Stabilisation of irrigation channels in sandy soils with old rice bags and Pandanus plants [Camboja]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Stefan Graf
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
បច្ចេកទេសដាក់បាវខ្សាច់ និងដាំដើមរំចេកតាមភ្លឺស្រែជាទំនប់ទប់ការហូរច្រោះ (Khmer)
technologies_1650 - Camboja
- Resumo completo em PDF
- Resumo completo em PDF para impressão
- Resumo completo no navegador
- Resumo completo (sem formatação)
- Stabilisation of irrigation channels in sandy soils with old rice bags and Pandanus plants: 28 de Fevereiro de 2017 (inactive)
- Stabilisation of irrigation channels in sandy soils with old rice bags and Pandanus plants: 11 de Março de 2019 (inactive)
- Stabilisation of irrigation channels in sandy soils with old rice bags and Pandanus plants: 7 de Fevereiro de 2024 (public)
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Khun Lean Hak
SOFDEC/LAREC, www.sofdec.org
Camboja
Especialista em GST:
Pith Khonhel
LAREC
Camboja
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Society for Community Development in Cambodia (SOFDEC) - CambojaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Local Agricultural Research and Extension Centre (LAREC) - Camboja1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
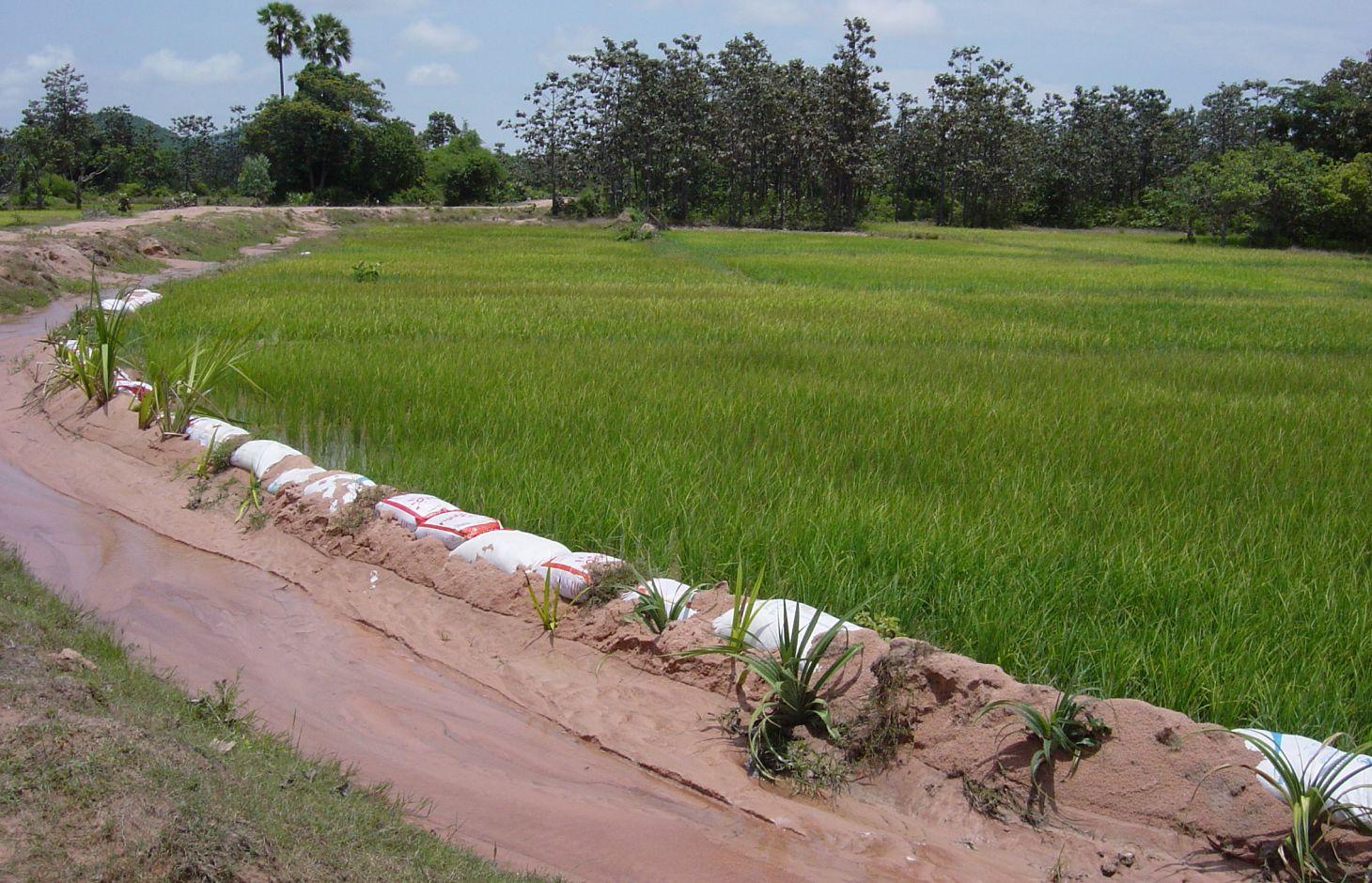
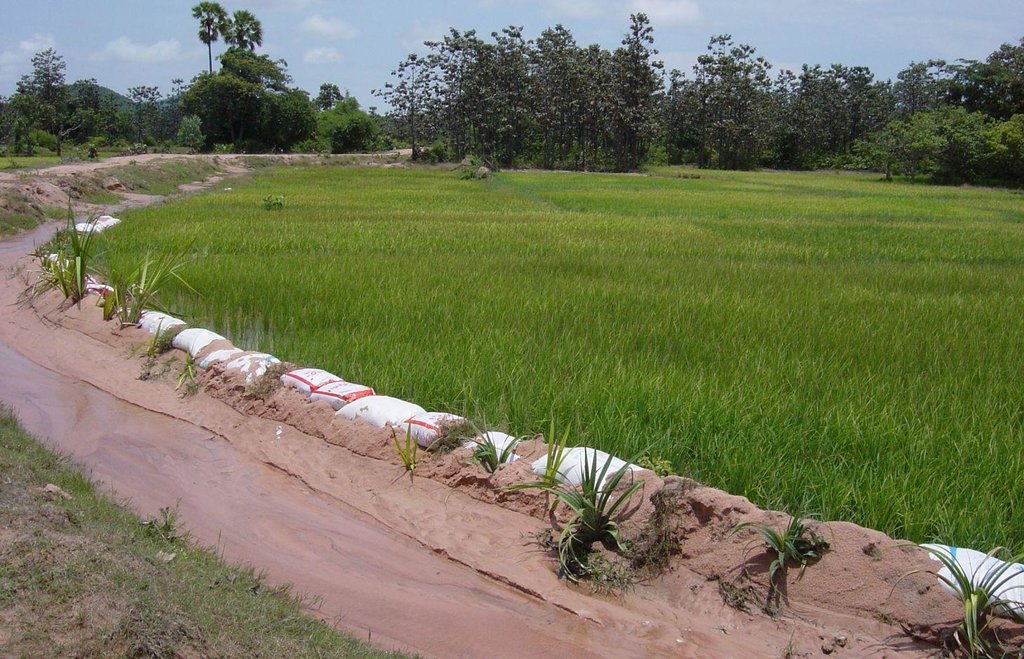
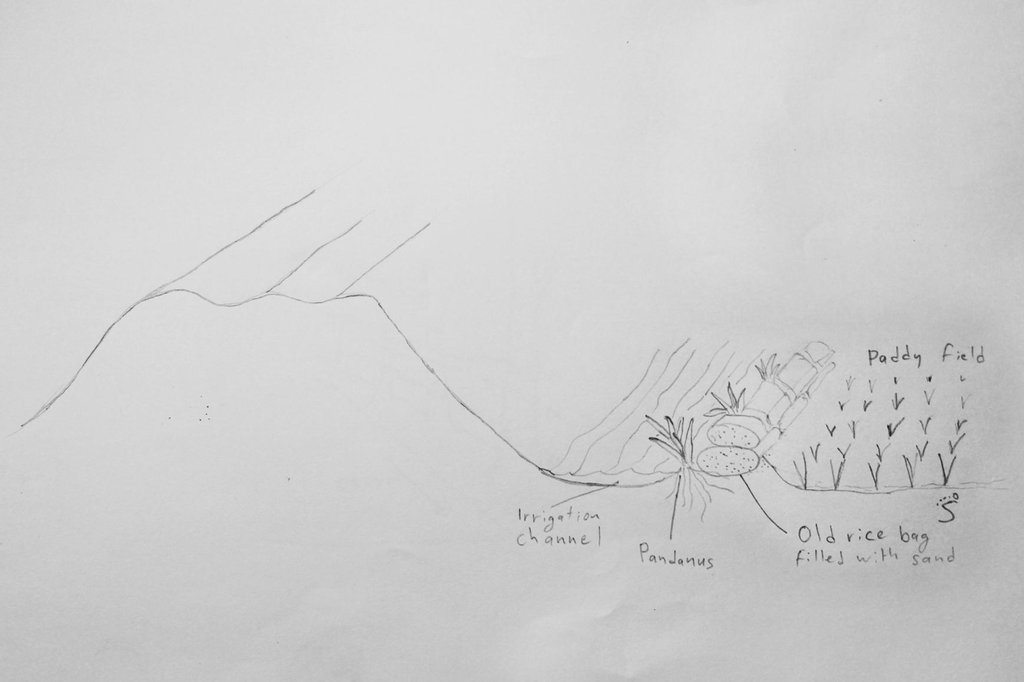
In sandy areas, old rice bags are filled with sand and piled up as dikes bordering irrigation channels, and Pandanus plants are used to stabilize them on the long term.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
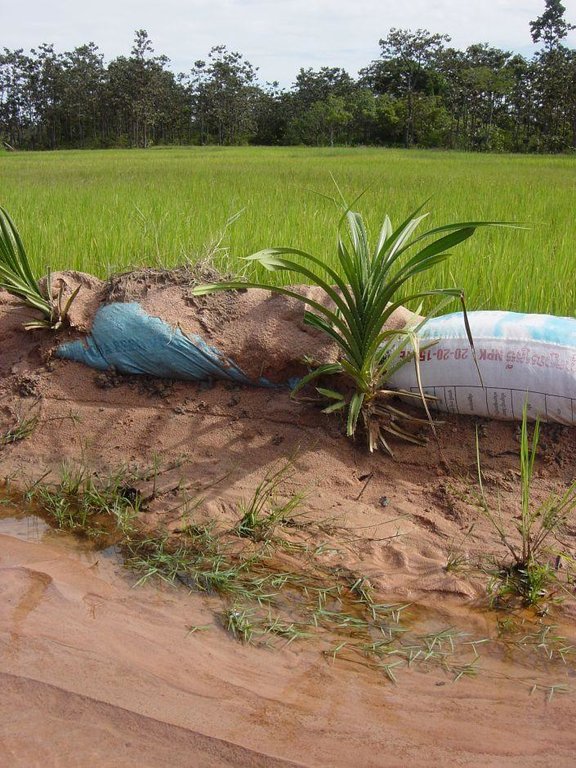
The paddy fields are surrounded by dikes and fed by local temporary streams and irrigation channels, as well as by rain. In sandy soils the dikes around the irrigation channels and fields cannot hold the water due to erosion. Old rice bags are filled with sand and piled up to form stable dikes on the short term, and Pandanus suckers are planted every 0.5 – 1 m to ensure a stability on the long term due to the root system.
The purpose of the dikes, stabilized for short and long term, is to ensure the flow of water to the paddy fields by reducing the riverbank erosion. It also helps to keep the water in the paddy fields. The Pandanus can be used to make mats and baskets, although this use diminishes due to the low cost of plastic. After a few years, the Pandanus on the dike is tall and spiky enough to fence off cattle and protect the rice from grazing.
To stabilize 50 m of dike, around 100 old rice bags are filled with sand and piled up on a height of 2 bags. Pandanus suckers are planted on the water side, between the bags, and sand is used to cover the plants and bags. Poles and sticks are used to stabilize the bags and plants until the root system is established. This is done in the beginning of the rainy season to ensure the growth of the sucker. In the first year, after each rain the eroded sand has to be added back to the dike. After the establishment phase, from the second year on, the Pandanus have to be cut back as they grow quickly and can grow tall.
The analysed area is flat (slope < 2%), with a tropical climate (dry season from November to May and wet season from June to October), and the soils are mostly sandy or loamy. The soil has a low fertility, contains little organic matter, and acidifies. The area has been deforested a long time ago, and the groundwater table is rather high (1-2 m during the dry season, on the surface during wet season).
Due to climate change, farmers notice more erratic rainfall, temperature rises and more recurrent droughts. Rice is the predominant crop grown in the area, since it serves as staple food (mix subsistence and commercial activities). Cattle are usually grazing on the fields after the harvest, without much control. Thus the cattle grazes too often and too much on the same spot, leading to degradation.
The increasing migration rate (the young generation leaves the villages to work in the cities, garment industry or abroad) results in a decrease of available labour force in the area which has detrimental effects on the agricultural activities. Furthermore, the civil war in the 1970s (Khmer Rouge) led to the loss of agricultural knowledge. Several NGOs are trying to re-establish the knowledge.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Camboja
Região/Estado/Província:
Kampong Chhnang
Especificação adicional de localização:
Chrey Bak/Rolea Pha’ear
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 1-10 km2
Comentários:
Traditionally the irrigation channels were stabilized with sticks and some fences (old sugar palm leaves roofs…) This is changing now, as old rice bags become available.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
The use of Pandanus plants to stabilise the irrigation channels and dikes is a traditional setting in the area. The use of rice bag is a newer setting.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Criar impacto econômico benéfico
- Cria impacto social benéfico
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - arroz (zona húmida)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 210, Longest growing period from month to month: June to December

Vias navegáveis, corpo d'água, zonas úmidas
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): low soil fertility, overgrazing, lack of irrigation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): lack of irrigation, low soil fertility
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Tecnologias de eficiência energética
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas
- V1: cobertura de árvores/arbustos

Medidas estruturais
- S3: Valas graduadas, canais, vias navegáveis
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wr: erosão das margens

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
Comentários:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Lack of organic matter), labour availability (Factory work in garment industry)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (mainly annuals are planted in monocultures (rice)), overgrazing (free ranging of cattle)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Next to a road, (left) there is an irrigation channel in sandy soil. To prevent the little dam next to the rice field (right) from eroding, old rice bags are filled with sand and piled up. Between the rice bags, Pandanus suckers are planted. Sometimes they are also used to stabilise roadsides (not shown in this picture).
Kampong Chhnang
Date: 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Vegetative measure: On dikes, allong irrigation channels
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.5 - 1 m
Vegetative measure: Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Trees/ shrubs species: Pandanus grown from suckers
Bund/ bank: graded
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.75
Construction material (other): Sand and sandbags
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Autor:
Stefan Graf, Switzerland
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Riels
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
4000,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
5.00
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fill the old rice bags with sand, pile them up, stabilize with sticks and add more sand after each rain, till the root system of the Pandanus plants have established (1 year) | Beginning of wet season (Jun/Jul) |
| 2. | Plant the Pandanus suckers between the bags | beginning of wet season (June/July) |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Construction of biodigester | 1,0 | 400,0 | 400,0 | 50,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 400,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 0,1 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Maintain the dikes | every rainy season |
| 2. | Cut back the Pandanus plants | Once a year, before planting rice |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | labour | 1,0 | 121,5 | 121,5 | 100,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 121,5 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 0,03 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: showel, knife, Shovel, knife
The costs were calculated in 2014 for 50 m of dike (50 m = 1 unit). To protect an irrigation channel of a 50 m, 100 m of dike would be needed, as the dikes would be on both sides.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The labour is the most costly part in this technology. Through the use of old rice bags filled with sand the costs are already reduced.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
1486.45 mm 2013 in Kampong Chhnang
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
Thermal climate class: tropics. 27° to 35°C
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
Na superfície
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Bom
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável precária (tratamento necessário)
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
during wet seasons
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
- Rico
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Off-farm income specification: handicraft, remittances and factory work
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Média escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Comunitário/rural
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Acesso livre (não organizado)
Comentários:
land users have a title which is not recognized by the state
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Dried residues are put in the garden (cucumber, pumpkin, watermelon) which increases nutrient availability.
Produção de forragens
Risco de falha de produção
Área de produção
Geração de energia
Comentários/especificar:
Before the installation of the biogas system, the land user bought firewood.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
He saves 50 $ on chemical fertilizer per year.
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
No smoke from open fire.
contribution to human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
On the long term livelihood is improved, because he saves over 60 $ per year in firewood and battery charging for light, as well as 50 $ for chemical fertilizer.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Qualidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Pollution of groundwater due to washing out of nutrients.
Solo
Umidade do solo
Perda de solo
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Most of the carbon is transformed into methane, not available as organic matter.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Controle de praga/doença
Outros impactos ecológicos
Reduced weed seeds
Comentários/especificar:
Compost usually not completely decomposed, as well as raw manure, contain lots of weed seeds.
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Poluição de água subterrânea/rio
Comentários/especificar:
Sludge is left to dry outside, nutrients washed out into groundwater. Not measurable.
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não conhecido |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não conhecido |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
Difficult question for farmers.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
The farmers guessed that around 10 % of the land users use this technology in the area. There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The sandbags reduce the labour, thus are used more and more even though they cost.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| The Pandanus leaves are used for baskets and mats. |
| The water is stored in the rice fields. Without stabilisation, the berms would not hold any water at all in sandy conditions. |
| Cattle is fenced off the rice fields through tall and thick (old) Pandanus plants growing on the dikes. |
| The irrigation channels are not eroded, water keeps flowing |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| The Pandanus grow too quickly and too tall, and require workload which is not available. | Select slow growing species or individuals. |
| Rodents use the Pandanus as niches. | Protect natural predators (snakes), or hunt/trap the rodents. |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| the plastic from the rice bags disintegrates with time and causes river pollution. | Use organic material (e.g. rice bags) to stabilize the dike for the first year. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
29/08/2014
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
NBP National Biodigester Program
Disponível de onde? Custos?
www.nbp.org.kh
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Lam et al. 2009. Domestic Biogas Compact Course. University of Oldenburg.
Disponível de onde? Custos?
http://www.nbp.org.kh/publication/study_report/2_domestic_biogas%20.pdf
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Gurung. 2009. Review of Literature on Effects of Slurry Use on Crop production. The Biogas Support Program
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos