Progressive bench terrace [China]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Fei WANG
- Editor: –
- Revisor: Deborah Niggli
树盘,逐年扩盘
technologies_1522 - China
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Chen Yunming
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
China
Especialista em GST:
Liu Guobin
Institute of Soil and Water Conservation, CAS and MWR
China
Especialista em GST:
Cao Qingyu
China
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Northwest A&F University (NWAFU) - China1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
14/06/2011
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Bench terraces are progressively expanded to form a fully developed terrace system in order to reduce runoff and soil erosion on medium- to high- angled loess slopes.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
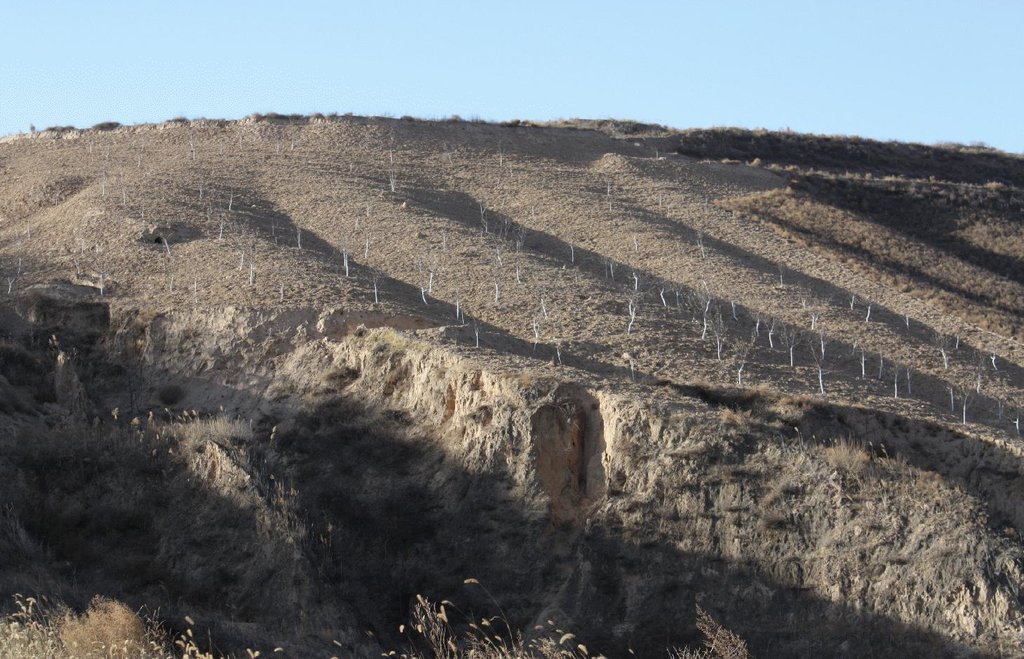
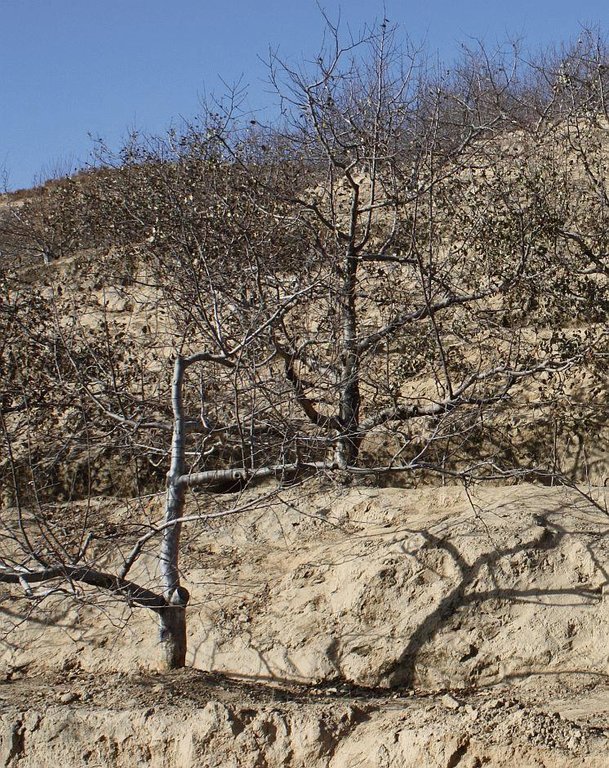
n Miaowan Village, the technology is mainly applied to apple tree plantations. Tree seedlings are planted in rows every 4 m along the contour with a spacing of 2.5-3.5 m between rows. Trees are planted in pits 40 cm diameter and 3040 cm deep. Manure and/or fertilizer are applied and the seedlings are watered.
Around each tree, soil from the upper parts of the slope is removed and deposited below in order to extend the flat terrain. Over 5-10 years, the terraces become enlarged around each tree and form a terrace with the neighbouring trees along the contour, such that the slopes are transformed into level bench terraces. The fruit trees are located in the middle of the terrace. All the work is done manually using shovels.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of this technology is to reduce runoff and soil erosion on the slope and to improve soil quality and soil moisture retention. It is a sustainable land use technology for small farmers because farmers can use their spare time to improve the land’s condition during the growth of the trees.
A major aim is to conserve water and reduce runoff. Soil erosion in this village is very severe and the soil erosion rate before amounted to 60-100 tonnes per hectare per year and was reduced practically to zero as a result of building the terraces. Slope gradients are very steep (around 20-35 degrees). The main income of local farmers is from orchards.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment phase thus takes 5-10 years. Afterwards maintenance inputs are restricted to repairing the terrace walls.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
China
Região/Estado/Província:
Shaanxi
Especificação adicional de localização:
Miaowan Village, Xuejiagou Watershed
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: The technology is around the village.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
It is a kind of traditional method.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Main cash crops: Apple
Main food crop: potatoe
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): On moderate- to high-angled slopes, water loss and soil erosion are very high. Outside the protected canopy of the trees rainsplash impact during heavy storms is very severe. The local farmers clear all the wild grasses and shrubs, such as Korshinsk Peashrub, Artemisia scoparia, Leymus secalinus, Stipa bungeana, Lespedeza davurica etc. to reduce competition with the fruit trees. Consequently, the soil is bare and unprotected
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 300Longest growing period from month to month: Mar - NovSecond longest growing period in days: 200Second longest growing period from month to month: Apr - Oct
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 2.55 m2.
The whole area of this watershed is about 7.5 Km^2. There are a lot of orchard, mostly apple, in this watershed. It is one of typical watershed with specially soil erosion problem despite the high plant coverage.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Storm are strong in summer.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (orchards on steep slopes without conservation measures), poverty / wealth (to increase the yield and income of orchard.)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (There is no natural grass cover here.), droughts (Lack of water for the cash trees)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
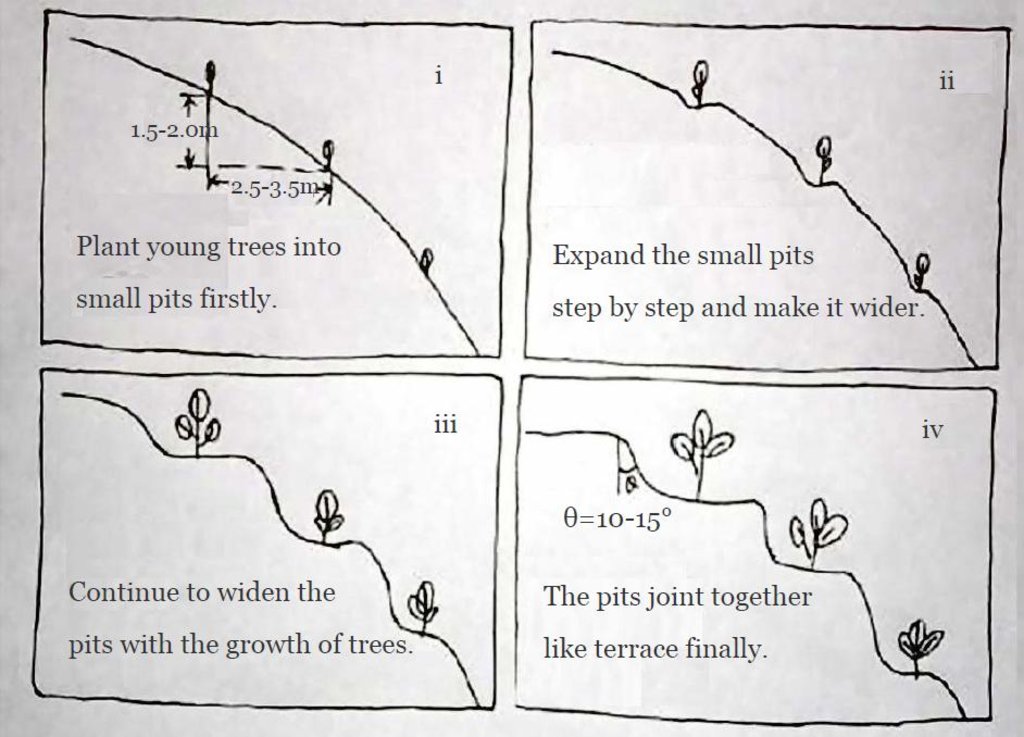
i: first year: planting of fruit trees along the contour in small pits
ii: after 3-4 years: a small terrace is built up around each tree (as the tree grows it needs more water, which is collected from the platform around the trees..
iii: after 5-8 years: terraces develop
iv: final stage: fully developed level bench terraces
Owing to the soil properties of loess, there is no need to separate surface and subsoil as there is little difference between them. Therefore, soil can be moved directly from upper to lower parts of the terrace without changing soil fertility.
Location: Miaowan Village, Xuejiagou Watershed. Ansai County, Shaanxi Province, China
Date: 2008-12-20
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (It is easy to understand and implement.)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, reduced soil loss
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration
Reshaping surface
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1
Spacing between structures (m): 2.5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1..5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100-150
Construction material (earth): Using the earth of the same land.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 45%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
14.2
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plant the young trees with small pits. | Estrutural | Before practice |
| 2. | The soils from the upper parts of the slope is shovelled away and deposited on the lower side of the trees | Estrutural | |
| 3. | Expand the pits into a large platform year by year. | Estrutural | |
| 4. | 3.4 years after planning the trees a level platform of 2 to 3 square meters around the trees is build. | Estrutural | |
| 5. | The platforms increase and the space between trees is change into terrace. | Estrutural |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Planting trees | Person/day | 120,0 | 7,3 | 876,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Building pits | Person/day | 750,0 | 7,3 | 5475,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 6351,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 60 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repair the bank of year-after-year terraced land | Estrutural | Annual after it formed |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Reparing of terraced land | Person/day | 15,0 | 14,6 | 219,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 219,0 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: spade and hoe
The costs are calculated assuming a local wage rate of 14.2 US$/day.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Slope is the most important factor. The steeper it is, the higher the cost. Labour was not considered as a cost before, but now it is expensive so that some local farmers do not use this technology.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The mean annual rainfall in the basin is 515.2 mm in the duration from 1952 to 2000. The rainfall from May to Oct accounts for 446.8 mm, up to 86.7%; and that from Jun to Sep accounts for 367.6 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: temperate. The accumulating time that temperature above 0 ℃ about 3800 hours, and that above 10 ℃ is more than 3200 hours
It is based on the classification sysytem only based on the rainfall
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Altitudinal zone 501-1,000 m a.s.l.: Most area is in this altitudinal zonation
Landforms: Based on 1:100 thousand scale landform map
Slopes on average: Based on 1:100 thousand scale landform map
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil depth on average: The depth of Loess varies from nearly 30 m to more than 100 m in Yanhe River Basin. The depth of soil is less than this but it could be nearly 10 meters in common
Soil texture (topsoil): Here are more than 50% soil particle are fine sand with size between 0.05 and 0.1 mm
Soil fertility very low: Lack of N, P and SOM
Topsoil organic matter: <0.5%
Soil drainage / infiltration good: The inflitration of Loess is very fast, but it is prone to sealing when flashing.
Soil water storage capacity low: It is easy to evaporation and drainage
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface also poor/ none: Nearly all the branches of Yanhe are seasonal river
Availability of surface water medium: It is very stable in this region
Water quality (untreated): Good quality for there are few pollution sources
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
It is very stable in this region
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No clear difference.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
30% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land (Higher yield and income.).
Off-farm income specification: Only a few land users have implemented this measure because there are other market based activities that bring higher returns. Sometimes farmers have enough money to buy more fertilizer for the orchard.
Level of mechanization: nearly all the work is done by hand.
Market orientation of production system: It is on apple production base and this generates good income of local farmers
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
0.054 ha per capita
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
- Comunitário/rural
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
45000kg
Quantidade posterior à GST:
52500kg
Comentários/especificar:
Yield increasing by 16.7%
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Quantidade anterior à GST:
9883
Quantidade posterior à GST:
11530
Comentários/especificar:
Income increases by 1647 USD per ha.
Carga de trabalho
Quantidade anterior à GST:
1500
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1650
Comentários/especificar:
10% person days increases annually in the first 5 years
Impactos socioculturais
Situação de grupos social e economicamente desfavorecidos
Quantidade anterior à GST:
2700
Quantidade posterior à GST:
3200
Comentários/especificar:
Not excluding of the labour input of the local farmers themselves.
Livelihoods and human well-being
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
60 mm/yr
Quantidade posterior à GST:
<10 mm/yr
Comentários/especificar:
no runoff in common
Solo
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
60 t/yr/ha
Quantidade posterior à GST:
10 t/yr/ha
Comentários/especificar:
Soil erosion is well controlled
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Quantidade anterior à GST:
60mm/yr
Quantidade posterior à GST:
<10mm/yr
Cheias de jusante
Quantidade anterior à GST:
60 mm/yr
Quantidade posterior à GST:
<10 mm/yr
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
Comentários:
The technology increases infiltration, reduces soil erosion by water and improves soil moisture retention to reduce the negative impact of extreme drought. However, it does not protect the soil well from wind erosion. Soil cover could be increased to protect against strong winds and reduce
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
It is very cheap to maintain this measure. More trees could be planted on degraded land in future.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 10-50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
65 households (15percent of the stated area)
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 90-100%
Comentários:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: There are no outside input to do sunch thing.
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
65 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: In this area, there are many other practices, such as reforestation, enclosure (to prevent grazing) and terrace construction.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Even the local farmers know the benefits of progressive bench terraces, but with the increased labour costs, fewer people apply this technology.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Higher yield and income. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If they have time, they wish to adopt this technology. |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Establishing the technology over a long time. Local farmers have enough time to do it How can they be sustained / enhanced? Show to land users that they have time and can spread to work over many years and fit the labour into the time they have available. |
|
It can reduce water loss and soil erosion and prevent the degradation of land How can they be sustained / enhanced? Give subsidy to the local farmers to reduce the sediment delivery into the downstream river. |
|
It can increase soil moisture. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Makes people understand the importance of conserving water with such a technology. |
|
Higher yield and income. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Share ideas through meeting in the field. Present this measure to more people and show them how to apply it and promote the technology to more farmers. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| It takes a lot of time to establish it. | It is difficult to use it, because the people could balance the establishment costs and work at the labour market. If they can get some subsidy from government, they may adapt this measure. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| It takes considerable time to establish and labour is more and more expensive so that farmers are looking for paid work | Subsidy for farmers using this measure. |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Soil and water conservation records of Shaanxi Province. 2000. Shaanxi People's Press, Xi'an City, China
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Library of ISWC, CAS
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos