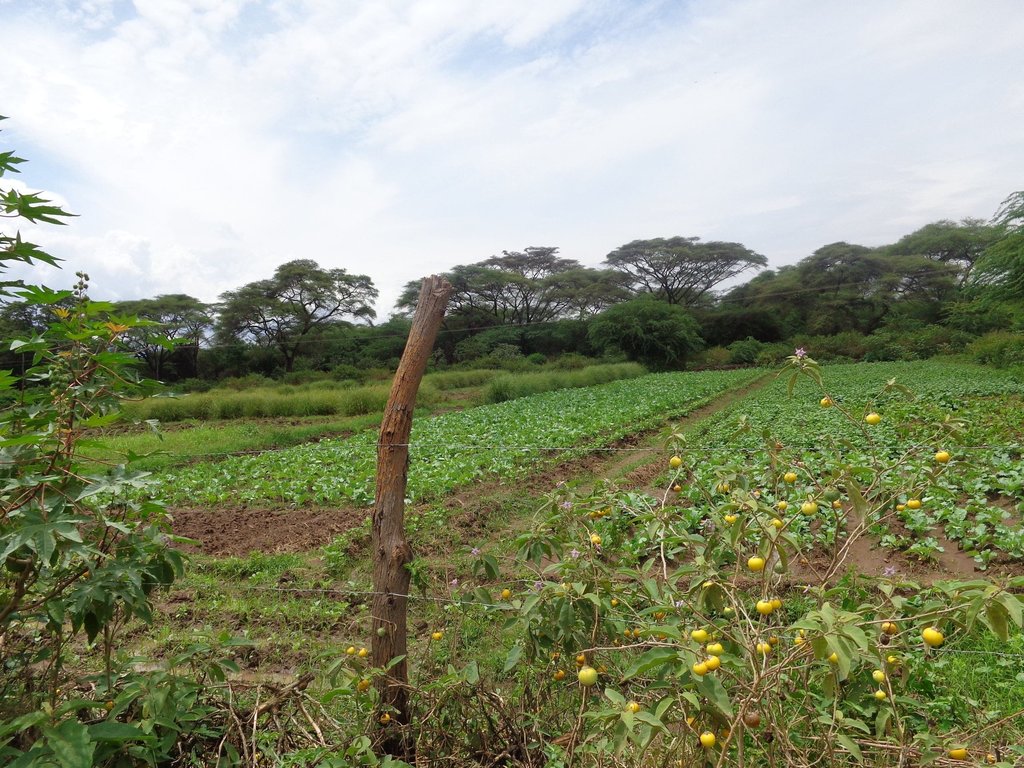
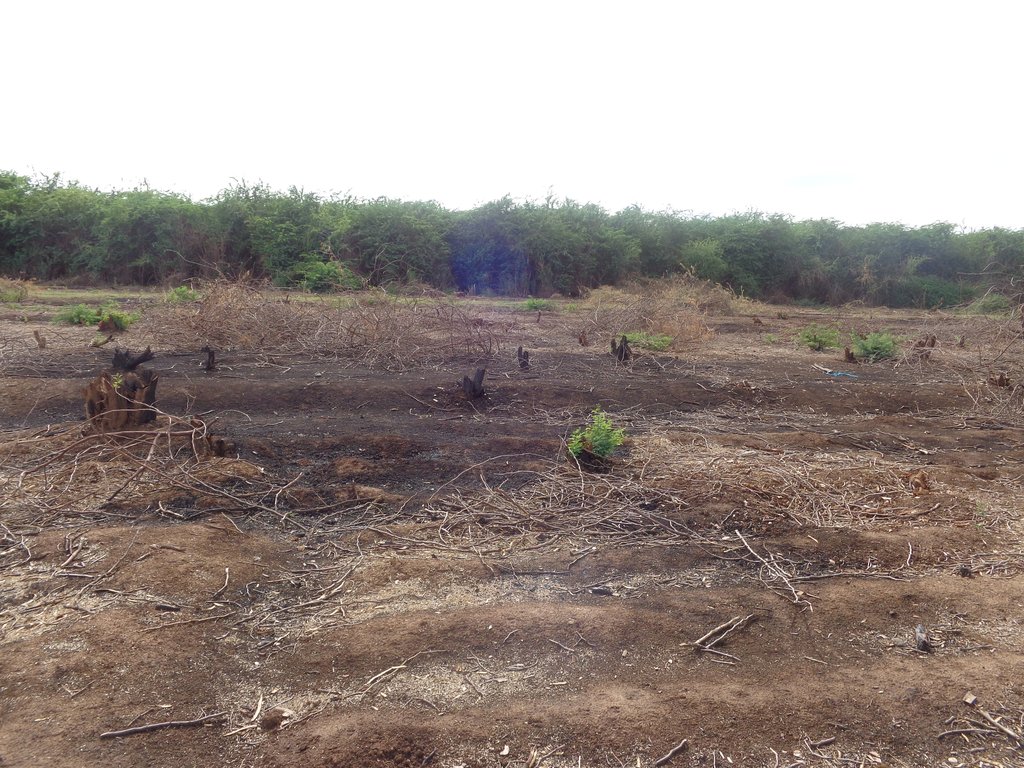
Irrigated farming in the scheme is carried out in 3 seasons a year due to availability of reliable water from the permanent Perkerra River. This also ensures that land is never left idle for re-invasion of Prosopis. Activities commence with land clearance conducted at the beginning of every planting season. Prosopis on invaded farmlands are manually cut, burnt and uprooted to minimize chances of the invasive tree from coppicing. The uprooted trunk is utilized in charcoal production for commercial purposes while the small branches are used as firewood for domestic cooking.
The cleared land is then ploughed using a tractor to break the soil structure and provide a fine tilth for planting. This is followed by mechanized ridging to create channels and buffer furrows to convey and retain water long enough to be infiltrated into the soil. Seeds are then sown, a joint activity carried out through farmers’ cooperation. The scheme was originally specialized for bulb onions plantation but has transformed into more diversified food crops for subsistence and commercial purposes. Crops under contractual farming are seed maize, rice, sunflower, green grams, pepper and cow peas while surplus crops under irrigation include tomatoes, vegetables, water melons, subsistence maize crops and commercial fruit trees. In addition, availability of assured market and payment has made the scheme popular for seed maize cultivation. Ongoing experimental research on a variety sweet potatoes to reduce overdependence on maize crops have also shown promising results and are likely to be recommended for implementation. During planting seasons, fallow periods are replaced by rotational cropping and crop diversification. This improves soil structure by alternating deep and shallow-rooted crops. Replacement of the crop during rotation disrupts the life cycle of disease causing organisms, thus controlling pests and diseases as well as improving crop productivity. Consequently, there is minimal application of chemical pesticides, hence reduced chances of pollution.
The irrigated cultivation has improved the welfare of the community by diversifying their sources of livelihood from pastoralism, enhancing food security, eradication of poverty and improving infrastructure such as access roads to the farms. It is a major source of income, directly supporting 1,625 farm households earning an approximate total net income of Ksh. 148, 192,259 Million (Perkerra scheme brief prepared by the National Irrigation board, 2017). Each household is assigned between 0.5 to 4 acres of land. This range might however be narrowed in the near future due to the increasing population in demand for the fixed land resource. The other option under consideration is to reclaim more invaded land and expand the scheme. The challenge facing this approach and is yet to be addressed is limited water resources to sustain the expansion. Lack of suitable market for non-contractual crops as well as poor pricing due to monopolization by contracting institutions is also a great setback to this technology. A good example is the abandonment of pawpaw production by farmers due to marketing problems.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Quênia
Região/Estado/Província:
Baringo County
Especificação adicional de localização:
Marigat sub-couty
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The scheme was established during the colonial period through local detainees in Marigat. This followed a feasibility study pointing to the suitability of the IIchamus plain for agricultute,
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Protege uma bacia/zonas a jusante – em combinação com outra tecnologia
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Agrofloresta
Principais produtos/serviços:
Contracted crops: Seed maize, green grams, sunflower
Surplus crops: tomatoes, vegetables, assorted fruit and tree seedlings, pepper

Vias navegáveis, corpo d'água, zonas úmidas
- Linhas de drenagem, vias navegáveis
Caso o uso da terra tenha mudado devido a implementação da tecnologia, indique seu uso anterior à implementação da tecnologia:
IIchamus plain was initially a pastoral land for grazing. Being a state owned land with no one held responsible for its management, the land was poorly managed by the society.
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Comentários:
Channeling of irrigation water into farms is restricted to dry seasons and temporarily halted during the rainy season.
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 3
Especifique:
The irrigation scheme is subjected to continuous cultivation with contracted crops planted in 2 seasons and a surplus crop on a third season in a year. Crop rotation and diversification is practiced to improve soil productivity, control pests, reduce soil erosion and enhance soil structure.
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- sistema rotativo (rotação de culturas, pousios, cultivo itinerante)
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Desvio e drenagem de água
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- > 10.000 km2
Comentários:
The technology are specifically applied along the irrigation scheme with sufficient water for irrigation
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A1: cobertura vegetal/do solo
- A2: Matéria orgânica/fertilidade do solo
- A5: Gestão de sementes, variedades melhoradas

Medidas vegetativas
- V3: Limpeza da vegetação
- V4: Substituição ou retirada de espécies exóticas/invasivas

Medidas estruturais
- S2: Barragens, bancos
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
- S7: coleta de água/ equipamento de abastecimento/irrigação

Medidas de gestão
- M1: Mudança no tipo de uso da terra
- M4: Principal mudança no calendário de atividades
- M5: Controle/mudança de composição de espécies
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Erosão do solo pelo vento
- Et: Perda do solo superficial

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
- Cs: salinização/alcalinização

Degradação biológica
- Bh: perda dos habitats
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade
- Bp: aumento de pragas/doenças, perda de predadores

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
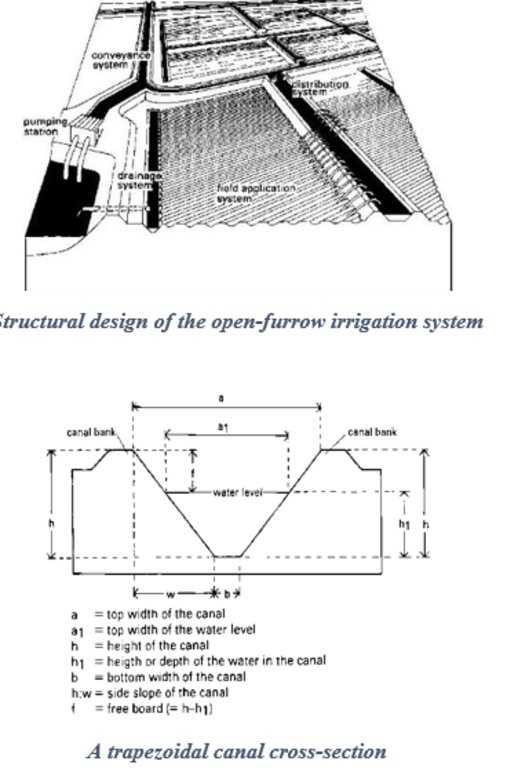
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
The intake structure convey water from the main water source to the irrigation system. It may consist of a water pump or a barrier designed for this purpose. The water is directed to a conveyance system of open canals which control the flow and direction of water to different field application and distribution systems. The canals depth (h) is preferred to exceed the expected maximum water level (h){h>h1} of water within the irrigation system to minimize bank overflow. The side slope is a ratio of the vertical height to the horizontal canal width (h:w). They are fitted with water measurement, erosion and distribution control structures to regulate accurate distribution of water to the farms with minimum siltation of the banks. The water is then distributed to field ditches which transfer it to the irrigated farm. These are narrow waterways dug along the farms with checks across their lengths to hold and raise the upstream water levels long enough before releasing it to the next segment of the field ditch. This is meant to increase the rate of water infiltration into the soil.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- Por unidade de tecnologia
Especifique a unidade:
hactares
Especifique volume, comprimento, etc (se relevante):
1
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
KES
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
100,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
500
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Construct gravity intake system | Estrutural | Once during establishment |
| 2. | Excavation of water canals | Estrutural | Once during establishment |
| 3. | Establishment of water control structures | Estrutural | Once during establishment |
| 4. | Land preparation ( Clearance and partitioning) | Estrutural | Once during establishment |
| 5. | Construction of a suitable road network | Estrutural | Once during establishment |
Comentários:
Activities involved are the construction of a gravity intake system, excavation of water canals, construction of a suitable road network and water control structures. Prior considerations are reliable water source, availability of irrigable land and labor for cultivation.
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Se possível, discrimine os custos de implantação de acordo com a seguinte tabela, especificando entradas e custos por entrada. Se não for possível, dê uma estimativa dos custos totais de implantação da tecnologia:
600000000,0
Comentários:
The initial establishment and construction of the irrigation infrastructure is often conducted by the national government due to associated high costs approximated by key informants to be Ksh, 600, 000,000 (600,000 USD). This is however an initial, one off expenditure that are non-recurrent.
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Clearing land | Agronômico | 3 times a year before every planting season. |
| 2. | Ploughing | Agronômico | 3 times a year before every planting season. |
| 3. | Ridging/Cutting furrows | Estrutural | 3 times a year before every planting season. |
| 4. | De-silting of canals | Gestão | 3 times a year before every planting season. |
| 5. | Planting | Agronômico | 3 times a year. |
| 6. | first irrigation | Estrutural | 3 times a year after planting (3 to 5 days per season) |
| 7. | Pest control | Agronômico | Whenever applicable |
| 8. | Weeding | Agronômico | Once every season |
| 9. | Second irrigation | Estrutural | 10 to 12 (each time withinn 3 to 4 days) per planting season. |
| 10. | Top dressing ( Apply fertilizer) | Agronômico | Once every season |
| 11. | Harvesting | Agronômico | Once every season |
| 12. | Shelling | Agronômico | Once every season |
Comentários:
Maintenance activities mentioned above are dependent on the status of an individual's farm, availability of resources and the purpose for cultivation. Farm produce cultivated under contracted terms will however need to follow strict procedures for them to meet the minimum requirements.
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Land clearance | Man-hour | 540,0 | 120,0 | 64800,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Partitioning | Man-hour | 180,0 | 100,0 | 18000,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Planting | Man-hour | 90,0 | 100,0 | 9000,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Ploughing tractor | Hours | 18,0 | 420,0 | 7560,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Ridging tractor | Hours | 18,0 | 420,0 | 7560,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seeds and seedlings | Kg | 75,0 | 150,0 | 11250,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Channeling water for irrigation | Season | 3,0 | 2000,0 | 6000,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Fertilizer | Kg | 150,0 | 50,0 | 7500,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 131670,0 | |||||
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Size of land
Disease and pest outbreak
Crop variety as contracted crops minimum requirements which may be costly to meet
Occurrence of rainy seasons especially during harvesting which affect the drying cost and output of produce. Seed maize, for example, may not meet the required moisture content when aired during the rainy season hence lowering the net income from them.
Condition of the farm e.g invasion level by Prosopis
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
671,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Rainfall is characterized by seasonal and annual fluctuations
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
The area is in a semi-arid zone with temperatures ranging between 16 to 36 degrees, averagely 24.6 degrees, accompanied by high evaporation rates of up to 6mm. It experiences an average rainfall of 671 mm annually which are very erratic.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
The technology is applied in relatively flat land to increase water retention long enough to be infiltrated into the soil
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Clay soil with alkaline pH of 7.5 , rich in calcium phosphate but low in organic matter
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
apenas para uso agrícola (irrigação)
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Sim
Ocorre inundação da área?
Sim
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Prosopis has heavily invaded the land, encroaching agro-pastoral land and outcompeting native species leading to degradation of native species and habitats.
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- meia-idade
- idosos
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Grande escala
Comentários:
Current land allocated by the government for the practice is an estimate of 1,800 ha. Pressure due to population increase has however triggered plans for future expansion.
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
The scheme is state owned , leased to the community who nominate a 7 member advisory committee tasked with all land administration aspects ranging from land adjudication, allocation, succession and dispute management as well as set laws guiding water utilization and conservation.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Área de produção
Quantidade anterior à GST:
567 ha
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1,745 ha
Comentários/especificar:
the area developed for furrow irrigation has increased by 1,178 ha between 1958 when the operations begun to date. This is more than twice the initial land size allocated and utilized for irrigation purposes.
Gestão de terra
Comentários/especificar:
Development of the technology has transformed it from an open access to an organized communal tenure system with communally-designed restrictions to its access, utilization and management.
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Qualidade da água para criação de animais
Comentários/especificar:
There are chances of water pollution when contaminated irrigation water flows back to the animal watering points.
Demanda por água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
The progressive increase of area under cultivation as well as prolonged dry seasons over the years have culminated into increased water consumption hence a high demand for the same.
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade posterior à GST:
Net income of 148 192 259 million Kenya shillings
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Comentários/especificar:
Farming activities have diversified and increased income sources to the community who depended mainly on pastoralism. This has been enhanced by a wide variety of crops being cultivated through irrigation.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Farming activities (tedious cutting, burning and uprooting of Prosopis in invaded farms, ploughing, weeding and harvesting) are all physical activities that increase the workload of the communities involved.
Impactos ecológicos
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Cobertura vegetal
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade vegetal
Espécies exóticas invasoras
Comentários/especificar:
Irrigated land has to undergo clearance of all Invasive species, in this case, Prosopis during land preparation activities. This is carried out through a cut-burn-uproot approach to minimize chances of their proliferation. Any re-growing invasive plant is uprooted before maturity to prevent further competition for water and nutrient with cultivated crops. Chances of re-invasion are also minimized as land is never left idle for colonization by Prosopis. This has greatly decreased invasive cover on irrigated land.
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da seca
Comentários/especificar:
Drought related impacts such as malnutrition, famine and death have been reduced by irrigation practices which increases food insecurity independent of the season.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Diversion of water into open channels for irrigation reduce the downstream flow for offsite usage downstream.
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Potential flood water are diverted to farms hence reducing downstream flooding. However, this impact may not be significant during heavy downpours where diversion valves are closed to prevent unnecessary water logging on farmlands.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | estação úmida/das chuvas | aumento | moderadamente |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres biológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Doenças epidêmicas | não bem em absoluto |
| Infestação de insetos/vermes | não bem em absoluto |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 1-10%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
Direct beneficiaries of the technologies are about 13,000 people. However, indirect beneficiaries from the transportation and sale of the produce may double this number
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
All operation are carried out at the full expense of the land users. Credits advanced to them have to be repaid with at least 11% interest
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, indique as condições variáveis as quais ela foi adaptada:
- Mudança climática/extremo
Especifique a adaptação da tecnologia (desenho, material/espécie, etc):
Water conveyance along the furrows to the farms is halted during heavy downpour to minimize water logging.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| A source of finance to land users through sale of their produce. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Continuous farming activities have ensured that land is constantly managed, limiting the proliferation of Prosopis weeds which have adverse impacts to the ecosystem and livelihoods. |
| Improved human welfare by enhancing their financial stability. An extension of this is indirect benefit through employment creation to farm laborers, merchants and buyers of the fresh and healthy farm produce. |
| Increased food security |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Poor market prices for their produce. | They feel they have no option due to inadequate knowledge and access to other available markets |
| Pests and disease out break such as the fall armyworm. | Advisory services are offered by research institutions to stakeholders on how to manage and control pests. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Monopoly of the market by the contracting institutions may lead to poor pricing or tight minimum requirements such as the quality of output leading to losses. | Diversification of market to tighten competition that may offer better prices to farmers. |
| High chances of water pollution by chemicals and fertilizers that may be washed away by the running water | Minimize application of chemicals as possible accompanied by integrated nutrient management practices. |
| Post harvest losses when supply exceeds demand | Proper timing of planting season whereby harvesting coincides with seasons of shortage and scarcity to maximize returns. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
2
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
2
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
3
- compilação de relatórios e outra documentação existente
2
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Brouwer, C., Goffeau, A., and Heibloem, M. (1985): Irrigation Water Management: Training Manual No. 1
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.fao.org/docrep/r4082e/r4082e00.htm#Contents
7.3 Links para informação relevante que está disponível online
Título/ descrição:
Perkerra Irrigation scheme Brief
URL:
https://www.nib.or.ke/projects/public-irrigation-schemes/perkerra-irrigation-scheme
Título/ descrição:
The 9 Benefits of Crop Rotation to the Environment
URL:
http://richmondvale.org/crop-rotation/
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos