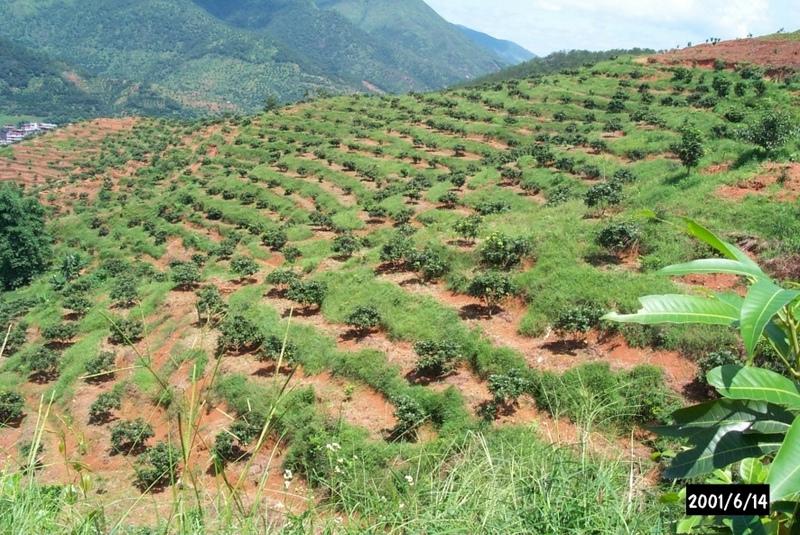
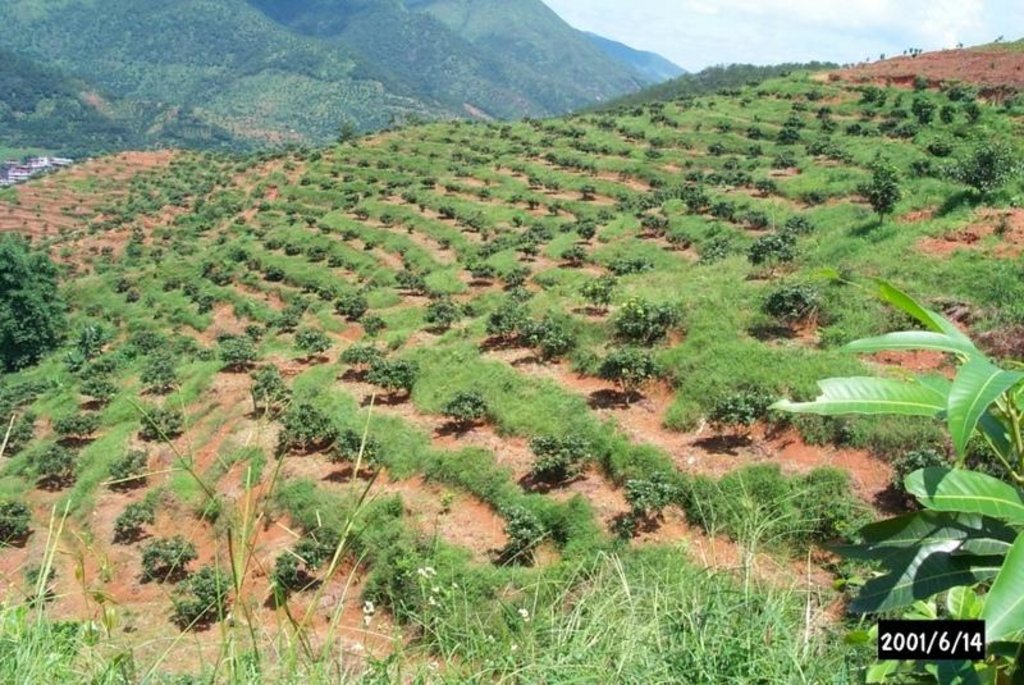
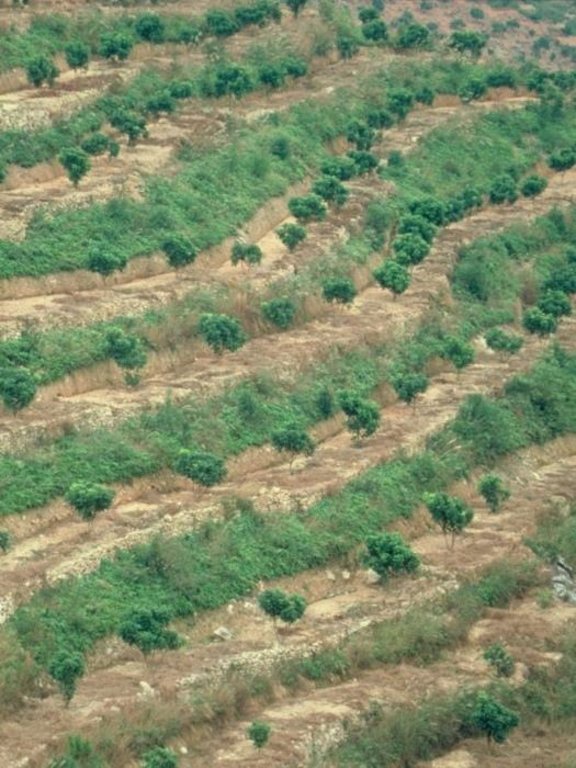
Orchard terraces with bahia grass cover [China]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Zhanguo Bai
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli
Bahia grass interplanted in orchard
technologies_1106 - China
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
Especialista em GST:
Liu Zhengming
Soil Conservation Office of Yongchun County
China
Especialista em GST:
Nie Bijuan
Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Experimental Station
China
Especialista em GST:
Yang Xuezhen
Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Experimental Station
China
Especialista em GST:
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
ISRIC World Soil Information (ISRIC World Soil Information) - Países BaixosNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Soil Conservation Office of Yongchun (SCOY) - ChinaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Office (Fujian Soil and Water Conservation Office) - China1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
16/06/2001
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Rehabilitation of degraded hillsides through the establishment of fruit trees on slope-separated orchard terraces, with bahia grass planted as protective groundcover.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
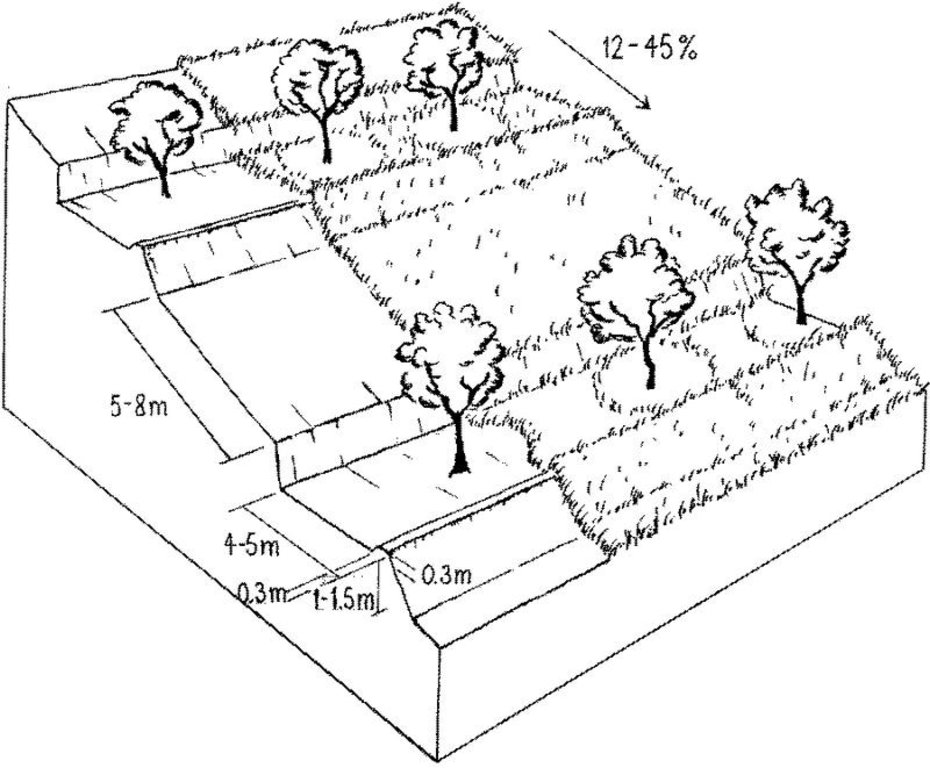
In this case study orchards were established between 1991 and 1992 on degraded and unproductive hillsides (wasteland), with slopes of 12-45%. This was achieved by constructing level beds on the contour, mainly as continuous slope-separated orchard terraces, but in some cases as individual planting platforms. Terrace construction was generally undertaken by hand using hoes and shovels.
Purpose of the Technology: A typical terrace has a 4-5 m wide bed and a 1.0-1.5 m high riser. Commonly, a raised earth lip (0.3 m high) is constructed on the terrace edge to retain rainwater. The terrace riser walls are not protected. Even before terrace construction there was little topsoil and in some places the upper subsoil had been lost to erosion. The establishment of fruit trees (lychee, Litchi chinensis and longan, Dimocarpus longan) therefore required deep planting holes (1 m3), filled with organic matter/manure, into which seedlings were planted. In subsequent years additional large quantities of organic matter/manure were applied in circular trenches to the side of the trees, succeeding trenches being gradually further away as the trees grew. Bahia grass (Paspalum notatum) was planted for SWC purposes as a cover crop, to stabilise terrace risers and to improve soil fertility. It has not been used for fodder in this case. The germination rate of bahia grass seeds is comparatively low; therefore instead of direct seeding, nurseries were established to produce seedlings. The bahia grass seedlings were transplanted onto the terrace risers and beds (leaving a space around each fruit tree) and on the hillside slopes between the terraces. The grass grew and spread quickly, restoring a protective vegetative cover following terrace construction.
Natural / human environment: The primary overall purpose of the technology was to rehabilitate degraded hillsides through the planting of economically valuable fruit trees. Terracing reduces soil erosion while retaining most of the rainwater. The application of organic matter creates improved rooting conditions, while restoring and maintaining soil fertility. The bahia grass further provides protective groundcover preventing splash erosion, increasing surface roughness, and thereby slowing down runoff velocity, while contributing to the restoration of the soil’s biological, chemical and physical properties. Irrigation ditches dug along the terraces help to reduce erosion further. This project was planned by SWC specialists: around 6,000 families were allocated orchard plots and provided with seedlings at a subsidised price.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
China
Região/Estado/Província:
Fujian Province
Especificação adicional de localização:
Yongchun County
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The technology comes from the soil conservation theory books and accumulated experiences over years.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Principais plantações (colheitas para venda e consumo próprio):
Tree and shrub cropping: lychee, longan

Floresta/bosques
Produtos e serviços:
- Madeira
- Frutas e nozes
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Degraded and unproductive hillside slopes (wasteland), with low and declining soil fertility, subject to severe soil erosion
(sheet, rill, gully and mass movement) during periods of heavy and prolonged rainfall.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Low fruit yield and little income after consideration of input.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The farmers\' consciousness of soil conservation are gradually improved and their ability of forest protection are also increased.
Forest products and services: timber, fruits and nuts, nature conservation / protection
Constraints of wasteland (before SWC)
Forest/ woodlands: Also nature conservation / protection
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 365Longest growing period from month to month: May - Sep
3.4 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- hillside stabilizing and restoration
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- 10-100 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 55 m2.
This is a part of the comprehensive development of Shan Huxi small watershed.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas agronômicas
- A6: Outros

Medidas vegetativas
- V5: Outros

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços
Comentários:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Secondary measures: management measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
- Wm: movimento de massas/deslizamentos

Deteriorização química do solo
- Cn: declínio de fertilidade e teor reduzido de matéria orgânica (não causado pela erosão)
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wm: mass movements / landslides, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), land tenure (land subdivision)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, other human induced causes (specify) (agricultural causes), poverty / wealth (lack of captial), education, access to knowledge and support services (lack of knowledge)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
Comentários:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
Fruit trees on slope-separated terraces with a spacing of 5-8 metres between (dependent on slope). Terrace risers and beds are protected by the fast spreading bahia grass (right): note a grass-free space is maintained around each tree.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in soil fertility, control of dispersed runoff
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of soil structure
Agronomic measure: organic matter application
Vegetative measure: aligned trees
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: dispersed grass
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 6
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Fruit trees / shrubs species: longan, lychee
Grass species: bahia
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 16.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 12.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 9.00%
Terrace: forward sloping
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-1.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 4-5
Construction material (earth): Using earth for the construction can reduce investment.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 20%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 6%
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:20
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Other type of management: Changing land use patterns - Mountain and hilly areas closure for recover of the forest and grass.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- Dólares norte-americanos
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
3.00
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 2.On each terrace one line of fruit trees was established. Deep planting | Vegetativo | winter of 1991 |
| 2. | 2.Fruit tree seedlings were planted. Spacing between trees was | Vegetativo | spring of 1992 |
| 3. | 3.Bahia grass was transplanted onto the terraced hillside | Vegetativo | spring of 1992 |
| 4. | Terraces were constructed by hand.Soil was excavated from the upper portion of the terrace and used to build up the lower portion behind the terrace riser wall to create a level platform (bed). Part of the excavated soil was used to build a terrace lip. | Estrutural | winter of 1991 |
| 5. | land preparation for the grass planting | Estrutural | winter of 1991 |
| 6. | hill closure | Gestão | Nov. 1999 |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Voluntary and paid | ha | 1,0 | 840,0 | 840,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Bahia transplants | ha | 1,0 | 435,0 | 435,0 | |
| Material vegetal | Fruit tree seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 350,0 | 350,0 | 60,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 145,0 | 145,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 70,0 | 70,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 1840,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
NA
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 2.Digging trenches by the side of the fruit trees and filling with organic | Agronômico | |
| 2. | prune, fertilize, pest control for the fruit trees of Longan and Litchi | Vegetativo | spring, autumn and winter /3 times/year |
| 3. | grass plantation, fertilizaion | Vegetativo | spring and summer /3 times/year |
| 4. | Filling any gaps in the bahia grass. | Vegetativo | |
| 5. | In the first 1–2 years maintenance also involves replacing any fruit tree | Vegetativo | |
| 6. | Weeding around the trees. | Vegetativo | |
| 7. | Repairing terraces damaged by storms. | Estrutural | after raining season/4 times/year |
| 8. | regular inspection and management | Gestão | Jan. 1991 / 6 times/year |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Voluntary and paid | ha | 1,0 | 144,0 | 144,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Bahia transplants | ha | 1,0 | 58,0 | 58,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Fruit tree seedlings | ha | 1,0 | 36,0 | 36,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | fertilizer | ha | 1,0 | 84,0 | 84,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | biocides | ha | 1,0 | 10,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | compost/manure | ha | 1,0 | 44,0 | 44,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 376,0 | |||||
Se o usuário da terra arca com menos que 100% dos custos, indique quem cobre os custos remanescentes:
NA
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: hoe, shovel
For establishment: 200 person days for terrace construction, 100 for digging pits and planting trees, 50 for transplanting
bahia grass. For maintenance: 15 person days for terrace maintenance, 40 for digging organic matter trenches, 5 for
bahia grass gap filling. The SWC department produces bahia transplants in nurseries; these are then distributed to the
farmers.
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
steep slope and lots of civil work.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Comercial/mercado
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Rico
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
5% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
40% of the land users are rich and own 35% of the land.
50% of the land users are average wealthy and own 45% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: off-farm income is mainly from factory labour
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Carga de trabalho
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
input constraints
Comentários/especificar:
organic matter/manure
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Atenuação de conflitos
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Comentários/especificar:
rainwater retention
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
70
Quantidade posterior à GST:
35
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
24.3
Quantidade posterior à GST:
3
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Outros impactos ecológicos
erosion due to raindrop splash
competition between fruit trees and bahia grass
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Cheias de jusante
Sedimentação a jusante
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- mais que 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
6593 Households (56 percent of the area)
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 10-50%
Comentários:
88% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
5755 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
12% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
784 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is a slow spontaneous adoption of the technology, based on the fact that bahia grass is remarkably helpful in controlling soil erosion.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
An increase in vegetative cover reduces erosion, improves the ecological environment, increases soil fertility and organic matter content, improves How can they be sustained / enhanced? Control weeds and fertilize well. |
|
The combination of structural and vegetative measures has a quick impact on reducing soil erosion and preventing mass movement on hillside slopes How can they be sustained / enhanced? ncrease the vegetative cover and improve soil properties through the addition of plenty of organic matter/manure. |
|
Improved land management practices bringing back degraded wasteland sites into economic production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Demonstration and extension while also improving the enabling legislative environment. |
|
Editors’ comments: In China, large areas of degraded hillsides have been brought back into production by constructing terraces on which fruit trees are planted. In this example the technology has been further improved through planting of bahia grass, as a groundcover, to restore the structure and increase the soil organic matter. On a much smaller scale a case of degraded land conversion is presented from Tajikistan. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Orchard development can extend too far up the slope, onto steep mountain sides | Reserve the upper slopes for forest, and restrict orchards to the lower slopes. |
| Potential competition for water and nutrients between the bahia grass | Clean weed (bahia grass included) in the area immediately around the fruit tree. |
| Increase in farm income becomes very positive only after fruit trees start | Consider replacing bahia grass with a more palatable perennial fodder plant to improve farm income in the short term. |
| Low germination rate of bahia seeds | Expand experimental studies (seed treatments, cuttings, taking splits, etc). |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Acceptance Materials of Shan Huxi Small Watershed.. 2001.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Soil Conservation Office of Yongchun County
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos