Alternate wetting and drying (AWD) method in rice cultivation [Bangladesh]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Mutasim Billah
- Editores: Md. Monzurul Haque, Matieu Henry
- Revisores: Nicole Harari, Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Ursula Gaemperli
Magic pipe er madhomme kom panite dhan chas
technologies_4671 - Bangladesh
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
usuário de terra:
Zaman Md. Shahid Uz
Farmer
Bangladesh
co-compilador/a:
Azad Md. Abul Kalam
Department of Agricultural Extension (DAE)
Bangladesh
co-compilador/a:
Jalal Uddin Dewan
Department of Agricultural Extension (DAE)
Bangladesh
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Decision Support for Mainstreaming and Scaling out Sustainable Land Management (GEF-FAO / DS-SLM)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
FAO Bangladesh (FAO Bangladesh) - BangladeshNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Department of Agricultural Extension (DAE) - BangladeshNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) - Bangladesh1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
1.4 Declaração de sustentabilidade da tecnologia descrita
A tecnologia descrita aqui é problemática em relação a degradação da terra de forma que não pode ser declarada uma tecnologia de gestão sustentável de terra?
Não
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Alternative Drying and Wetting (AWD) is a practice in rice cultivation which decrease water use, while having no impact on rice yield. It also decreases the amount of methane into the atmosphere and fuel consumption of water pumps.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The Rajshahi, Chapai Nawabganj and Naogaon regions of Bangladesh geographically belong to High Barind Tract (HBT) of Bangladesh under Agro Ecological Zone (AEZ) 26. This region is the hottest region of the country where water scarcity is a common problem. The annual precipitation is 1410 mm and the farmer is habituated to use deep tubewell underground water for their crops operated by Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA). Rice is the common crop in this region and in Boro season (from November to March) rice consumed the lion share of underground water through flood irrigation. And this flood irrigation system is very traditional cultivation method resulting the underground water table is consistently going down for heavy extraction by shallow or deep tube-well.
It is not always necessary to keep standing water in rice fields for its maximum production like aquatic plant. To address these problems ‘Alternate Wetting and Drying’ is a good choice, because it is not necessary to keep the water standing throughout the whole growing season of Boro rice (wet rice). In this method 20-25% less water is consumed, which may save approximately USD 30 per hectare.
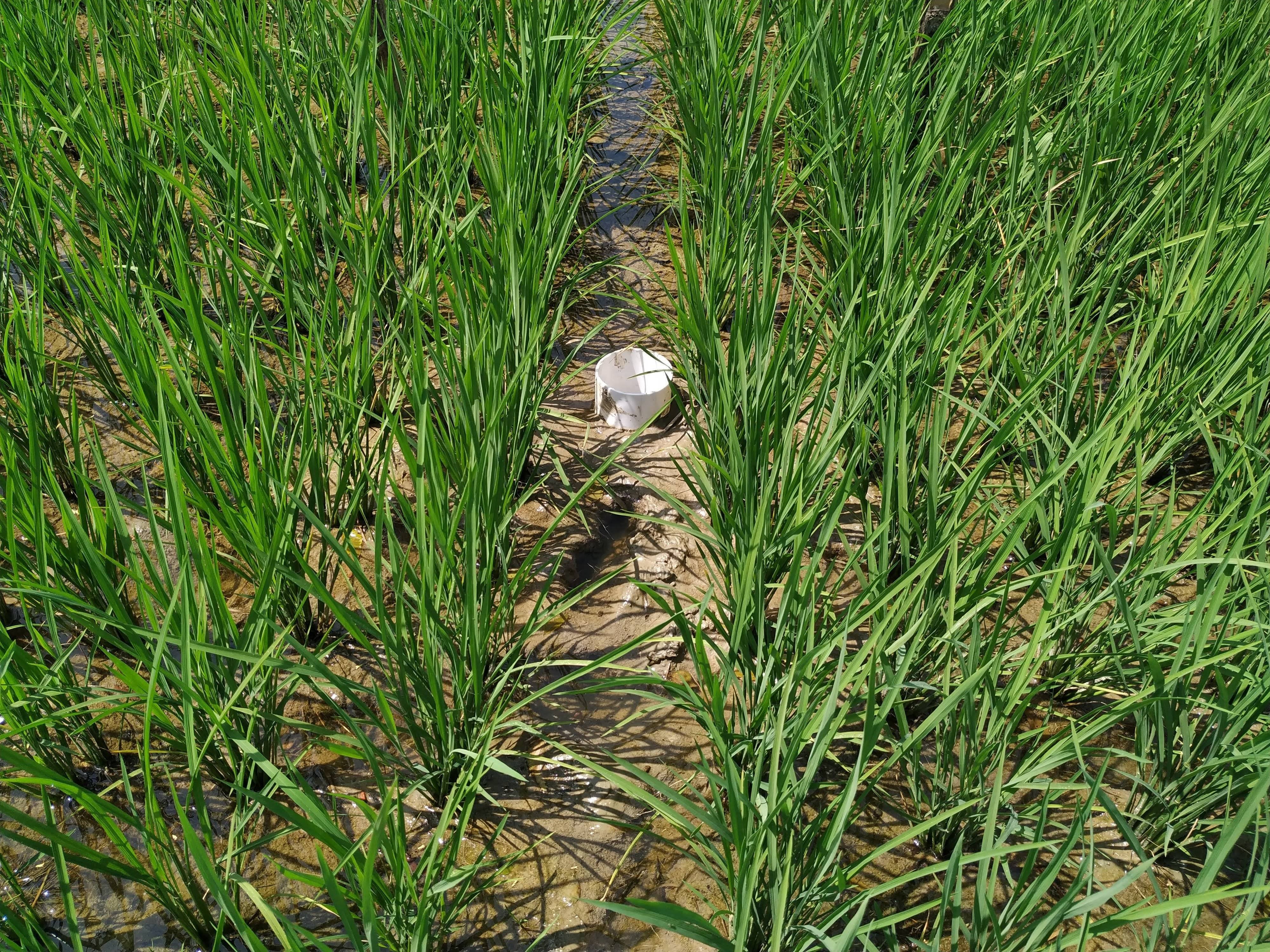
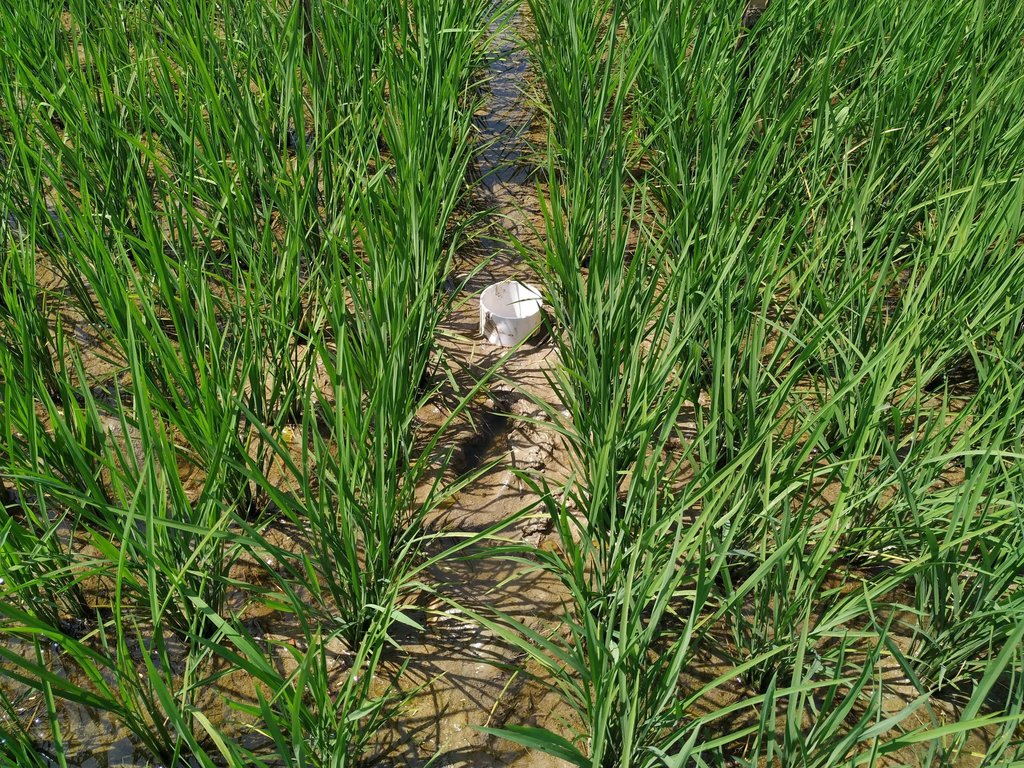
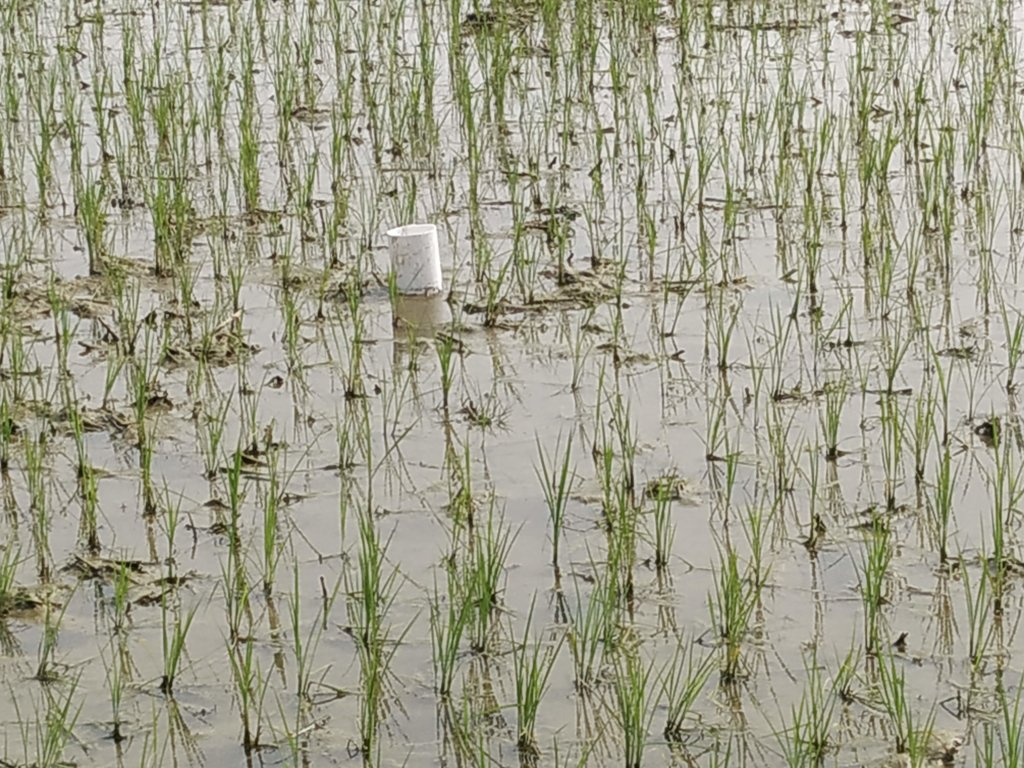
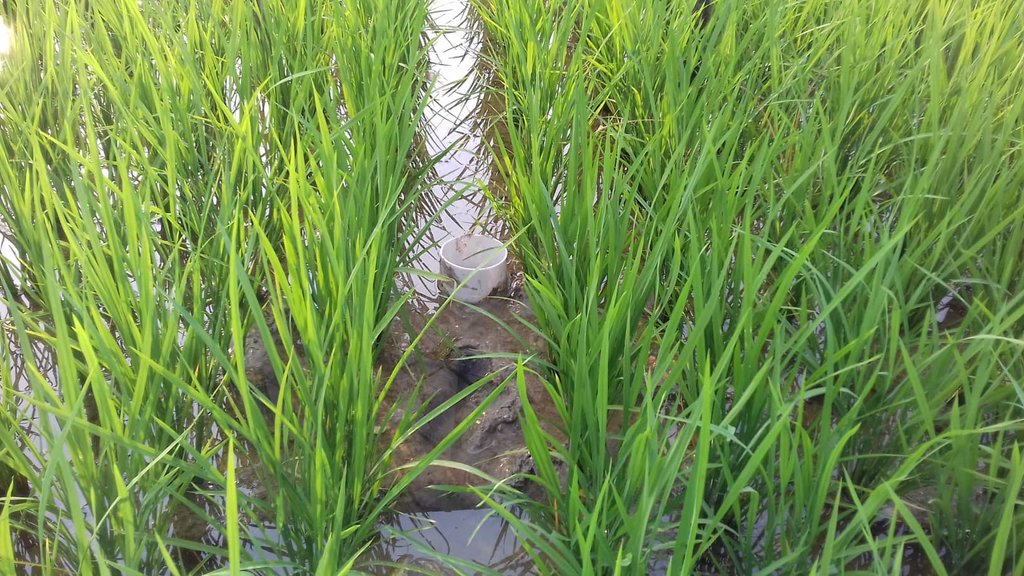
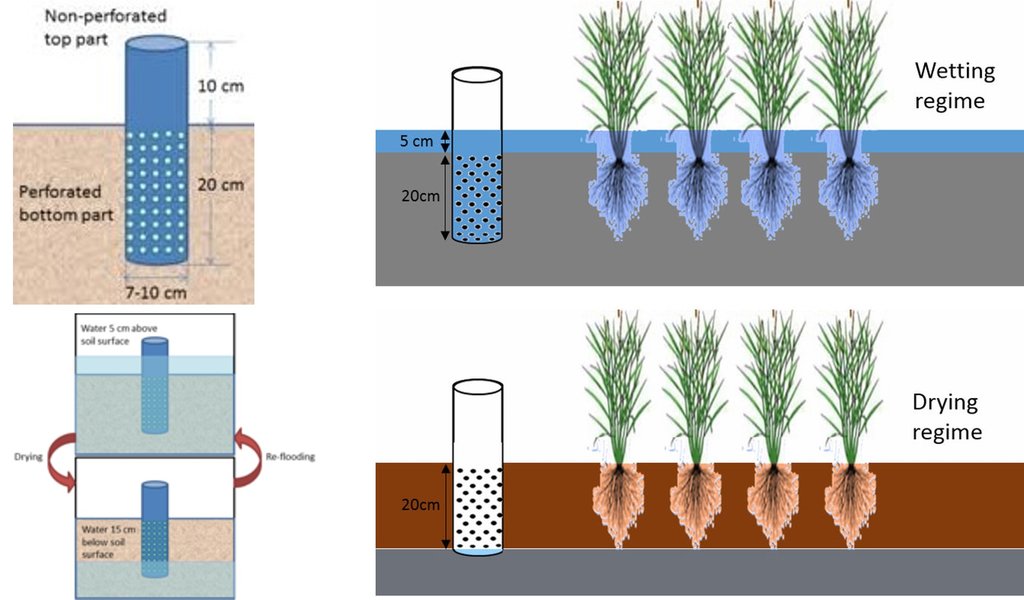
After 10-15 days of transplanting of rice seedling shallow standing water can be allowed and then the field can be drained and wetted alternately. To implement this method, first a perforated plastic pipe is installed to examine the water level and irrigate the rice field when necessary. The 25 cm long and 7-10 cm diameter perforated pipe is installed vertically. Only the lower 15 cm of the pipe should be perforated so that water can enter and exit, and then the pipe should be installed so that the non-perforated portion remains above the ground to protect it from debris.
In a leveled rice field of one hectare, seven to eight pipes are enough to monitor water depth. 10-15 days after seedling transplanting the AWD method can start. In each irrigation, the water level should reach 5-7 cm from the above the soil in wetting regime, and when the water level goes down to the soil level in drying regime, then the field can be irrigated again. This can continue until the panicle initiation stage. Then from panicle initiation to the milking stage, the field should be irrigated with 2-4 cm of water (also wetting regime). After the milking stage, the AWD can be continued until two weeks before harvesting from April to May (depending on rice variety).
Promotion of AWD in Bangladesh has been piloted and tested by different organisations like Bangladesh Rice Research Institute (BRRI), Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) and Department of Agricultural Extension (DAE) during 2008 to 2010. In HBT, the quantity of groundwater is continuously decreasing, so farmers applied AWD without installing the pipe. The farmers are experienced with this technology long-ago and know that the cracks appeared when the groundwater goes down to 18-20 cm below soil surface. When the farmers saw the "hair like crack" in their rice field, they irrigated. BMDA introduced the pre-paid card for irrigation, so the farmer irrigated his rice field several times when he saw the field cracks. The aim is to save money as well as to save groundwater.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Bangladesh
Região/Estado/Província:
Chapainawabganj
Especificação adicional de localização:
Amnura
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Aplicado em pontos específicos/concentrado numa pequena área
O(s) local(is) tecnológico(s) está(ão) localizado(s) em uma área permanentemente protegida?
Não
Comentários:
The land user use this technology in their rice field
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- menos de 10 anos atrás (recentemente)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- atráves de inovação dos usuários da terra
- durante experiências/ pesquisa
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
- From long ago, farmer observed "hair like crack" in rice field that indicate water goes down in 18-20 com
- Bangladesh Rice Research Institute (BRRI) has set up a lot of research plot on AWD use
- Department of Agricultural Extension (DAE) and Barind Multipurpose Development Authority (BMDA) also has projects to install AWD in farmers field through demonstration
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Melhora a produção
- Adaptar a mudanças climáticas/extremos e seus impactos
- Atenuar a mudanças climáticas e seus impactos
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada
Uso do solo misturado dentro da mesma unidade de terra:
Não

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura anual
Cultivo anual - Especificar culturas:
- cereais - arroz (zona húmida)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 3
Especifique:
Mustard/Potato/Pulse-Boro - Fallow - T.Aman
O cultivo entre culturas é praticado?
Não
O rodízio de culturas é praticado?
Sim
Caso afirmativo, especifique:
Mustard/Potato/Pulse then irrigated Boro rice then keep fallow for few days and then again Transplanted Aman rice
3.3 O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
O uso do solo mudou devido à implementação da Tecnologia?
- Não (Continuar com a pergunta 3.4)
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Misto de precipitação natural-irrigado
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Gestão de irrigação (inclusive abastecimento de água, drenagem)
- Gestão do lençol freático
- Tecnologias de eficiência energética
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S7: coleta de água/ equipamento de abastecimento/irrigação

Medidas de gestão
- M2: Mudança de gestão/nível de intensidade
- M4: Principal mudança no calendário de atividades
Comentários:
Because the cultivation technology in rice cultivation remains the same as before, except of the new irrigation regime, only S7, M2 and M4 are actually part of the measures associated with the new technology.
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação da água
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
- Hg: mudança no lençol freático/aquífero
- Hp: declínio da qualidade de água de superfície
- Hq: declínio da qualidade do lençol freático

Outro
Especifique:
Flooding rice cultivation increase GHG emission from nitrogen fertilizer
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Length of plastic tube: 30 cm
Width of plastic tube: 7-10 cm
Perforated portion of plastic tube : 20 cm
Non-perforated portion of plastic tube: 10 cm
Height of irrigated water: 5 cm (above surface)
Time for irrigation: When water goes down at bottom of plastic tube (approximately 15 cm below soil surface)
Number of plastic tube: 20 in one hectare of land
Autor:
RIAZ, A. et al. 2017.
Data:
06/02/2017
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Especifique como custos e entradas foram calculados:
- por área de tecnologia
Indique o tamanho e a unidade de área:
1 Hectare
Especifique a moeda utilizada para os cálculos de custo:
- USD
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
USD 5.0
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Plastic tube installation | March - April |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Labour for plastic tube installation | Person-day | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Plastic tube | Number | 20,0 | 0,64 | 12,8 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 17,8 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 17,8 | |||||
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Land preparation (cleaning land, repairing border, repairing canal etc. manual work) | January - February |
| 2. | Plowing | January - February |
| 3. | Seedling transplanting | January - February |
| 4. | Irrigation in different vegetative and reproductive stages | January - May |
| 5. | Fertilization | January - April |
| 6. | Herbicide and pesticide application | January - March |
| 7. | Harvesting | May - June |
| 8. | Threshing | May - June |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Land preparation | Person-day | 6,0 | 5,0 | 30,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Seedling transplanting | Person-day | 37,0 | 5,0 | 185,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Herbicide and pesticide application | Person-day | 8,0 | 5,0 | 40,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Irrigation | Person-day | 18,0 | 5,0 | 90,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Power tiller rent for plowing | Machine-hour | 16,0 | 2,0 | 32,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Sprayer | Machine-hour | 24,0 | 1,0 | 24,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Cost for irrigation | Machine-hour | 22,0 | 2,5 | 55,0 | 100,0 |
| Material vegetal | Seed | kg | 15,0 | 1,3 | 19,5 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Chemical fertilizer | Kg | 70,0 | 0,35 | 24,5 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Manure | Kg | 1500,0 | 0,05 | 75,0 | 100,0 |
| Fertilizantes e biocidas | Herbicide and pesticide | Kg | 18,0 | 2,4 | 43,2 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour for harvesting | Person-day | 24,0 | 5,0 | 120,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour for threshing | Person-day | 10,0 | 5,0 | 50,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour for drying | Person-day | 4,0 | 5,0 | 20,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour for repairing spray machine | Person-day | 2,0 | 5,0 | 10,0 | 100,0 |
| Outros | Labour for cleaning plastic tube | Person-day | 1,0 | 5,0 | 5,0 | 100,0 |
| Custos totais para a manutenção da tecnologia | 823,2 | |||||
| Custos totais de manutenção da Tecnologia em USD | 823,2 | |||||
Comentários:
For the sake of completeness, all recurring costs relating to rice growing have been listed here. However, the recurring costs for AWD technology are actually only those related to irrigation (work for irrigation, patching and cleaning). Irrigation pump installation and maintenance cost belongs to BMDA, the farmer have no responsibility on irrigation pump. They just purchase irrigation water through pre-paid card.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
- Irrigation according to wetting and drying regimes
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especifique a média pluviométrica anual em mm (se conhecida):
1400,00
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
The average rainfall in High Barind Tract is low than other parts of Bangladesh
Indique o nome da estação meteorológica de referência considerada:
Weather Atlas; {https://www.weather-atlas.com/en/bangladesh/rajshahi-climate#rainfall}
Zona agroclimática
- Subúmido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Indique se a tecnologia é aplicada especificamente em:
- Posições convexas
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Textura do solo (>20 cm abaixo da superfície):
- Fino/pesado (argila)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Precário/nenhum
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
A qualidade da água refere-se a:
águas subterrâneas
A salinidade da água é um problema?
Não
Ocorre inundação da área?
Não
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Baixo
Diversidade de habitat:
- Baixo
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Sedentário ou nômade:
- Sedentário
Orientação de mercado do sistema de produção:
- Subsistência (autoabastecimento)
- misto (subsistência/comercial)
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Muito pobre
- Pobre
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Indivíduo/unidade familiar
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
- Tração animal
Gênero:
- Mulheres
- Homens
Idade dos usuários da terra:
- Jovens
- meia-idade
- idosos
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Arrendado
- Indivíduo
Direitos do uso da água:
- Indivíduo
Os direitos de uso da terra são baseados em um sistema jurídico tradicional?
Sim
Especifique:
In Chapai Nawabganj, there are two types of land viz. Government owned and (popularly known as Khas land) and public owned land. The public owned land has registered to a person and that person paid tax to Government in yearly basis, this is the way of traditional legal system.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
AWD increases the crop production (yield) than traditional method. So, more crop yield increases the socio-economic condition of farmer. Moreover, this method reduces the input cost for crop production.
Risco de falha de produção
Área de produção
Comentários/especificar:
AWD method decreases the production cost for irrigation. So, the land area under this method is increasing gradually.
Gestão de terra
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Comentários/especificar:
The irrigation water and the drinking water come from same underground source by deep tube-well. So, when the water extraction is reduce for irrigation, the availability for drinking water is increase.
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Demanda por água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Despesas com insumos agrícolas
Rendimento agrícola
Carga de trabalho
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Drenagem de excesso de água
Lençol freático/aquífero
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
In dry regime of AWD method, the evaporation is decrease on land
Solo
Ciclo e recarga de nutrientes
Comentários/especificar:
Some plant nutrient like Zinc (Zn) is much available when the soil going from wet to dry regime. Constant wet condition inhibit some other plant nutrient also.
Matéria orgânica do solo/carbono abaixo do solo
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Biomassa/carbono acima do solo
Controle de praga/doença
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da seca
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Microclima
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Impacto dos gases de efeito estufa
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem | |
| Temperatura sazonal | estação seca | aumento | bem |
| Precipitação pluviométrica anual | redução/diminuição | bem | |
| Precipitação pluviométrica sazonal | verão | redução/diminuição | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Tornado | moderadamente |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | muito bem |
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- 11-50%
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
6.6 Adaptação
A tecnologia foi recentemente modificada para adaptar-se as condições variáveis?
Não
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| Easy to monitor irrigation schedule in AWD method. Farmer able to understand about dry and wet regime of rice cultivation that reduce the irrigation cost. |
| This Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) system enhance the tillering of rice resulting yield would be higher than traditional continuous flooding cultivation system |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
| AWD facilitate drying rice field for certain period. This practice inhibit the chemical reaction of nitrogen fertilizer that emit low greenhouse gas |
| Water is the most demandable input and in AWD system the requirement of irrigation water become low that reduces input cost |
| Potentials for scale-up of this AWD method, because the groundwater scarcity became increase that would be popular to all farmer |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/desvantagens/riscos na visão do usuário da terra | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Magic pipe is not available everywhere | Department of Agricultural Extension (DAE) support them to use AWD |
| Technical knowledge | Sub-Assistant Agriculture Officer (SAAO) and resource farmer provide technical support |
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Technical knowledge of land user | Consultation with SAAO and resource farmer |
| Misunderstanding on yield to use AWD; Land user think yield is lower when using Alternative Wetting and Drying method | Show results by taking farmers to visit demonstration plots, field day, cross visit etc. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
- visitas de campo, pesquisas de campo
3
- entrevistas com usuários de terras
4
- entrevistas com especialistas em GST
3
Quando os dados foram compilados (no campo)?
14/02/2019
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Bangladesh Rice Research institute (BRRI), Gazipur
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Internet, free
7.3 Links para informações on-line relevantes
Título/ descrição:
Use of irrigation water saving technology (AWD) in rice field
URL:
http://www.knowledgebank-brri.org/Rice_Production_Training_Manual/Day_2/Module_7/Factsheet%204%20-%20water%20saving%20technology%20(AWD).pdf
7.4 Comentários gerais
In the case of annual crop cultivation, the questionnaire should be revised.
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos