Sand dams [Quênia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Ian Neal
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Sand storage dams, Groundwater dams
technologies_1537 - Quênia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Especialista em GST:
Musila Andrew
Africa Sand Dam Foundation
Quênia
Nome do projeto que facilitou a documentação/avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Book project: Water Harvesting – Guidelines to Good Practice (Water Harvesting)Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Africa Sand Dam Foundation (ASDF) - QuêniaNome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Excellent Development Ltd. (Excellent Development Ltd.) - Reino Unido1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
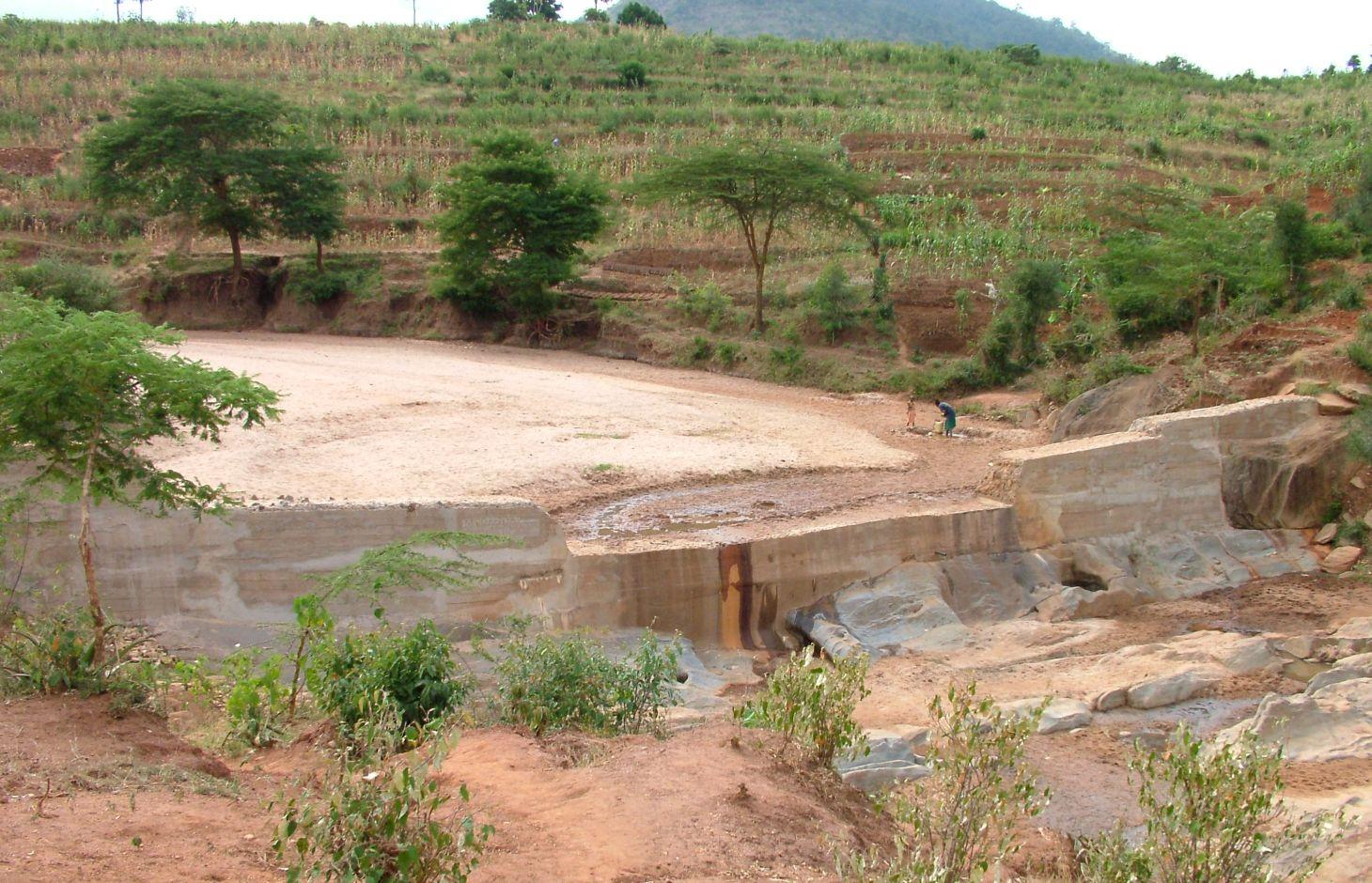
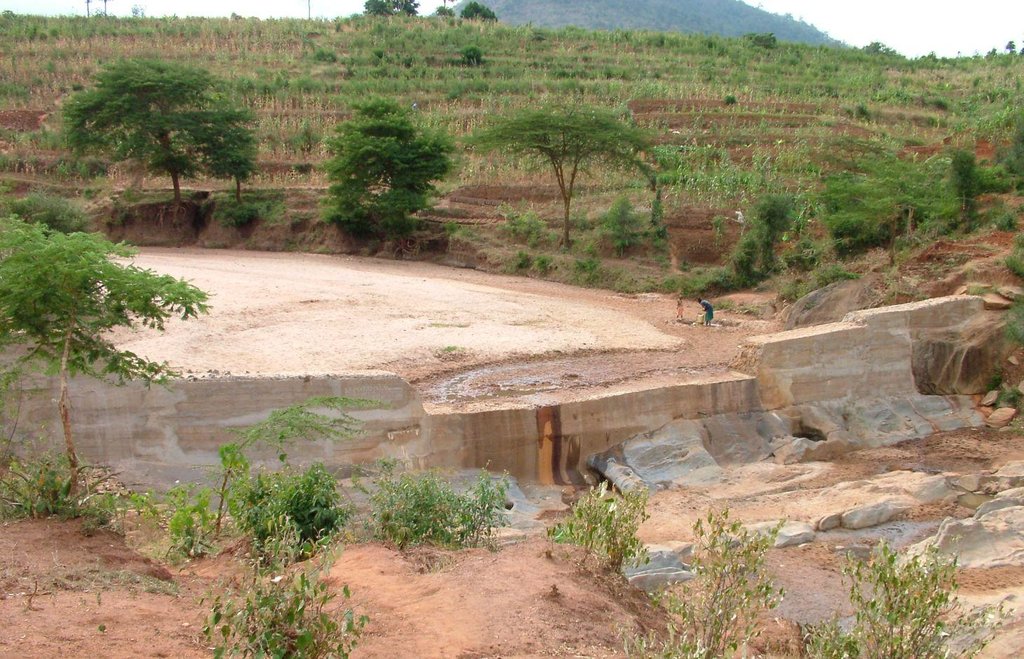
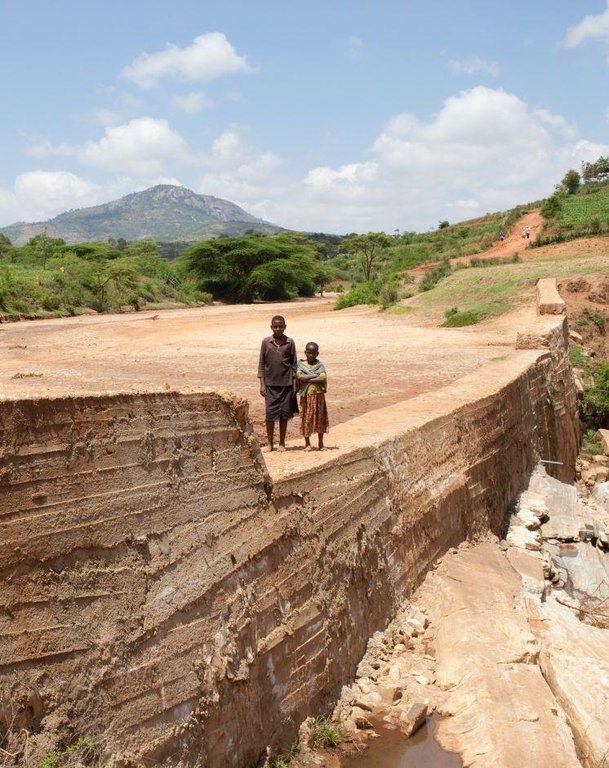
A sand dam is a stone masonry barrier across a seasonal sandy riverbed that traps rainwater and sand flowing down the catchment.
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
A sand dam is typically 1 - 5 metres high and 10-50 metres across. When it rains the dam captures soil laden water behind it – the sand in the water sinks to the bottom, whilst the silt remains suspended in the water. Eventually the dams fill with sand - sometimes after only one rainfall or over 1 – 3 seasons. 25 to 40% of the volume of the sand held is actually water. A mature sand dam can store millions of litres of water – refilling after each rainfall providing a year round supply to over 1,000 people.
Purpose of the Technology: Sand dams are a simple, low cost and low maintenance, replicable rainwater harvesting technology. They provide a clean, local water supply for domestic and farming use and are suited to arid and semi-arid areas of the world. It is a solution that is scaleable and has a broader application for use as a rural and game park road crossing to replace less effective culvert bridges.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Sand dams are the lowest cost form of rainwater harvesting and its robust nature and very low operational and maintenance costs make it particularly suited to remote and poorly served regions. A typical dam using 500 bags of cement would approx be 40 metres in length with a spillway 2 metres above the bedrock. The dam is constructed using stone masonry placed in timber formwork. Such a dam costs approximately USD 11,800 (in 2012 prices). This consists of materials (cement, steel reinforcement, timber, transport) and dam permit USD 8,800 (75%), project management including technical support from skilled local artisans and dam designers USD 2150 (18%) and finance and administration costs of implementing organisation USD 850 (7%). Local people freely contribute their labour to collect rock, sand and water, terrace and protect the immediate catchment and construct the dam. If this contribution was costed and included the cost of the dam would almost double. The maintenance and repair costs of the dam provided it has been well designed and constructed is negligible. Local users are responsible for the management and repair of the dam and its abstraction system. Where a hand pump is fitted, local users fund the repair and replacement of the pump as required. The purchase and repair of petrol powered water pumps which some groups use to irrigate adjacent land is the responsibility of the members of the local group.
Natural / human environment: Because the water is stored within the sand, evaporation losses are very low, the sand filters the water and water-vector diseases such as malaria are controlled. Sand dams provide significant environmental benefits such as aquifer recharge, increased downstream flows in the dry-season, rejuvenation of river ecologies and moderation of floods. As such, it contributes to ecosystem services and climate change adaption.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Quênia
Região/Estado/Província:
Machakos, Kitui and Makueni Counties
Especificação adicional de localização:
Eastern Province, Kenya
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- 1.000-10,000 km2
Comentários:
Boundary points of the Technology area: An approx. triangular area bordered by Machakos, Kitui and Mitio Andei.
Over 1000 dams have been built to date in these counties, predominantly by 3 organisations: Utooni Development organisation, SASOL and Africa Sand Dam Foundation in an approx. triangular area bordered by Machakos, Kitui and Mitio Andei.
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- 10-50 anos atrás
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- através de projetos/intervenções externas
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
Sand dams are an ancient technology. Examples are found across the world's drylands although the greatest concentration is found in Kenya. They were introduced to Kenya in the 1950s from India. Dams were pioneered in Machakos and Makueni counties of Kenya by Joshua Mukusya, a visionary farmer and development worker, in 1978. He worked with a range of agencies to develop and implement the technology. In 1990, staff trained by Joshua set up SASOL to pioneer sand dams in the neighbouring county of Kitui. In 2002, Joshua teamed up with Simon Maddrell, Excellent Development's director, to establish Excellent Development Kenya, now Utooni Development Organisation (UDO) to scale up the work. Sadly, in 2011, Joshua passed away. In 2010, Excellent Development formed a strategic partnership with the Kenyan NGO, Africa Sand Dam Foundation (ASDF), to support the wider uptake beyond Kenya. Today, ASDF, SASOL and UDO are the three NGOs with the most experience of building successful sand dams, approx. 130 dams / year, although many other NGOs have adopted the technology.
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- access to water
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Vias navegáveis, corpo d'água, zonas úmidas
- Linhas de drenagem, vias navegáveis
- Lagos, represas
Comentários:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Drylands are characterised by intense and variable rainfall and a lack of vegetative cover. As a result, drylands are prone to droughts, flooding and soil erosion which result in endemic water and food scarcity.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): “We used to fetch water from Londokwe; we could spend a night to collect water. One way was 3 to 10 km and up to 12 hours or more to go and come back [because of the time taken to queue]. If we could not make it to the river, we would send our children to fetch water. When they went fetching water that would mean they did not go to school. At times people would fight over fetching water from other people’s scoop holes. Scoop holes would be guarded in turns. The gourds [water containers] would be damaged and the water poured down. Children would not go to school [as they needed to] take care of the young ones as the parents went to fetch water. Children would fail to go to school because they were hungry – just because there was no water to cook."
Yikiuuku SHG
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Coleta de água
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas estruturais
- S3: Valas graduadas, canais, vias navegáveis
- S5: Represa, bacia, lago
Comentários:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Degradação biológica
- Bq: quantidade/ declínio da biomassa
- Bs: Qualidade e composição de espécies/declínio de diversidade

Degradação da água
- Ha: aridificação
- Hs: mudança na quantidade de água de superfície
- Hg: mudança no lençol freático/aquífero
Comentários:
Main type of degradation addressed: Hs: change in quantity of surface water
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline, Ha: aridification, Hg: change in groundwater / aquifer level
Main causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), droughts
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Prevenir degradação do solo
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
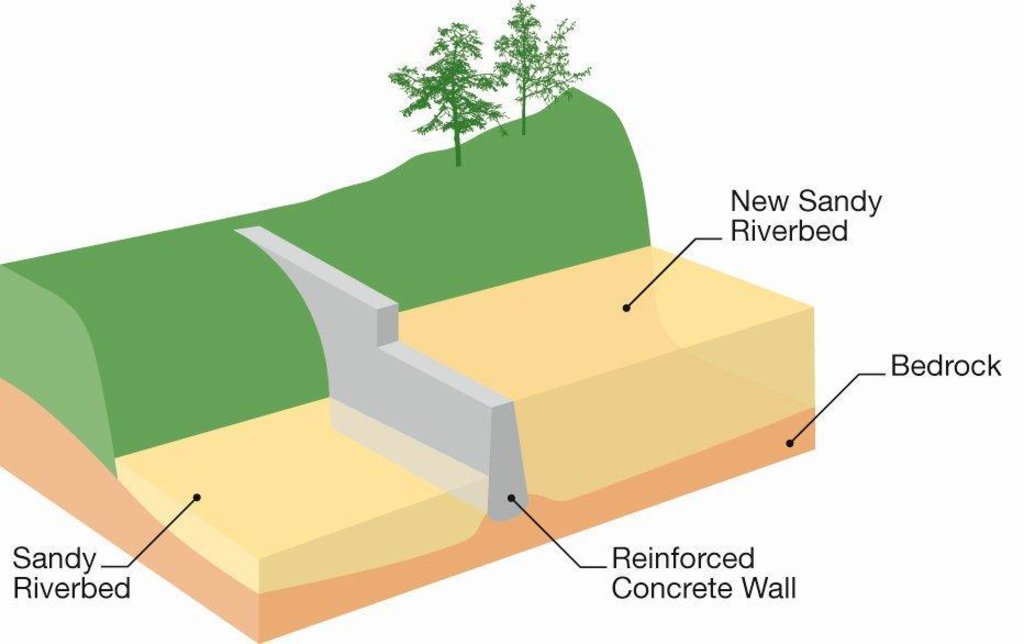
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Cross-section of sand dam
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (The technical skills required to site, design and supervise construction. These skills have and can be developed locally.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (Knowledge of local rivers and their flood levels essential. Basic knowledge of stone masonry useful)
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, water harvesting / increase water supply, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Dam/ pan/ pond
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1-5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1-2
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 5-50
Specification of dams/ pans/ ponds: Capacity 5,000m3
Catchment area: 300 km2m2
Autor:
Excellent Development
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
Kenyan Shilling
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
83,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
2.50
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of rock, sand and water | 1-3 months before construction |
| 2. | Construct dam | During dry season |
| 3. | Cure dam | For 4 weeks after construction |
| 4. | Terracing and protection of immediate catchment | 1-3 months before construction |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
| Especifique a entrada | Unidade | Quantidade | Custos por unidade | Custos totais por entrada | % dos custos arcados pelos usuários da terra | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mão-de-obra | Collection of rock, sand and water | Persons/day | 220,0 | 2,5 | 550,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Terracing and protection of immediate catchment | Persons/day | 100,0 | 2,5 | 250,0 | 100,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Construct dam | Persons/day | 500,0 | 2,5 | 1250,0 | 90,0 |
| Mão-de-obra | Cure dam | Persons/day | 50,0 | 2,5 | 125,0 | 100,0 |
| Equipamento | Tools | per dam | 1,0 | 300,0 | 300,0 | |
| Material de construção | Cement (bag = 50kg) | bags | 500,0 | 9,15 | 4575,0 | |
| Material de construção | Steel (12m x Y20 steel bar) | pieces | 7,0 | 45,7 | 319,9 | |
| Material de construção | Steel | per dam | 1,0 | 1000,0 | 1000,0 | |
| Outros | Skilled labour | per dam | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | |
| Custos totais para a implantação da tecnologia | 11369,9 | |||||
| Custos totais para o estabelecimento da Tecnologia em USD | 136,99 | |||||
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Inspect and if necessary extend spillway or repair erosion around dam | As required / annually |
| 2. | Maintain hand pump if fitted | As required / annually |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
In 2012, in Machakos County, Kenya, the cost of materials and technical support for a dam using 250 bags of cement is USD 7,000 and USD 11,700 for a 500 bag dam. The costs in 2.6.1 are based on a 500 bag dam. The volume of a 500 bag dam is approx 140m3 of stone masonry of which 40% is mortar (sand and cement) and 60% is rock. Such a dam will typically be appropriate on rivers 30m wide and with a spillway 3 metres above the bedrock in the river bed level. Costs rise by up to 50% in more remote regions or countries. Sand dams require a lot of hard work. Community members collect the required stones, sand and water, support construction and terrace the land around the dam. If this in-kind contribution is included the costs would rise by 100%. In Kenya, with a long tradition of building sand dams, it takes from 6 to 12 weeks to plan and prepare for construction and 2 days to 2 weeks to build the dam. In other areas, with less experience and/or less community commitment, building a dam may take 6 months or more.
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
Each dam is individually designed. The size, design and cost of a dam varies considerably with the size of the river and to a lesser extent, location and transport costs. Sand dams are the world’s lowest cost method of capturing rainwater in dry rural areas by a factor of 3 to 30 times compared to rain water harvesting tanks, earth dams, haffirs and rock catchments.
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Especificações/comentários sobre a pluviosidade:
Sand dams suit dryland climate: dry sub-humid, semi-arid and arid climates
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a topografia:
Land forms: Sand dams only suit seasonal rivers with sufficient sandy sediment and an accessible bedrock
Altitudinal zone: Also 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
Slopes on average: Also moderate
5.3 Solos
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil water storage capacity: The aquifer behind the dam must consist of sandy sediments with a high porosity and drainable porosity
5.4 Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Lençol freático:
5-50 m
Disponibilidade de água de superfície:
Excesso
Qualidade da água (não tratada):
Água potável boa
Comentários e outras especificações sobre a qualidade e a quantidade da água:
Availability of surface water: Sand dams only suit seasonal rivers
Water quality (untreated): Good drinking water because the sand filters the water. Water abstracted through an infiltration gallery has a high bacterialogical quality but water is often used for small scale irrigation and livestock watering.
5.5 Biodiversidade
Diversidade de espécies:
- Alto
Comentários e outras especificações sobre biodiversidade:
Sand dams rejuvenate riverine ecologies and increase local biodiversity
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível relativo de riqueza:
- Pobre
- Média
Indivíduos ou grupos:
- Grupos/comunidade
Gênero:
- Mulheres
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: The dams are built by members of registered self-help groups, typically 50 members / group and two-thirds women. The primary concerns of these groups tend to be food and water. Sand dams provide for people, livestock and crops. Water collection and farming are primarily undertaken by women in Kikamba culture and hence women have the greatest vested interest to imrpove food and water availability. Many men migrate away from the area in search of work.
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
Off-farm income specification: This varies considerably, but most self-help group members are subsistence farmers
5.7 Área média de terrenos utilizados pelos usuários de terrenos que aplicam a Tecnologia
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1.000 ha
- 1.000-10.000 ha
- > 10.000 ha
É considerado pequena, média ou grande escala (referente ao contexto local)?
- Pequena escala
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Estado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Direitos do uso da água:
- Comunitário (organizado)
Comentários:
Legal agreements for construction and access between the self-help group and the owners of land adjacent to the dam and registering the dam and its associated water rights by the self-help group with the Kenyan Water Resources Management Authority (WRMA) is vital to safeguarding water rights, controlling water and sand abstraction, formalising the authority of the self-help group to levy water tarriffs if appropriate and ensuring there is open access to all to water from scoop holes.
5.9 Acesso a serviços e infraestrutura
Saúde:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Educação:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Assistência técnica:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Emprego (p. ex. não agrícola):
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Mercados:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Energia:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Vias e transporte:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Água potável e saneamento:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
Serviços financeiros:
- Pobre
- Moderado
- Bom
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção agrícola
Produção de forragens
Qualidade da forragem
Produção animal
Produção de madeira
Risco de falha de produção
Diversidade de produtos
Geração de energia
Comentários/especificar:
Tree planting enabled by dams increases fuel wood availability
Disponibilidade e qualidade de água
Disponibilidade de água potável
Disponibilidade de água para criação de animais
Qualidade da água para criação de animais
Disponibilidade de água para irrigação
Qualidade da água para irrigação
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Diversidade de fontes de rendimento
Carga de trabalho
Comentários/especificar:
Construction of sand dams is labour intensive. This is more than offset by the time savings created by reducing the time required to collect water.
Outros impactos socioeconômicos
School attendance
Impactos socioculturais
Segurança alimentar/auto-suficiência
Comentários/especificar:
Sand dams are integrated within a wider programme that promotes food security and self sufficiency
Estado de saúde
Comentários/especificar:
Reduced water borne disease. Increased access to higher quality water and improved food security improves health.
Oportunidades culturais
Comentários/especificar:
Working through and strengthening self help groups builds on the local tradition of self-help called mwethya
Instituições comunitárias
Comentários/especificar:
Increases the capacity of self-help groups
Conhecimento de GST/ degradação da terra
Comentários/especificar:
Learning exchanges between self-help groups and demonstration plots builds knowledge and adoption of conservation farming
Atenuação de conflitos
Comentários/especificar:
If ownership and management of dam is not clear and legally protected this can result in conflict
Fuel security
Comentários/especificar:
Tree nursersies and agro-forestry enabled by sand dams improves access to fuel food
Livelihood and human well-being
Comentários/especificar:
Sand dams save farmers hours every day that they can invest in improving their farms to grow more food and create the potential for farmers to irrigate trees and crops, water livestock and generate an income. It is strongly advised that sand ams are integrated within a wider land management and livelihoods programme in order to realise these opportunities to the maximum. Community ownership and management is critical to achieving this
Livestock health
Comentários/especificar:
Sand dams provide secure water source for livestock
Income
Comentários/especificar:
Irrigated horticulture and tree nurseries improves farmer incomes
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Quantidade de água
Quantidade anterior à GST:
<1000m3
Quantidade posterior à GST:
2-10,000m3
Qualidade de água
Comentários/especificar:
Sand filters the water
Colheita/recolhimento de água
Comentários/especificar:
Sand dams capture excess flood flows
Escoamento superficial
Comentários/especificar:
Terracing the immediate dam catchment reduces surface runoff
Lençol freático/aquífero
Comentários/especificar:
Studies of Kitui dams found watertable increased by several metres
Evaporação
Comentários/especificar:
Once the water level in the dam aquifer is below 60cm, evaporation losses from the sand are negligible
Solo
Umidade do solo
Comentários/especificar:
Sand dams recharge the aquifer and raises the watertable above and below the dam
Salinidade
Comentários/especificar:
Salinity of sand dam water is often less than surrounding groundwater
Biodiversidade: vegetação, animais
Diversidade vegetal
Comentários/especificar:
Rejuvenation of riverine ecologies and planting indigenous trees increases diversity
Diversidade de habitat
Comentários/especificar:
Riverine ecologies rejuvenated
Clima e redução de riscos de desastre
Impactos da inundação
Comentários/especificar:
By creating a buffer, flooding downstream of a dam or series of dams is reduced
Emissão de carbono e gases de efeito estufa
Comentários/especificar:
Tree nursersies enabled by sand dams capture store carbon and reduce deforestation
6.2 Impactos externos mostrados pela tecnologia
Disponibilidade de água
Cheias de jusante
Capacidade de tamponamento/filtragem
Danos em áreas vizinhas
Danos na infraestrutura pública/privada
6.3 Exposição e sensibilidade da tecnologia às mudanças climáticas graduais e extremos/desastres relacionados ao clima (conforme o ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)
Mudança climática gradual
Mudança climática gradual
| Estação do ano | aumento ou diminuição | Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperatura anual | aumento | bem |
Extremos (desastres) relacionados ao clima
Desastres meteorológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Temporal local | bem |
| Tempestade de vento local | bem |
Desastres climatológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Seca | bem |
Desastres hidrológicos
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Inundação geral (rio) | bem |
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
Outras consequências relacionadas ao clima
| Como a tecnologia lida com isso? | |
|---|---|
| Período de crescimento reduzido | bem |
Comentários:
The capacity of the spillway would be increased to control peak flood events
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
muito positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Comentários:
The very low cost of operating and maintaining sand dams means they are well suited to remote, poorly served regions. Because it is a low cost technology that requires a major community contribution and the knowledge and skills of locally trained artisans, it’s a solution particularly suited to community ownership and self-supply. This contributes to effective implementation.
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 0-10%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Sand dams require external material support including technical advice to correctly site, design and construct
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is some evidence of spontaneous adoption amongst development agencies working in regions suited to sand dams.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do usuário da terra |
|---|
| “I will be able to rent a plot of land near to the sand dam and grow vegetables (tomatoes, peppers, and French beans). My animals will also be healthy because they will always be able to drink here, even during the droughts.” Mauwa Maingi, self-help group member, aged 87, 2010 |
|
Mbatha Mbuli, 83. "My family collects water from a near-by well, about ½ Km away, but the water is very salty. It takes one hour to collect water, and needs 6 trips to fetch enough to last the day. There is a pipeline nearby but we must pay 2 shillings per 20 litres. I planted 9 different crops last year, but only 2 survived. I wanted to work with Excellent on this project because I had heard that the projects you support help communities like us to build sand dams, grow trees and create seed banks. I would like to grow trees like Neem in the future and a sand dam here will really help with that. Excellent shares in the interests of the community and they listen to the community and take direction from us" |
| Stephen Hussey, Dabane Trust, 2011 “Dabane has made its name by getting water out of sand rivers – Our next step is to ensure we don’t over abstract – the answer to that, especially upstream, is sand dams. Without a doubt.” |
| Milka Mutunga, Kilili Catchment SHG, Kenya 2009-10 "The distance that I used to travel in order to fetch water has been reduced..now I am able to plant more vegetables close to my home. I have learnt how to dig terraces which have helped in increasing the yields that I harvest from my farm..If this is not development then I do not know what development means" |
| Kimanthi Ngovi, Yikiuuku SHG “The sand dams have done an incredible work for us – water availability at a shorter distance has helped me in saving time for other activities. When water was a long way away I had to get time to collect water in one day and dig terraces on the other day. Today I can fetch water and dig terraces on the same day.” |
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Sand dams provide a safe, reliable, year round, local supply of water for people, crops and livestock in water scarce environments How can they be sustained / enhanced? The very low cost of operating and maintaining sand dams means they are well suited to remote, poorly served regions. Community ownership is critical to their effective management. |
|
Sand dams save farmers hours every day that they can invest in improving their farms to grow more food and create the potential for farmers to irrigate trees and crops, water livestock and generate an income How can they be sustained / enhanced? Don’t build a sand dam in isolation. An independent evaluation in 2010 of 2 sand dam programmes found the long term impacts on poverty, food security and incomes were greatest when sand dams were integrated within a wider community development programme aimed at improving food production, livestock management and land management practice. |
|
Because it is a low cost technology that requires a major community contribution and the knowledge and skills of locally trained artisans, it’s a solution particularly suited to community ownership and self-supply. This contributes to effective implementation. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Don’t short cut community ownership. Communities better understand and are able to implement solutions to their problems if they are central to the planning of the solution. Genuine community commitment and ownership from initial planning to on-going management is vital to realise the intended benefits and full potential created by a dam. Legal registration and agreements to safeguard community access and water rights help this. |
|
Sand dams provide significant environmental benefits such as aquifer recharge, increased downstream flows in the dry-season, rejuvenation of river ecologies and moderation of floods. As such, it contributes to eco-system services and climate change adaption. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Support terracing, tree planting and conservation farming in the wider catchment. This conserves soil and water on farms, increases aquifer recharge and base flows into the dam and reduces the amount of silt in the sand dam aquiver. Research and disseminate evidence of these benefits and the value of these eco-system services |
|
The technology is scaleable and has a broader application for use as a rural and game park road crossing to replace less effective culvert bridges. How can they be sustained / enhanced? In order to upscale this solution, there is a need for greater awareness and advocacy of the technology and its benefits amongst these groups. Nothing generates interest in sand dams more than exposure to successful examples |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| Although sand dams are technically replicable, their application in new contexts requires careful understanding and consideration. | Excellent Development has developed a framework tool to help agencies identify the political, economic, social, technical, legal and environmental factors that should be taken account of when introducing sand dams to a new context. |
| Sand dams require the technical knowledge and skills of local artisans in order to correctly site, design and construct them | The technical barriers to adoption are low: The technical skills required have and can be developed locally. Learning exchanges between implementing organisations and developing technical manuals and resources aids this learning |
| This is a drylands solution. Sand dams can only be built on seasonal rivers with sufficient sandy sediment and where the bedrock or impermeable layer is accessible in the river bed. | Increase awareness of the criteria that determine the technical suitability of a site. Use simple field tests, such as sediment seiving and probing, to assess potential sites and to map the potenial application of sand dams. |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Be buffered website including Managing the Water Buffer for Development and Climate Change Adaptation. Groundwater recharge, retention, reuse and rainwater storage. Steenbergen F. van and A. Tuinhof. (2009) which includes sand dams
Disponível de onde? Custos?
www.bebuffered.com/3rbook
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos