Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough [República Unida da Tanzânia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: ALLAN BUBELWA
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger, Donia Mühlematter
elyeshero ne elyato (Haya tribe)
technologies_1157 - República Unida da Tanzânia
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 29 de Dezembro de 2016 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 5 de Junho de 2017 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 28 de Junho de 2018 (inactive)
- Indigenous water collecting pond and livestock watering trough: 6 de Agosto de 2019 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Pessoa(s) capacitada(s)
government:
Kagaruki Annagrace
Misseny District Council
Especialista em GST:
government:
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - República Unida da TanzâniaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - Itália1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
28/08/2012
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
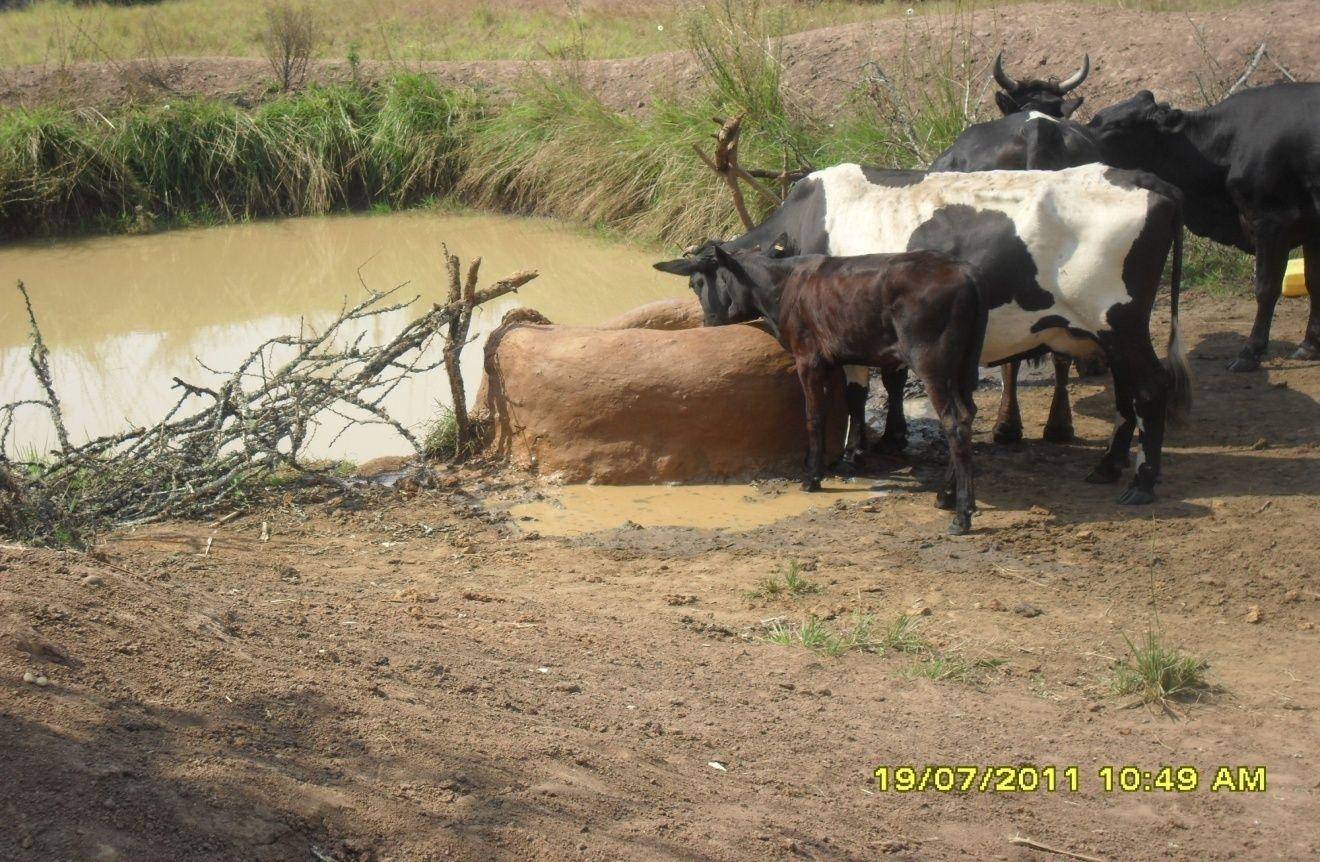
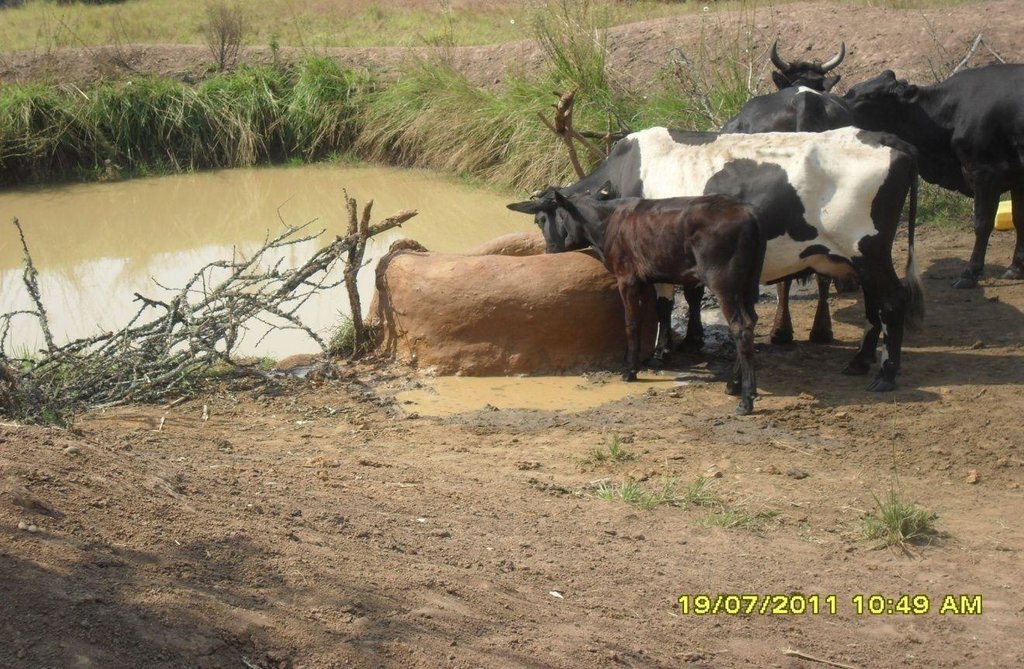
Construction of indigenous water pond and a livestock watering trough along an underground water source.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
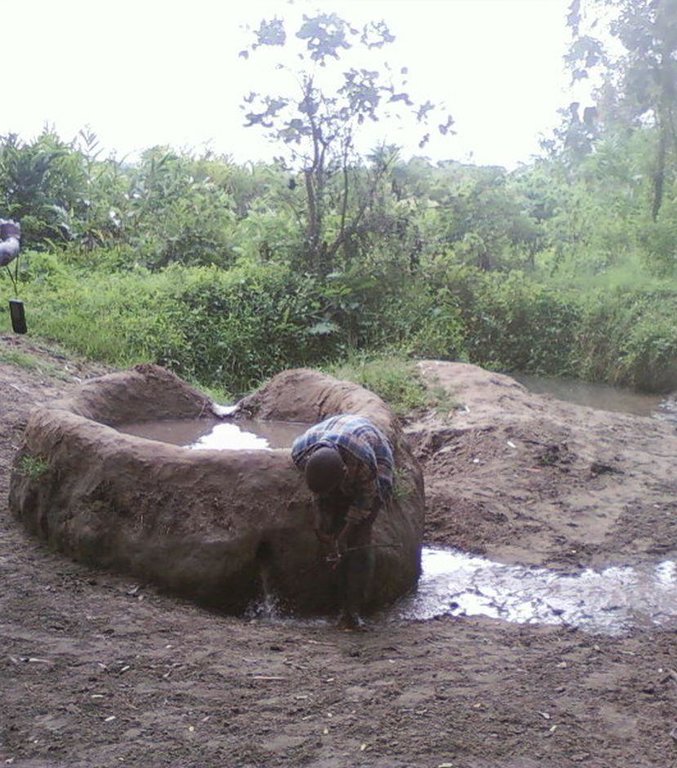
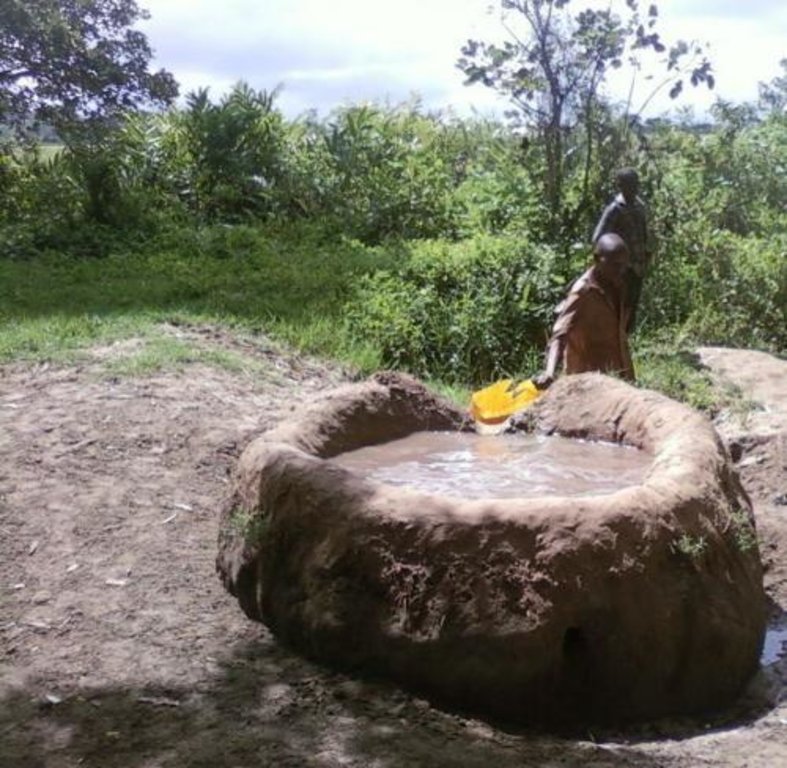
This technology is used during the dry seasons and where ground water level is high and there is natural water stream flowing from underground water source. Water pond is excavated along the naturally flowing water stream and is recharged by natural ground water. The size of the pond will vary depending on the area available, groundwater table, slope and soil characteristic. Groundwater collection ponds described in this technology on average are 4m long, 3m wide and 1m deep of 12m3 (12 000 liter) capacity and the slope is moderate 5% to 8% and soil characteristics is clay loam with deep soil. Water troughs (Elyato by local name) are constructed adjacent to the water pond to allow livestock to access clean drinking water. The number of troughs per pond is usually 1 to 2. Materials used in construction of water trough include clay, red termite mound soil, grass and wooden poles. The number of ponds needed usually depends on the expected number of animals and are arranged at irregular intervals ranging from 10 to 20 meters apart. The average size of a water trough is 0.14 m3 and can cater for 5 cattle at a time. The Pond is stabilized by naturally growing grass on its banks. Common pond stabilizer species are Leodicatiar digitalia and Hyperrhenia rufa. Management of the natural water source is through preventive village/customary by-laws which prohibit tree and grass cutting around the water source. The dominant indicator tree species normally found are Erythrina abysinica, Ficus thorgii and Phoenix recrinata. The animal watering troughs are usually used in the dry period. Before watering the troughs are coated (smeared) with red termite mound soil (normally hand carried by herders) to provide a good taste which is attractive to animals. Water is transferred from the pond to the water trough manually using cans or buckets. Animals drink directly from the troughs. This water from the trough is rich in iron (Fe) from red termite mound soil. The troughs are constructed with outlets used to spill out water immediately after drinking in order to prevent their damage through excessive water saturation.
Purpose of the Technology: This technology is preferred by livestock keepers as it provides for animals to drink clean and mineralized water and for health improvement. User fee payed to land owners also enable them to expand and diversify there income sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment: Land clearing, excavation and shaping of water pond and construction of animal watering trough.
Maintenance: repair of water pond and water trough (de-siltation, grass slashing and gap refilling).
Inputs: labour, implements (machete, spade, hand hoe, sickle), clay, red termite mound soil, wooden poles, buckets, grass and tying rope. Average establishment cost for one pond and its water trough is 41.27 American dollars. Average annual maintenance and recurrent costs (filling and emptying of water trough) for one pond and its water trough stands at 458.76 dollars and labour is a core cost determinant factor.
Natural / human environment: Natural environment: Extensive grazing land. The technology is largely structural (excavation and shaping of water ponds and construction of water troughs) supported by the use of by-laws which prohibit destruction of the protective natural and indicative trees and grasses around. The technology is common in sub-humid climatic zone.
Social economic environment: Level of mechanization is handy tools with subsistence production systems on individual fields.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
República Unida da Tanzânia
Região/Estado/Província:
Tanzania
Especificação adicional de localização:
Missenyi District (Minziro)
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -1.11472, 31.655 ; -1,09972, 31.70194
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
the technology has been in use for about 80 years ago
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Pastagem
Pastagem extensiva:
- Seminomadismo/pastoralismo
Principais espécies animais e produtos:
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: cattle, goats and sheeps

Misto (plantação, pastagem, árvores) inclusive agrofloresta
- Agropecuária
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Eutrophication, siltation, water shortage, deforestation and wildfire outbreaks
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Drying of the underground water source.
Constraints of mines and extractive industries
Constraints of settlement / urban
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
Constraints of wastelands / deserts / glaciers / swamps
Constraints of recreation
3.3 Mais informações sobre o uso da terra
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: September to DecemberSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May
Densidade animal (se relevante):
10-25 LU /km2
3.5 Difusão da tecnologia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Caso a tecnologia seja uniformemente difundida numa área, indique a área coberta aproximada:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
The area is owned by individual farmer. The area is found adjacent to extensive grazing land. Water table is high and there is a permanent underground natural water flows.
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos
- V2: gramíneas e plantas herbáceas perenes

Medidas estruturais
- S11: Outros

Medidas de gestão
- M7: Outros
Comentários:
Specification of other structural measures: water collection pond and animal watering trough
Specification of other management measures: protect water source enclosure by naturally regenerating vegetation
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Deteriorização física do solo
- Pc: Compactação

Degradação biológica
- Bc: redução da cobertura vegetal

Degradação da água
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (cutting of natural tree and removal of grass along the natural water flow way), overgrazing (Compaction by trampling animals, rainfall runoff, siltation of water collection point and disapearence of vegatative cover.), discharges (point contamination of water) (spoilage and contamination of surface water by human and livestock feaces.), population pressure (Overstocking due to increase in the number of livestock), poverty / wealth (low capacity to invest in enviromental friendly energy sources), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Unavailable improved and reliable water ponds and animal watering troughs), education, access to knowledge and support services (limited knowledge on sustainable use of natural water sources), governance / institutional (limited enforcement of existing environmental regulatory systems.)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (excavation and layout that contradict the natural environment), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (fire wood collection from the natural water source), industrial activities and mining, urbanisation and infrastructure development, release of airborne pollutants (urban/industry…), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), other human induced causes (specify), change in temperature, change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, floods, droughts, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, land tenure, labour availability, war and conflicts
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
4.2 Especificações técnicas/ explicações do desenho técnico
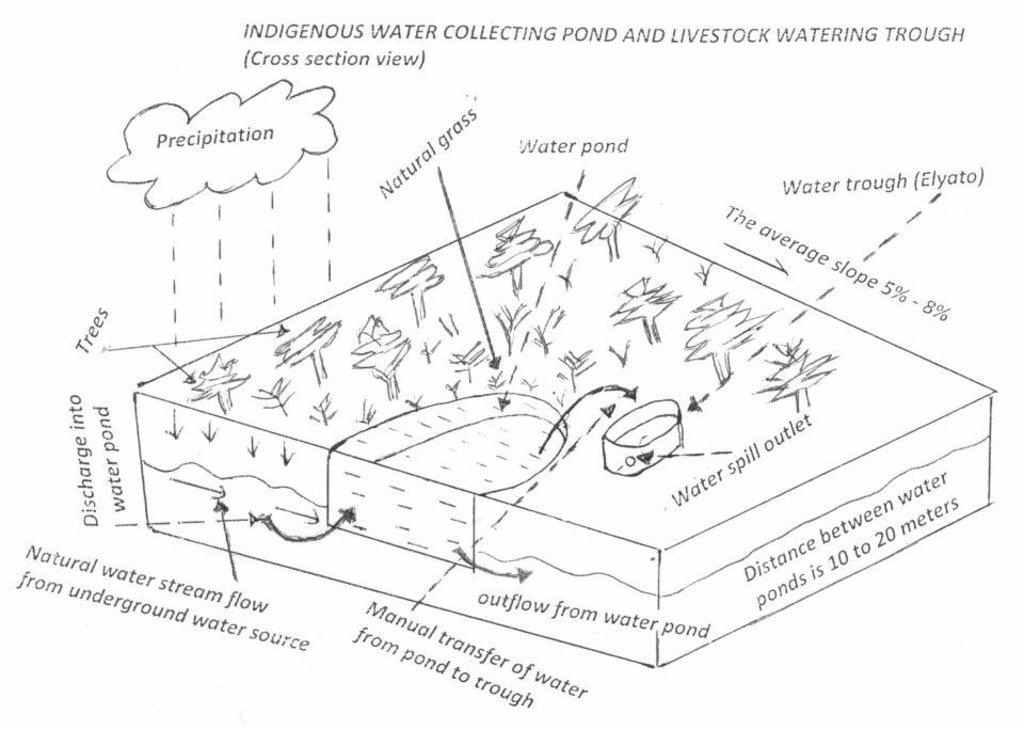
Water pond and water trough cross section view.
The water pond has an average internal capacity of size of 12m3 (4m length, 3m width and 1m depth).
Water troughs are constructed on the side of the water ponds. The water trough outside height is 0.2 - 0.4m above ground, inner depth is 0.5m, and diameter varies from 0.6 to 1m. It is made of cylindrical walls whose average width is 0.1m.
The average slope of the water catchment is 5% to 8%.
Location: Minziro village, Minziro ward, Missenyi division. Missenyi Dist, Kagera Reg, United Rep of Tanzania
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (At least primary school leaver with the basic indigenous technical knowledge.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water spreading, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), control of fires, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): 0
Spacing between structures (m): 10 to 20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 3
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 4
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 4
Structural measure: water trough
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6 to 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6 to 1
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.1
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Construction material (earth): mostry used clay soil and red termite mound soil.
Construction material (wood): for water pond and trough stabilization
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 8%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 5%
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 10.6m3
Catchment area: 4 acresm2
For water harvesting: the ratio between the area where the harvested water is applied and the total area from which water is collected is: 1:4
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.3 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Tanzanian shillings
Indique a taxa cambial do dólar norte americano para a moeda local (se relevante): 1 USD =:
1600,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
3.13
4.4 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation for pond excavation | Estrutural | During dry season |
| 2. | Construction of pond | Estrutural | During dry period |
| 3. | Construction of water trough | Estrutural | During dry season |
4.5 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Land preparation for pond excavation | person/day | 1,0 | 1,25 | 1,25 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of pond | person/day | 1,0 | 21,88 | 21,88 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Construction of water trough | person/day | 1,0 | 3,13 | 3,13 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | piece | 1,0 | 3,13 | 3,13 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | piece | 3,0 | 9,38 | 28,14 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Wood | pieces | 2,0 | 1,25 | 2,5 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Earth | kg | 20,0 | 1,25 | 25,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 85,03 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.6 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Tipo de medida | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desiltation | Estrutural | During dry season |
| 2. | Wall and bank strengthening and repair (reshaping and grass slashing/gap filling) | Estrutural | During dry season |
| 3. | Water trough repairing | Estrutural | dry season |
| 4. | Filling to and emptying water from water trough and collection and application of red termite mound soil. | Estrutural |
4.7 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Desiltation | person days | 5,0 | 6,25 | 31,25 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Wall and bank strengthening and repair (reshaping and grass slashing/gap filling) | person days | 5,0 | 6,25 | 31,25 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Water trough repairing | person days | 8,0 | 10,0 | 80,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Filling to and emptying water from water trough and collection and application of red termite mound soil. | person days | 450,0 | 1,25 | 562,5 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | pieces | 2,0 | 5,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Water can | pieces | 2,0 | 1,88 | 3,76 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Wood | pieces | 6,0 | 3,75 | 22,5 | 100,0 |
| Material de construção | Earth | kg | 60,0 | 3,75 | 225,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 966,26 | |||||
Comentários:
The cost is calculated per one water pond and its one trough and as per 28 August 2012
4.8 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Labour is the most determinant factor affecting the costs
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- úmido
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: tropics. all months temperature is above 18
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate
Thermal climate class: boreal
Thermal climate class: polar/arctic
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
Na superfície
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Misto (subsistência/comercial)
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: little involvement of women because at large/traditionally livestock rearing is done by men.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
5% of the land users are rich and own 5% of the land.
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 35% of the land (the techology is used by rich and average livestock keepers who have the animal).
75% of the land users are poor and own 40% of the land (the village poors usually do not have the animals though most of them are cattle herders).
10% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
5.7 Média da área de terra própria ou arrendada por usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção animal
Diversidade de produtos
Geração de energia
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Renda e custos
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Disparidades econômicas
Impactos socioculturais
Instituições comunitárias
Instituições nacionais
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Escoamento superficial
Lençol freático/aquífero
Evaporação
Solo
Umidade do solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Diversidade de habitat
Controle de praga/doença
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Risco de incêndio
Velocidade do vento
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Caudal confiável e estável em período seco
Cheias de jusante
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Danos em áreas vizinhas
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | Tipo de mudança climática/extremo | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | não conhecido |
Comentários:
Improving structure on the pond (use impermeable materials to prevent seepage, use concrete as a building material)
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Comentários:
The technology requires low establishment and maintenance cost and benefit surpass the costs.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
Entre todos aqueles que adotaram a tecnologia, quantos adotaram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo material/pagamentos?
- 10-50%
Comentários:
12% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
250 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
All livestock keepers use the technology to water their animals voluntary and through self mobilization.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The technology is cheap and requires low investment costs.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
|
Income generation due to water use fee. How can they be sustained / enhanced? improve service to water users. . |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Reduce conflict between livestock keepers and domestic water users. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Bylaws reinforcement, Area enclosure and Demarcation |
|
Improve accessibility of water to animals (improved animal water intake) How can they be sustained / enhanced? sensitization on regular maintenance. |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Not durable and requires frequent and regular maintenance | Sensitize on regular maintenance. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| not durable | Sensitize on regular maintenance. |
| high labor demand to fill the troughs | Use simple leverage pump |
7. Referências e links
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos