Gully Rehabilitation [Quênia]
- Criação:
- Atualização:
- Compilador/a: Kithinji Mutunga
- Editor: –
- Revisores: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1488 - Quênia
Veja as seções
Expandir tudo Recolher tudo1. Informação geral
1.2 Detalhes do contato das pessoas capacitadas e instituições envolvidas na avaliação e documentação da tecnologia
Especialista em GST:
Kiio Jacqueline
MOARD
Quênia
usuário de terra:
Kirimi Patrick
MOARD
Quênia
Especialista em GST:
Gitau Mary
MOARD
Quênia
Nome da(s) instituição(ões) que facilitou(ram) a documentação/ avaliação da Tecnologia (se relevante)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - Itália1.3 Condições em relação ao uso da informação documentada através de WOCAT
O/a compilador/a e a(s) pessoa(s) capacitada(s) aceitam as condições relativas ao uso de dados documentados através da WOCAT:
Sim
2. Descrição da tecnologia de GST
2.1 Descrição curta da tecnologia
Definição da tecnologia:
Erosion control by use of physical barriers and vegetative materials
2.2 Descrição detalhada da tecnologia
Descrição:
The innovation comprises control of gully erosion by use of constructed barriers (check dams) combined with vegetative materials. The end result is a stabilized gully that is prevented from advancing further. The system also involves fruit trees/banana establishment and fodder grass planting for structure stabilization. Establishment of the technology involves excavation of pits, planting fruit trees/bananas and grass cuttings.
Purpose of the Technology: This is a structural measure that is vegetated for stabilization. Its purpose is to rehabilitate a gully bed, through control of concentrated runoff by reduction of slope length and both trapping of runoff and sediment harvesting. The productive use of the innovation is mainly for perennial crops (fruit trees and
bananas) and for fodder production.
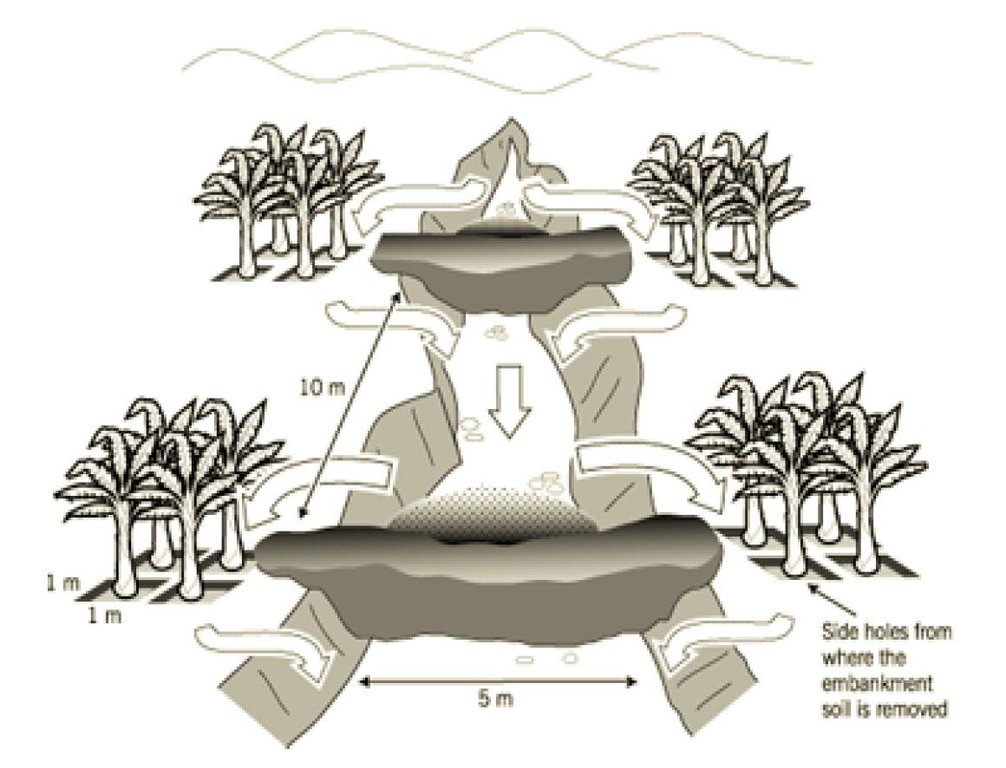
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Earth check dams are constructed in the gully, using borrow spoil from square pits in the walls of the gully (see diagram). The earth embankment of the dams are then stabilized with grass. Pawpaws are planted on the original gully floor. Initially the innovator left the pits empty: now she plants bananas in them.The 5 check dams, each 1 m or more in height, are spaced at about 10 m apart in the gully. The excavated pits are about 1 m x 1 m wide and 1 m deep. Four pits are dug separately on each side of each check dam. Makarikari grass (Panicum coloratum var. makarikariensis) is used for stabilization, while bananas and pawpaws are planted within the rehabilitated area. When it rains, runoff generated from the neighbouring plots upstream flows down and is slowed by the check dams. The runoff passes around both wings of each embankment, filling and flowing through the pits. Sediment is trapped in the pits. Excess runoff flows on to the second embankment, then through the second set of pits and so on. Only during heavy rains does water pass through and out of the system, though its velocity is reduced. Thus the gully heals slowly with time and vegetation becomes established. Regular maintenance work is required, involving repair of broken sections from time to time, using manual labour with a panga, shovel and jembe. Also of importance is manure application every season to the planted areas before the rains to sustain fertility and thus productivity.
Natural / human environment: Kalekye Mutua is a single household head in her mid thirties. Although she has no partner to help support her three children, she manages quite well through farming her 6 hectares of land - where she grows various crops and keeps a few local cattle. She had a small trading venture but has recently abandoned
this. Kalekye is not amongst the poorest in Mwingi, but represents a number of female-headed households who prosper through hard work and enterprise. In fact she even employs labourers part-time to help with the farming activities.
2.3 Fotos da tecnologia
2.5 País/região/locais onde a tecnologia foi aplicada e que estão cobertos nesta avaliação
País:
Quênia
Região/Estado/Província:
Eastern Province
Especifique a difusão da tecnologia:
- Uniformemente difundida numa área
Se a área precisa não for conhecida, indicar a área aproximada coberta:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Comentários:
a very small portion of the individual farm is covered by the technology
Map
×2.6 Data da implementação
Caso o ano exato seja desconhecido, indique a data aproximada:
- mais de 50 anos atrás (tradicional)
2.7 Introdução da tecnologia
Especifique como a tecnologia foi introduzida:
- Como parte do sistema tradicional (>50 anos)
Comentários (tipos de projeto, etc.):
farmers own intiative
3. Classificação da tecnologia de GST
3.1 Principal/principais finalidade(s) da tecnologia
- Reduz, previne, recupera a degradação do solo
3.2 Tipo(s) atualizado(s) de uso da terra onde a tecnologia foi aplicada

Terra de cultivo
- Cultura perene (não lenhosa)
- Cultura de árvores e arbustos
Cultivo perene (sem lã) - Especificar culturas:
- banana/planta/abacá
Cultivo de árvores e arbustos - Especificar culturas:
- frutas de pomóideas (maçãs, peras, marmelos, etc.)
Número de estações de cultivo por ano:
- 2
Especifique:
Longest growing period in days: 60 Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Dec Second longest growing period in days: 75 Second longest growing period from month to month: Mar - May
Comentários:
Fruit trees / shrubs species: pawpaws (Asimina triloba)
Perennial crops species: bananas
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): soil erosion, overgrazing, declining soil fertility
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): low yields
3.4 Abastecimento de água
Abastecimento de água para a terra na qual a tecnologia é aplicada:
- Precipitação natural
3.5 Grupo de GST ao qual pertence a tecnologia
- Solo/cobertura vegetal melhorada
- Coleta de água
- Desvio e drenagem de água
3.6 Medidas de GST contendo a tecnologia

Medidas vegetativas

Medidas estruturais
- S3: Valas graduadas, canais, vias navegáveis
Comentários:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
3.7 Principais tipos de degradação da terra abordados pela tecnologia

Erosão do solo pela água
- Wg: Erosão por ravinas/ravinamento
3.8 Redução, prevenção ou recuperação da degradação do solo
Especifique o objetivo da tecnologia em relação a degradação da terra:
- Reduzir a degradação do solo
4. Especificações técnicas, implementação de atividades, entradas e custos
4.1 Desenho técnico da tecnologia
Especificações técnicas (relacionada ao desenho técnico):
Gully under reclamation: note flow of runoff
Kenya
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, increase of infiltration, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Fruit trees / shrubs species: pawpaws
Perennial crops species: bananas
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10.00%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is (see figure below): 5.00%
Construction material (earth): Local soil excavated from pits on the side of the gully
Construction material (other): Grass for stabilization Makarikari grass prefeered
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 10%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 8%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
4.2 Informação geral em relação ao cálculo de entradas e custos
Outro/moeda nacional (especifique):
kenya shillings
Se for relevante, indique a taxa de câmbio do USD para moeda local (por exemplo, 1 USD = 79,9 Real): 1 USD =:
70,0
Indique a média salarial da mão-de-obra contratada por dia:
2.14
4.3 Atividades de implantação
| Atividade | Periodicidade (estação do ano) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | digging banana holes | dry season |
| 2. | acquisition of grass cuttings | dry season |
| 3. | acquisition of banana cuttings | before |
| 4. | planting of grass and bananas | onset of rain |
| 5. | manure application | before the rains |
| 6. | Excavation | Dry season |
4.4 Custos e entradas necessárias para a implantação
Comentários:
Duration of establishment phase: 24 month(s)
4.5 Atividades recorrentes/manutenção
| Atividade | Periodicidade/frequência | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | repair of broken structures | after rains /seasonally |
| 2. | weeding | during rains /twice /season |
| 3. | banana prunning | after rains /biannually |
| 4. | manure application | dry season /annually |
| 5. | Repair of broken sections | during /after rains/seasonally |
| 6. | Stabilization with grass | during rains/when required |
4.6 Custos e entradas necessárias pata a manutenção/atividades recorrentes (por ano)
Comentários:
1100 banana/ fruit trees holes/ha
4.7 Fatores mais importantes que afetam os custos
Descreva os fatores mais determinantes que afetam os custos:
slope, soil type, timeliness of operation
5. Ambiente natural e humano
5.1 Clima
Precipitação pluviométrica anual
- <250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1.000 mm
- 1.001-1.500 mm
- 1.501-2.000 mm
- 2.001-3.000 mm
- 3.001-4.000 mm
- > 4.000 mm
Zona agroclimática
- Semiárido
5.2 Topografia
Declividade média:
- Plano (0-2%)
- Suave ondulado (3-5%)
- Ondulado (6-10%)
- Moderadamente ondulado (11-15%)
- Forte ondulado (16-30%)
- Montanhoso (31-60%)
- Escarpado (>60%)
Formas de relevo:
- Planalto/planície
- Cumes
- Encosta de serra
- Encosta de morro
- Sopés
- Fundos de vale
Zona de altitude:
- 0-100 m s.n.m.
- 101-500 m s.n.m.
- 501-1.000 m s.n.m.
- 1.001-1.500 m s.n.m.
- 1.501-2.000 m s.n.m.
- 2.001-2.500 m s.n.m.
- 2.501-3.000 m s.n.m.
- 3.001-4.000 m s.n.m.
- > 4.000 m s.n.m.
5.3 Solos
Profundidade do solo em média:
- Muito raso (0-20 cm)
- Raso (21-50 cm)
- Moderadamente profundo (51-80 cm)
- Profundo (81-120 cm)
- Muito profundo (>120 cm)
Textura do solo (solo superficial):
- Grosso/fino (arenoso)
Matéria orgânica do solo superficial:
- Baixo (<1%)
Caso disponível anexe a descrição completa do solo ou especifique as informações disponíveis, p. ex. tipo de solo, PH/acidez do solo, nitrogênio, capacidade de troca catiônica, salinidade, etc.
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.6 Características dos usuários da terra que utilizam a tecnologia
Rendimento não agrícola:
- Menos de 10% de toda renda
Nível de mecanização:
- Trabalho manual
Indique outras características relevantes dos usuários da terra:
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
1% of the land users are very rich and own 10% of the land.
4% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
25% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
40% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: the are few members of the household who are in formal employment
5.8 Propriedade de terra, direitos de uso da terra e de uso da água
Propriedade da terra:
- Indivíduo, não intitulado
Direitos do uso da terra:
- Indivíduo
6. Impactos e declarações finais
6.1 Impactos no local mostrados pela tecnologia
Impactos socioeconômicos
Produção
Produção de forragens
Área de produção
Renda e custos
Rendimento agrícola
Comentários/especificar:
Sale of bananas
Impactos ecológicos
Ciclo hídrico/escoamento
Escoamento superficial
Quantidade anterior à GST:
60
Quantidade posterior à GST:
10
Solo
Umidade do solo
Cobertura do solo
Perda de solo
Quantidade anterior à GST:
610
Quantidade posterior à GST:
1
6.4 Análise do custo-benefício
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos de implantação (do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
levemente positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
muito positivo
Como os benefícios se comparam aos custos recorrentes/de manutenção(do ponto de vista dos usuários da terra)?
Retornos a curto prazo:
positivo
Retornos a longo prazo:
positivo
6.5 Adoção da tecnologia
- casos isolados/experimental
Se disponível, determine a quantidade (número de unidades familiares e/ou área abordada):
1 household
De todos aqueles que adotaram a Tecnologia, quantos o fizeram espontaneamente, ou seja, sem receber nenhum incentivo/ pagamento material?
- 91-100%
Comentários:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Kalekye only started the innovation two years ago, and while there has been a policy of taking women’s groups to visit Kalekye, this is a relatively recent occurrence (starting approximately a year ago). Despite the visitors obviously being inspired, there have been no reports as yet of direct adoption of the technology.
6.7 Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades da tecnologia
| Pontos fortes/vantagens/oportunidades na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada |
|---|
|
Reclamation of land for production of fodder and bananas How can they be sustained / enhanced? Possible improvements would include planting improved fruit trees that are rapidly maturing and yield more: grafted mangoes for example |
6.8 Pontos fracos, desvantagens/riscos da tecnologia e formas de superá-los
| Pontos fracos/vantagens/riscos na visão do/a compilador/a ou de outra pessoa capacitada | Como eles podem ser superados? |
|---|---|
| High labour requirements |
7. Referências e links
7.1 Métodos/fontes de informação
7.2 Referências às publicações disponíveis
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Farm Management handbook of Kenya Vol II
Disponível de onde? Custos?
Ministry of Agiculture, Nairobi
Título, autor, ano, ISBN:
Kithinji M., Critchley W. 2001. Farmers' initiatives in land husbandry: Promising technologies for the drier areas of East Africa. RELMA Technical Report series no. 27
Links e módulos
Expandir tudo Recolher tudoLinks
Não há links
Módulos
Não há módulos