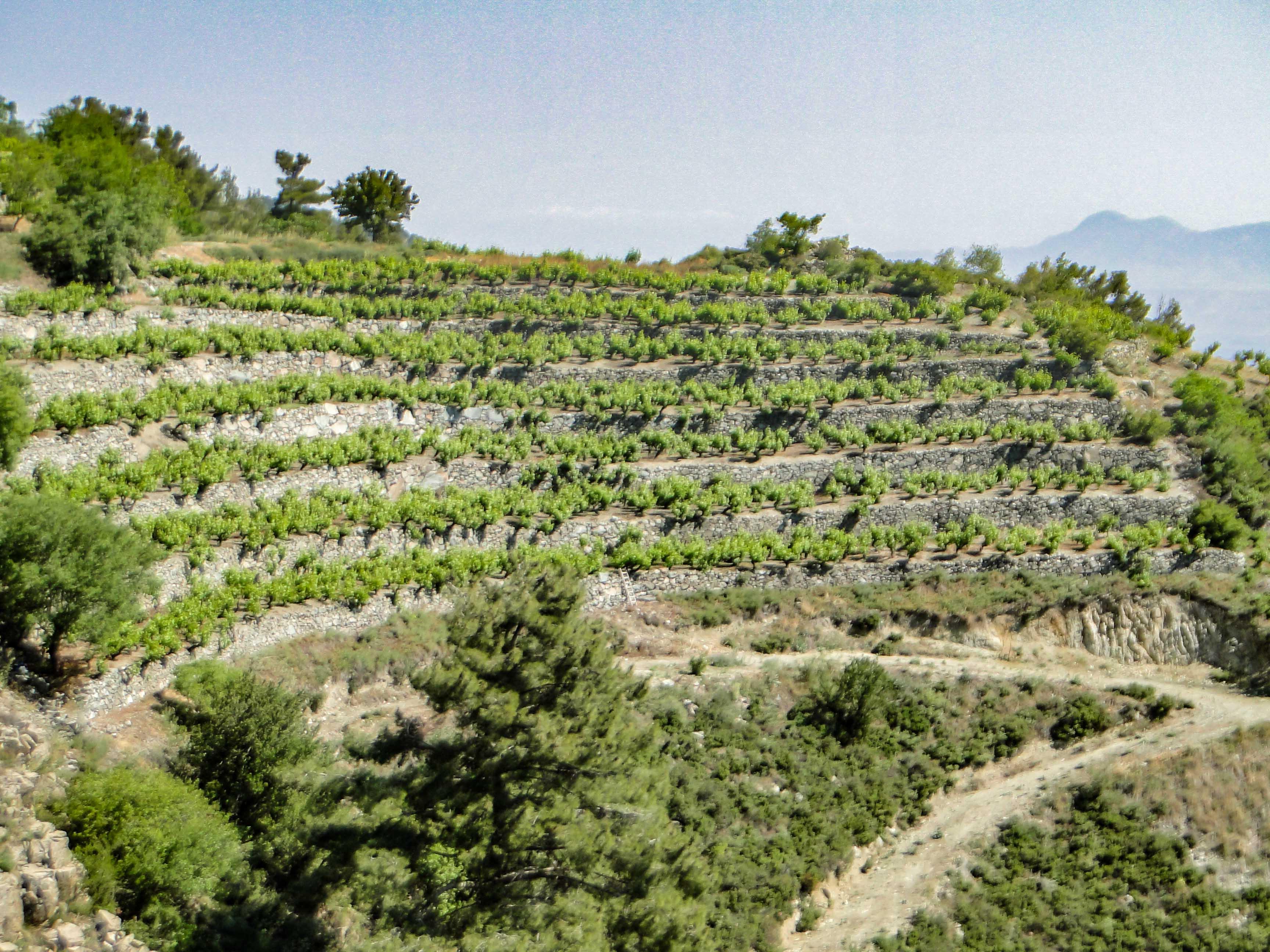
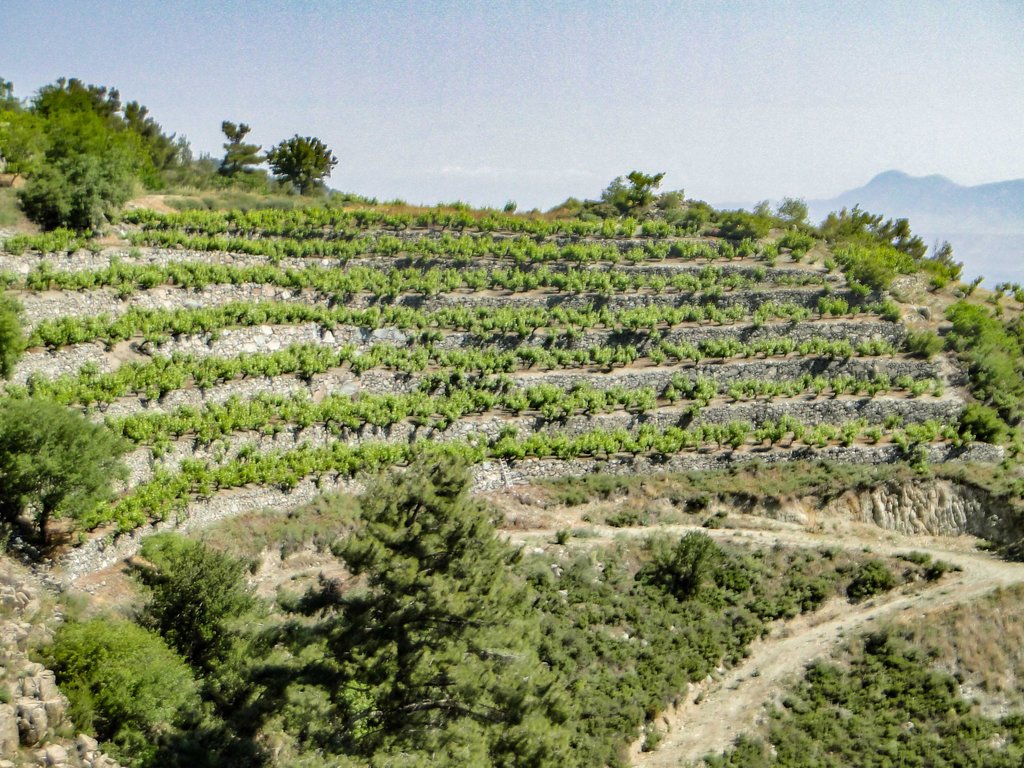
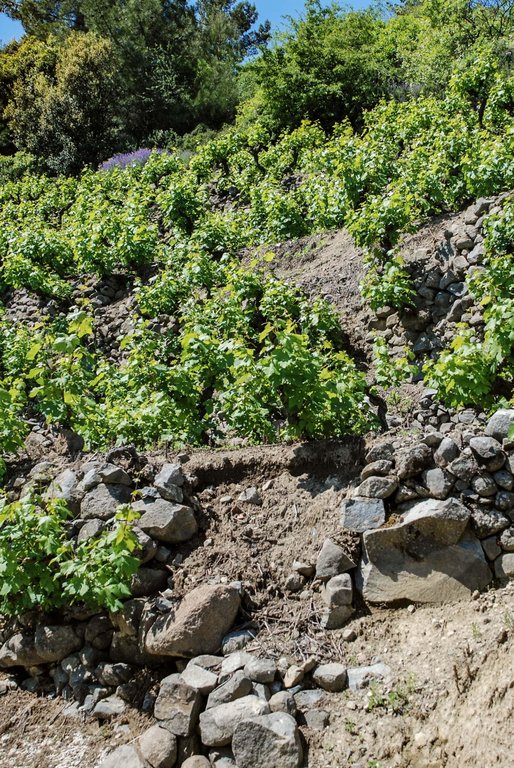
Agricultural terraces with dry-stone walls [Chipre]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Christos Zoumides
- Editor: –
- Revisores: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Γεωργικές αναβαθμίδες με τοίχους ξερολιθιάς (Greek)
technologies_1702 - Chipre
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Bruggeman Adriana
The Cyprus Institute
Chipre
Especialista em GST:
Camera Corrado
The Cyprus Insitute
Chipre
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
The Cyprus Institute (The Cyprus Institute) - Chipre1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
1.5 Referência ao(s) questionário(s) sobre abordagens GST (documentado(s) usando WOCAT)

Community-based maintenance and rehabilitation of agricultural terraces in … [Chipre]
Maintenance and rehabilitation of traditional dry-stone terrace walls for agricultural use, through science-society cooperation, community engagement and motivation, and assistance to land users.
- Compilador/a: Christos Zoumides
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Dry-stone terraces built to create agricultural land, minimise soil erosion and retain soil moisture on steep mountain slopes.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
Dry-stone terraces consist of a series of nearly levelled platforms built along contour lines at suitable intervals. These structures characterise a large part of the landscape in Cyprus, and especially in communities around Troodos Mountains where large areas have been converted to agricultural terraces. The typical terraces found in the study-area are narrow (1-3 m) to medium-base (3-6 m) bench terraces, constructed by cutting and filling in slopes between 20-40%. The terraces are supported by walls, whereby stone is the only construction material without any binding mortar.
Terracing is one of the oldest means of cultivating slopes while saving soil and water. Due to the steep terrain of Troodos Mountains, the establishment of terraces acts as sediment trap storing the washed-off soil material within the slope. In general, terraces were created to stop or reduce the degrading effect of soil erosion by intercepting and controlling the surface run-off velocity and by facilitating its slower infiltration. In such a way, the sediment that accumulates behind the terraces has created suitable land for farming. In addition, the construction of dry-stone walls serves a dual purpose: to clear the land from large rock and stones, and to enhance the stability of the bench terraces against loss of top-soil. This is a type of technology that was very much used in the past and seen today as an important cultural landscape and heritage for these communities.
The construction of dry-stone walls was usually completed by the family who owned the field. Men undertook the building while the rest of the family carried the stones; assistance was also offered by relatives and friends of the family. First, the topography, the height and shape of the terrace is evaluated. Using a fuse, the craftsman shapes a straight line which would follow while building the wall. The foundations are created by excavating a pit of ~0.3-0.5 m, depending on the type of soils and the size of the wall; fuse, pick, mattock and shovel are the typical tools used. The pit is filled with large, irregular-shaped stones.
The stones are used in their natural shape for the construction of the walls without any processing. They are separated according to their shape, size and texture. The stones usually come from the cleaning of fields which will be cultivated or from a small-scale quarrying of the mountain slope using pick and lever. Large and irregular stones are used for the foundations, and the more regular ones for the construction of walls. The smaller stones are placed in between the large stones as the linchpin, to provide better stability to the structure.
The wall follows the land inclination and is laid over the foundation. Large stones are placed on the lower courses of the wall and on the exterior side. The stones are placed by hand one over the other, while smaller stones and rubbles are put between them in order to achieve more stability and better positioning; the stones cross both vertically and horizontally in order to avoid the creation of columns which will make the structure less stable. The wall is built lengthwise following the foundations and it reclines inwards; declination from the foundations does not exceed 5%. The back side of the wall is filled-up with more irregular stones which are not suitable to be placed on the front side. The filling connects the wall with the soil and stabilises the structure, and allows the drainage of water that is collected from the terrace and is discharged through the stones of the wall.
Terrace farming of grapes, nut and fruit trees, along with natural (mainly sclerophylous) vegetation constitute the predominant land uses in this area. The total population in the eight mountain communities of Peristerona Watershed has decreased by more than 50% over the past 30 years. The depopulation of mountain communities is associated with the urbanisation trends and the high farming costs which led to the gradual reduction of agricultural activities in the area. These socio-economic attributes form the main constraining factors for soil conservation. Thus, although terraces have a particularly beneficial effect in maintaining the productive capacity of soils in these communities, the significant changes in the socio-economic structure of the agricultural population over the last decades and the high maintenance and labour required, has led farmers to gradually abandon terrace farming. Consequently, many of the mountain terraces are no longer cultivated and dry stone walls are not maintained, causing sometimes a domino effect of collapsing terraces.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Chipre
Região/Estado/Província:
Nicosia
Especificação adicional de localização:
Northeast Pitsilia
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a Tecnologia estiver uniformemente distribuída por uma área, especifique a área coberta (em km2):
30,9
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 10-100 km2
Comentários:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 30.9 km2.
Dry-stone terraces characterise a large part of the landscape in Cyprus, and especially in communities around Troodos Mountains. There is a large variety of dry-stone terraces on the island, according to the morphology of each area and the accessibility to raw materials. The information reported here refer to the mountain communities in Northeast Pitsilia and particularly to the Peristerona watershed upstream communities (RECARE project case-study site).
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Dry-stone terracing has been practice for centuries in Cyprus and in the study area. The rehabilitation of dry-stone terraces through community-based activities has been introduced in 2015 by the RECARE project case-study team and the local communities.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas, outros
- uvas
- frutos secos (castanhas do Brasil, pistache, nozes, amêndoas, etc.)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 1
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 240, Longest growing period from month to month: Mid March to early November (grapevines)
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion by water from degraded and collapsing dry-stone terraces.
Loss of productive capacity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Gradual collapse of dry-stone walls.
Root rot and yield failure as a result of water-logging which is linked to poor drainage in terraced fields.
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Medidas de curva de nível
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S1: Terraços
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wt: Perda do solo superficial/erosão de superfície
- Wo: efeitos de degradação externa
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: other human induced causes (specify) (Gradual abandonment of mountain agriculture), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Steep mountain terrain)
Secondary causes of degradation: land tenure (Small, fractured agricultural plots), governance / institutional (Lack of institutions for terrace maintenance)
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Recuperar/reabilitar solo severamente degradado
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
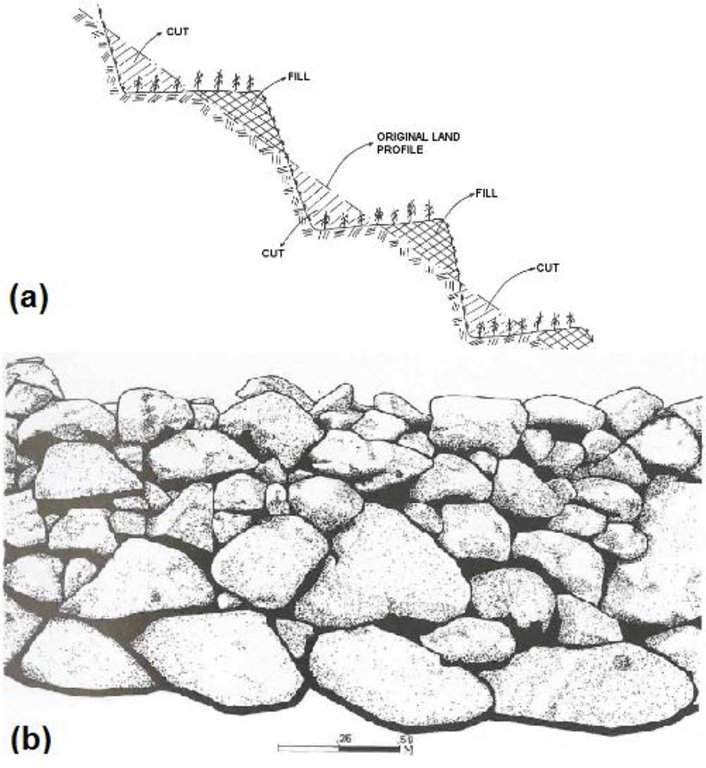
(a) The typical terraces found in the study-area are narrow (1-3 m) to medium-base (3-6 m) bench terraces, constructed by cutting and filling in slopes between 20-40%. The height of terraces range between 0.75 to 2 meters, depending on the steepness and the morphology of each slope.
(b) The terraces are supported by walls, whereby stone - typically volcanic rock - is the only construction material without any binding mortar. Large and irregular stones are used for the foundations, while the more regular for the construction of walls. The smaller stones are placed in between the large stones as the linchpin, to provide better stability to the structure. The wall is built lengthwise following the foundations and it reclines inwards; declination from the foundations does not exceed 5%. The back side of the wall is filled-up with more irregular stones which are not suitable to be placed on the front side. The filling connects the wall with the soil and stabilises the structure, and allows the drainage of water that is collected from the terrace and is discharged through the stones of the wall.
Northeast Pitsilia, Nicosia
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (To maintain dry-stone wall terraces)
Technical knowledge required for Dry-stone artisans (experts builders): high (To reconstruct collapsed terraces)
Main technical functions: reduction of slope angle, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1-2
Spacing between structures (m): 1-15
Construction material (stone): Natural volcanic rock available on the sites (mostly gabbro & diabase)
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0-8%
Autor:
a: FAO, 2000 & b: TPH, 2007
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Euro
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
0,88
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
72.97
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land leveling and foundation | Early autumn or late spring |
| 2. | Collection and transfer of stones | Early autumn or late spring |
| 3. | Construction of stone-wall | Early autumn or late spring |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | 4000,0 | 45,6 | 182400,0 | 100,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 182400,0 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 207272,73 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 83 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Repairing collapsed walls | Early autumn (before onset of rains), only on collapsed walls |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour | 200,0 | 9,12 | 1824,0 | 100,0 | |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 1824,0 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 2072,73 | |||||
Comentários:
Machinery/ tools: Wedge, hammer, pick, hoe and bucket are the typical tools used for by stone builders for the construction and maintenance of dry-stone terraces.
The costs estimates are averages and were calculated for the length of terrace structures, i.e. per running meter of terrace walls. The average height of dry-stone walls is 1.5 meter and it takes approximately 5 hours/meter for a builder to fully construct it. This includes 1 hour/meter for land levelling and foundation, 1 hour/meter for the collection and transfer of the necessary stones and 3 hours/meter for building the wall. Stones are abundant in the area; builders do not charge for the stones but for the time required to collect and transfer. Also, each builder has its own tools (i.e. wedge, hammer, pick, hoe and bucket). Terrace builders charge 8 €/hour (or 9.12 $/hour). On average, there are approximately 4000 running meters of terrace walls per hectare. The above information is used to convert the construction cost per hectare.
Maintenance activities include reconstruction of the terrace walls, only in case of collapsing. The reconstruction takes 1 hour/meter. For the annual maintenance estimates, it is assumed that 200 out of 4000 meters of terrace walls per hectare (or 5%) will require maintenance. In other words, a newly constructed wall will be maintained once every 20 years, on average.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
The principal input cost for the construction and maintenance of terraces is manual labour. There are only few dry-stone builders in the area.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
500-750mm: Seasonal rainfall (October to May) - Peristerona watershed upstream
250-500mm: Seasonal rainfall (October to May) - Peristerona watershed downstream
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: subtropics. Below 1000m a.s.l.
Thermal climate class: temperate. Above 1000m a.s.l.
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Não relevante
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
- Médio (limoso, siltoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Médio (1-3%)
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
> 50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Médio
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Médio
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- 10-50% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Mecanizado/motorizado
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: negative; 4%
100% of the land users are average wealthy.
Off-farm income specification: Farming is a part-time activity for most land users in the area.
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
Comentários:
The average for Cyprus is 3.4 ha/holding
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
Comentários:
Agricultural land is privately owned
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Terraces create agricultural land for crop production in slopes. However, the establishment of terraces does not imply increased crop yield.
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
Without terraces on mountain slopes, crop farming would have been almost impossible
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Demanda por água para irrigação
Comentários/especificar:
Well constructed and maintained terraces improve water drainage and retain soil moisture.
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Comentários/especificar:
More costly to grown on mountain terraces than in the plains. Also, maintenance of collapsed terrace walls is costly.
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Farming in the study-site is practiced almost exclusively on terraces; well maintained terraces can increase farm income.
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Maintenance of collapsed terrace walls requires manual labour
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Partly for those land users that still practice mountain terrace farming.
Oportunidades culturais
Comentários/especificar:
When terraces are maintained/rehabilitated through community-based activities.
Oportunidades de lazer
Comentários/especificar:
When terraces are maintained/rehabilitated through community-based activities.
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
When terraces are maintained/rehabilitated through community-based activities.
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Dry-stone terracing is the typical soil conservation technology in the study-site
Atenuação de conflitos
Contribution to human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Terraced landscapes in the Troodos mountains represent a longstanding tradition of self-sustained communities. In the past, terrace farming was a main activity and has contributed to the livelihoods and well-being of these communities. Nowadays, terrace farming is still practiced by much fewer land users, mainly on part-time basis.
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Comentários/especificar:
One of the main functions of terraces.
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
One of the main functions of terraces.
Solo
Cobertura do solo
Comentários/especificar:
When terraces are maintained
Perda de solo
Comentários/especificar:
One of the main functions of terraces.
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
Dry-stone terraces create biodiversity habitats, especially for reptiles and arthropods
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Risco de incêndio
Comentários/especificar:
Well maintained terraces have less weeds than abandoned terraces, thus reducing the fire risk
Outros impactos ecológicos
Abandoned or poorly maintained terraces can result in increased erosion, e.g. through the collapsing
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Cheias de jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Upstream terraces can reduce to a certain extent reduced downstream flooding
Sedimentação a jusante
Comentários/especificar:
Upstream terraces can reduce to a certain extent downstream siltation
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
Comentários/especificar:
Well maintain terraces reduce damage (erosion) on public (e.g. roads) and private (e.g. neighbours fields) infrastructure
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | não bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | não conhecido |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | não bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente negativo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- > 50%
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
90% of the land user families and 8% of the stated area
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 11-50%
Comentários:
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The majority of existing terraces in the area were subsidized.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There are very few farmers that maintain existing terraces or construct new ones.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| Indigenous technology of great agro-ecological value, adapted to local conditions. |
| Soil maintained on steep mountain slopes, thus reducing soil loss due to water erosion. |
| Terraces maintain the productive capacity of soils on steep slopes. |
| Water retention and longer storage of soil moisture, thus improving water use efficiency. |
| Terraces are part of cultural landscapes and heritage |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Maintenance of dry-stone wall terraces is costly and labour intensive. | Promote community-based terrace maintenance and utilise available community/subsidy funds for small cash compensation to terrace experts. |
| Terrace maintenance requires expert knowledge. | Motivate the younger generation to engage in part-time terrace farming. |
| Aging of the dry-stone experts. | Train young land users/owners on dry-stone terracing. |
| Technology does not lend itself to mechanisation. | Not possible to overcome. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
01/09/2015
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
FAO, 2000. Manual on integrated soil management and conservation practices. FAO Land and Water Bulletin 8, Rome, Italy: 230 pp.TPH, 2007. Dry stone constructions of Cyprus. PIO, Nicosia.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks

Community-based maintenance and rehabilitation of agricultural terraces in … [Chipre]
Maintenance and rehabilitation of traditional dry-stone terrace walls for agricultural use, through science-society cooperation, community engagement and motivation, and assistance to land users.
- Compilador/a: Christos Zoumides
Módulos
Não há módulos